2022牛客寒假算法基础集训营1
A - 九小时九个人九扇门
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
9
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
样例输出
56 56 58 56 56 58 56 56 59
思路
这里有一个运算规则是这样的数字根(a + b) = 数字根(a) + 数字根(b)
想了半天也不知道为什么会想出DP这个思路, 我们要记录的是选择的数字根为i的方案数, 对于每个人, 都有选和不选两种
状态转移就是选和不选这个人两种
- 选, f[i][数字根(\(a_1\) + \(a_2\) + ... + \(a_i\))] = f[i - 1][\(a_1\) + \(a_2\) + ... + \(a_{i-1}\)]
- 不选, f[i][数字根(\(a_1\) + \(a_2\) + ... + \(a_i\))] = f[i - 1][数字根(\(a_1\) + \(a_2\) + ... + \(a_i\))]
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 998244353;
int n;
int f[N][20];
LL fac(LL u) {
while (u >= 10) {
LL c = 0;
while (u) {
c += u % 10;
u /= 10;
}
u = c;
}
return u;
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
LL x;
cin >> x;
f[i][fac(x)] ++;
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j ++) {
f[i][fac(j + x)] = (f[i][fac(j + x)] + f[i - 1][fac(j + x)] + f[i - 1][j]) % mod;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i ++) cout << f[n][i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
C - Baby's first attempt on CPU
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
4
0 0 0
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
样例输出
3
样例说明
输入表示发生先写后读相关问题的语句有:第二句读了第一句所写的寄存器、第三句读了第一句所写的寄存器。
一种插入三个空语句的最优策略为变成:
原第一句、空语句、空语句、空语句、原第二句、原第三句、原第四句。
思路
按照题目所描述的扫描一遍即可
每次遇到一个新的语句, 一定是看他最左边的1, 如果他和对应的语句下标相差不满足要求, 就要为其补充空语句
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
#include <queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n;
vector<int>a[N];
int b[N];
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
for (int j = 1 ; j <= 3 ; j ++)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
if (x == 1)a[i].push_back(i - j);
}
int res = 0;
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)
{
if (a[i].size() == 0)
{
b[i] = cnt ++;
}
else
{
int s = cnt - b[a[i][0]];
if (s < 4)//相差
{
cnt += 4 - s;
res += 4 - s;
b[i] = cnt ++;
}
else b[i] = cnt ++;
}
}
//for (int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i ++)cout<<b[i]<<" ";
cout<<res<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int T;
T = 1;
while(T --)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D - 牛牛做数论
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
3
2
5
1
样例输出
2 2
2 5
-1
样例说明
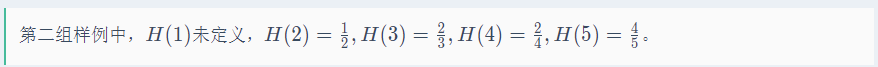
思路
欧拉函数
- 最小的, 是[2, n]中, 约数最多的数
- 最大的, 是[2, n]中, 最大的指数
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
#include <queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e7 + 10;
int n;
bool st[N];
int p[N];
int cnt = 0;
void getp()
{
for (int i = 2 ; i <= N ; i ++)
{
if (!st[i])p[cnt ++] = i;
for (int j = 0 ;p[j] <= N / i ; j ++)
{
st[p[j] * i] = true;
if(i % p[j] == 0)break;
}
}
}
bool zhi(int x)
{
if (x == 1) return false;
if (x == 2)return true;
for (int i = 2 ; i <= x / i ; i ++)
if (x % i == 0) return false;
return true;
}
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
if (n == 1)puts("-1");
else
{
int res = 1;
int cnt2 = 0;
while(res * p[cnt2] <= n)
{
res *= p[cnt2 ++];
//cout<<p[cnt2 - 1]<<" ";
}
cout<<res<<" ";
for (int j = n ; j >= 2 ; j --)
{
if (zhi(j))
{
cout<<j<<endl;
return;
}
}
cout<<n<<endl;
}
}
signed main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
getp();
while(T --)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E - 炸鸡块君的高中回忆
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
3
6 3
10 10
10 1
样例输出
5
1
-1
思路
蜗牛爬井都听过吧, 和那个一样, 注意最后一队人进去就不会出来了
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
