第二次大作业分析
一,前言
1,第四次作业(针对四边形分析)
四边形的有关计算,判断是否四边形,平行四边形,判断是否为规则四边形,判断四边形凹凸。后面是判断直线和四点构成多边形的交点和面积,以及第一个点是否在四点构成多边形的内部。考查了我们对多边形的规则凹凸判断,以及面积计算。本题题量不多,但难度还是比较大的,就比如四个点要判断构成四边形和三角形,并且是点是按顺序排的,如果是随意排的话会比较简单一点。
2,第五次作业(针对五边形分析)
7-1和7-2就是一题,一起来分析。五边形的有关计算,判断是否五边形,,判断五边形凹凸,并且输出周长。后面是判断直线和五点构成多边形的交点和面积,以及第一个点是否在四点构成多边形的内部。后面题型比较新颖,判断两个凸多边形位置关系,计算两个凸多边形交叉面积。第四次作业考察的知识点本题全来了,新加的知识点就是两个凸多边形位置关系,以及计算两个凸多边形交叉面积。这题题量虽小难度却是很大的,相比前两次,输入五个点判断是什么多边形,这里类型就很多了工程量就很大。
3,期中考试
期中考试有三题,点线面的类的构造,以及父类的构造。期中考试还是很简单的,基本上前几次的多边形脑海里就构造了差不多的点线面了。而且面与前面的点线也没有什么关联,如果有关联的话难度就会增加一等。
二,设计与分析(代码部分已折叠)
1,第四次作业(针对四边形分析)
蛟龙号与银行业务很简单,就不做分析设计了。
看看四边形的题目
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
设计:
怎么判断四边形呢咱们?没错,相邻两边不平行,和对边没有交点

1 quadrilateral(point a, point b, point c, point d) {//输入四个点判断是否为四边形,判断是否存在两点重合, 2 Collinear_jud(a, b, c, d); 3 line jud3 = new line(d, a, b, c); 4 line jud3_1 = new line(b, c, d, a); 5 line jud4 = new line(a, b, c, d); 6 line jud4_1 = new line(c, d, a, b); 7 if (!collinear_jud && (!jud3.jud || !jud3_1.jud) && (!jud4.jud || !jud4_1.jud)) 8 quadrilateral_jud = true;//true为是四边形 9 10 if ((a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y) || (a.x == c.x && a.y == c.y) || (a.x == d.x && a.y == d.y) 11 || (b.x == c.x && b.y == c.y) || (b.x == d.x && b.y == d.y) || (c.x == d.x && c.y == d.y) 12 ) coincide_jud = true;//true为存在两点重合 13 area_quadrilateral(a, b, c, d);//判断凹凸,计算面积 14 }
轻松get
判断是什么样的多边形,我就在主函数体现了

judging.dot_num(4); if (judging.k) return; quadrilateral quadrilateral_jud2 = new quadrilateral(the_dot.dots[1], the_dot.dots[2], the_dot.dots[3], the_dot.dots[4]); if (!quadrilateral_jud2.quadrilateral_jud||quadrilateral_jud2.coincide_jud) { System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); return; } triangle right_angle_jud = new triangle(the_dot.dots[1], the_dot.dots[2], the_dot.dots[3]); line l12 = new line(the_dot.dots[1], the_dot.dots[2]); line l23 = new line(the_dot.dots[2], the_dot.dots[3]); line l34 = new line(the_dot.dots[3], the_dot.dots[4]); line l41 = new line(the_dot.dots[4], the_dot.dots[1]); if (l12.len == l23.len && l12.len == l34.len && l12.len == l41.len) System.out.print("true" + " "); else System.out.print("false" + " "); if (l12.len == l34.len && l23.len == l41.len && right_angle_jud.right_angled_triangle) System.out.print("true" + " "); else System.out.print("false" + " "); if (l12.len == l23.len && l12.len == l34.len && l12.len == l41.len && right_angle_jud.right_angled_triangle) System.out.print("true"); else System.out.print("false");
这三种四边形各有各的特点,只要四条边相等的都是菱形,矩形呢只要对边相等,再加一个九十度就好了,正方形就要再菱形的基础上加一个九十度。还是比较轻松的。
对于剩下的凹凸判断呢,怎么样才是一个凹的四边形呢,不就是有一个点在另外三个点构成的三角形内部嘛,排除掉在三角形边上的情况,剩下的不就是在外部嘛。说干就干,直接上代码

public void area_quadrilateral(point a, point b, point c, point d) {//判断凹凸,计算面积 triangle Concave_quadrilateral1 = new triangle(a, b, c, d); triangle Concave_quadrilateral2 = new triangle(b, c, d, a); triangle Concave_quadrilateral3 = new triangle(c, d, a, b); triangle Concave_quadrilateral4 = new triangle(d, a, b, c); if (Concave_quadrilateral1.in_the_triangle || Concave_quadrilateral2.in_the_triangle || Concave_quadrilateral3.in_the_triangle || Concave_quadrilateral4.in_the_triangle ) Concave_quadrilateral = true;//凹四边形 if (Concave_quadrilateral1.in_the_triangle) quadrilateral_area = area(a, b, c, d); else if (Concave_quadrilateral2.in_the_triangle) quadrilateral_area = area(b, c, d, a); else if (Concave_quadrilateral3.in_the_triangle) quadrilateral_area = area(c, d, a, b); else if (Concave_quadrilateral4.in_the_triangle) quadrilateral_area = area(d, a, b, c); else quadrilateral_area = area(a, b, c, d); }
凹凸判断完了之后还要算边长面积,代码也放在上面了。最后也是拿下
选项4呢是判断交点和切割面积的问题,判断是什么图形是最难的部分,最离谱的呢,是首尾不相连的也算三角形(其实到了下一次才是最令人崩溃的,五个点判断三角形,首尾不相连判断)首先我们要做的就是判断四边形还是三角形,然后输出交点,然后输出面积

quadrilateral(point m, point n, point a, point b, point c, point d) {//计算四边形被切割面积
area_quadrilateral(a,b,c,d);
double total_s=quadrilateral_area;
int i=0,j=0,k=0;
point[] p1=new point[4];//存储凹四边形在切割直线上方的点
point[] p2=new point[4];//存储直线与凹四边形的交点
point[] p3=new point[4];//存储凹四边形在切割直线下方的点
line ab=new line(m,n,a,b);
line bc=new line(m,n,b,c);
line cd=new line(m,n,c,d);
