机器学习-线性回归和多项式回归
线性回归模型
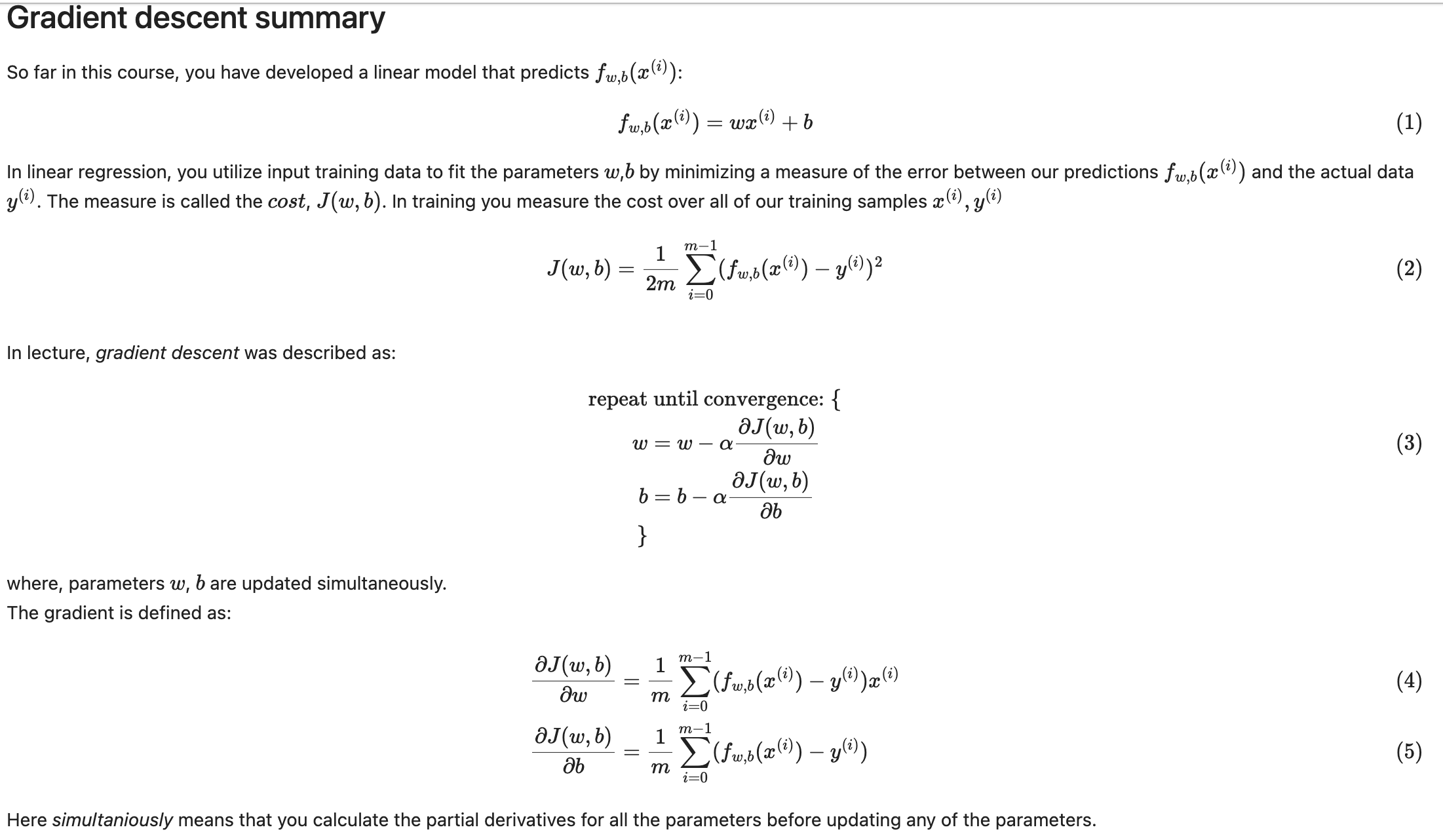
多元线性回归模型

多元线性回归模型实例
源数据
The housing data was derived from the Ames Housing dataset compiled by Dean De Cock for use in data science education.
