Python——day1_基础2
Python 条件语句
Python条件语句是通过一条或多条语句的执行结果(True或者False)来决定执行的代码块。
可以通过下图来简单了解条件语句的执行过程:
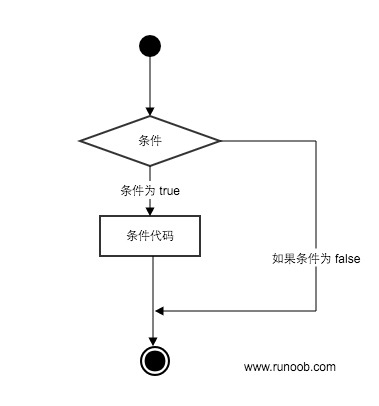
Python程序语言指定任何非0和非空(null)值为true,0 或者 null为false。
Python 编程中 if 语句用于控制程序的执行,基本形式为:
if 判断条件:
执行语句……
else:
执行语句……
其中"判断条件"成立时(非零),则执行后面的语句,而执行内容可以多行,以缩进来区分表示同一范围。
else 为可选语句,当需要在条件不成立时执行内容则可以执行相关语句,具体例子如下:
#Author:D lee
import getpass
_username = "li"
_passwd = "123"
username = input("username:")
#passwd = getpass.getpass("passwd:")
passwd = input("passwd:")
if _username==username and _passwd==passwd:
print("welcome {name}--- login " .format(name=username))
else:
print("input username and password erro")
输出结果:
D:\Python3.6.1\python.exe C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Python/p1/day1/passwd.py
username:li
passwd:123
welcome li--- login
Process finished with exit code 0
Python语言要求强制缩进,这是Python的特性。
else:
print("input username and password erro") #print输出的这句话表示属于else条件下。
#else语句是父级
另,如果Python语句是父级,必须顶格写。
if 语句的判断条件可以用>(大于)、<(小于)、==(等于)、>=(大于等于)、<=(小于等于)来表示其关系。
当判断条件为多个值时,可以使用以下形式:
if 判断条件1: 执行语句1…… elif 判断条件2: 执行语句2…… elif 判断条件3: 执行语句3…… else: 执行语句4……
实例如下:
#!/usr/bin/python2.0
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# 例2:elif用法
num = 5
if num == 3: # 判断num的值
print 'boss'
elif num == 2:
print 'user'
elif num == 1:
print 'worker'
elif num < 0: # 值小于零时输出
print 'error'
else:
print 'roadman' # 条件均不成立时输出
输出结果为:
>>> roadman # 输出结果
由于 python 并不支持 switch 语句,所以多个条件判断,只能用 elif 来实现,如果判断需要多个条件需同时判断时,可以使用 or (或),表示两个条件有一个成立时判断条件成功;使用 and (与)时,表示只有两个条件同时成立的情况下,判断条件才成功。
#!/usr/bin/python2.0
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# 例3:if语句多个条件
num = 9
if num >= 0 and num <= 10: # 判断值是否在0~10之间
print 'hello'
>>> hello # 输出结果
num = 10
if num < 0 or num > 10: # 判断值是否在小于0或大于10
print 'hello'
else:
print 'undefine'
>>> undefine # 输出结果
num = 8
# 判断值是否在0~5或者10~15之间
if (num >= 0 and num <= 5) or (num >= 10 and num <= 15):
print 'hello'
else:
print 'undefine'
>>> undefine # 输出结果
当if有多个条件时可使用括号来区分判断的先后顺序,括号中的判断优先执行,此外 and 和 or 的优先级低于>(大于)、<(小于)等判断符号,即大于和小于在没有括号的情况下会比与或要优先判断。
简单的语句组
你也可以在同一行的位置上使用if条件判断语句,如下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
var = 100
if ( var == 100 ) : print("变量 var 的值为100")
print("Good bye!")
以上代码执行输出结果如下:
变量 var 的值为100
Good bye!