line da=new line(m,n,d,a);
if(!ab.jud&&!bc.jud&&!cd.jud&&!da.jud){System.out.println(0);return;}//0
else if((ab.s1==0&&((ab.s2>0&&cd.s1>0&&cd.s2>0)||(ab.s2<0&&cd.s1<0&&cd.s2<0)))||
(ab.s2==0&&((ab.s1>0&&cd.s1>0&&cd.s2>0)||(ab.s1<0&&cd.s1<0&&cd.s2<0)))||
(cd.s1==0&&((ab.s1>0&&ab.s2>0&&cd.s2>0)||(ab.s1<0&&ab.s2<0&&cd.s2<0)))||
(cd.s2==0&&((ab.s1>0&&ab.s2>0&&cd.s1>0)||(ab.s1<0&&ab.s2<0&&cd.s1<0)))
)
{System.out.println(1);return;}//1
// else if(ab.jud&&bc.jud&&cd.jud&&da.jud&&(ab.s1==0||ab.s2==0||cd.s1==0||cd.s2==0))
// {System.out.println(3);return;}
// // else if(ab.jud&&bc.jud&&cd.jud&&da.jud&&(ab.s1!=0||ab.s2!=0||cd.s1!=0||cd.s2!=0))
// // {System.out.println(4);return;}
if(ab.jud){point temp=new point(ab.jiaodian_a,ab.jiaodian_b);p2[i]=temp;i++;}
if(bc.jud){point temp=new point(bc.jiaodian_a,bc.jiaodian_b);p2[i]=temp;i++;}
if(cd.jud){point temp=new point(cd.jiaodian_a,cd.jiaodian_b);p2[i]=temp;i++;}
if(da.jud){point temp=new point(da.jiaodian_a,da.jiaodian_b);p2[i]=temp;i++;}
line lmn=new line(m,n);
if(lmn.A*a.x+lmn.B*a.y+lmn.C<0){p1[j]=a;j++;}
if(lmn.A*b.x+lmn.B*b.y+lmn.C<0){p1[j]=b;j++;}
if(lmn.A*c.x+lmn.B*c.y+lmn.C<0){p1[j]=c;j++;}
if(lmn.A*d.x+lmn.B*d.y+lmn.C<0){p1[j]=d;j++;}
if(lmn.A*a.x+lmn.B*a.y+lmn.C>0){p3[k]=a;k++;}
if(lmn.A*b.x+lmn.B*b.y+lmn.C>0){p3[k]=b;k++;}
if(lmn.A*c.x+lmn.B*c.y+lmn.C>0){p3[k]=c;k++;}
if(lmn.A*d.x+lmn.B*d.y+lmn.C>0){p3[k]=d;k++;}
if(j==1||k==1)
{ point dot = null;
if(j==1) dot=p1[0];
if(k==1) dot=p3[0];
line l=new line(p2[0],p2[1]);
line z=new line(m,n,dot);
double s1=z.len_c_ab*l.len/2;
System.out.print(2+" ");
Print(Math.min(s1,total_s-s1));
System.out.print(" ");
Print(Math.max(s1,total_s-s1));
}
else if(j==2||k==2){
point dot1 = null,dot2=null;
if(j==2) {dot1=p1[0];dot2=p1[1];}
if(k==2) {dot1=p3[0];dot2=p3[1];}
area_quadrilateral(p2[0],p2[1],dot1,dot2);
double s1=quadrilateral_area;
System.out.print(2+" ");
Print(Math.min(s1,total_s-s1));
System.out.print(" ");
Print(Math.max(s1,total_s-s1));
}
}
}
计算面积的时候,我用了三个数组,一个存储交点,一个存储直线上的端点,一个存储直线下面的端点。然后利用这些点计算面积。
这里老是有一个点过不去,最后截至了也没有找到
选项5,判断点在四边形的位置,这不就是为下次判断凹凸五边形做基础嘛,果断使用面积法,面积相等在内部否则在外部。

public void in_the_quadrilateral_jud(point m, point a, point b, point c, point d) { line lab1 = new line(b, a, m, c); line lbc1 = new line(b, c, m, a); line lcd1 = new line(c, d, m, a); line lda1 = new line(a, d, m, c); if (lab1.s1 * lcd1.s1 < 0 && lbc1.s1 * lda1.s1 < 0) in_the_quadrilateral = true; else if (lab1.s1 * lcd1.s1 > 0 || lbc1.s1 * lda1.s1 > 0) in_the_quadrilateral = false; else on_the_quadrilateral = true; }
最后也是成功拿捏了
接下来看看我的类图
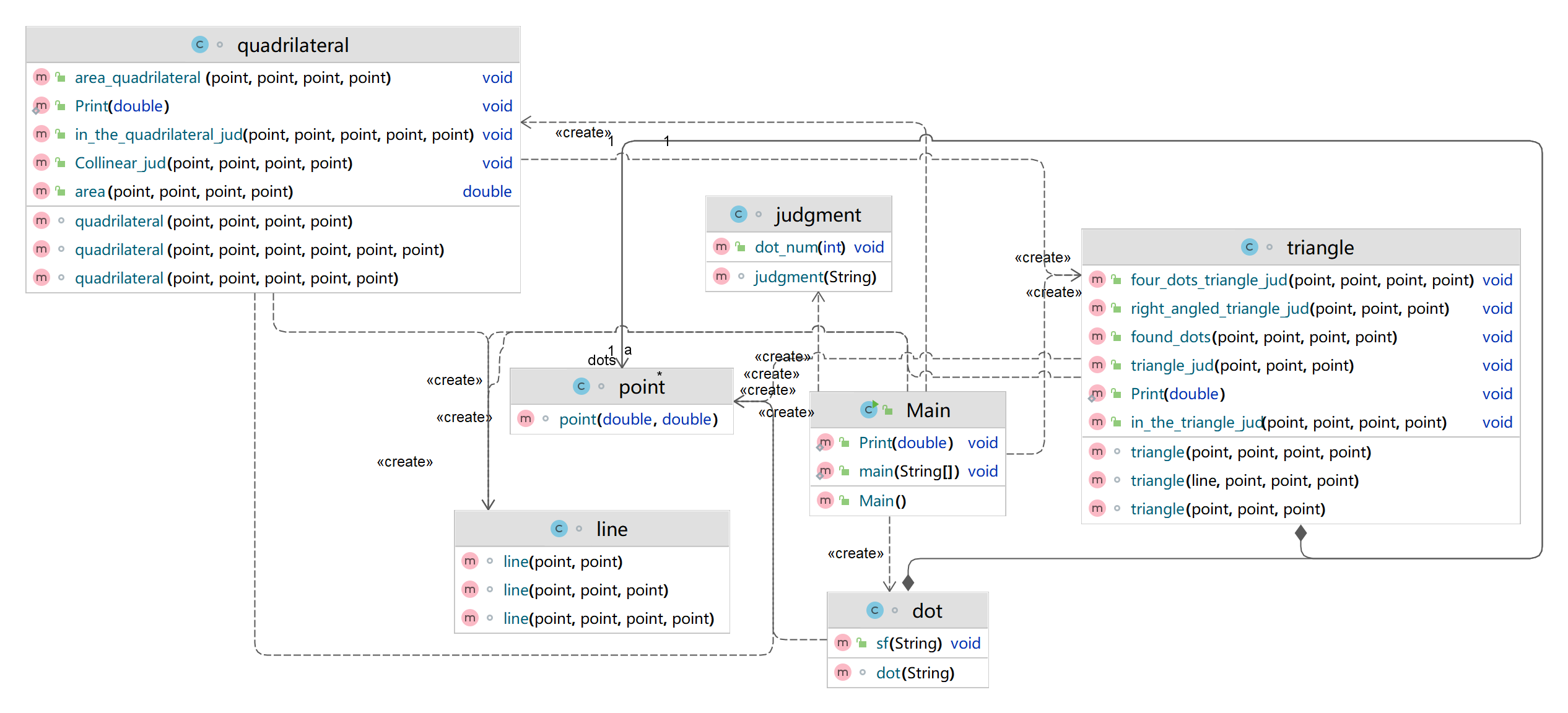
judgment是判断输入的格式对不对,这里只需要比较终极正则表达式即可
([1-9]:)([+|-]?(0|[1-9][0-9]*)(\\.\\d+)?,[+|-]?(0|[1-9][0-9]*)(\\.\\d+)? ?)+
这一条表达式真的已经是最终版了,已经可以判断任何的输入了。
另外呢,就加了一个四边形类,对四边形处理计算。其他的没什么变化。
看看代码质量
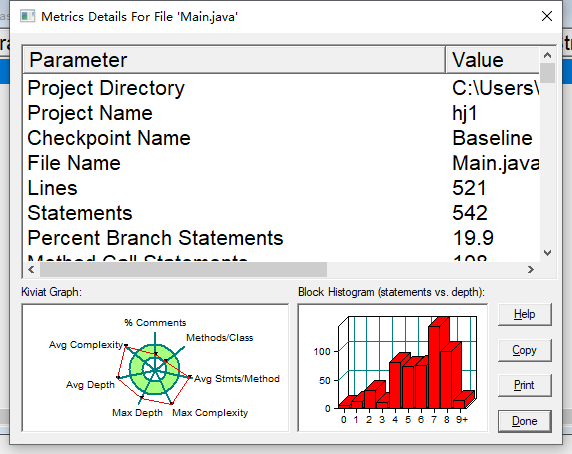
521行
声明 542
分支声明百分比 19.9
方法调用语句 108
带注释的行数百分比 10.9
类和接口 7
每类方法 4.43
每个方法的平均语句数 16.90
最复杂方法的行数 325
最复杂方法四边形() 的名称
最大复杂度 83
最深块的行数 417
最大块深 9+
平均区块深度 5.80
平均复杂度 11.35
2,第五次作业(五边形)
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
设计:
这是前半部分的题目,在上次前提上,我在本次作业中加了父类,多边形类,面积和周长什么的都在里面算好来,只需传入多边形的点数组就可以算出来
选项1是判断五边形,与上一次的区别是,上次只需要判断与一条对边没有交点,这次判断的是与不相邻的边没有交点,见代码

private void jud_Pentagon() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { if(lines[i%5].slope==lines[(i+1)%5].slope){is_Pentagon = false;return;} lines[i%5].segment_intersection(lines[i%5],lines[(i+2)%5]); if(lines[i%5].jud){is_Pentagon = false;return;} lines[i%5].segment_intersection(lines[i%5],lines[(i+3)%5]); if(lines[i%5].jud){is_Pentagon = false;return;} } if(is_Pentagon){ p=new pentagon(points);} }
最后也是拿下
对于选项二,凹凸判断,以及面积计算,凹凸判断不多说,调用上次作业点是不是在四边形内即可,面积我在本次作业里面有了一定改进。这次我采用了鞋底公式直接算多边形面积,只要是多边形都可以运用这个公式。顺序传入多边形的坐标即可。周长也是,在每一个子类上加了点的数组,边的数组,调用边的的数组即可算周长。看看关键代码

public double get_area(point[] dot) { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) sum+=(dot[i%5].x*dot[(i+1)%5].y)-(dot[i%5].y*dot[(i+1)%5].x); return Math.abs(sum)/2; }
传入数组直接算出面积周长,相比之前还要计算点到直线的距离,好麻烦。
拿下拿下
