java线程之CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture介绍
在线jdk中文文档 https://www.matools.com/api/java8
CompletableFuture 位于 java.util.concurrent包下面
- 在Java8中,CompletableFuture提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,也提供了转换和组合 CompletableFuture 的方法。
- 它可能代表一个明确完成的Future,也有可能代表一个完成阶段( CompletionStage ),它支持在计算完成以后触发一些函数或执行某些动作。
- 它实现了Future和CompletionStage接口
CompletableFuture方法介绍
静态方法
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
static CompletableFuture<Void> |
allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当所有给定的CompletableFutures完成时,完成。
|
static CompletableFuture<Object> |
anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当任何一个给定的CompletableFutures完成时,完成相同的结果。
|
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> |
completedFuture(U value)
返回已经使用给定值完成的新的CompletableFuture。
|
static CompletableFuture<Void> |
runAsync(Runnable runnable)
返回一个新的CompletableFuture,它在运行给定操作后由运行在
ForkJoinPool.commonPool()中的任务 异步完成。 |
static CompletableFuture<Void> |
runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
返回一个新的CompletableFuture,它在运行给定操作之后由在给定执行程序中运行的任务异步完成。
|
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> |
supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
返回一个新的CompletableFuture,它通过在
ForkJoinPool.commonPool()中运行的任务与通过调用给定的供应商获得的值 异步完成。 |
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> |
supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
返回一个新的CompletableFuture,由给定执行器中运行的任务异步完成,并通过调用给定的供应商获得的值。
|
以Async结尾并且没有指定Executor的方法会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
runAsync方法:它以Runnabel函数式接口类型为参数,所以CompletableFuture的计算结果为空。
supplyAsync方法以Supplier<U>函数式接口类型为参数,CompletableFuture的计算结果类型为U。
runAsync(Runnable runnable)与supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
这两个功能一样,只是一个没有返回值,一个有返回值,示例代码如下:
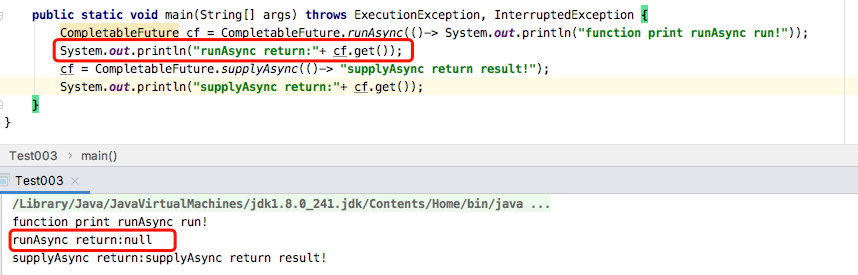
这两个方法的重构方法不在说明。
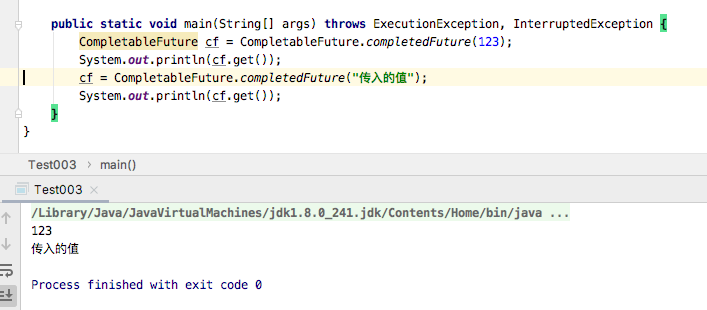
completedFuture
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value)
返回已经使用给定值完成的新的CompletableFuture。
如api介绍,既传入什么值就返回什么值。代码示例:
anyOf与allOf
这两个方法参数可以传入多个CompletableFuture,如方法名字所示一个为全部执行完(allOf),一个为任意一个执行结束(anyOf)
如下分别演示allOf、anyOf
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now()); CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.allOf(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("执行完成"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); return 123; }),CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now()); } System.out.println("执行完成"+Thread.currentThread().getName()); })); System.out.println(cf.get()); }
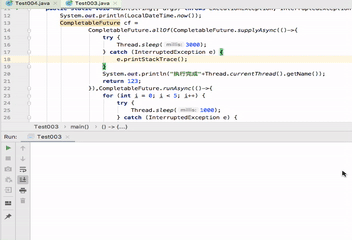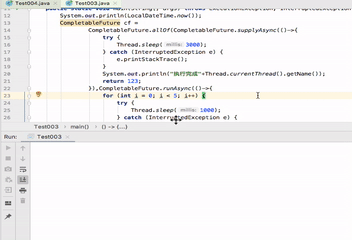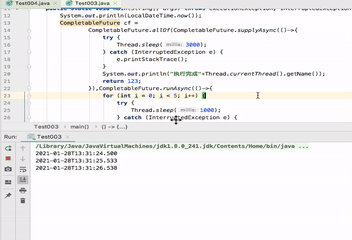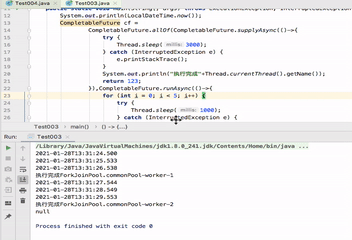