long long a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (a == b) puts("1");
else if (b == 1) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << (a - 2) / (b - 1) * 2 + 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
F - 中位数切分
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
4
5 4
10 3 2 3 2
5 3
5 2 3 3 2
2 5
4 5
5 2
10 3 2 3 2
样例输出
-1
1
-1
5
思路
切分数组, 主要还是看这一段中有没有一个数大于等于m
- 每个大于等于的 都尽可能分出一段
- 小于的, 不仅不能增加, 而且还需要两个大于等于的来平衡
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t --) {
int n, m, ans = 0, a;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) {
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a >= m) {
ans ++;
} else {
ans --;
}
}
if (ans <= 0) {
printf("-1\n");
} else {
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
}
H - 牛牛看云
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
4
500 501 500 499
样例输出
8
思路
暴力枚举是不可能的, 化简式子也是因为绝对值的存在太过复杂, 我们可以从数据范围出发
在原数组中, 每个下标都要和别的下标进行一次组合, 对应在数字上, 每个数字都要和别的数字进行一次组合
特别的对于本身, 自己和自己之外, 任意两个还要组合一次, 而不是简单的乘积
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
LL a[1010];
LL ans;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[x] ++;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 1000; i ++) {
if (a[i] > 1) ans += (a[i] + a[i] * (a[i] - 1) / 2) * abs(i + i - 1000);
else ans += a[i] * abs(i + i - 1000);
for (int j = i + 1; j <= 1000; j ++)
ans += (a[i] * a[j]) * fabs(i + j - 1000);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
I - B站与各唱各的
嘿嘿, 小姐姐真好听
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
1
1 100
样例输出
0
思路
高中数学
对于每句话, 每个人都可能唱可能不唱, 总方案数为\(2^n\), 而全部不唱和全部都唱就会失败, 所以有效方案是 \(2^n\) - 2, 并且有这样的m句话
注意取模
代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
LL qmi(LL a, LL b) {
LL ans = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) ans = (ans * a) % mod;
b >>= 1;
a = (a * a) % mod;
}
return ans;
}
LL fac(LL a, LL b) {
return ((a * b % mod) + mod) % mod;
}
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
LL n, m;
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
LL t = qmi(2, n);
printf("%lld\n%", fac(m, fac(t - 2, qmi(t, mod - 2))));
}
}
J - 小朋友做游戏
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
3
3 6 7
1 3 4
5 4 3 4 3 5
4 6 7
1 3 4 1
5 4 3 4 3 5
7 7 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
9 8 7 6 5 4 3
样例输入
-1
23
46
思路
在吵闹的小朋友之间至少要间隔一个安静的小朋友, 而且要尽可能的选幸福值较高的小朋友
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int a, b, n;
int A[N], B[N];
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
cin >> a >> b >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= a; i ++) cin >> A[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= b; i ++) cin >> B[i];
if (a < (n + 1) / 2) puts("-1");
else {
sort(A + 1, A + a + 1);
sort(B + 1, B + b + 1);
int cnt = 0, l = a, r = b;
int ans = 0;
while (cnt < n) {
if (cnt < (n + 1) / 2) {
ans += A[l --];
}
else if (l > 0 && A[l] >= B[r]) {
ans += A[l --];
}
else ans += B[r --];
cnt ++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
L - 牛牛学走路
题目描述

输入描述

输出描述

样例输入
3
4
LLLR
4
ULLD
5
LUDDL
样例输出
3.000000000000
2.236067977500
2.236067977500
思路
两点间距离
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T --) {
int n;
cin >> n;
string a;
cin >> a;
int x = 0, y = 0;
double ans = 0;
for (auto i : a) {
if (i == 'L') x --;
else if (i == 'R') x ++;
else if (i == 'U') y ++;
else y --;
ans = max(ans, sqrt(x * x + y * y));
}
printf("%.12lf\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号