Python 循环语句
本章节将向大家介绍Python的循环语句,程序在一般情况下是按顺序执行的。
编程语言提供了各种控制结构,允许更复杂的执行路径。
循环语句允许我们执行一个语句或语句组多次,下面是在大多数编程语言中的循环语句的一般形式:
Python提供了for循环和while循环(在Python中没有do..while循环):
| 循环类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| while 循环 | 在给定的判断条件为 true 时执行循环体,否则退出循环体。 |
| for 循环 | 重复执行语句 |
| 嵌套循环 | 你可以在while循环体中嵌套for循环 |
循环控制语句
循环控制语句可以更改语句执行的顺序。Python支持以下循环控制语句:
| 控制语句 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| break 语句 | 在语句块执行过程中终止循环,并且跳出整个循环 |
| continue 语句 | 在语句块执行过程中终止当前循环,跳出该次循环,执行下一次循环。 |
| pass 语句 | pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性。 |
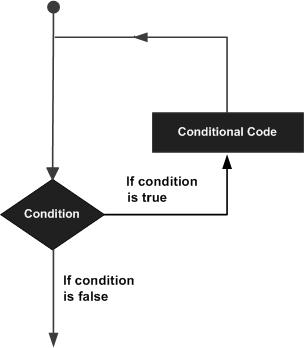
Python While 循环语句
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务。其基本形式为:
while 判断条件:
执行语句……
执行语句可以是单个语句或语句块。判断条件可以是任何表达式,任何非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当判断条件假false时,循环结束。
执行流程图如下:
![python_while_loop]()
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
count = 0
while (count < 9):
print 'The count is:', count
count = count + 1
print("Good bye!")
运行实例 »
以上代码执行输出结果:
The count is: 0
The count is: 1
The count is: 2
The count is: 3
The count is: 4
The count is: 5
The count is: 6
The count is: 7
The count is: 8
Good bye!
while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环,continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外"判断条件"还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
# continue 和 break 用法
i = 1
while i < 10:
i += 1
if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出
continue
print i # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10
i = 1
while 1: # 循环条件为1必定成立
print i # 输出1~10
i += 1
if i > 10: # 当i大于10时跳出循环
break
无限循环
如果条件判断语句永远为 true,循环将会无限的执行下去,如下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
var = 1
while var == 1 : # 该条件永远为true,循环将无限执行下去
num = input("Enter a number :")
print ("You entered: ", num)
print("Good bye!")
以上实例输出结果:
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,while … else 在循环条件为 false 时执行 else 语句块:
#!/usr/bin/python
count = 0
while count < 5:
print count, " is less than 5"
count = count + 1
else:
print count, " is not less than 5"
以上实例输出结果为:
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5
简单语句组
类似 if 语句的语法,如果你的 while 循环体中只有一条语句,你可以将该语句与while写在同一行中, 如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/python
flag = 1
while (flag): print ('Given flag is really true!')
print ("Good bye!")
注意:以上的无限循环你可以使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
猜年龄的while循环例子
#Author:D lee
age_of_boy = 58
count = 0
while count < 3:
guess_age = int(input ("guess_age:"))
if guess_age == age_of_boy:
print("yes , you got it ")
break
elif guess_age > age_of_boy:
print("too big")
else:
print("too small")
count += 1
else:
print ("you have tired too many time ")
执行结果:
D:\Python3.6.1\python.exe C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/Python/p1/day1/guess.py
guess_age:45
too small
guess_age:78
too big
guess_age:58
yes , you got it
Process finished with exit code 0
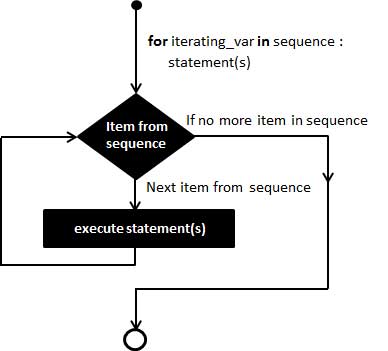
Python for 循环语句
Python for循环可以遍历任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
流程图:
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for i in range(0,10):
if i < 5:
print("loop",i)
else:
continue
print("hehhe...")
循环套循环实例:
for i in range(10):
print("---------",i)
for j in range(10):
print(j)
if j > 5:
break



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号