python快速入门
python快速入门
一、python3安装
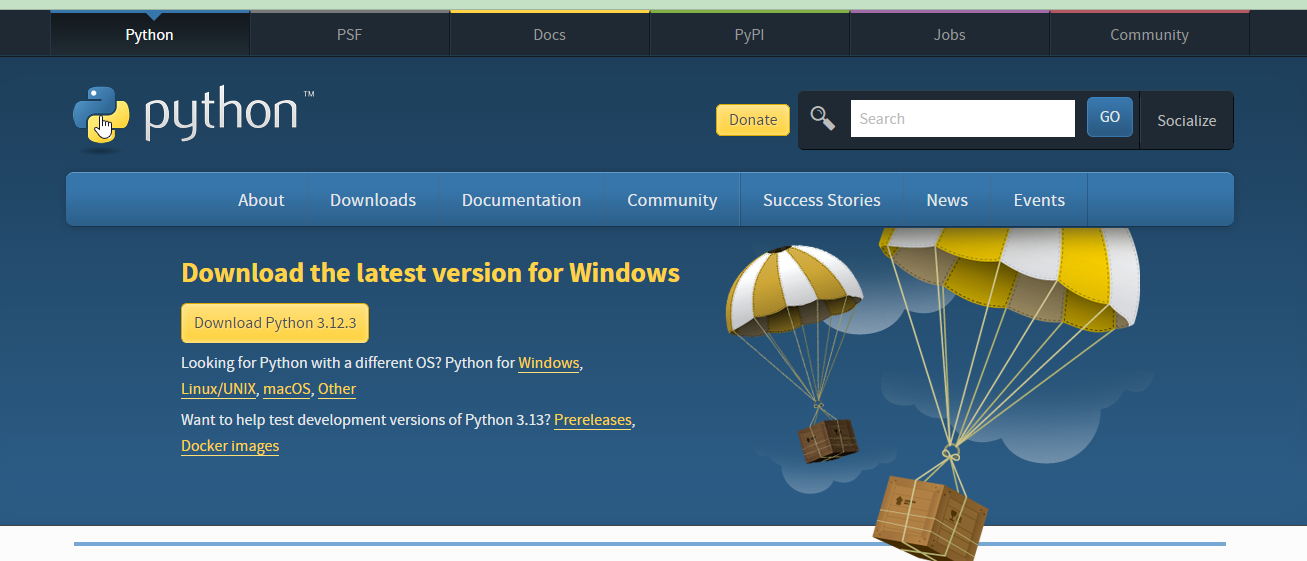
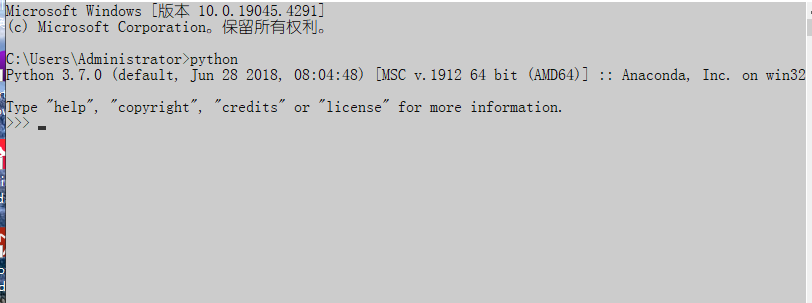
测试python解释器是否安装成功!
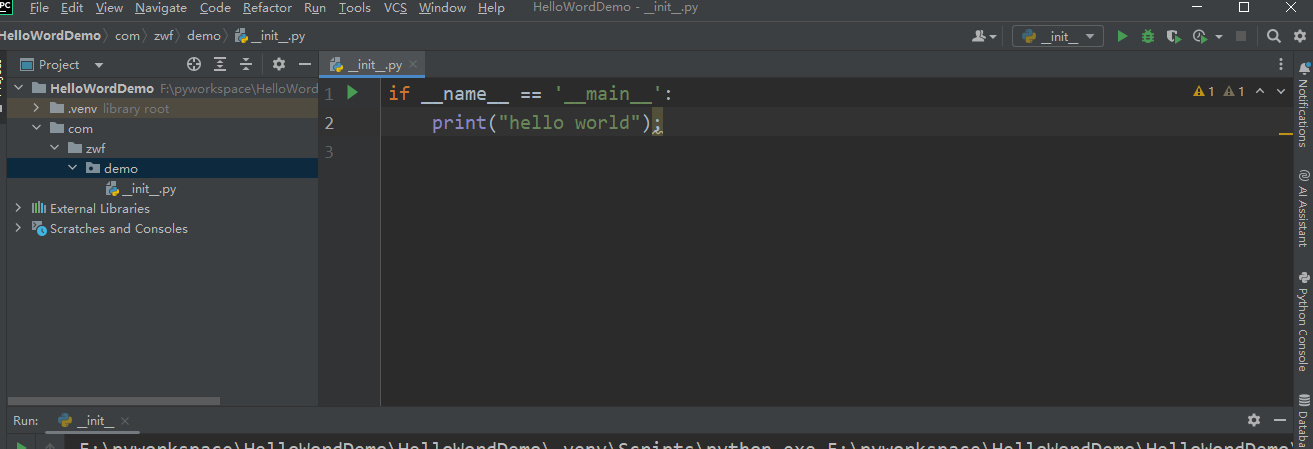
二、使用python建立py工程
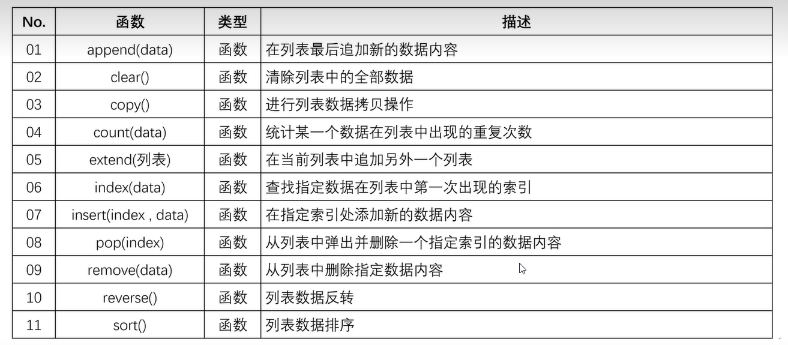
三、集合
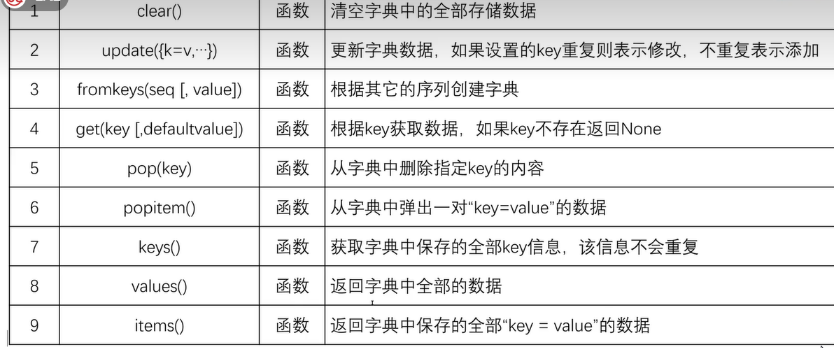
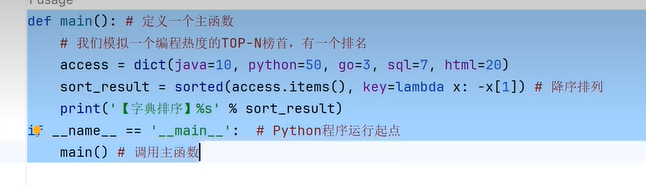
四、字典
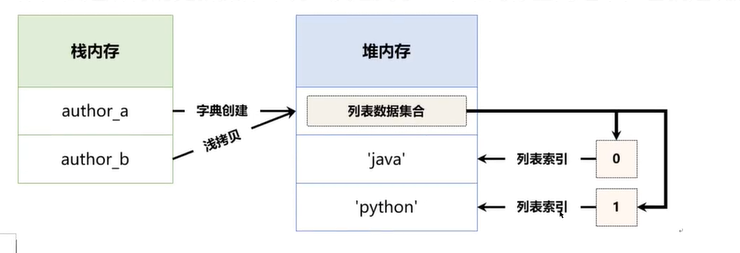
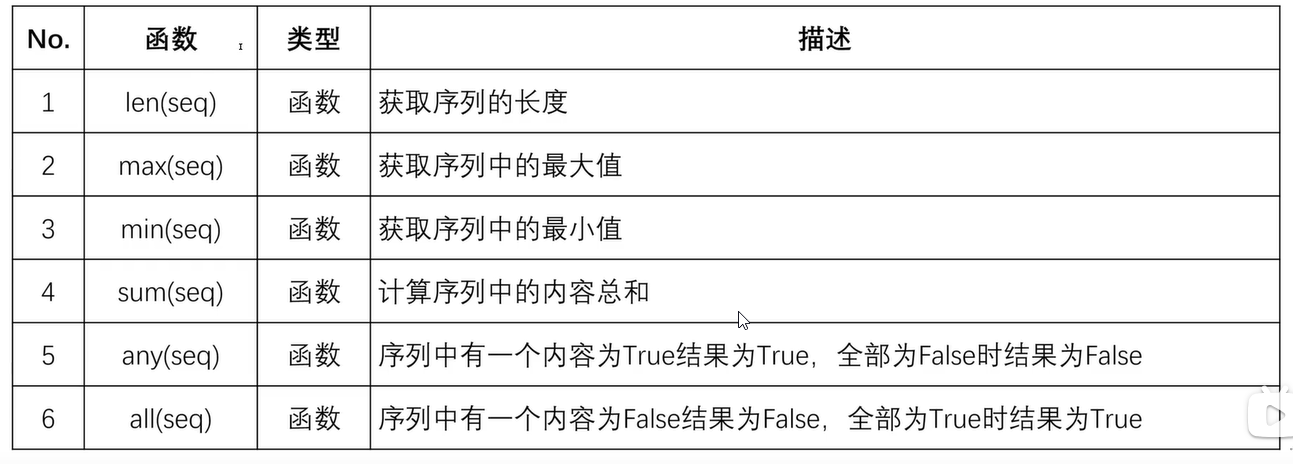
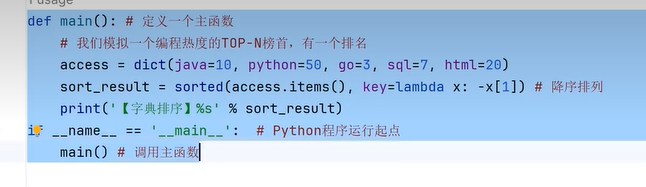
五、序列统计函数
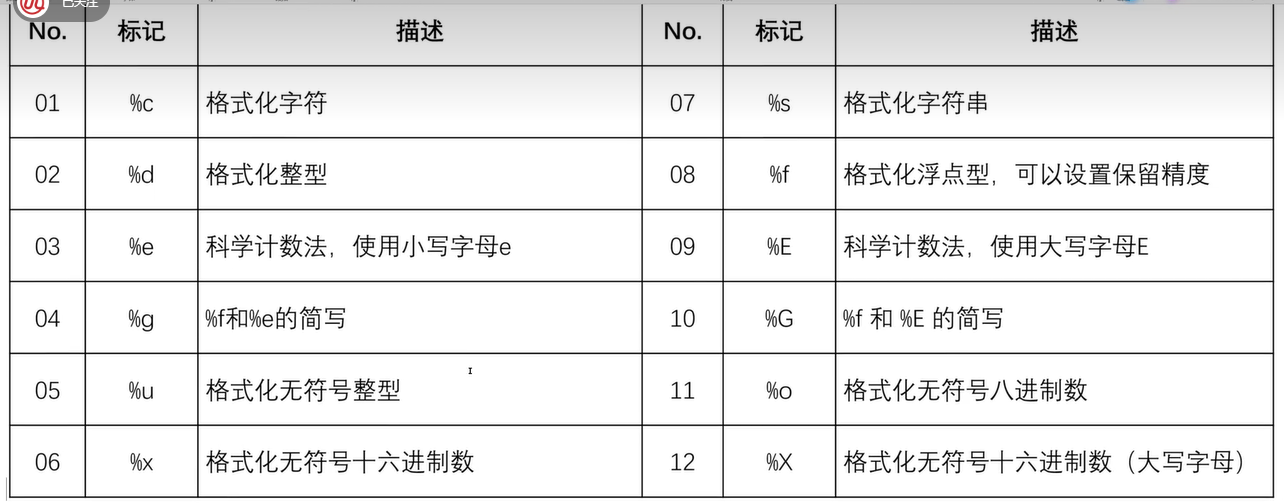