代码实现
z-score标准化
# z-score标准化
def zscore_normalize_features(X):
mu = np.mean(X, axis=0) # MUST SET axis=0
sigma = np.std(X, axis=0) # MUST SET axis=0
x_norm = (X - mu)/sigma
return x_norms
损失函数
def compute_cost(x_train, y, w, b):
'''
m : 训练数据个数
n : 自变量个数
'''
m = x_train.shape[0]
sum_cost = 0
for idx in range(m):
f_wb = np.dot(x_train[idx], w) + b
cost = (f_wb - y[idx])**2
sum_cost += cost
sum_cost = sum_cost/(2*m)
return sum_cost
计算梯度
def compute_gradient(x_train, y, w, b):
'''
m : 训练数据个数
n : 自变量个数
'''
m, n = x_train.shape
sum_w = np.zeros(n)
sum_b = 0
for idx in range(m):
f_wb = np.dot(x_train[idx], w) + b
diff = f_wb - y[idx]
sum_w += diff * x_train[idx]
sum_b += diff
w_gradient = sum_w / m
b_gradient = sum_b / m
return w_gradient, b_gradient
梯度下降实现
def gradient_descent(x_train, y, iter_cnt, alpha, func_cost, func_gradient):
m, n = x_train.shape
w_initial = np.zeros(n)
b_initial = 0
cost_list = []
w_history = []