下一个点,直线和多边形我觉得每次都是这种最难了,这次要判断的是五个点可以构成五边形,四边形,三角形,可算是把人整麻了,五个点五边形简单,选项1已经搞完了,那么四边形呢,四边形有五种情况,然后把点交换一下又有五种情况,所以这里我采用循环,首先把第0个点移掉,另外四个点拿出来构成四边形,然后就是对第0个点进行判断,它可以与第4,第1,第2个点重合,可以在14边上,可以在12边上,这就是无五种情况。然后每个点加一,此时的点0就变成了点1,点四就被拿出来判断了,一直循环,找出一种情况构成四边形,存储起来计算。三角形也是类似的过程,只不过要拿出两个点来判断,判断这两个点在另外三个点构成的三角形里面的位置符不符合输入。不过比较遗憾的是,我在题目截至时间内没有写,因为那段时间刚刚解封,驾校教练催着我考驾照,我一直在刷科目一的题目,没什么时间写。三角形的就没有写了,后半部分的题目也没有写。但是写了的都对了。
代码:

public void incise(line l,line[] line,point[] dot){ point[] pl= new point[6]; int k=0;double sums=0,totals,sum=0,s; for(int i=0;i<line.length;i++) { if(l.A*dot[i].x+l.B*dot[i].y+l.C<0) { pl[k]=dot[i]; k++; } line temp=new line(); temp.segment_intersection(l,line[i]); if(temp.jud2) { point d= new point(temp.jiaodian_a,temp.jiaodian_b); pl[k]=d; k++; } if(line[i].dot1.x*l.A+line[i].dot1.y*l.B+l.C==0&&line[i].dot2.x*l.A+line[i].dot2.y*l.B+l.C==0) {System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");return;} } for(int i=0;i<dot.length;i++) sums+=(dot[i%dot.length].x*dot[(i+1)%dot.length].y)-(dot[i%dot.length].y*dot[(i+1)%dot.length].x); totals=Math.abs(sums)/2; for(int i=0;i<k;i++) sum+=(pl[i%k].x*pl[(i+1)%k].y)-(pl[i%k].y*pl[(i+1)%k].x); s=Math.abs(sum)/2; min_area=Math.min(s,totals-s); max_area=Math.max(s,totals-s); System.out.print(2+" "); Print(min_area); System.out.print(" "); Print(max_area); }
判断三角形这里都没有写
附上全部代码

package others; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; import static java.lang.System.arraycopy; public class Main { public static void Print(double data) { //保留三位小数 DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0##"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.print(df.format(data)); } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String str = in.nextLine();//输入一串字符 judge judging = new judge(str); if (judging.f) return; String[] str1 = str.split(":", 2); String new_str = str1[1];//冒号后的字符串new_str dot the_dot = new dot(new_str); the_dot.sf(new_str);//对new_str进行点的采取 char num = str.charAt(0);//提取冒号前的选项 switch (num) { case '1': judging.dot_num(5); if (judging.k) return; polygon Polygon=new polygon(); Polygon.receive(the_dot.dots); Polygon.get_shape(); if(Polygon.is_Pentagon) System.out.println("true"); else System.out.println("false"); break; case '2': judging.dot_num(5); if (judging.k) return; polygon Polygon1=new polygon(); Polygon1.receive(the_dot.dots); Polygon1.get_shape(); if(!Polygon1.is_Pentagon) {System.out.println("not a pentagon");return;} Polygon1.p.bump_pentagon(Polygon1.p); if(Polygon1.p.concave_pentagon) System.out.println("false"); else { Polygon1.p.set_circumference(); Polygon1.p.set_area(); System.out.print("true "); Print(Polygon1.p.pentagon_circumference); System.out.print(" "); Print(Polygon1.p.pentagon_area); } break; case '3': judging.dot_num(7); if (judging.k) return; point[] point_arr =new point[5]; arraycopy(the_dot.dots,2, point_arr,0,5); line l=new line(the_dot.dots[0],the_dot.dots[1]); polygon Polygon2=new polygon(); Polygon2.receive(point_arr); Polygon2.get_shape(); if(Polygon2.is_Pentagon)Polygon2.p.f(l); if(Polygon2.is_Triangle)Polygon2.t.f(l); if(Polygon2.is_Quadrilateral)Polygon2.q.f(l); break; } } } class line { point dot1,dot2; double x1,x2,y1,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4; double A,B,C,two_point_length,slope; double point_to_line_distance; boolean jud1=false,jud=false,jud2=false; double jiaodian_a,jiaodian_b; line(){} line(point dot1,point dot2){ this.dot1=dot1;this.dot2=dot2; this.x1=dot1.x;this.x2=dot2.x;this.y1=dot1.y;this.y2=dot2.y; this.two_point_length=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1-x2,2)+Math.pow(y1-y2,2)); A = y2 - y1;B = x1- x2;C = x2 * y1 - x1 * y2; this.slope=A/(-B); } public void point_to_line(line l, point c){ this.x1=l.dot1.x;this.x2=l.dot2.x;this.x3=c.x;this.y1=l.dot1.y;this.y2=l.dot2.y;this.y3=c.y; this.point_to_line_distance=(Math.abs((y2 - y1) * x3 +(x1 - x2) * y3 + ((x2 * y1) -(x1 * y2))))/Math.sqrt(Math.pow(y2 - y1, 2) + Math.pow(x1 - x2, 2)); } public void segment_intersection(line l1, line l2){ this.x1=l1.dot1.x;this.x2=l1.dot2.x;this.x3=l2.dot1.x;this.x4=l2.dot2.x; this.y1=l1.dot1.y;this.y2=l1.dot2.y;this.y3=l2.dot1.y;this.y4=l2.dot2.y; if((x1-x2)/(y1-y2)!