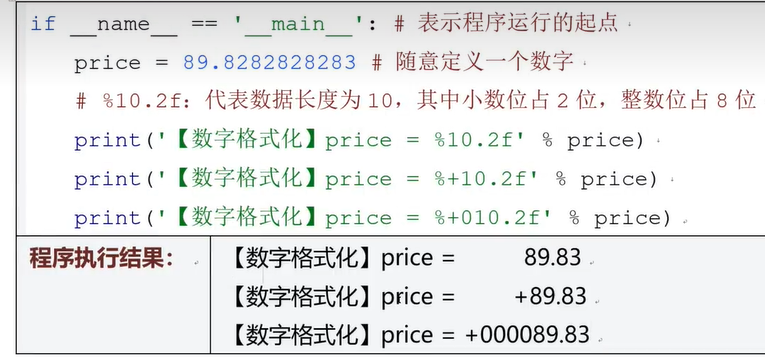
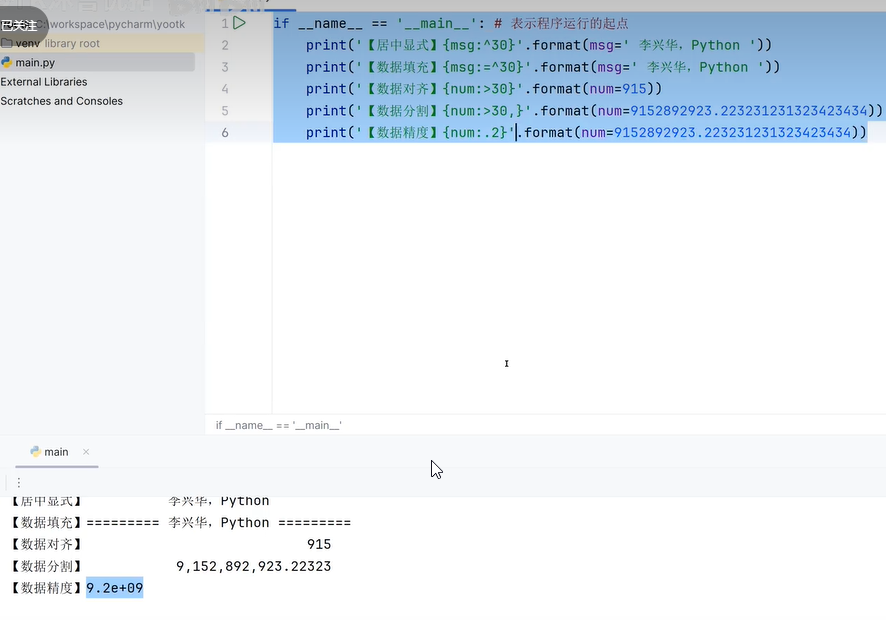
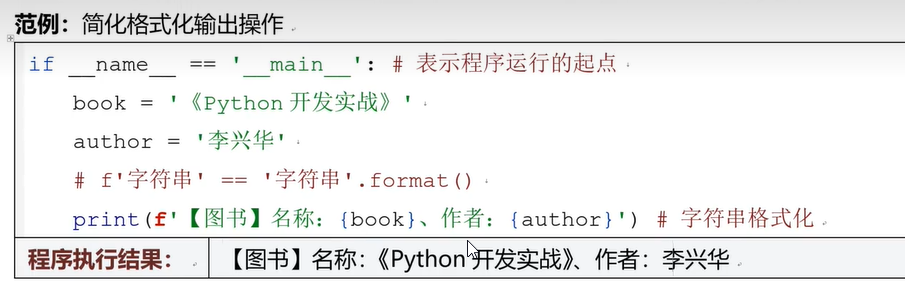
六、数据格式化输出
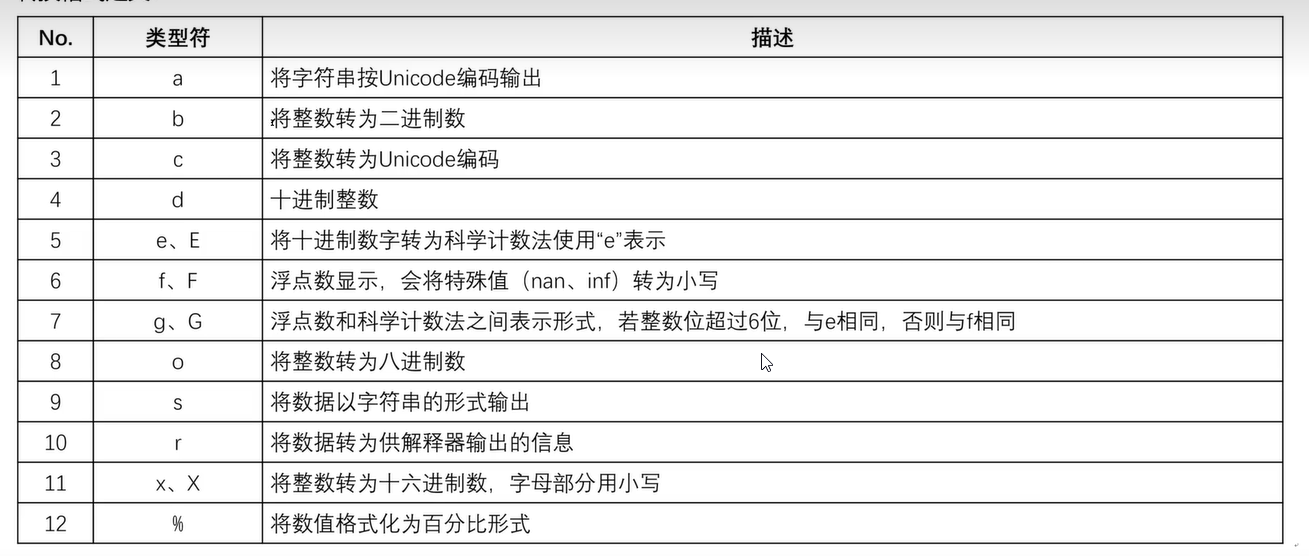
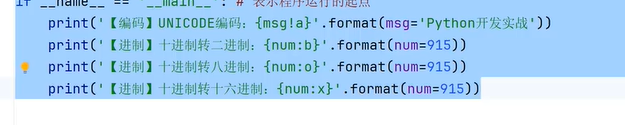
七、字符串转义


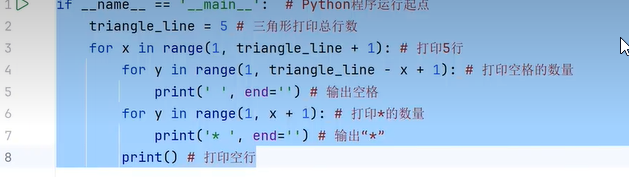


八、变量的作用域

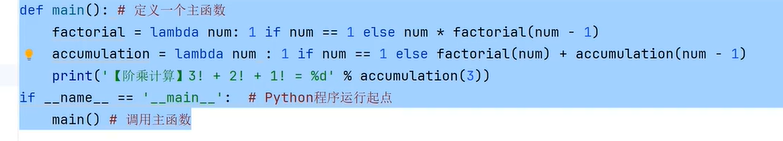
九、Lambda表达式



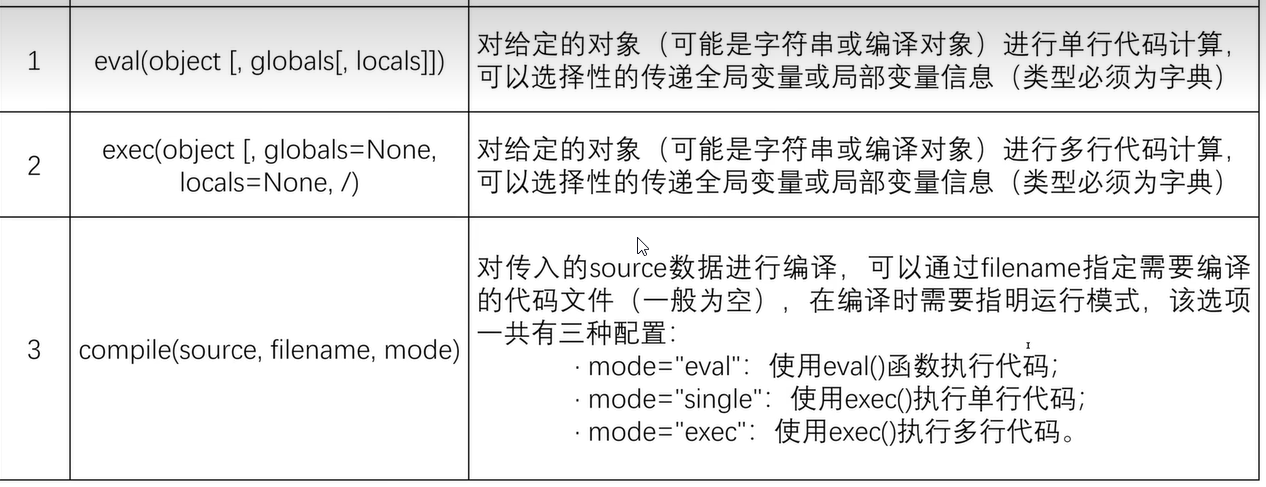
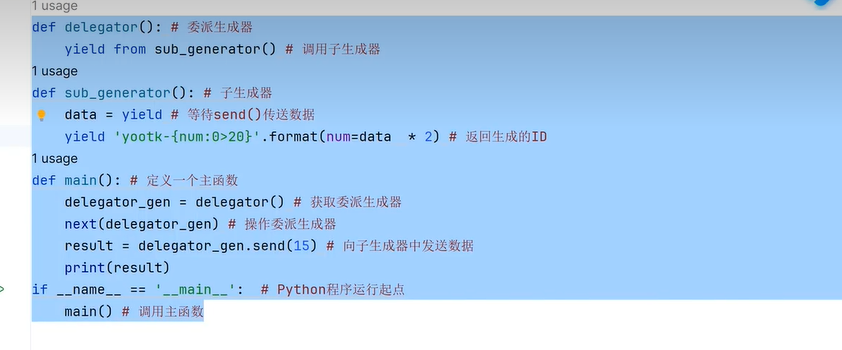
十、yield懒加载机制

十一、面向对象
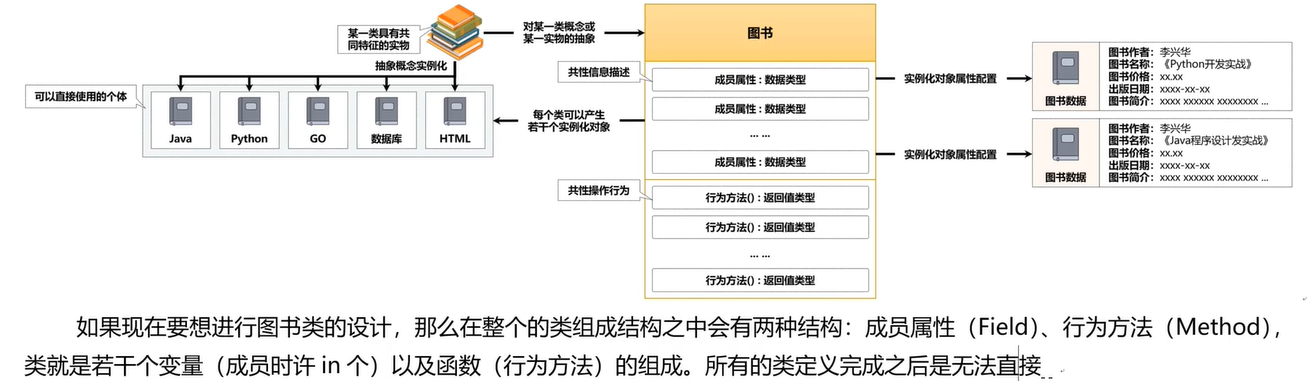
十二、内部类

