学习率调度
什么是学习率调度程序
学习率调度程序(Learning Rate Scheduler)是一种在训练过程中调整学习率的方法,通常会随着训练的进行而降低学习率。这有助于模型在训练开始时(此时参数远离其最佳值)进行较大的更新,并在稍后参数更接近其最佳值时进行较小的更新,从而实现更多的微调。
实践中广泛使用了几种学习率调度器。在本文中,我们将重点介绍三种流行的:
- 步进衰减(Step Decay)
- 指数衰减(Exponential Decay)
- 余弦退火(Cosine Annealing)
让我们通过直观的示例深入了解每个调度程序。
1. Step Decay
步进衰减每隔几个时期就会将学习率降低一个常数倍。步进衰减的形式定义为:
\[\Large lr = lr_{0} \cdot d^{(floor(1+epoch)/s)}
\]
- _lr_0 is the initial learning rate,
- d is the decay rate,
- s is the step size, and
- epoch is the index of the epoch.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Parameters
initial_lr = 1.0
decay_factor = 0.5
step_size = 10
max_epochs = 100
# Generate learning rate schedule np.floor(x)向下取整
lr = [
initial_lr * (decay_factor ** np.floor((1+epoch)/step_size))
for epoch in range(max_epochs)
]
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.plot(lr)
plt.title('Step Decay Learning Rate Scheduler')
plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
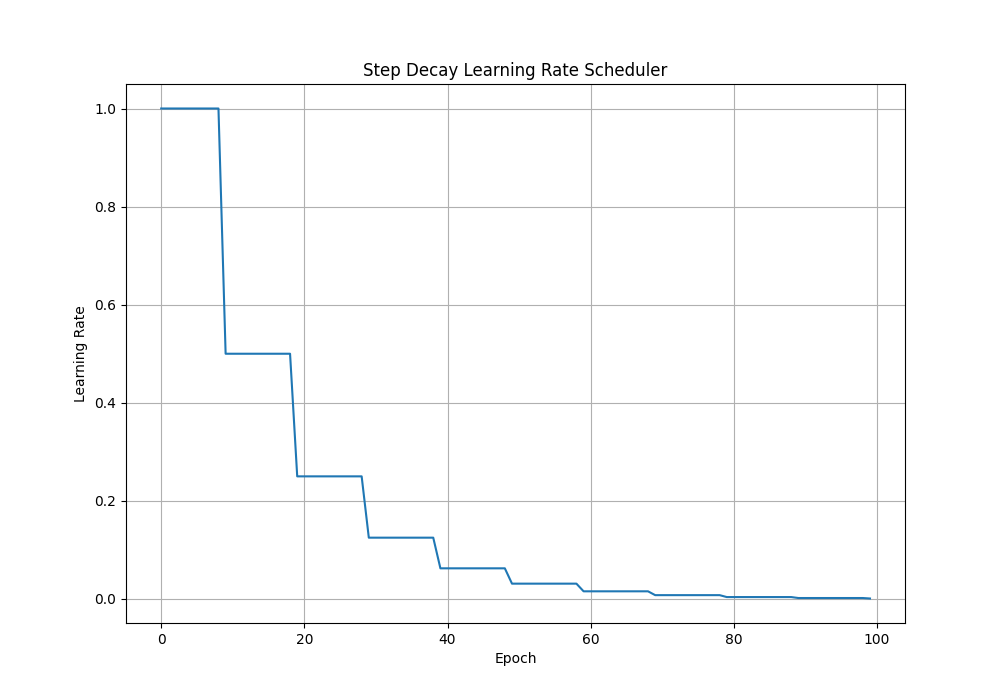
学习率每 5 个 epoch 下降 0.5 倍
2. Exponential Decay
\[\Large lr = lr_{0} \cdot e^{-k \cdot epoch}
\]
- _lr_0 is the initial learning rate,
- k is the decay rate, and
- epoch is the index of the epoch.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Parameters
initial_lr = 1.0
decay_rate = 0.05
max_epochs = 100
# Generate learning rate schedule
lr = [
initial_lr * np.exp(-decay_rate * epoch)
for epoch in range(max_epochs)
]
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.plot(lr)
plt.title('Exponential Decay Learning Rate Scheduler')
plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
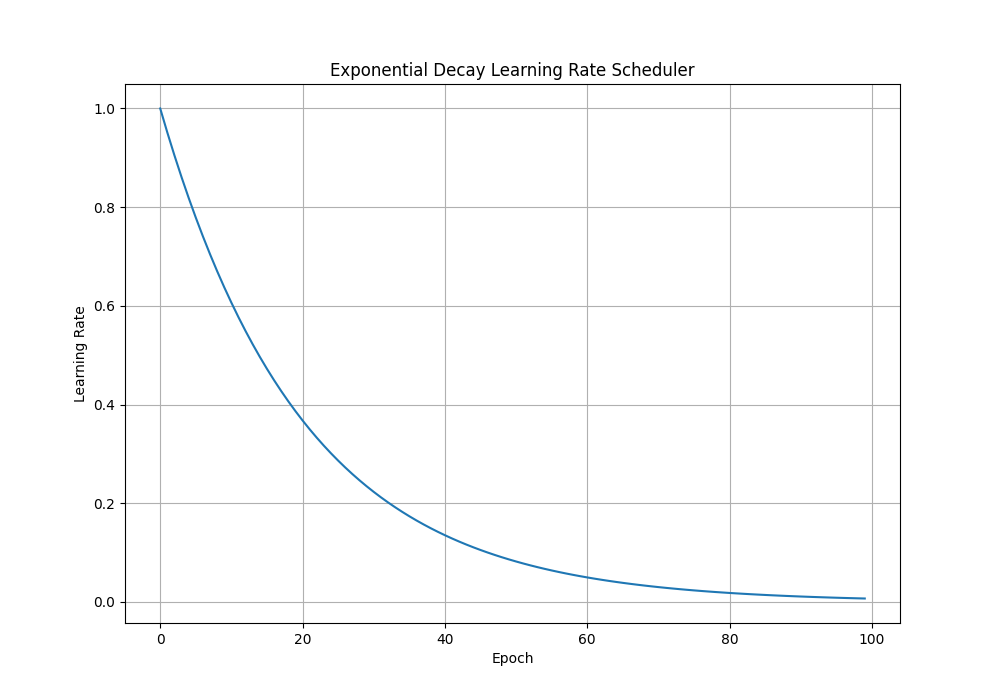
3. Cosine Annealing
余弦退火使用基于余弦的时间表来降低学习率。余弦退火的形式定义为:
\[\Large lr=lr_{\min}+0.5\cdot(lr_{\max}-lr_{\min})\cdot\left(1+\cos\left(\frac{\text{epoch}}{\text{max}_\text{epochs}}\cdot\pi\right)\right)
\]
- _lr_min_ is the minimum learning rate,