b_history = []
cnt = int(iter_cnt / 10)
for idx in range(iter_cnt):
w_g, b_g = func_gradient(x_train, y, w_initial, b_initial)
w_initial = w_initial - alpha * w_g
b_initial = b_initial - alpha * b_g
w_history.append(w_initial)
b_history.append(b_initial)
# 先计算梯度,再计算损失
_c = func_cost(x_train, y, w_initial, b_initial)
cost_list.append(_c)
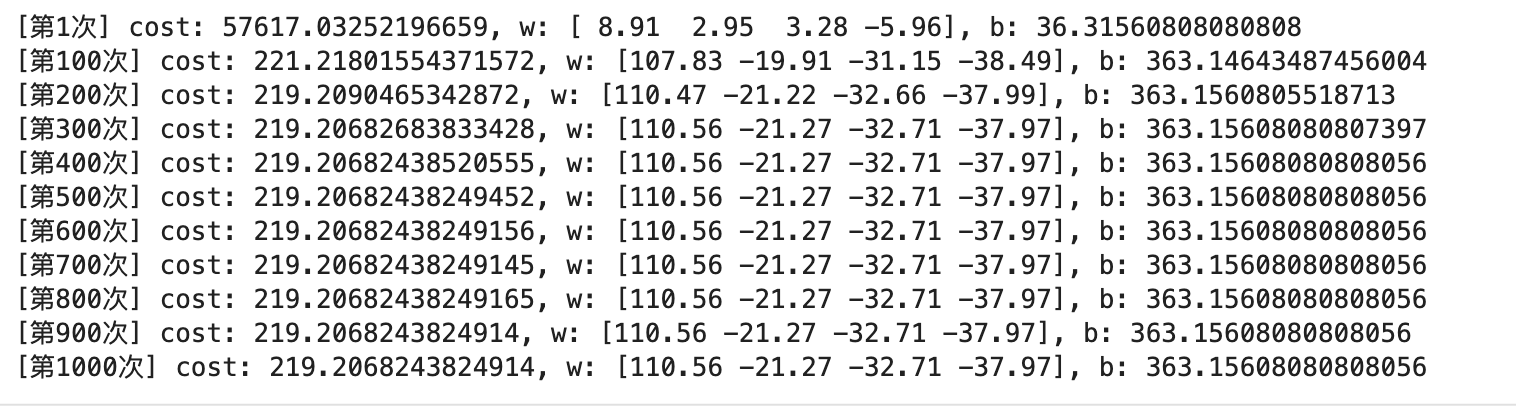
if idx == 0:
print(f"[第{idx+1}次] cost: {_c:e}, w: {w_initial}, b: {b_initial:e}")
if (idx+1) % cnt == 0:
print(f"[第{idx+1}次] cost: {_c:e}, w: {w_initial}, b: {b_initial:e}")
return cost_list, w_history, b_history, w_initial, b_initial
main()
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 数据载入
data = np.loadtxt("./data/houses.txt", delimiter=',', skiprows=1)
X_train = data[:,:4]
y_train = data[:,4]
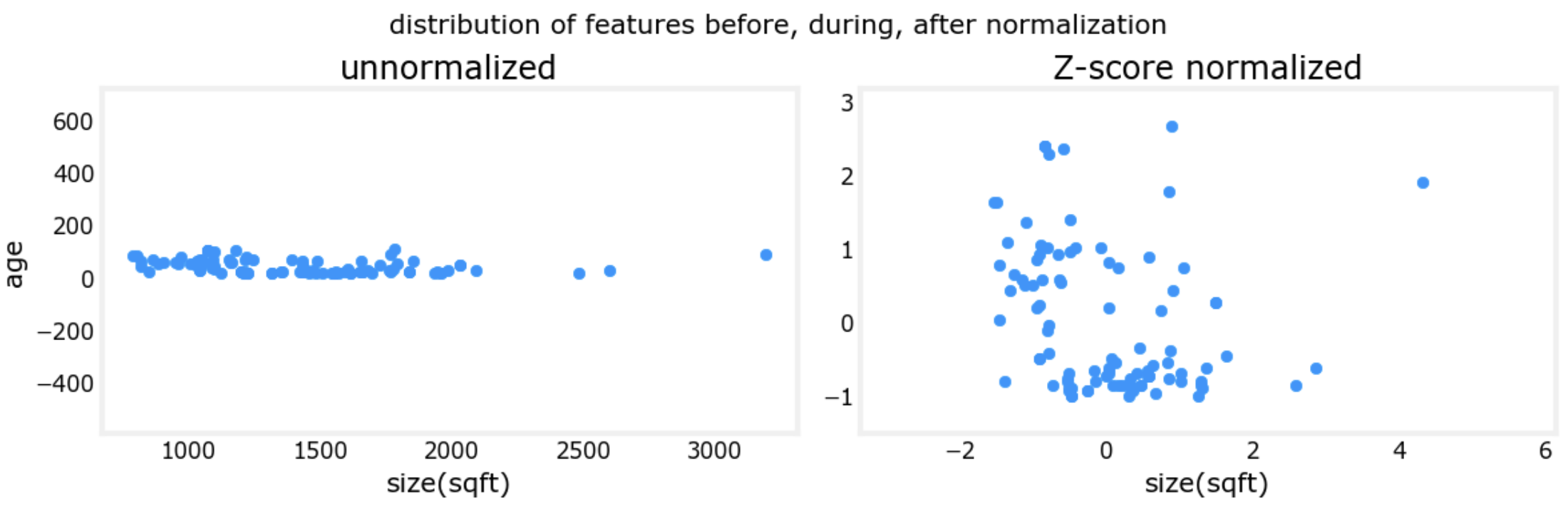
# 数据标准化
X_norm = zscore_normalize_features_fixed(X_train)
fig,ax=plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 4))