十三、继承子类
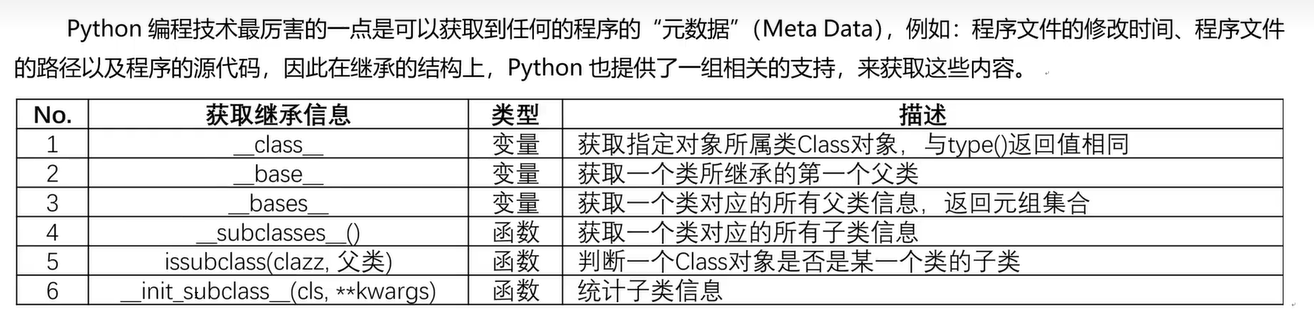
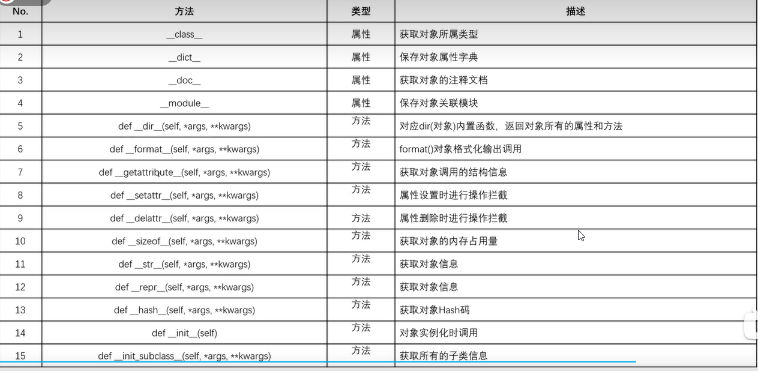
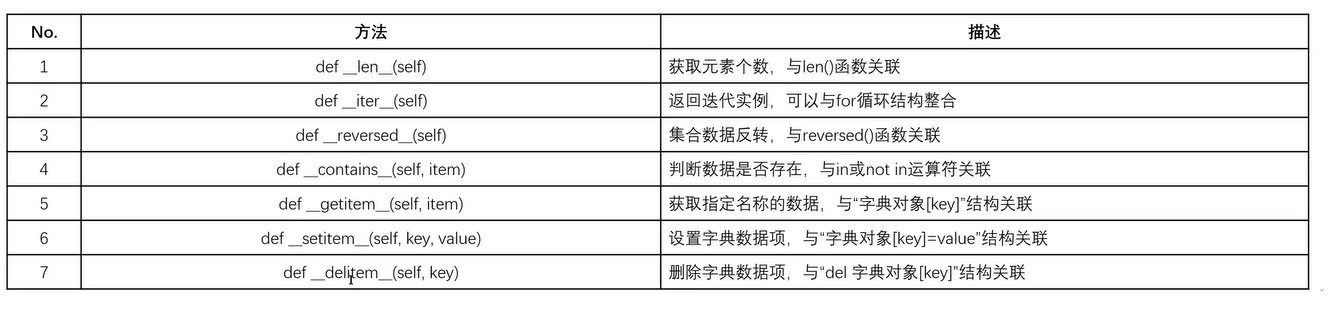
十四、object类常用方法
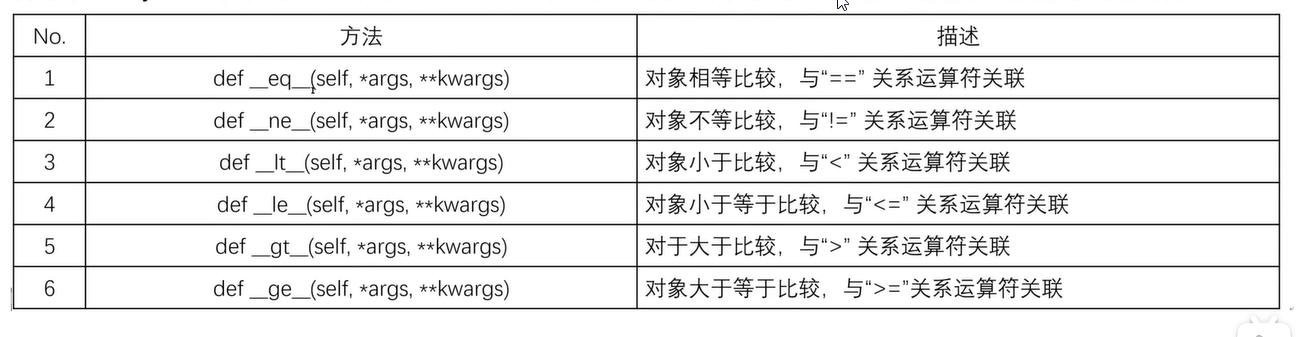
十五、对象比较
十六、数据类型转换
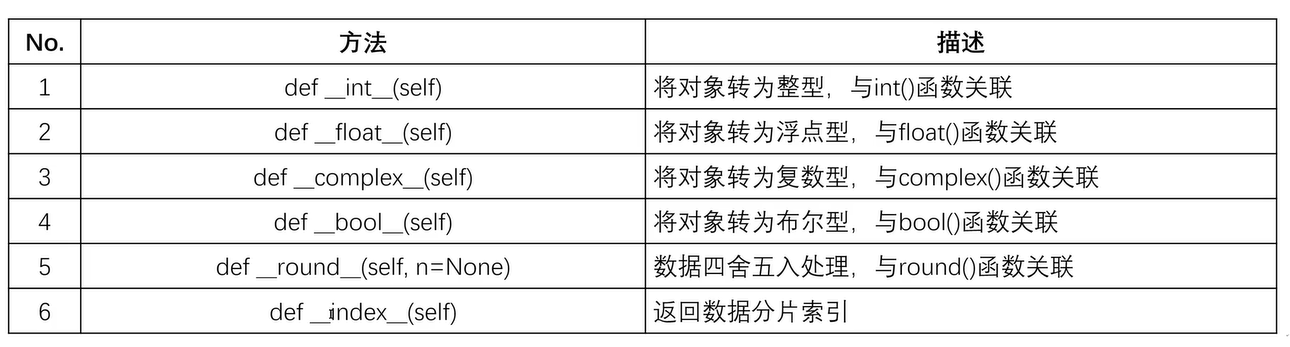

十七、Math类
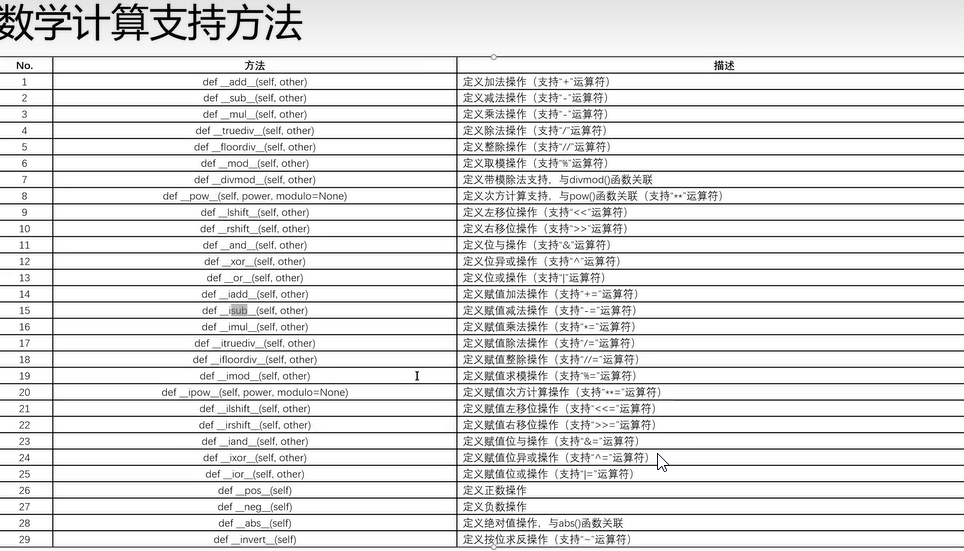
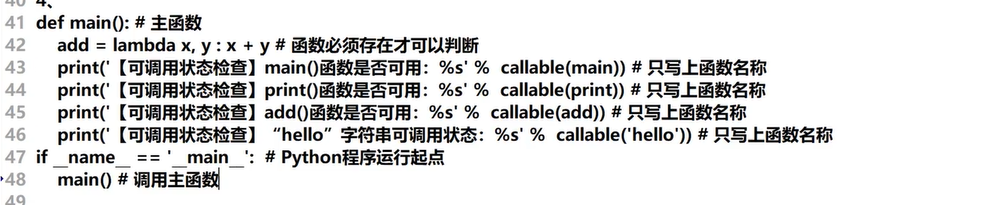
十八、可调用对象(Call()方法)
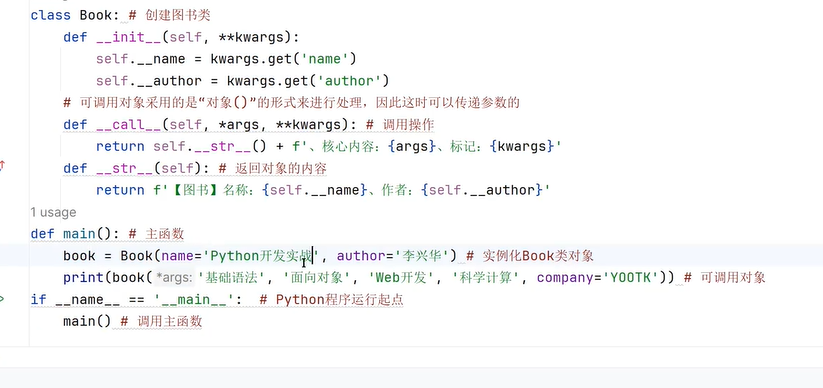
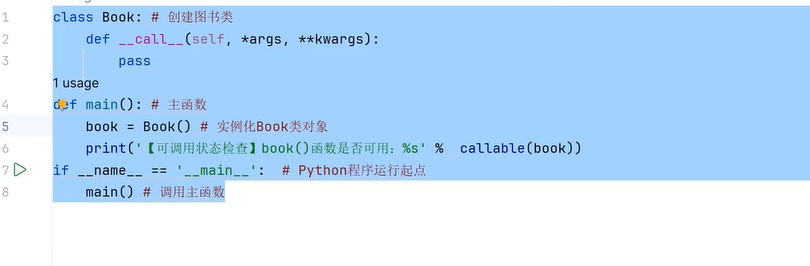
十九、链表
二十、装饰器
# 代理函数模式
def log(level = 'INFO'):