可以看到打印信息,执行完成ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1后 执行完成ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2仍然在执行。
如果把allOf改为anyOf后执行如下:
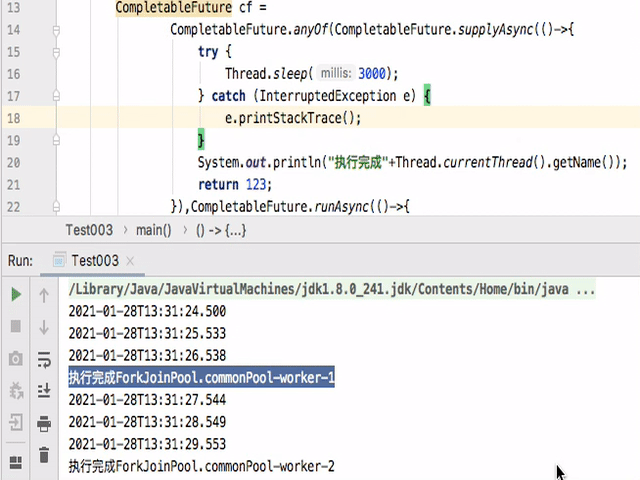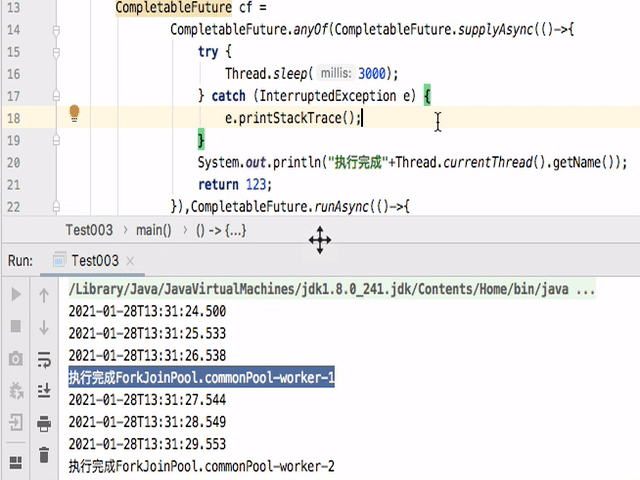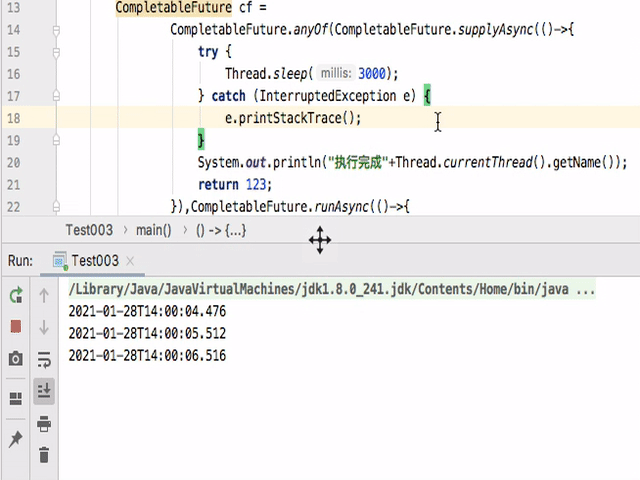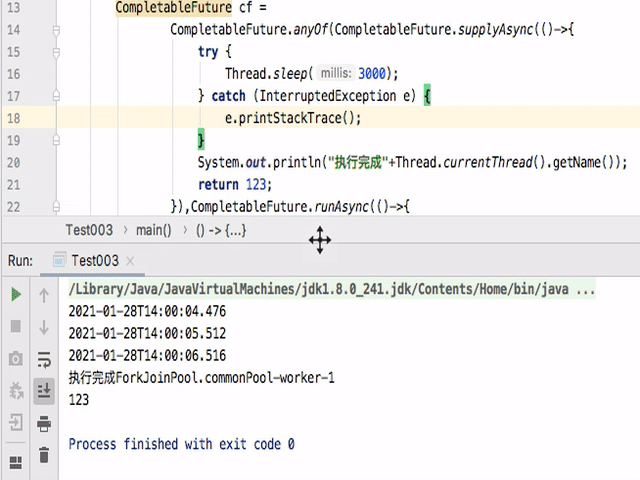
可以看到只要有一个完成,那么整个都就会停止。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
CompletableFuture<Void> |
acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action)
返回一个新的CompletionStage,当这个或另一个给定阶段正常完成时,执行相应的结果作为提供的操作的参数。
|
CompletableFuture<Void> |
acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action)
返回一个新的CompletionStage,当这个或另一个给定阶段正常完成时,将使用此阶段的默认异步执行工具执行,其中相应的结果作为提供的操作的参数。
|
CompletableFuture<Void> |
acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor)
返回一个新的CompletionStage,当这个或另一个给定阶段正常完成时,将使用提供的执行器执行,其中相应的结果作为参数提供给函数。
|
acceptEither
-
两个中那个先执行完,则使用最先完成的进行action操作
-
其中一个执行完毕然后执行action操作,如果主线程没有关闭则另一个线程会继续执行。
-
如果执行cf.get()则会造成主线程阻塞。等待cf执行完毕。如果不执行则主线程与其他几个线程一起执行
public static void acceptEitherOrAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { // 1、两个中那个先执行完,则使用最先完成的进行action操作 // 2、其中一个执行完毕然后执行action操作,如果主线程没有关闭则另一个线程会继续执行。 // 3、如果执行cf.get()则会造成主线程阻塞。等待cf执行完毕。如果不执行则主线程与其他几个线程一起执行 CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+LocalDateTime.now()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return 1; }).acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ // }).acceptEitherAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+LocalDateTime.now()); } return 2; }),(x)->{ System.out.println(x); }); System.out.println(cf.get()); }
测试代码main:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now()); acceptEitherOrAsync(); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 主线程:"+LocalDateTime.now()); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 主线程结束"); }
打印结果如下,可以看到代码是顺序执行:
2021-01-29T11:10:03.053 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 2021-01-29T11:10:04.078 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 2021-01-29T11:10:04.078 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 2021-01-29T11:10:05.079 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 2021-01-29T11:10:05.079 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 2021-01-29T11:10:06.084 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 2021-01-29T11:10:06.084 1 null main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:07.085 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 2021-01-29T11:10:07.085 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2 2021-01-29T11:10:08.085 main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:08.085 main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:09.087 main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:10.087 main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:11.090 main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:12.091 main 主线程:2021-01-29T11:10:13.092 main 主线程结束