ax[0].scatter(X_train[:,0], X_train[:,3])
ax[0].set_xlabel(X_features[0]); ax[0].set_ylabel(X_features[3]);
ax[0].set_title("unnormalized")
ax[0].axis('equal')
ax[1].scatter(X_norm[:,0], X_norm[:,3])
ax[1].set_xlabel(X_features[0]); ax[0].set_ylabel(X_features[3]);
ax[1].set_title(r"Z-score normalized")
ax[1].axis('equal')
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0.03, 1, 0.95])
fig.suptitle("distribution of features before, during, after normalization")
plt.show()
# 开始训练
alpha = 1.0e-1
cost_list_norm, w_history_norm, b_history_norm, w_final_norm, b_final_norm = gradient_descent(X_norm, y_train, 1000, alpha, compute_cost, compute_gradient)
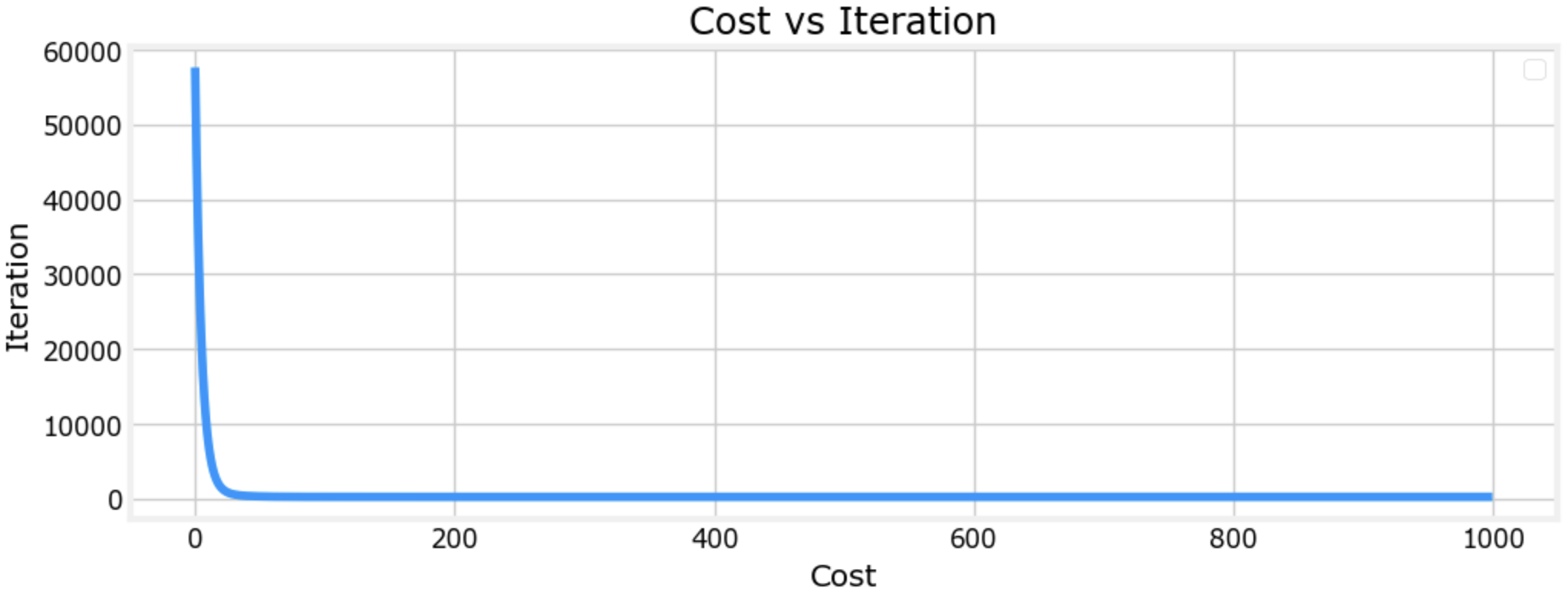
# 检验训练结果
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.plot(cost_list_norm)
plt.title("Cost vs Iteration")
plt.xlabel('Cost')
plt.ylabel('Iteration')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
执行结果
