Python 类对象、类属性、类方法、静态方法。
类对象
我们在 class 类名: 进行定义后当解释器执行到class 语句的时候就会创建一个类对象
class Student:
pass
print(type(Student))
print(id(Student))
Stu2 = Student
s1 = Stu2()
print(s1)
====
<class 'type'>
42634280
<__main__.Student object at 0x0000000002285AC8>类属性
类级别的 属性也可以创建, 被所有实例所共享的
class Student:
company = "sowhat" # 类属性
count = 0 # 类属性
def __init__(self,name,score):
self.name = name
self.score = score
Student.count += 1
def say_score(self):
print("my company is:",Student.company)
print(self.name,' score is :',self.score)
s1 = Student('张三',80)
s1.say_score()
print('一共创建{0}个Student对象'.format(Student.count))
===
my company is: sowhat
张三 score is : 80
一共创建1个Student对象类方法
类方法是从属与 类对象 的方法,类方法通过装饰器 @classmethod 来定义,个数如下
@classmethod
def 类方法名字(cls,[,形参列表]):
函数体1. @classmethod 必须位于方法上面一行
2. 第一个cls 必须有,cls 指的就是 ‘类对象’ 本身。
3. 调用类方法的格式 : 类名(实例化对象).类方法名(参数列表)。参数列表不能也不可以给cls传值。
4. 类方法中访问实例属性跟实例方法会报错。
5. 子类继承父类方法的时候,传入cls是子类的对象,而非父类对象。
class Student:
company = "sowhat"
@classmethod
def printCompany(cls):
print(cls.company)
Student.printCompany()静态方法
Python 中允许定义跟 ‘类对象’ 无关的方法,称为 静态方法, 静态方法跟模块中定义的普通函数没有区别,只不过 静态方法放到了 类的名字空间,需要通过类调用。静态方法通过 @staticmethod 来定义。
1. @staticmethod 必须位于方法的第一行
2. 调用静态方法的格式: 类名(实例化对象). 静态方法名字(参数)
3. 静态方法中访问实例属性跟实例方法会报错。
内存分析实例对象跟类对象创建过程
class Student:
company = "sowhat"
count = 0
def __init__(self,name,score):
self.name = name
self.score = score
Student.count += 1
def say_score(self):
print("my company is :",Student.company)
print(self.name, ' score is :' ,self.score)
s1 = Student('张三',88)
s1.say_score()
print('一共创建{0}个Student实例化对象'.format(Student.count))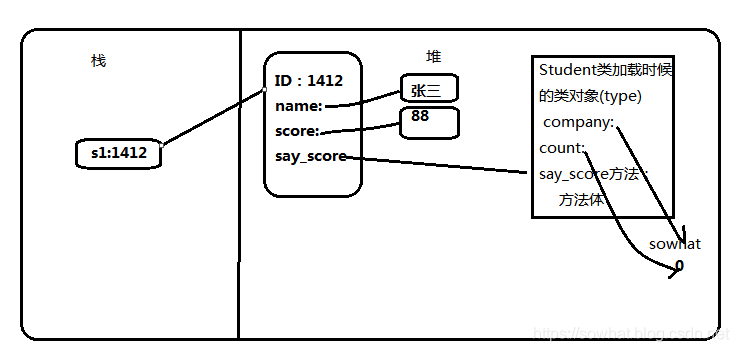
关注公众号 海量干货等你




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号