=(x3-x4)/(y3-y4)) { jud1 = true;//true表示点构成的直线有交点 jiaodian_a = (y3 * x4 * x2 - y4 * x3 * x2 - y3 * x4 * x1 + y4 * x3 * x1 - y1 * x2 * x4 + y2 * x1 * x4 + y1 * x2 * x3 - y2 * x1 * x3) / (x4 * y2 - x4 * y1 - x3 * y2 + x3 * y1 - x2 * y4 + x2 * y3 + x1 * y4 - x1 * y3); jiaodian_b = (-y3 * x4 * y2 + y4 * x3 * y2 + y3 * x4 * y1 - y4 * x3 * y1 + y1 * x2 * y4 - y1 * x2 * y3 - y2 * x1 * y4 + y2 * x1 * y3) / (y4 * x2 - y4 * x1 - y3 * x2 + x1 * y3 - y2 * x4 + y2 * x3 + y1 * x4 - y1 * x3); point dot = new point(jiaodian_a, jiaodian_b); line lx1 = new line(l1.dot1, dot); line lx2 = new line(l1.dot2, dot); line lx3 = new line(l2.dot1, dot); line lx4 = new line(l2.dot2, dot); if (lx1.two_point_length + lx2.two_point_length -l1.two_point_length<0.01 && lx3.two_point_length + lx4.two_point_length - l2.two_point_length<0.01) jud = true;//两线段有交点 if (lx3.two_point_length + lx4.two_point_length - l2.two_point_length<0.01) jud2 = true;//直线l1与线段l2有交点 } } } class pentagon extends polygon{ double pentagon_area; double pentagon_circumference; boolean concave_pentagon; point[] dot; line[] line =new line[5]; pentagon(point[] dot){ this.dot =dot; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) line[i]=new line(this.dot[i%5], this.dot[(i+1)%5]); } public void set_area(){ pentagon_area=get_area(this.dot); } public void set_circumference(){ pentagon_circumference=get_circumference(this.line); } public void bump_pentagon(pentagon p){ for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { quadrilateral q=new quadrilateral(p.dot[i%5],p.dot[(i+1)%5],p.dot[(i+2)%5],p.dot[(i+3)%5]); q.bump_quadrilateral(q); if(q.concave_quadrilateral){concave_pentagon=true;return;} q.position_of_quadrilateral(q,p.dot[(i+4)%5]); if(q.in_quadrilateral){concave_pentagon=true;return;} else concave_pentagon=false; } } public void f(line l){ incise(l,line,dot); } } class polygon { boolean is_Pentagon = true; boolean is_Quadrilateral = false; boolean is_Triangle = false; pentagon p; quadrilateral q; triangle t; point[] points; line[] lines=new line[5]; double min_area,max_area; public static void Print(double data) { //保留三位小数 DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0##"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.print(df.format(data)); } public final void receive(point[] dot){ points=dot; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { lines[i]=new line(dot[i%5],dot[(i+1)%5]); } } private void jud_Pentagon() { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { if(lines[i%5].slope==lines[(i+1)%5].slope){is_Pentagon = false;return;} lines[i%5].segment_intersection(lines[i%5],lines[(i+2)%5]); if(lines[i%5].jud){is_Pentagon = false;return;} lines[i%5].segment_intersection(lines[i%5],lines[(i+3)%5]); if(lines[i%5].jud){is_Pentagon = false;return;} } if(is_Pentagon){ p=new pentagon(points);} } private void jud_Triangle(){ } private void jud_Quadrilateral(){ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ quadrilateral Q=new quadrilateral(points[(i + 1)%5],points[(i + 2)%5],points[(i + 3)%5],points[(i + 4)%5]); if(Q.is_quadrilateral(points[(i + 1)%5],points[(i + 2)%5],points[(i + 3)%5],points[(i + 4)%5])) { Q.position_of_quadrilateral(Q,points[i]); if (points[i].equals(points[(i+1)%5]) || points[i].equals(points[(i+2)%5]) || points[i].equals(points[(i+4)%5])|| (lines[(i+1)%5].A*points[i].x+lines[(i+1)%5].B*points[i].y+lines[(i+1)%5].C==0&& Q.in_quadrilateral)|| (lines[(i+4)%5].A*points[i].x+lines[(i+4)%5].B*points[i].y+lines[(i+4)%5].C==0&& Q.in_quadrilateral)) { is_Quadrilateral = true; } if(is_Quadrilateral) { q=new quadrilateral(points[(i + 1)%5],points[(i + 2)%5],points[(i + 3)%5],points[(i + 4)%5]);return;} } } } public final void get_shape() { jud_Pentagon(); jud_Triangle(); jud_Quadrilateral(); } public double get_area(point[] dot) { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) sum+=(dot[i%5].x*dot[(i+1)%5].y)-(dot[i%5].y*dot[(i+1)%5].x); return Math.abs(sum)/2; } public double get_circumference(line[] line) { double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<line.length;i++) sum+=line[i].two_point_length; return sum; } public void incise(line l,line[] line,point[] dot){ point[] pl= new point[6]; int k=0;double sums=0,totals,sum=0,s; for(int