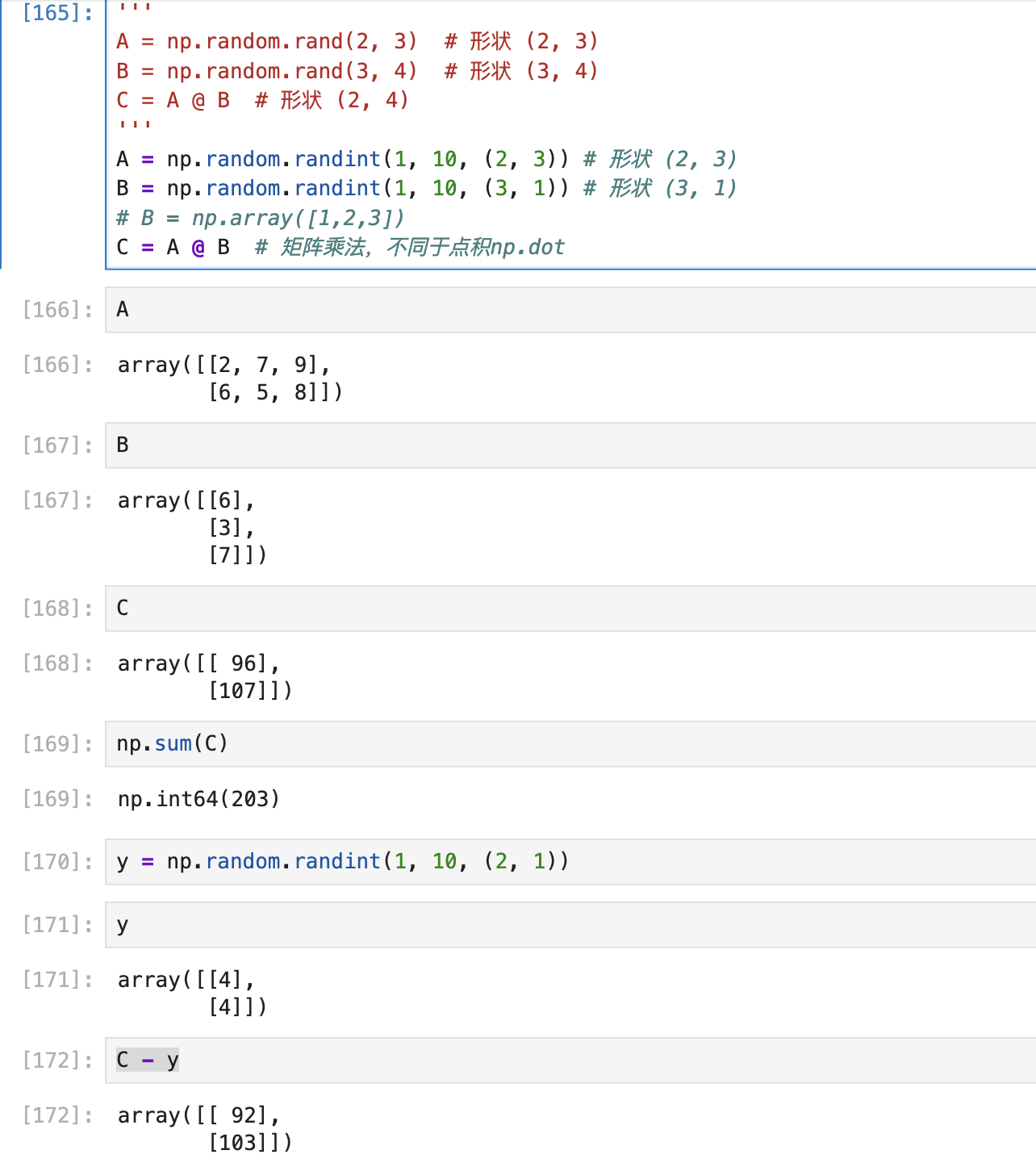
矩阵乘法版本
矩阵乘法示例
代码实现
# Loop version of multi-variable compute_cost
def compute_cost(X, y, w, b):
"""
compute cost
Args:
X : (ndarray): Shape (m,n) matrix of examples with multiple features
w : (ndarray): Shape (n) parameters for prediction
b : (scalar): parameter for prediction
Returns
cost: (scalar) cost
"""
m = X.shape[0]
cost = 0.0
for i in range(m):
f_wb_i = np.dot(X[i],w) + b
cost = cost + (f_wb_i - y[i])**2
cost = cost/(2*m)
return(np.squeeze(cost))
# Matrix version of multi-variable compute_cost
def compute_cost_matrix(X, y, w, b, verbose=False):
"""
Computes the gradient for linear regression
Args:
X : (array_like Shape (m,n)) variable such as house size
y : (array_like Shape (m,)) actual value
w : (array_like Shape (n,)) parameters of the model
b : (scalar ) parameter of the model
verbose : (Boolean) If true, print out intermediate value f_wb
Returns
cost: (scalar)
"""