- _lr_max_ is the maximum learning rate, and
- epoch and max_epochs are the current and maximum number of epochs respectively.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Parameters
lr_min = 0.001
lr_max = 0.1
max_epochs = 100
# Generate learning rate schedule
lr = [
lr_min + 0.5 * (lr_max - lr_min) * (1 + np.cos(epoch / max_epochs * np.pi))
for epoch in range(max_epochs)
]
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.plot(lr)
plt.title("Cosine Annealing Learning Rate Scheduler")
plt.ylabel("Learning Rate")
plt.xlabel("Epoch")
plt.show()
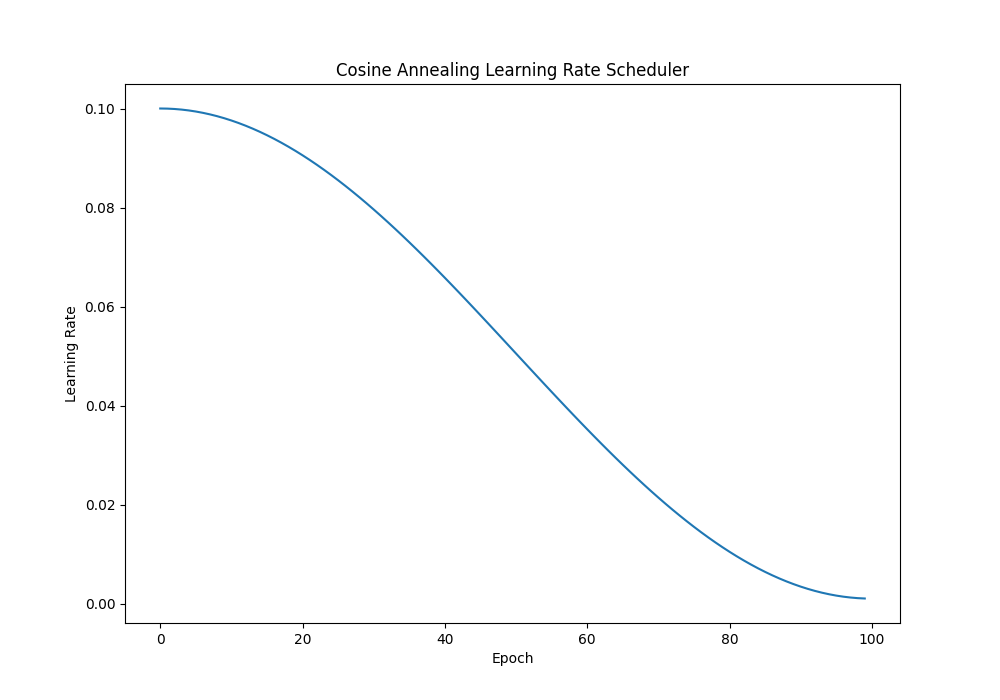
余弦退火策略 + warmup
对于 transformer 架构,学习率计划的设计与 CNN 不同。
先前的研究表明,学习率的预热对于使用 transformer 架构训练模型很有用。
预热计划
- 一开始将学习率设置为 0。
- 在预热期间,学习率从 0 线性增加到初始学习率。
import math
import torch
from torch.optim import Optimizer
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import LambdaLR
# 余弦退火策略 + warmup 前 xxx 轮为热身,之后使用余弦退火更新学习率
def get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(
optimizer: Optimizer, # 如 Adam、SGD
num_warmup_steps: int, # 热身阶段的步数,在此阶段学习率从 0 线性增加到初始学习率
num_training_steps: int, # 总的训练步数,用于计算余弦退火的进度
num_cycles: float = 0.5, # 余弦调度的周期数,默认为 0.5
last_epoch: int = -1, # 用于恢复训练时的最后一个epoch的索引,默认为 -1
):
def lr_lambda(current_step):
# Warmup
if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
return float(current_step) / float(max(1, num_warmup_steps))
# decadence
progress = float(current_step - num_warmup_steps) / float(
max(1, num_training_steps - num_warmup_steps)
)
return max(
0.0, 0.5 * (1.0 + math.cos(math.pi * float(num_cycles) * 2.0 * progress)) # max(0.0, ...) 确保学习率不会变为负值
)
return LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda, last_epoch)
具体使用例子:
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
scheduler = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, warmup_steps, total_steps)
# Updata model
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号