i=0;i<line.length;i++) { if(l.A*dot[i].x+l.B*dot[i].y+l.C<0) { pl[k]=dot[i]; k++; } line temp=new line(); temp.segment_intersection(l,line[i]); if(temp.jud2) { point d= new point(temp.jiaodian_a,temp.jiaodian_b); pl[k]=d; k++; } if(line[i].dot1.x*l.A+line[i].dot1.y*l.B+l.C==0&&line[i].dot2.x*l.A+line[i].dot2.y*l.B+l.C==0) {System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");return;} } for(int i=0;i<dot.length;i++) sums+=(dot[i%dot.length].x*dot[(i+1)%dot.length].y)-(dot[i%dot.length].y*dot[(i+1)%dot.length].x); totals=Math.abs(sums)/2; for(int i=0;i<k;i++) sum+=(pl[i%k].x*pl[(i+1)%k].y)-(pl[i%k].y*pl[(i+1)%k].x); s=Math.abs(sum)/2; min_area=Math.min(s,totals-s); max_area=Math.max(s,totals-s); System.out.print(2+" "); Print(min_area); System.out.print(" "); Print(max_area); } } class quadrilateral extends polygon{ double quadrilateral_area; double quadrilateral_circumference; boolean concave_quadrilateral,in_quadrilateral; point[] dot =new point[4]; line[] line =new line[4]; quadrilateral(){} quadrilateral(point dot1,point dot2,point dot3,point dot4){ dot[0]=dot1; dot[1]=dot2; dot[2]=dot3; dot[3]=dot4; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { line[i]=new line(dot[i%4], dot[(i+1)%4]); } } public void set_area(){ } public void set_circumference(){ } public void bump_quadrilateral(quadrilateral q){ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { triangle t=new triangle(q.dot[i%4],q.dot[(i+1)%4],q.dot[(i+2)%4]); t.position_of_triangle(t, dot[(i+3)%4]); if(t.in_triangle){concave_quadrilateral=true;return;} } } public void position_of_quadrilateral(quadrilateral q,point dot){ double sum=0; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) sum+=(q.dot[i%4].x*q.dot[(i+1)%4].y)-(q.dot[i%4].y*q.dot[(i+1)%4].x); double s=Math.abs(sum)/2; double sums=0; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { q.line[i].point_to_line(line[i],dot); sums+=q.line[i].point_to_line_distance*q.line[i].two_point_length/2; } in_quadrilateral= s == sums; } public boolean is_quadrilateral(point...dot){ line[] line=new line[4]; for (int i=0;i<4;i++) { line[i]=new line(dot[i%4],dot[(i+1)%4]); } for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { if(line[i%4].slope==line[(i+1)%4].slope){return false;} line[i%4].segment_intersection(line[i%4],line[(i+2)%4]); if(line[i%4].jud){return false;} } return true; } public void f(line l){ incise(l,line,dot); } } class triangle extends polygon{ double triangle_area; double triangle_circumference; boolean in_triangle; point[] dot =new point[3]; line[] line =new line[3]; triangle(point dot1,point dot2,point dot3){ dot[0]=dot1; dot[1]=dot2; dot[2]=dot3; for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { line[i]=new line(dot[i%3], dot[(i+1)%3]); } } public void set_area(){ } public void set_circumference(){ } public void position_of_triangle(triangle t,point dot){ t.line[0].point_to_line(line[0], this.dot[2]); double s=t.line[0].two_point_length*t.line[0].point_to_line_distance/2; double sums=0; for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { t.line[i].point_to_line(line[i],dot); sums+=t.line[i].point_to_line_distance*t.line[i].two_point_length/2; } in_triangle= sums == s; } public void f(line l){ incise(l,line,dot); } } class dot { String str; dot(String str){ this.str=str; } int momma_num; point[] dots= new point[7]; String[] array=new String[30]; public void sf(String str){//对输入的字符串切割,转化为坐标 array[1]=str; String[] temp=str.split(","); momma_num=temp.length-1; for(int i=0;i<7;i++) { array=array[1].split(",",2); double a=Double.parseDouble(array[0]); array=array[1].split(" ",2); double b=Double.parseDouble(array[0]); this.dots[i]=new point(a,b);if(momma_num==i+1)return; } } } class point{ double x,y; point(double x,double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; } } class judge{ boolean f=false,k=false;String str; String gre = "([1-9]:)([+|-]?(0|[1-9][0-9]*)(\\.\\d+)?,[+|-]?(0|[1-9][0-9]*)(\\.\\d+)? ?)+"; judge(String str){ this.str=str; if(!str.matches(gre)) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");f=true;} } public void dot_num(int point_num){ String[] array=str.split(" "); if(array.length!=point_num) {System.out.println("wrong number of points");k=true;} } }