m,n = X.shape
# calculate f_wb for all examples.
f_wb = X @ w + b
# calculate cost
total_cost = (1/(2*m)) * np.sum((f_wb-y)**2)
if verbose: print("f_wb:")
if verbose: print(f_wb)
return total_cost
# Matrix version of multi-variable compute_gradient
def compute_gradient(X, y, w, b):
"""
Computes the gradient for linear regression
Args:
X : (ndarray Shape (m,n)) matrix of examples
y : (ndarray Shape (m,)) target value of each example
w : (ndarray Shape (n,)) parameters of the model
b : (scalar) parameter of the model
Returns
dj_dw : (ndarray Shape (n,)) The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters w.
dj_db : (scalar) The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b.
"""
m,n = X.shape #(number of examples, number of features)
dj_dw = np.zeros((n,))
dj_db = 0.
for i in range(m):
err = (np.dot(X[i], w) + b) - y[i]
for j in range(n):
dj_dw[j] = dj_dw[j] + err * X[i,j]
dj_db = dj_db + err
dj_dw = dj_dw/m
dj_db = dj_db/m
return dj_db,dj_dw
# Matrix version of multi-variable compute_gradient
def compute_gradient_matrix(X, y, w, b):
"""
Computes the gradient for linear regression
Args:
X : (array_like Shape (m,n)) variable such as house size
y : (array_like Shape (m,1)) actual value
w : (array_like Shape (n,1)) Values of parameters of the model
b : (scalar ) Values of parameter of the model
Returns
dj_dw: (array_like Shape (n,1)) The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters w.
dj_db: (scalar) The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b.
"""
m,n = X.shape
f_wb = X @ w + b
e = f_wb - y
dj_dw = (1/m) * (X.T @ e)
dj_db = (1/m) * np.sum(e)
return dj_db,dj_dw
def gradient_descent(X, y, w_in, b_in, cost_function, gradient_function, alpha, num_iters):
"""