def decorator(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# func.__name__获取被代理函数名 args:一个元组 第一个值是对象 第二个值是参数
# kwargs: 命名参数
print(f'[{func.__name__}]-{level};{args};{kwargs}')
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper # 返回内部函数
return decorator # 返回外部函数
class Message: # 网络消息
# 方法覆写
@log(level='DEBUG')
def connect(self):
# 核心代码
print('建立网络连接....')
return True
# 引用装饰器
@log()
#方法覆写
def echo(self, msg,**kwargs):
name = kwargs.get('name')
return '[ECHO]' + msg +f',{name}'
def main():
message = Message()
if message.connect():
print(message.echo('Hello I am UDP,TCP', name='xiaoZeng'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 代理类
# 代理类
class Log:
# 设置参数
def __init__(self, level='INFO'):
self.__level = level
# 设置代理内容
def __call__(self, func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(f'[被代理的方法名:{func.__name__}]:参数:{args},命名参数:{kwargs}')
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
class Message:
@Log(level='DEBUG')
def connect(self):
print('网络连接成功!!')
return True
@Log()
def echo(self, msg, **kwargs):
return f'[网络发送消息]:{msg},发送方:{kwargs.get('person')}'
def main():
message = Message()
if message.connect():
print(message.echo('你好,我是代理类!', person='小曾'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()


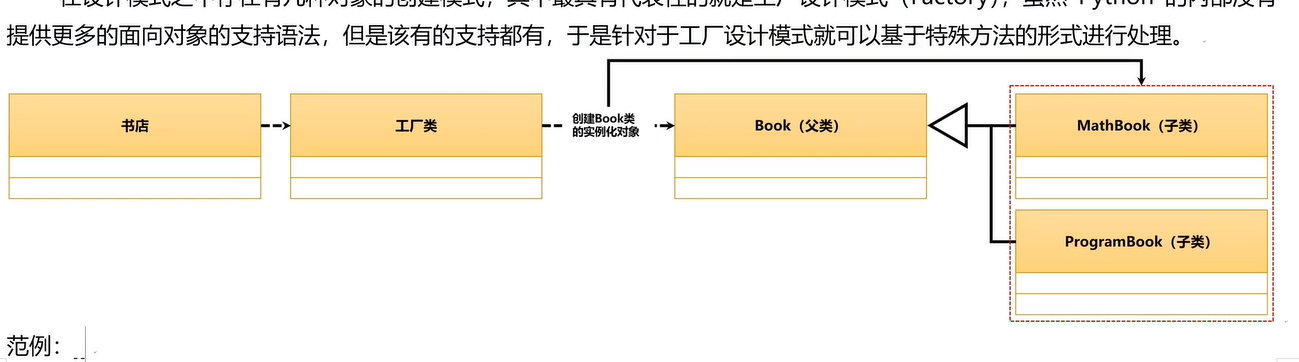
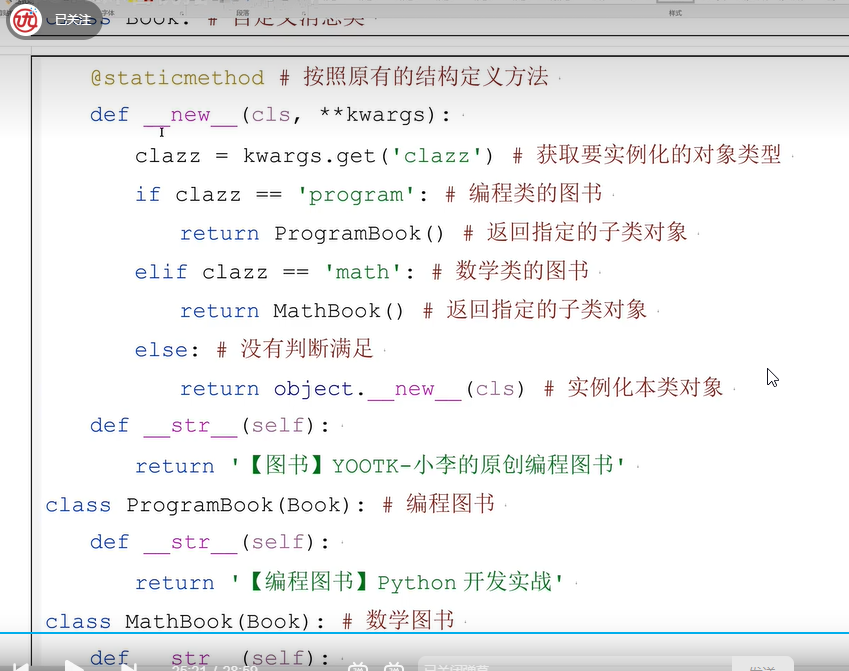
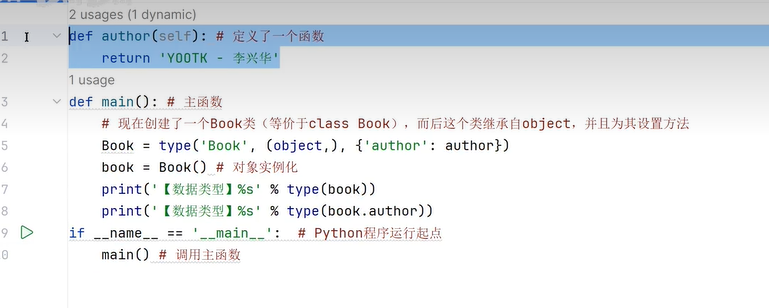
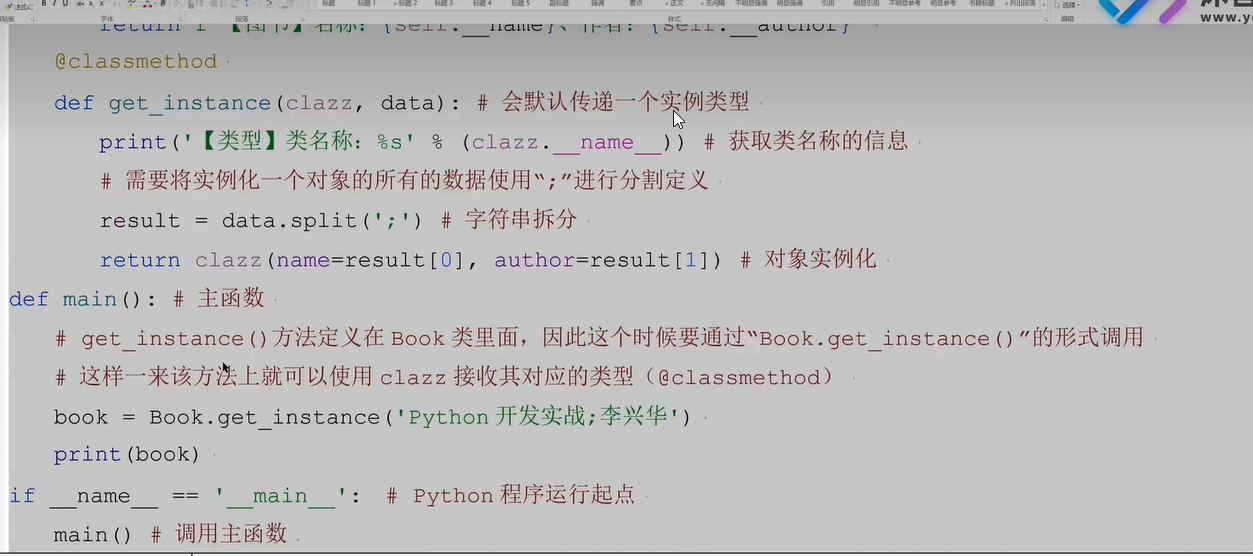
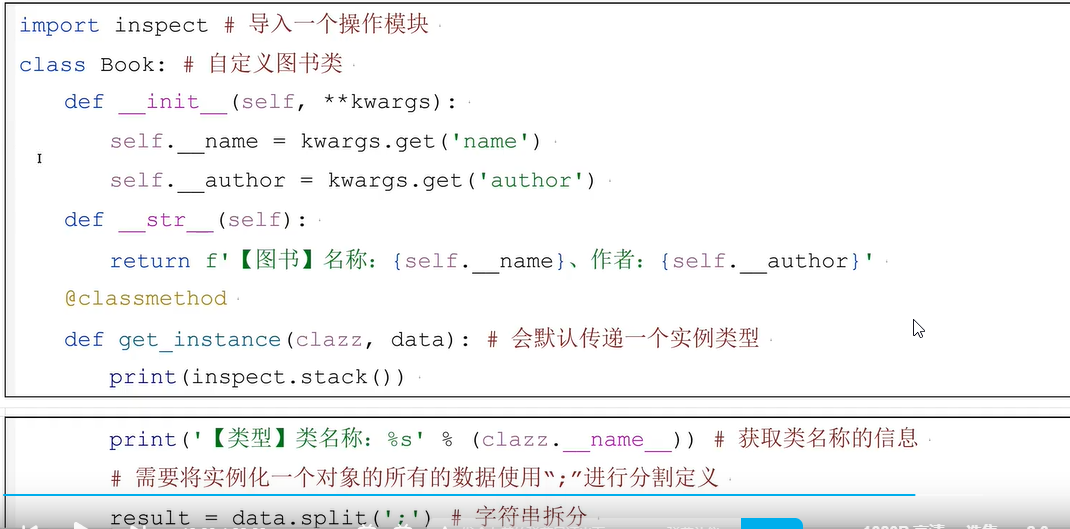
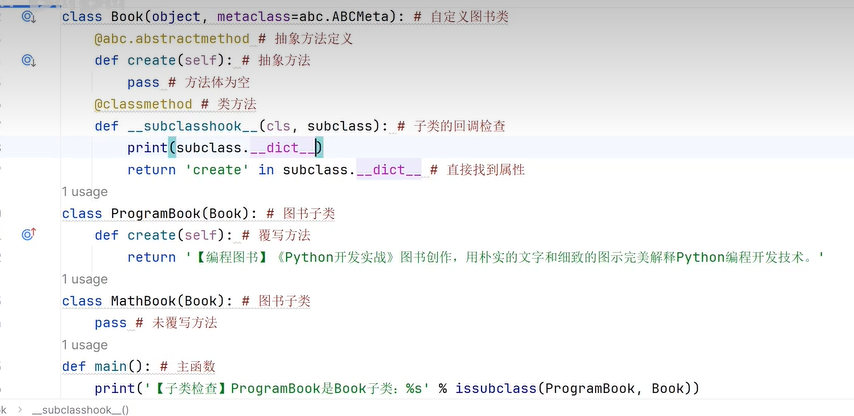