看看这次代码的类图把
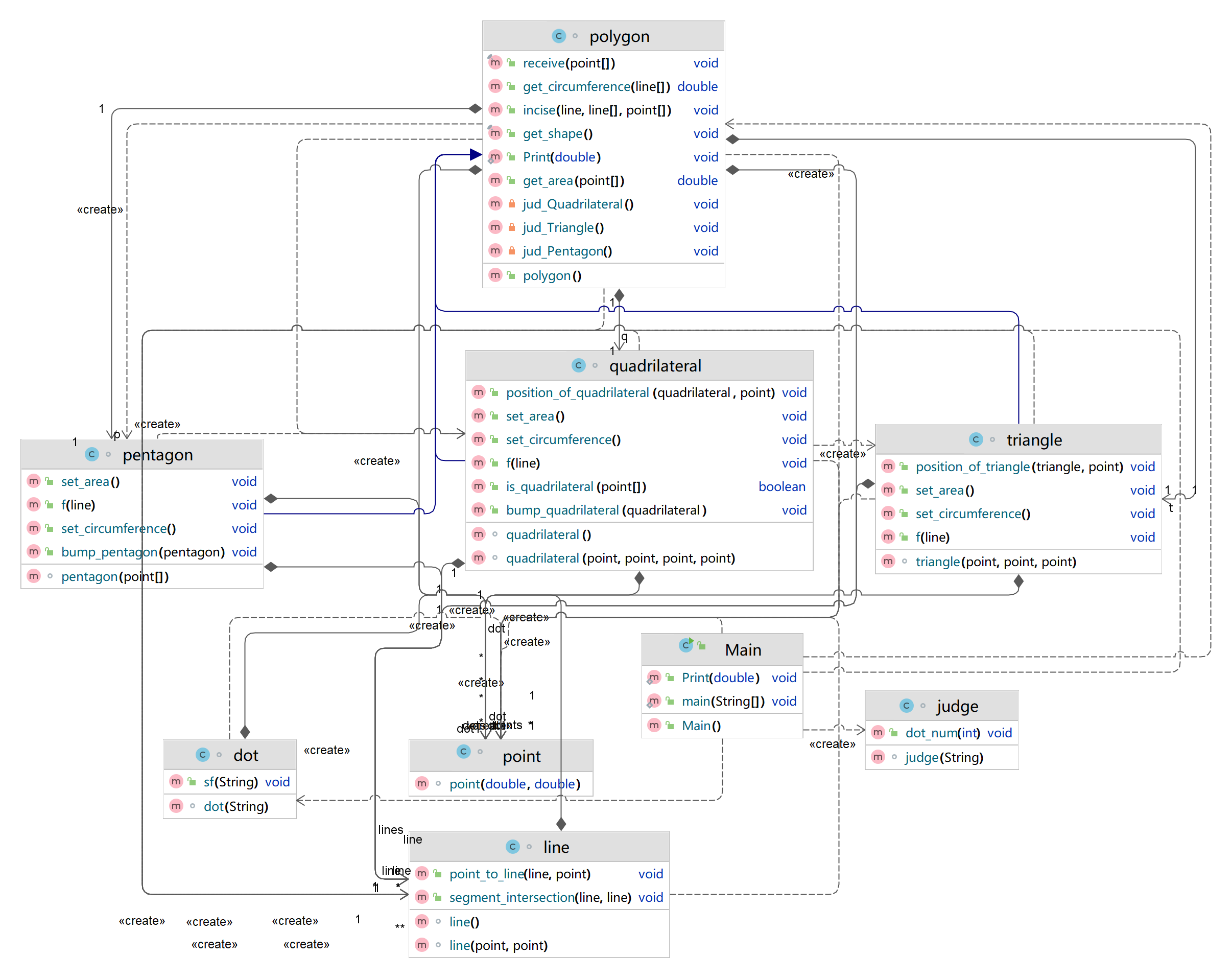
我感觉这次代码逻辑还是挺清楚的,最起码类不再像一个函数了,类就是类,蓝色线条的是三个字类连着父类,相对于上次代码,我这次重构代码花费了大量的时间,就是为了使用父类。
看看代码质量
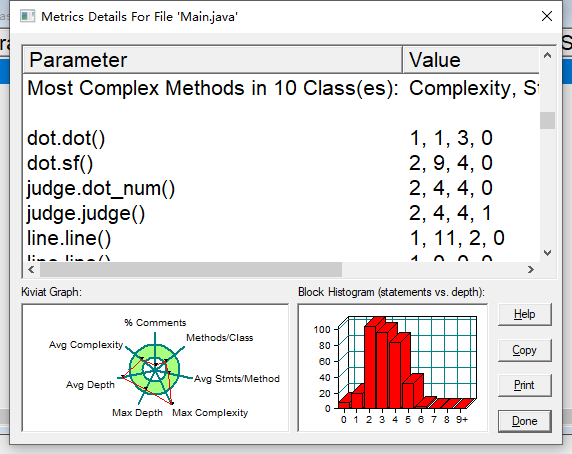
390行
声明 342
分支声明百分比 17.0
方法调用语句 83
带注释的行数百分比 2.6
类和接口 9
每类方法 4.33
每个方法的平均语句数 6.46
最复杂方法的行数 15
最复杂方法名称 main.main()
最大复杂度 17
最深块的行数 185
最大块深度 6
平均区块深度 2.98
平均复杂度 2.69
对于后半部分题目而言因为没时间我没有写但是也来看看吧
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
设计:
虽然我没有写,但是还是讲一下的设计思路:选项4是判断两个多边形位置关系,分离怎么判断呢,这个好像有点难,我们就最后来判断。连接,只需要一条直线相等,一个点相等就欧克了。完全重合也是一样,五个点一样就欧克了。那么被包含和包含呢,我们可以这样,被包含就是前面的多边形的点全是在后面多边形里面的,点在不在多边形里面就用面积法。包含就是相反,第二个多边形的全部点在第一个多边形里面。交错呢,就是存在边的相交,最后一个else就留给分离了。第一题就这样完事了,现在看题目也挺简单的。对于公共面积这里我只想到了特殊的情况,包含的,只需要输出一个最小的面积即可,交错的我没有想到什么方法。最后一问也是和以前的一样,面积法判断在不在多边形里面。这就是我对这道题目的理解。
至此,第五次作业就结束了。
3,期中考试
1,点和线设计
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
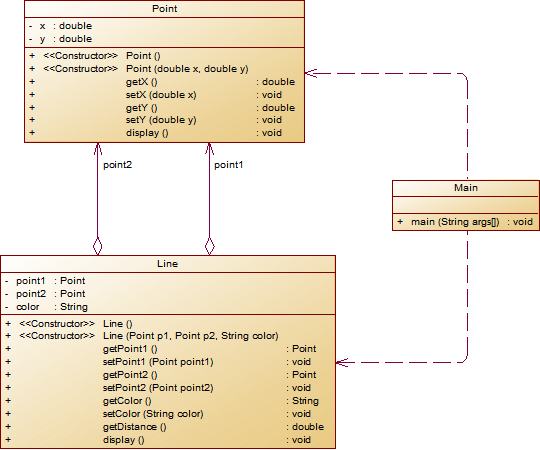
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 ```其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用
String.format("%.2f", data)方法。设计类图如下图所示。
** 题目要求:在主方法中定义一条线段对象,从键盘输入该线段的起点坐标与终点坐标以及颜色,然后调用该线段的display()方法进行输出
设计:
我的思路呢就是按照类图来写,类图有什么就写什么,主要讲一下主函数,主函数只需要输入两个点,创建两个点的对象,然后传进线,并且输入一个颜色给线,最后输出一下线的状态,两个点和颜色就行了。
我的代码:

import java.util.Scanner; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.text.DecimalFormat; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); point p1 =new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); point p2 =new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); line l=new line(p1,p2,in.next()); l.display(l); } } class point { private double x,y; point(){} point(double x,double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; if(x<=0||x>200) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");System.exit(0);} if(y<=0||y>200) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");System.exit(0);} } public void set_x(double x){ this.x=x; } public void set_y(double y){ this.y=y; } public double get_x(){ return x; } public double get_y(){ return y; } public void display(point p){ System.out.print("("); System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", p.get_x())); System.out.print(","); System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", p.get_y())); System.out.println(")"); } } class line { public static void Print(double data) { DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0#"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.print(df.format(data)); } private point p1,p2; private String color; line(){} line(point p1,point p2,String color){ this.p1=p1; this.p2=p2; this.color=color; } public point get_point1(){ return p1; } public void set_point1(point p){ this.p1=p; } public point get_point2(){ return p2; } public void set_point2(point p){ this.p2=p; } public String get_color(){ return this.color; } public void set_color(String color){ this.color=color; } public double get_distance(line l){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(l.p1.get_x()- l.p2.get_x(),2)+Math.pow(l.p1.get_y()-l.p2.get_y(),2)); } public void display(line l){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+l.get_color()); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); l.get_point1().display(l.get_point1()); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); l.get_point2().display(l.get_point2()); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); Print(l.get_distance(l)); } }
我的类图
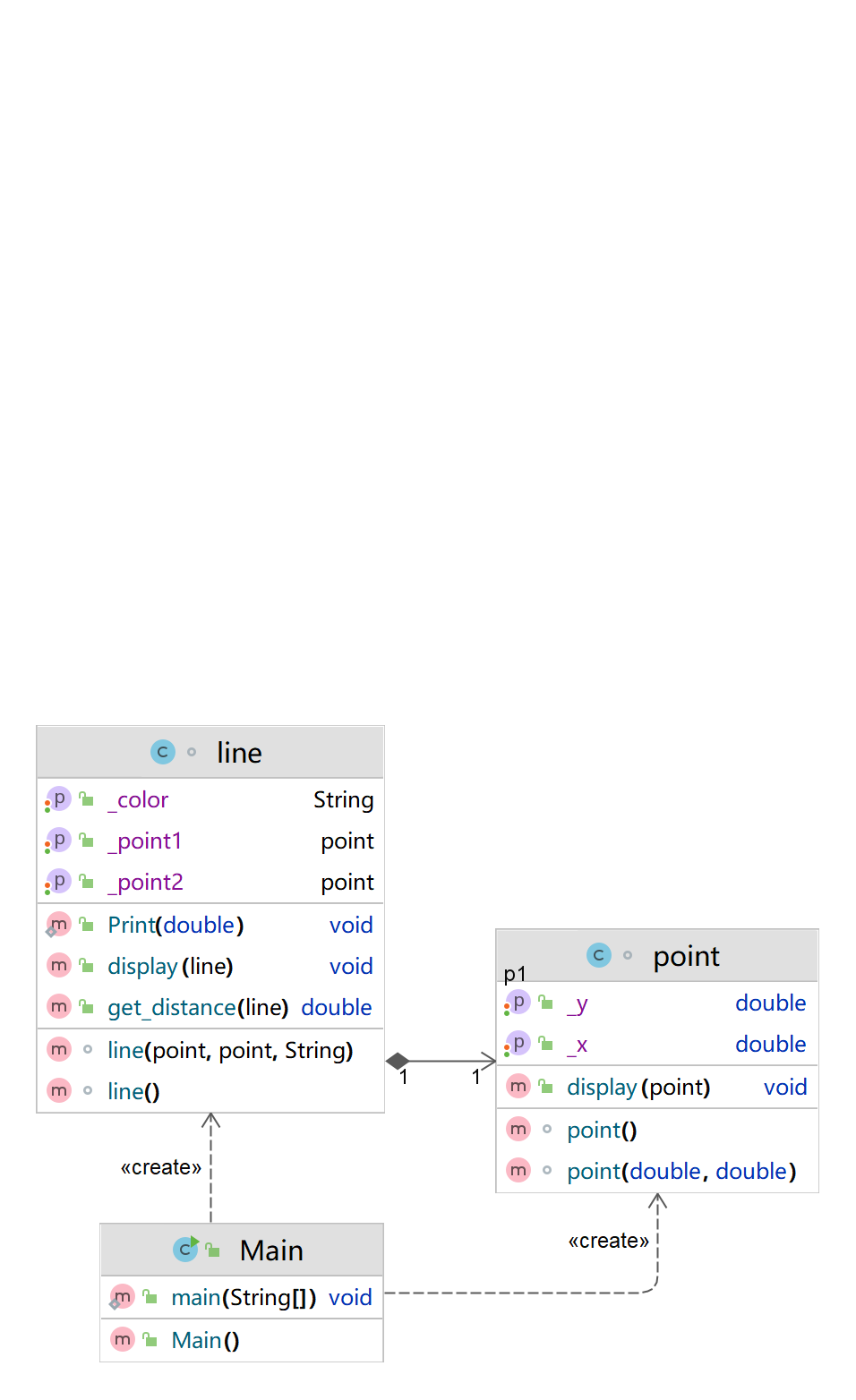
看看代码质量
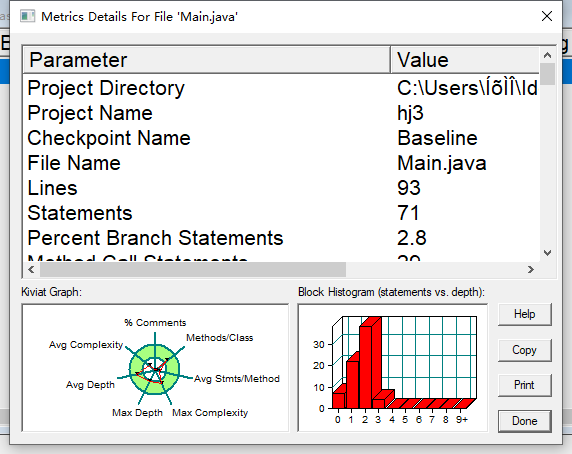
93行
声明 71
分支声明百分比 2.8
方法调用语句 29
带注释的行的百分比 0.0
类和接口 3
每类 6.33 的方法
每个方法的平均语句数 2.21
最复杂方法的行数 19
最复杂方法点()的名称
最大复杂度 3
最深块的行数 23
最大块深度 3
平均区块深度 1.55
平均复杂度 1.11
2,点线面问题重构
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();类结构如下图所示。
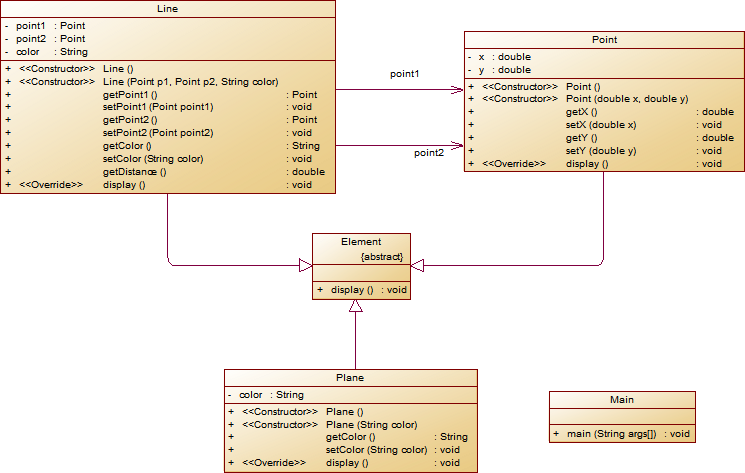
本题与上一题的区别在于添加了面类,并且添加了父类,这里的面类和前面的点线是没有什么关联的,只需要把线的颜色传进去就好了。本题还有一个要求,就是重写display,这就要求display里面不能含有参数,每一个子列重写父类display方法;和上一题一样创建两个点的对象,然后传进线,并且输入一个颜色给线,最后传这个颜色给面。最后,我们需要使用抽象父类调用每个子类的display方法输出状态。
但是好可惜,写出来的居然不对,测试点都是过了的,答案就是不正确
代码如下:

