Spring MVC Hello World Example(转)
In Spring MVC web application, it consist of 3 standard MVC (Model, Views, Controllers) components :
- Models – Domain objects that are processed by service layer (business logic) or persistent layer (database operation).
- Views – Usually JSP page written with Java Standard Tag Library (JSTL).
- Controllers – Interact with service layer for business processing and return a Model.
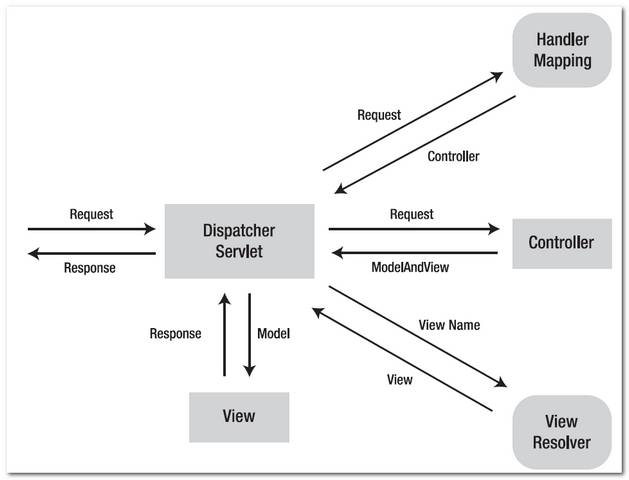
See following figures 1.1, 1.2 to demonstrate how Spring MVC web application handle a web request.
Figure 1.1 – Image copied from Spring MVC reference with slightly modification.
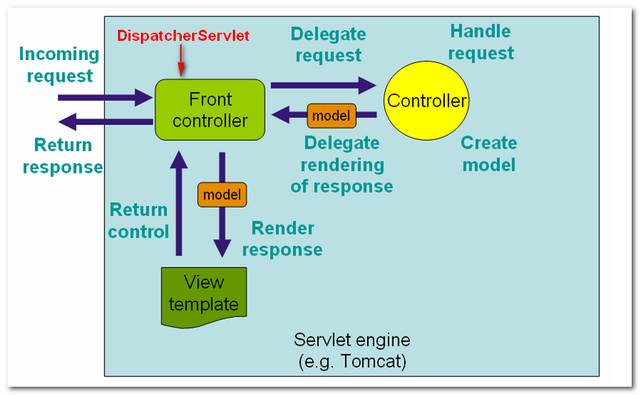
Figure 1.2 – P.S Image copied from book : Spring Recipes
Spring MVC Tutorial
In this tutorial, you will create a simple Spring MVC hello world web application in order to understand the basic concepts and configurations of this framework.
Technologies used in this tutorial.
- Spring 2.5.6
- JDK 1.6
- Eclipse 3.6
- Maven 3
1. Directory Structure
Final directory structure of this tutorial.

2. Dependency library
Spring MVC required two core dependency libraries, spring-version.jar and spring-mvc-version.jar. If you are using JSP page with jstl, include the jstl.jar and standard.jar as well.
File : pom.xml
<!-- Spring framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring MVC framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSTL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- for compile only, your container should have this -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
3. Spring Controller
Spring comes with many Controllers, normally, you just need to extend the AbstractController, if you do not have other special requirement, and override the handleRequestInternal() method and return a ModelAndView object.
File : HelloWorldController.java
package com.mkyong.common.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.AbstractController;
public class HelloWorldController extends AbstractController{
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("HelloWorldPage");
model.addObject("msg", "hello world");
return model;
}
}
- ModelAndView(“HelloWorldPage”) – The “HelloWorldPage” will pass to Spring’s viewResolver later, to indentify which view should return back to the user. (see step 6)
- model.addObject(“msg”, “hello world”) – Add a “hello world” string into a model named “msg”, later you can use JSP EL ${msg} to display the “hello world” string.
4. View (JSP page)
In this case, “view” is a jSP page, you can display the value “hello world” that is store in the model “msg” via expression language (EL) ${msg}.
File : HelloWorldPage.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Spring MVC Hello World Example</h1>
<h2>${msg}</h2>
</body>
</html>
5. Spring Configuration
In web.xml, declared a DispatcherServlet servlet, named “mvc-dispatcher“, and act as the front-controller to handle all the entire web request which end with “htm” extension.
File : web.xml
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Spring Web MVC Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Alternatively, you can explicitly specify the Spring configuration file in the “contextConfigLocation” servlet parameter, to ask Spring to load your configurations besides the default “mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml“.
File : web.xml
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Spring Web MVC Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/SpringMVCBeans.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
6. Spring Beans Configuration
Declared the Spring Controller and viewResolver.
File : mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean name="/welcome.htm"
class="com.mkyong.common.controller.HelloWorldController" />
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" >
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/pages/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- Controller – Declared a bean name “/welcome.htm” and map it to HelloWorldController class. It means, if an URL with “/welcome.htm” pattern is requested, it will send to the HelloWorldController controller to handle the request.
- viewResolver – Define how Spring will looking for the view template. In this case, the controller “HelloWorldController” will return a ModelAndView object named “HelloWorldPage”, and the viewResolver will find the file with following mechanism : “prefix + ModelAndView name + suffix“, which is “/WEB-INF/pages/HelloWorldPage.jsp“.
7. Demo
Run it and access via URL : http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome.htm , the “SpringMVC” is your project context name.

How it works?
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome.htm is requested.
- URL is end with “.htm” extension, so it will redirect to “DispatcherServlet” and send request to the default BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping return HelloWorldController to the DispatcherServlet.
- DispatcherServlet forward request to the HelloWorldController.
- HelloWorldController process it and return a ModelAndView object named “HelloWorldPage”.
- DispatcherServlet received the ModelAndView and call the viewResolver to process it.
- viewResolver return the “/WEB-INF/pages/HelloWorldPage.jsp” back to the DispatcherServlet.
- DispatcherServlet return the “HelloWorldPage.jsp” back to user.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号