二十一、工厂模式

二十三、metaclass




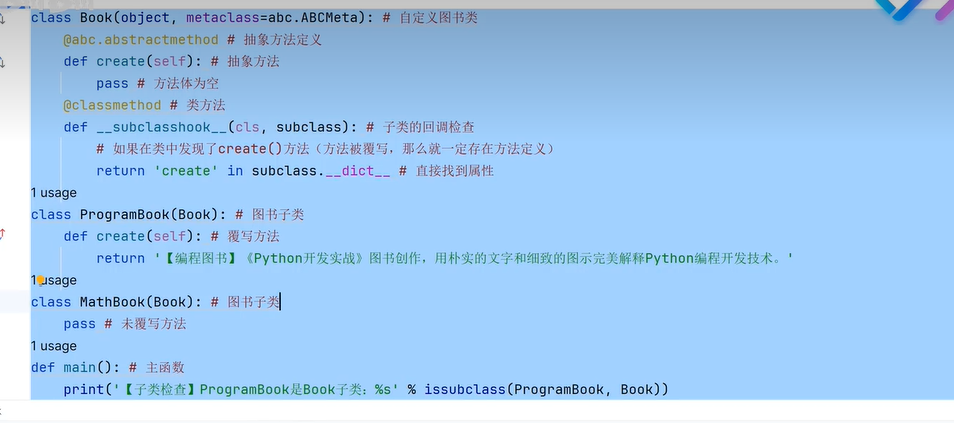
二十四、异常处理

二十五、模块化开发





二十六、Math类
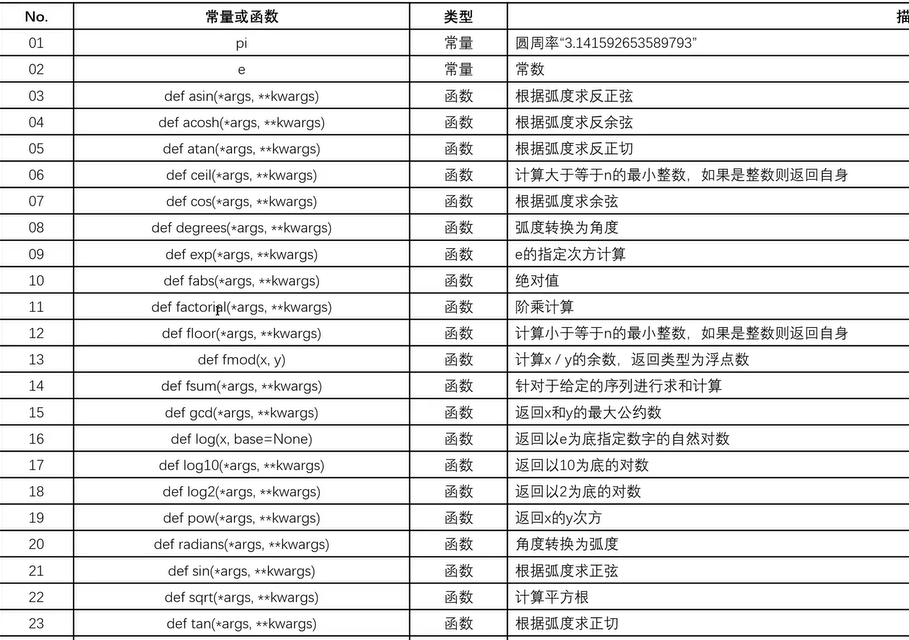
二十七、随机数
- 随机数案例
import random
# 编写一个中奖系统
def main():
# 存放中奖号码集合
sltos=[]
while len(sltos)!=7:
temp_number = random.randint(1,37) # 随机生产1~36随机数包括1,36
sltos.append(temp_number)
# 排序
sltos.sort()
# 打印中奖号码
print(f'打印中奖号码:{sltos}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 偏函数
import functools
def write_book(*args,**kwargs):