如果注释掉上面的cf.get(),执行结果则是并发打印
applyToEither
这个与acceptEither 只是action操作有返回值与无返回值区别,这里不再演示。
join
如果正常完成则返回结果值,如果异常则返回异常。
public static void join() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Integer result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ return 1/1; }).join(); System.out.println(result); }
handle
当此阶段正常或异常完成时,将使用此阶段的结果和异常作为所提供函数的参数执行。跟上面join的区别在于上面抛出异常,这里进行异常拦截
public static void handle() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ return 1/0; }).handle((x,y)->{ System.out.println(y.getMessage()); return x; }); System.out.println(cf.get()); }
打印如下:
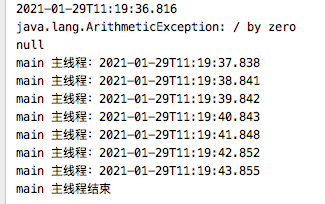
该方法可以处理异常与正常结果。并进行再次处理。
void |
obtrudeException(Throwable ex)
强制导致后续调用方法
get()和相关方法抛出给定的异常,无论是否已经完成。 |
void |
obtrudeValue(T value)
强制设置或重置随后方法返回的值
get()和相关方法,无论是否已经完成。 |
这两个方法如描述所示,
runAfterBoth
返回一个新的CompletionStage,当这个和另一个给定的阶段都正常完成时,执行给定的动作。
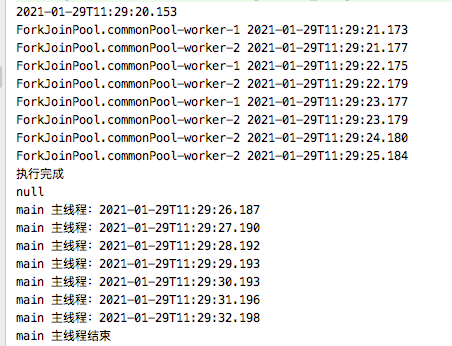
public static void runAfterBoth() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { // 1、两个同时执行完成则执行action // 2、跟acceptEither是对立的,acceptEither是那个先执行完成再执行action,这个是全部完成。与allOf/anyOf类似 CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+LocalDateTime.now()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return 1; }).runAfterBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+LocalDateTime.now()); } return 2; }),()->{ System.out.println("执行完成"); }); System.out.println(cf.get()); }
方法:thenApply
类似管道一样的方法值多重处理,代码仅是演示无实际意义
public static void thenApply() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { // 1、两个同时执行完成则执行action // 2、跟acceptEither是对立的,acceptEither是那个先执行完成再执行action,这个是全部完成。与allOf/anyOf类似 CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+LocalDateTime.now()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return 1; }).thenApply((x)->{ return x+1; }).thenApply((x)->{ return x+1; }); System.out.println(cf.get()); }
方法:thenAcceptBoth
返回一个新的CompletionStage,当这个和另一个给定的阶段都正常完成时,两个结果作为提供的操作的参数被执行。
既:两个结果都完成后一起传给action并执行逻辑。如下代码:
public static void thenAcceptBoth() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ return 1; }).thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+LocalDateTime.now()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return 2; }),(x,y)->{ System.out.println("结果:"+x+y); }); System.out.println(cf.get()); }
打印可以看出,结果的输出为两个任务都执行完毕才打印。
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/cjsblog/p/9267163.html
https://blog.csdn.net/finalheart/article/details/87615546
https://blog.csdn.net/cainiao_user/article/details/76423495



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号