import java.util.Scanner; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.text.DecimalFormat; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); point p1=new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); point p2=new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); String str=in.next(); line line=new line(p1,p2,str); Plane plane=new Plane(str); Element element; element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display(); } } abstract class Element { public void display() { } } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; Plane(){} Plane(String color){ this.color=color; } public String getColor(){ return color; } public void setColor(){ } @Override public void display(){ System.out.print("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } class line extends Element{ public static void Print(double data) { DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0#"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.print(df.format(data)); } private point p1,p2; private String color; line(){} line(point p1, point p2, String color){ this.p1=p1; this.p2=p2; this.color=color; } public point get_point1(){ return p1; } public void set_point1(point p){ this.p1=p; } public point get_point2(){ return p2; } public void set_point2(point p){ this.p2=p; } public String get_color(){ return this.color; } public void set_color(String color){ this.color=color; } public double get_distance(){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.get_x()- p2.get_x(),2)+Math.pow(p1.get_y()-p2.get_y(),2)); } @Override public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); p1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); p2.display(); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); Print(get_distance()); System.out.println(); } } class point extends Element{ private double x,y; point(){} point(double x, double y){ this.x=x; this.y=y; if(x<0||x>200) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");System.exit(0);} if(y<0||y>200) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");System.exit(0);} } public void set_x(double x){ this.x=x; } public void set_y(double y){ this.y=y; } public double get_x(){ return x; } public double get_y(){ return y; } @Override public void display(){ System.out.print("("); System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",get_x())); System.out.print(","); System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",get_y())); System.out.println(")"); } }
代码质量
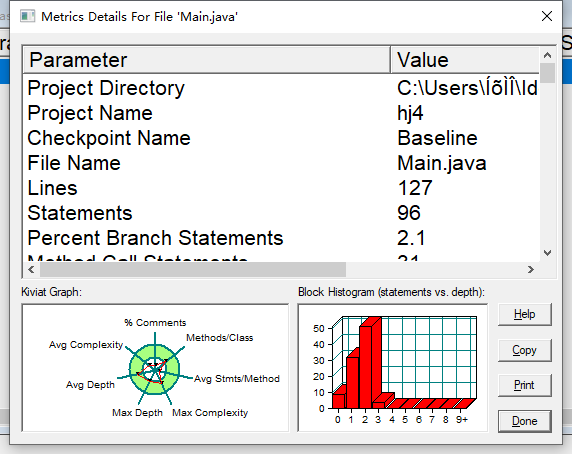
127行
声明 96
分支语句百分比 2.1
方法调用语句 31
带注释的行的百分比 3.1
类和接口 5
每类 5.00 的方法数
每个方法的平均语句数 2.20
最复杂方法的行数 98
最复杂方法点()的名称
最大复杂度 3
最深块的行数 102
最大块深度 3
平均区块深度 1.52
平均复杂度 1.08
3,点线面问题再重构(容器类)
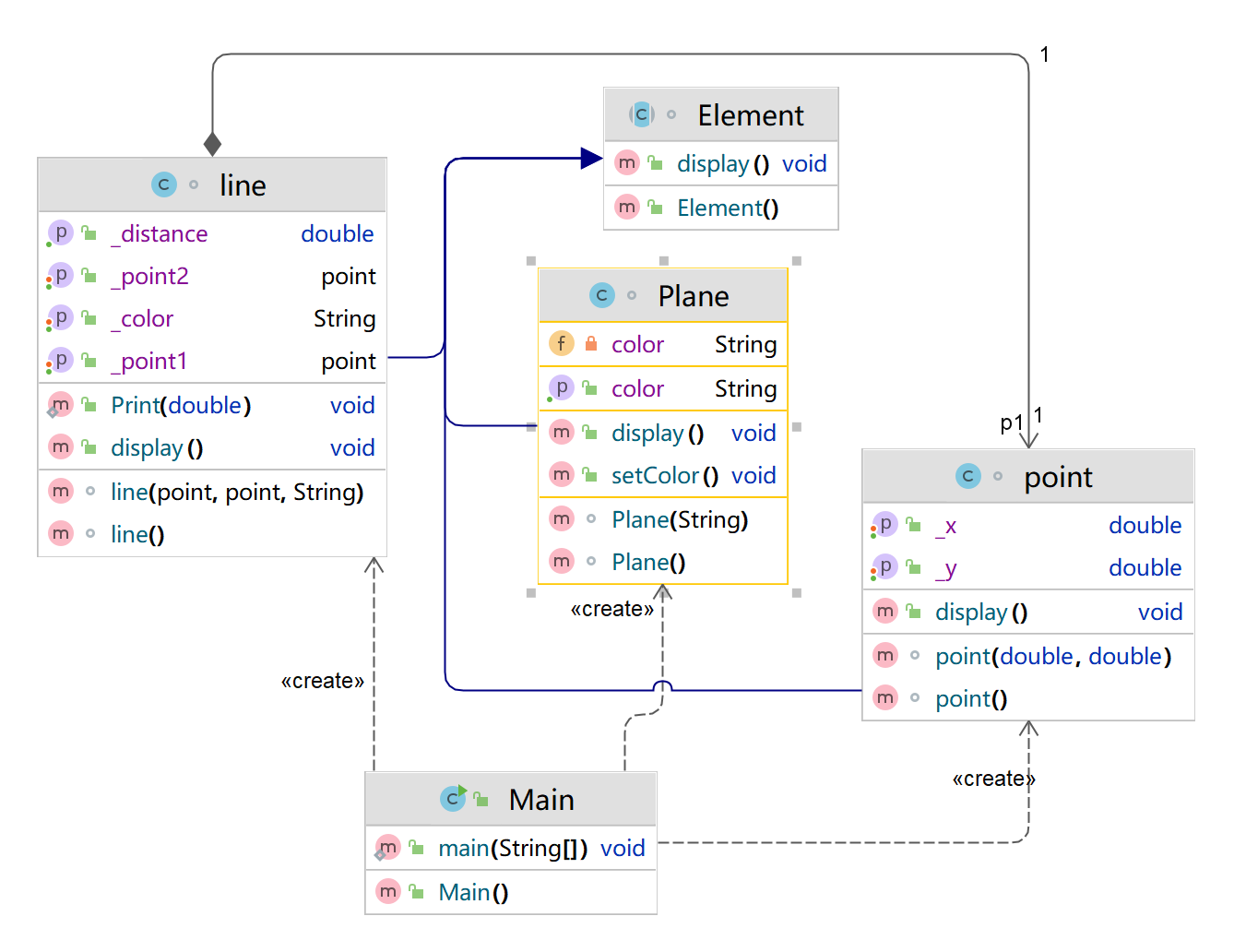
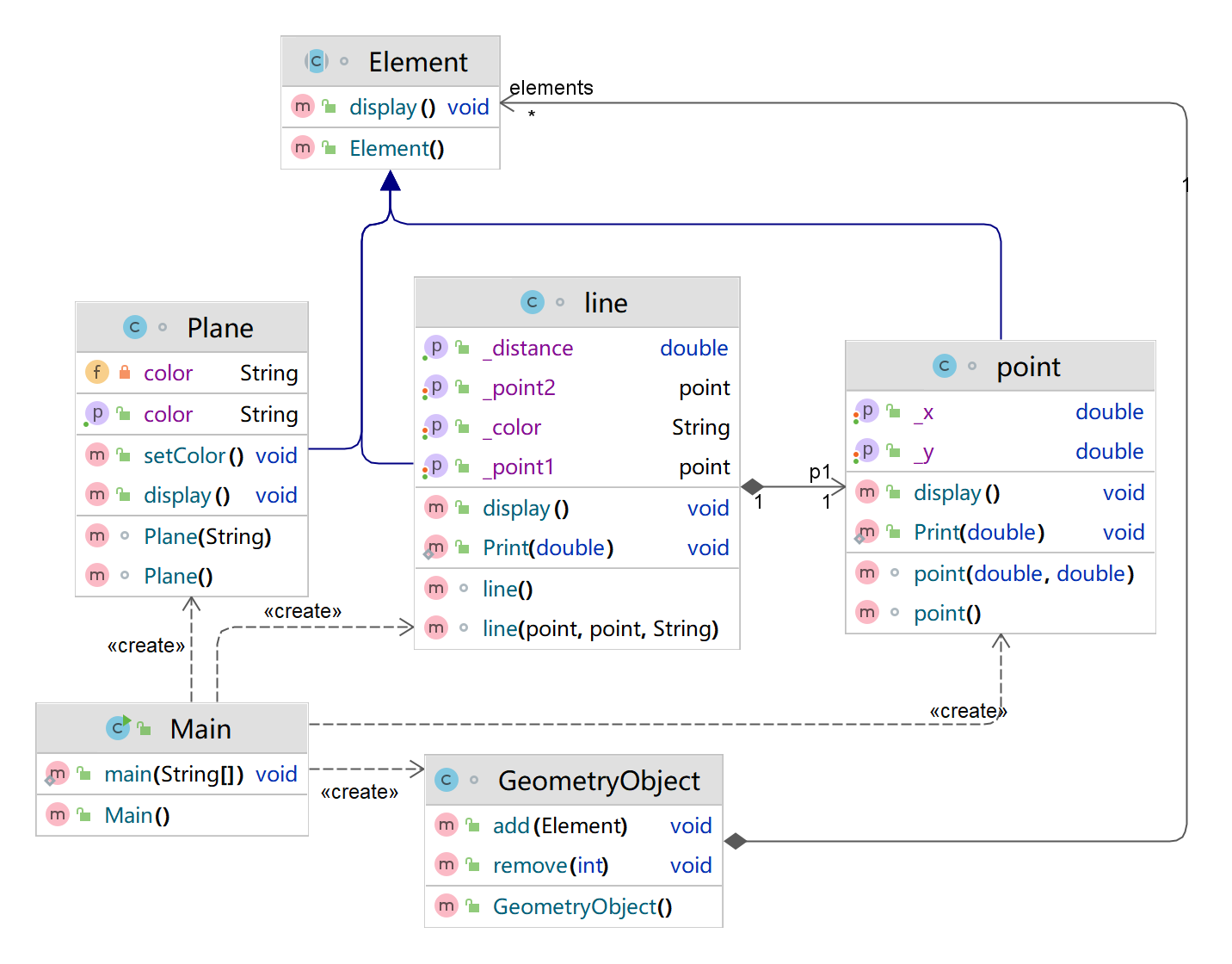
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list ... break; case 2://insert Line object into list ... break; case 3://insert Plane object into list ... break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); ... } choice = input.nextInt(); }输入结束后,按容器中的对象顺序分别调用每个对象的display()方法进行输出。
类图如下所示:
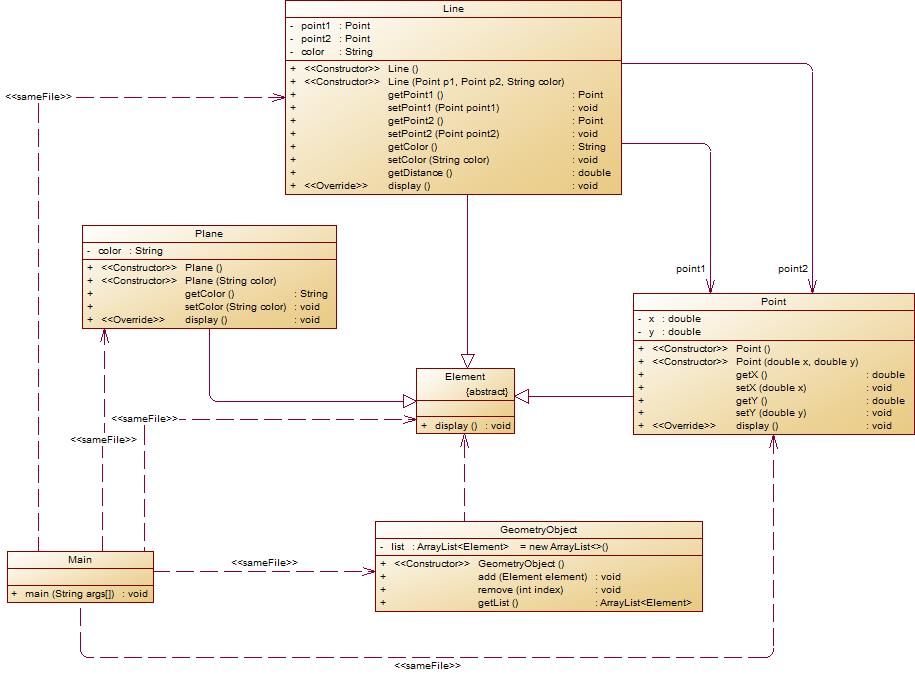
设计:
在上一题的基础上本题加了一个容器,容器里面只有一个element的动态数组,它的方法就是对这个动态数组处理,例如添加或删除,以及获得这个动态数组。主函数是switch的格式对容器的一些操作,最后get动态数组输出还在数组里的。
代码

import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.text.DecimalFormat; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); // Element p1= new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble());//起点Point // Element p2= new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble());//终点Point // Element l= new line((point) p1, (point) p2,in.next());;//线段 // Element P= new Plane(((line) l).get_color());//面 // p1.display(); // p2.display(); // l.display(); // P.display(); GeometryObject G=new GeometryObject(); Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); int choice = in.