MySQL文本处理函数
在MySQL使用中,有时不可避免的使用到文本处理函数。这些函数给数据的处理和转换提供了方便。
本文用到的表如下
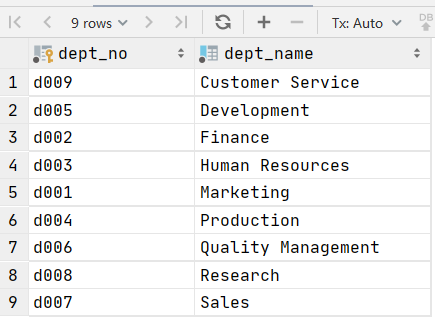
建表语句,点击查看
create table departments
(
dept_no char(4) not null
primary key,
dept_name varchar(40) not null,
constraint dept_name
unique (dept_name)
);
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d009', 'Customer Service');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d005', 'Development');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d002', 'Finance');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d003', 'Human Resources');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d001', 'Marketing');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d004', 'Production');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d006', 'Quality Management');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d008', 'Research');
INSERT INTO employees.departments (dept_no, dept_name) VALUES ('d007', 'Sales');常用的文本处理函数:
| 函数 | 说明 |
| left() | 返回串左边的字符 |
| length() | 返回串的长度 |
| lower() | 将串转换为小写 |
| Ltrim() | 去掉串左边的空格 |
| Right() | 返回串右边的字符 |
| rtrim() | 去掉串右边的空格 |
| soundex() | 返回串的soundex值 |
| substring() | 返回串的一个子串 |
| locate() | 找出串的一个子串 |
| upper() | 将串转换为大写 |
使用:
将改表的部门名称字段作为实验字段,验证upper(),lower(),left(),right(),length(),locate() 这几个函数。
select dept_no,
dept_name,
upper(dept_name) as '转为大写',
lower(dept_name) as '转为小写',
left(dept_name, 4) as '左边的4个字符',
right(dept_name, 4) as '右边的4个字符',
length(dept_name) as '字符串的长度',
locate('an', dept_name) as '文本an出现的位置'
from departments;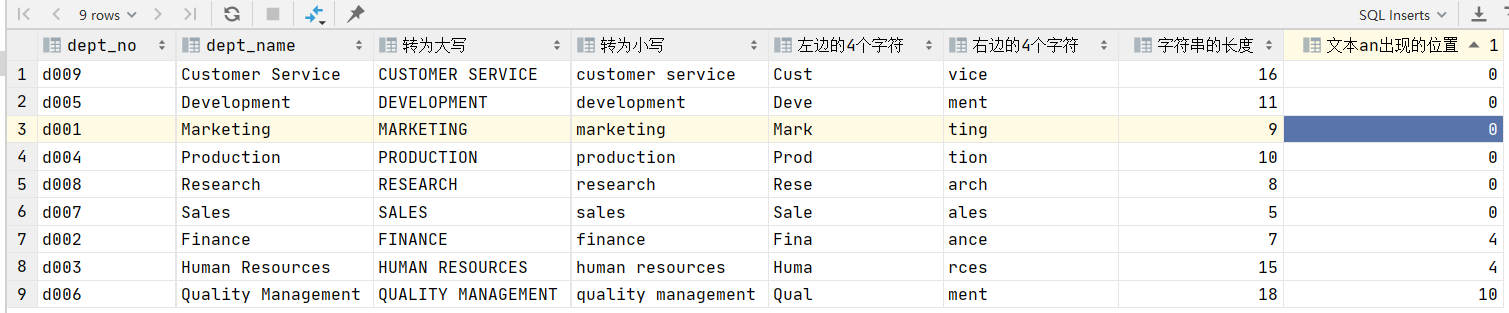
以下是单独说明LOCATE(),RTRIM(),LTRIM(),substring()这几个函数的用法
locate()函数是代表,子串在字符串中第一次出现的位置
mysql> SELECT LOCATE('bar', 'foobarbar'); --查询子串'bar'在字符串'foobarbar'中第一次出现的位置
-> 4
mysql> SELECT LOCATE('xbar', 'foobar'); --这是查询子串'xbar'在字符串 'foobar'中出现的位置,因为 没有所以返回0
-> 0
mysql> SELECT LOCATE('bar', 'foobarbarbar', 5); --这是从字符串'foobarbarbar'中第5个位置开始找子串'bar'第一次出现的位置
-> 7
利用concat()函数验证rtrim()和ltrim()
select concat('|',rtrim(' nothing '),'|',ltrim(' nothing '),'|');运用竖线|做分隔符,验证rtrim函数去除右空格,验证ltrim函数去除左空格。

subString()函数是截图一个字符串,第一个参数是要被截取的字符串,第二个参数是开始截取的位置,第三个参数是截取的长度如果为空,则代表截取全部
mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Quadratically',5); --从第5个位置开始截取子串,
-> 'ratically'
mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('foobarbar' FROM 4); --从第4个位置开始截取子串
-> 'barbar'
mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Quadratically',5,6); --从Quadratically这个字符串的第5个的位置开始截取6位的长度
-> 'ratica'
mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Sakila', -3); --位置为负数时,代表从右边往左数,-3代表从右数三位,一直到最后
-> 'ila'
mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Sakila', -5, 3); --Sakila这个字符串从右往左数5位开始截取3位字符
-> 'aki'
mysql> SELECT SUBSTRING('Sakila' FROM -4 FOR 2); --这个从右往左数4位开始截取2位字符
-> 'ki'
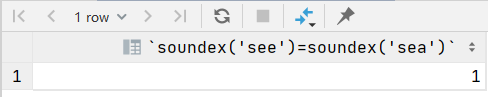
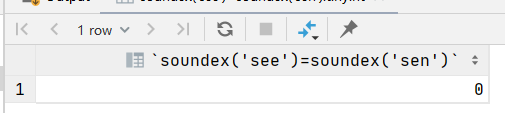
soundex()函数将文本串转换为描述其语音表示的字母数字模式的算法,soundex()函数考虑了类似发音字符和音节,使得能对串发音比较而不是字母比较。
是不是比较难以理解,通俗点说就是soundex()函数比较的时发音,就是发的音是否类似,see和sea的发音就类似,see和sen的发音就不同,这个函数比较的发音的类似性,跟组成单词的字母是无关
select soundex('san')=soundex('sam') ;
select soundex('see')=soundex('sea') ;
select soundex('see')=soundex('sen');





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号