Performs batch gradient descent to learn theta. Updates theta by taking
num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
Args:
X : (array_like Shape (m,n) matrix of examples
y : (array_like Shape (m,)) target value of each example
w_in : (array_like Shape (n,)) Initial values of parameters of the model
b_in : (scalar) Initial value of parameter of the model
cost_function: function to compute cost
gradient_function: function to compute the gradient
alpha : (float) Learning rate
num_iters : (int) number of iterations to run gradient descent
Returns
w : (array_like Shape (n,)) Updated values of parameters of the model after
running gradient descent
b : (scalar) Updated value of parameter of the model after
running gradient descent
"""
# number of training examples
m = len(X)
# An array to store values at each iteration primarily for graphing later
hist={}
hist["cost"] = []; hist["params"] = []; hist["grads"]=[]; hist["iter"]=[];
w = copy.deepcopy(w_in) #avoid modifying global w within function
b = b_in
save_interval = np.ceil(num_iters/10000) # prevent resource exhaustion for long runs
for i in range(num_iters):
# Calculate the gradient and update the parameters
dj_db,dj_dw = gradient_function(X, y, w, b)
# Update Parameters using w, b, alpha and gradient
w = w - alpha * dj_dw
b = b - alpha * dj_db
# Save cost J,w,b at each save interval for graphing
if i == 0 or i % save_interval == 0:
hist["cost"].append(cost_function(X, y, w, b))
hist["params"].append([w,b])
hist["grads"].append([dj_dw,dj_db])
hist["iter"].append(i)
# Print cost every at intervals 10 times or as many iterations if < 10
if i% math.ceil(num_iters/10) == 0:
print(f"Iteration {i:4d}: Cost {cost_function(X, y, w, b):8.2f} ")
cst = cost_function(X, y, w, b)