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list point p=new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); G.add(p); break; case 2://insert Line object into list point p1=new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); point p2=new point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble()); line l=new line(p1,p2,in.next()); G.add(l); break; case 3://insert Plane object into list Plane P=new Plane(in.next()); G.add(P); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = in.nextInt(); G.remove(index-1); } choice = in.nextInt(); } for (int i=0;i<G.elements.size();i++){ G.elements.get(i).display(); } } } class GeometryObject { ArrayList<Element> elements=new ArrayList<>(); public void add(Element E){ elements.add(E); } public void remove(int index){ if(index>=elements.size())return; elements.remove(index); } } abstract class Element { public void display() { } } class Plane extends Element{ private String color; Plane(){} Plane(String color){ this.color=color; } public String getColor(){ return color; } public void setColor(){ } @Override public void display(){ System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } class line extends Element{ public static void Print(double data) { DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0#"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.print(df.format(data)); } private point p1,p2; private String color; line(){} line(point p1, point p2, String color){ this.p1=p1; this.p2=p2; this.color=color; } public point get_point1(){ return p1; } public void set_point1(point p){ this.p1=p; } public point get_point2(){ return p2; } public void set_point2(point p){ this.p2=p; } public String get_color(){ return this.color; } public void set_color(String color){ this.color=color; } public double get_distance(){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p1.get_x()- p2.get_x(),2)+Math.pow(p1.get_y()-p2.get_y(),2)); } @Override public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); p1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); p2.display(); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); Print(get_distance()); System.out.println(); } } class point extends Element{ private double x,y; public static void Print(double data) { DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.0#"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); System.out.print(df.format(data)); } point(){} point(double x, double y){ if(x<=0||x>200) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");System.exit(0);} if(y<=0||y>200) {System.out.println("Wrong Format");System.exit(0);} this.x=x; this.y=y; } public void set_x(double x){ this.x=x; } public void set_y(double y){ this.y=y; } public double get_x(){ return x; } public double get_y(){ return y; } @Override public void display(){ System.out.print("("); System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",get_x())); System.out.print(","); System.out.print(String.format("%.2f",get_y())); System.out.println(")"); } }
类图
代码质量
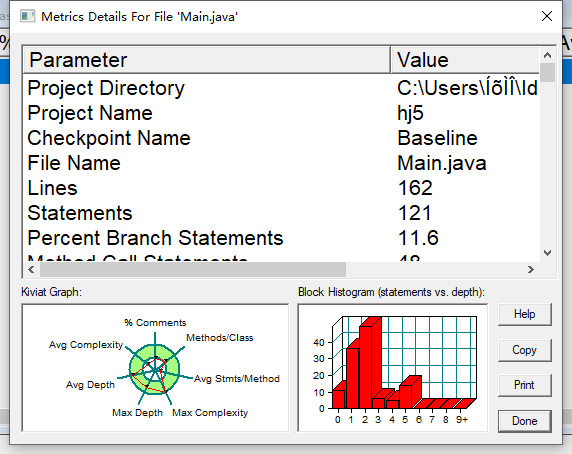
162行
声明 121
分支语句百分比 11.6
方法调用语句 48
带注释的行数百分比 7.4
类和接口 6
每类的方法 4.67
每个方法的平均语句数 2.64
最复杂方法的行数 8
最复杂方法名称 main.main()
最大复杂度 8
最深块的行数 23
最大块深度 5
平均区块深度 2.00
平均复杂度 1.36
三,采坑心得
第四次作业的四边形的格式处理时,简直是有史以来最坑的,其实在上一次作业以及显现出来了,就是有一个测试点后面是有空格的,我以为是老师打错了,那个时候正则表达式我是没有判断最后一个点后面有没有空格的,那个时候我的是可以有空格,作业居然全对了,实则上是不可以有空格的,老师在上一题没有测那个点,到了下一题就折磨了我好久,格式老是不对我就纳闷了好久,我一直以为最后可以有空格。。
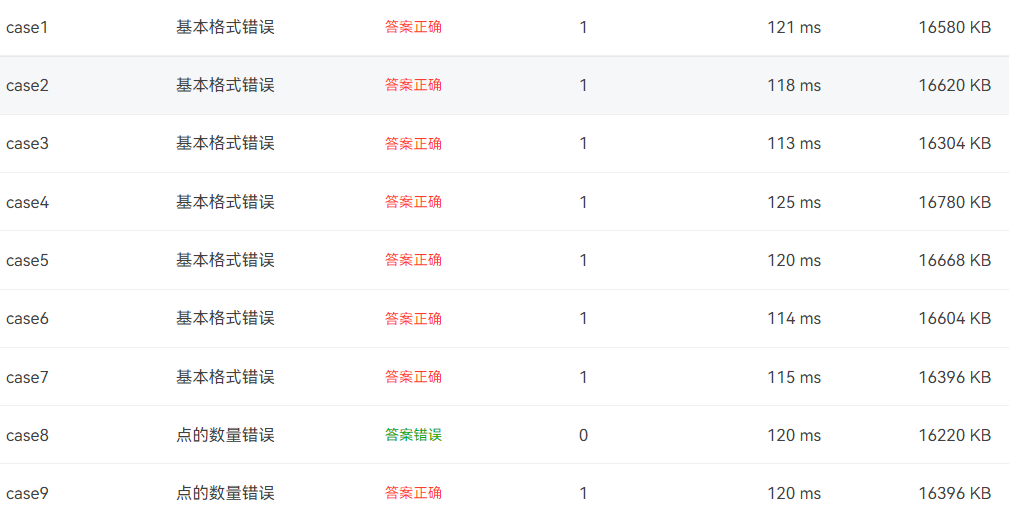
第五次好像没有踩什么坑,平平常常的写,写了的都对了,感觉五个点判断三角形麻烦了点,一定要考虑周到,不然判断不出三角形就做不出下一题了。
期中考试呢也好像没什么坑,对我来说最大的坑就是不知道他是什么坑,明明测试点对了答案就是不对
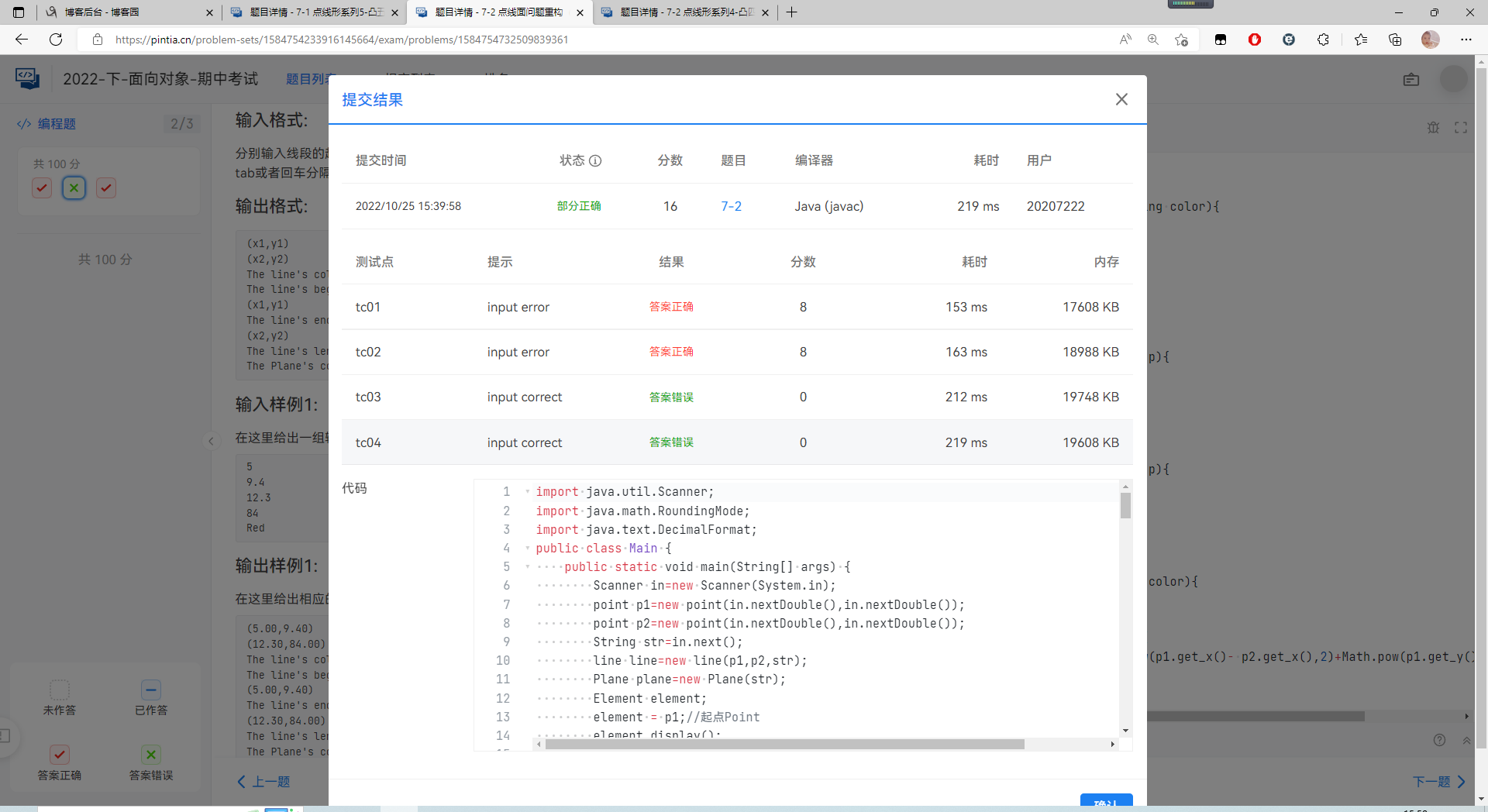
真的就很无语,就也很可惜,明明都写完了就是不对。(已经无法提交了这里的测试样例图片就上不了了)
四,改进建议
图形的题目一路走来,我对类的理解也越来越深,从开始的以为类就是函数,到现在的继承多态。我现在发现以前写的真的是烂,就比如第四次的题目,那个线类,一个线类里面放了好多构造器,构造器里面甚至传了好多点,完完全全把类当作函数去了,真正的类应该是,一个线类传入两个点,构成一根线,属性放长度,斜率,两个点也保存一下。其他的通通写进线类的方法里,这样才有类的可比较性。还有那三个子类也是一样的,三角形只需要传入三个点,多边形传入多个点,构成一个多边形。属性就放点的数组,边的数组。以及面积周长,这样才是一个类,才有可比较性。对于我的第五次作业,我已经对第四次作业进行了重构,面向对象显得更加明显,某些方法都可以传入三角形,四边形,五边形。
五,总结
本阶段我收获最大的就是理解了继承和多态:以前是创建对象并指挥对象做事情。有了多态以后,我们可以找到对象的共性类型,直接操作共性类型做事情即可,这样可以指挥一批对象做事情,即通过操作父类或接口实现。以及抽象类的构建,抽象方法的构建 以及他们的特点抽象方法只能定义在抽象类中,抽象类和抽象方法必须由abstract关键字修饰(可以描述类和方法,不可以描述变量)。抽象方法只定义方法声明,并不定义方法实现。抽象类不可以被创建对象(实例化)。只有通过子类继承抽象类并覆盖了抽象类中的所有抽象方法后,该子类才可以实例化。否则,该子类还是一个抽象类。还有就是工程化思想,只留getter setter接口修改得到隐藏属性:隐藏内部实现细节,保证代码的安全,同时也可以提升数据的安全性。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号