print(f"Iteration {i:9d}, Cost: {cst:0.5e}")
return w, b, hist #return w,b and history for graphing
def run_gradient_descent(X,y,iterations=1000, alpha = 1e-6):
m,n = X.shape
# initialize parameters
initial_w = np.zeros(n)
initial_b = 0
# run gradient descent
w_out, b_out, hist_out = gradient_descent(X ,y, initial_w, initial_b, compute_cost, compute_gradient_matrix, alpha, iterations)
print(f"w,b found by gradient descent: w: {w_out}, b: {b_out:0.4f}")
return(w_out, b_out)
多项式回归
x = np.arange(0,20,1)
y = np.cos(x/2)
# f_wb(x) = w0*x + w1*x**2 + w2*x**3 + w3*x**4 + w4*x**5
X = np.c_[x, x**2, x**3, x**4, x**5]
X = zscore_normalize_features(X)
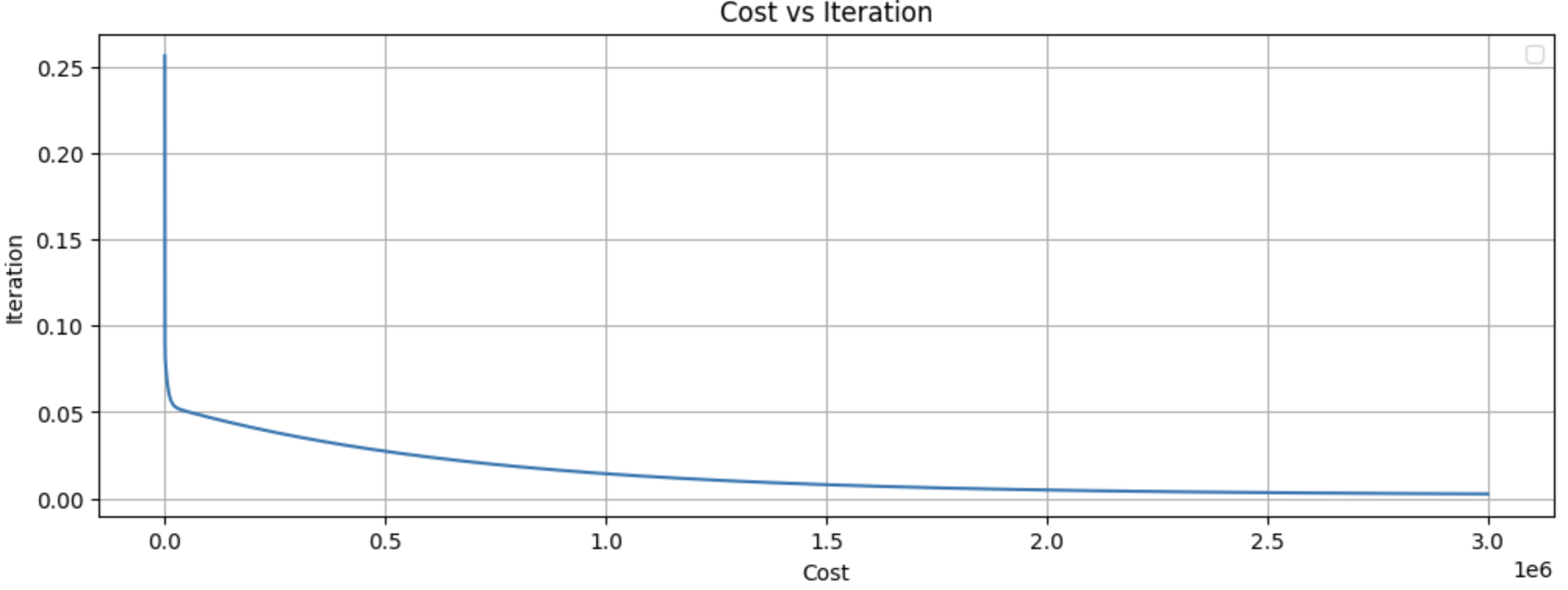
cost_list, w_history, b_history, w_final, b_final = gradient_descent(X, y, 3000000, 4e-1, compute_cost, compute_gradient)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.plot(cost_list)
plt.title("Cost vs Iteration")
plt.xlabel('Cost')
plt.ylabel('Iteration')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
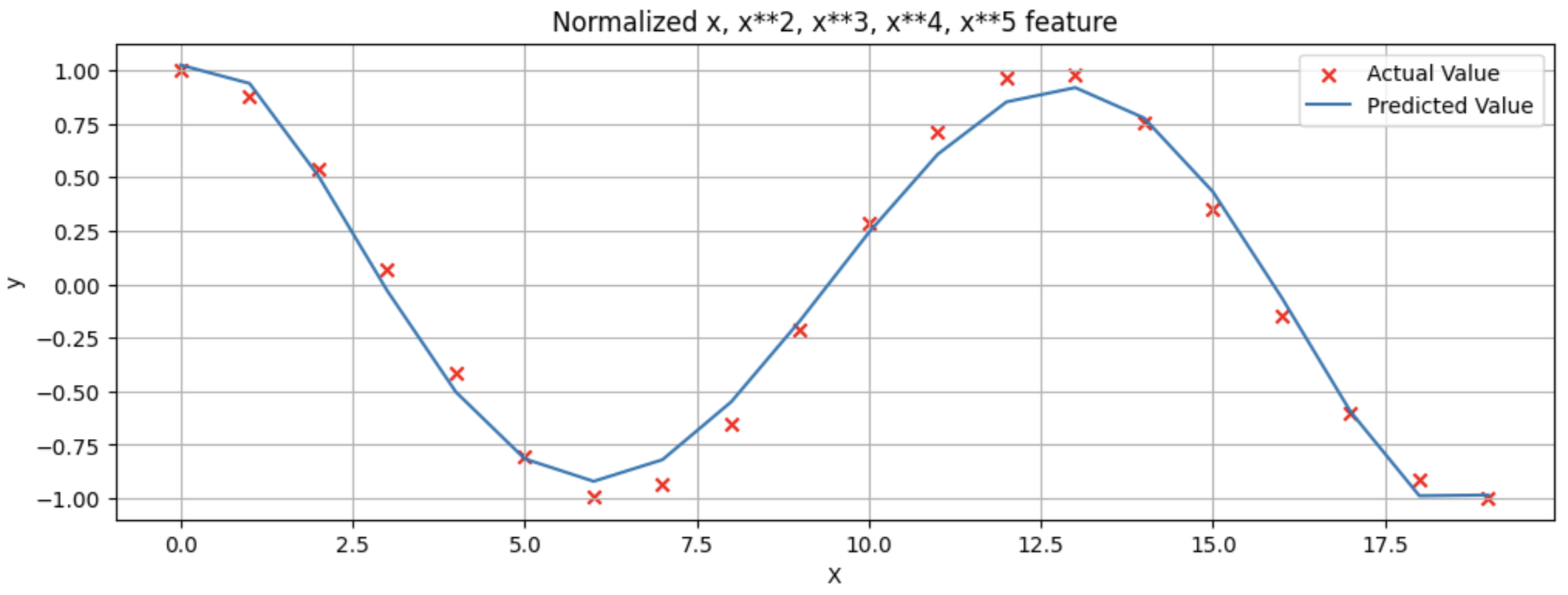
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.scatter(x, y, marker='x', c='r', label="Actual Value"); plt.title("Normalized x x**2, x**3, x**4, x**5 feature")
plt.plot(x, X@w_final + b_final, label="Predicted Value"); plt.xlabel("X"); plt.ylabel("y")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
执行结果
参考
吴恩达团队在Coursera开设的机器学习课程:https://www.coursera.org/specializations/machine-learning-introduction
在B站学习:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Pa411X76s
作者:Standby — 一生热爱名山大川、草原沙漠、风情名城、雪域高原!
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/standby/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/standby/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号