return f'[图书创作]名称:{kwargs.get('name')}、作者:{kwargs.get('author')},特点:{args}'
def main():
# 偏函数的目的是封装相同的方法 提高系统的扩展性
wrapper=functools.partial(write_book,'图书','系统','案例',author='李兴华')
print(wrapper('零基础',name='python开发实战'))
print(wrapper('零基础', name='java开发实战'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
二十八、枚举类型
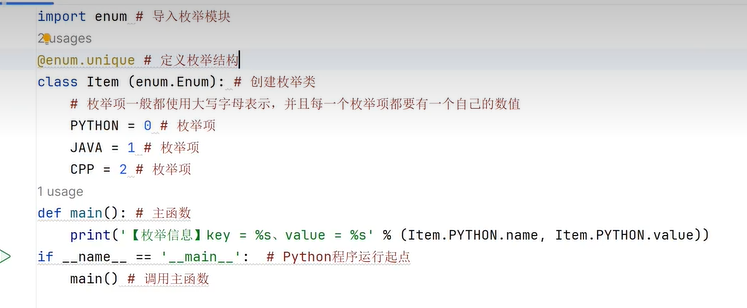
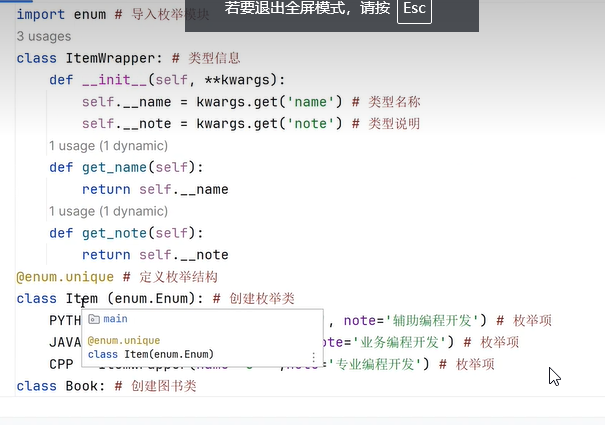
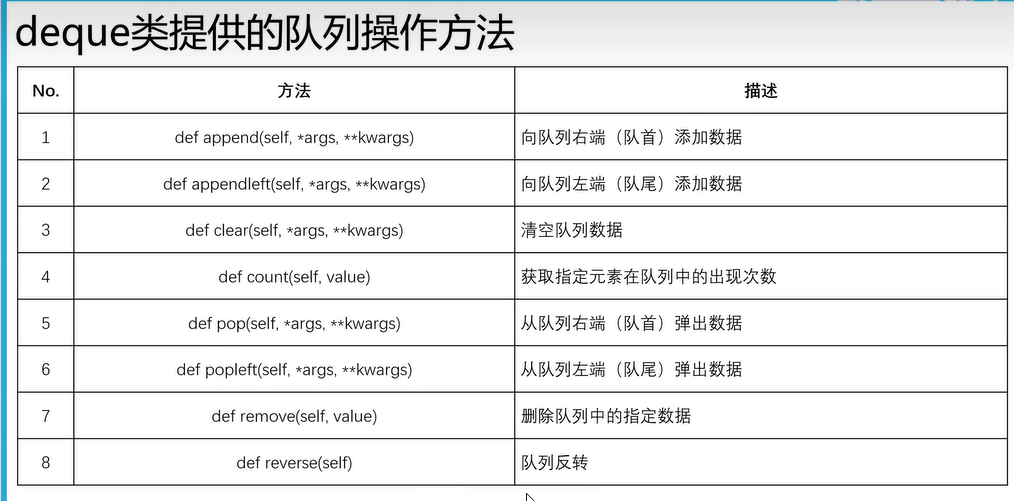
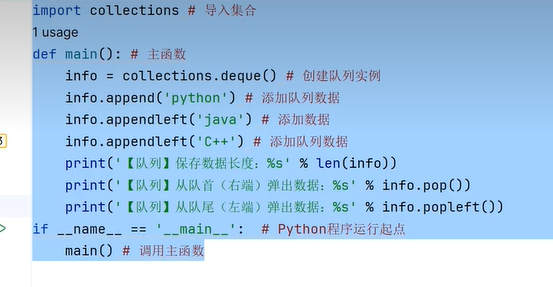
二十九、双端队列
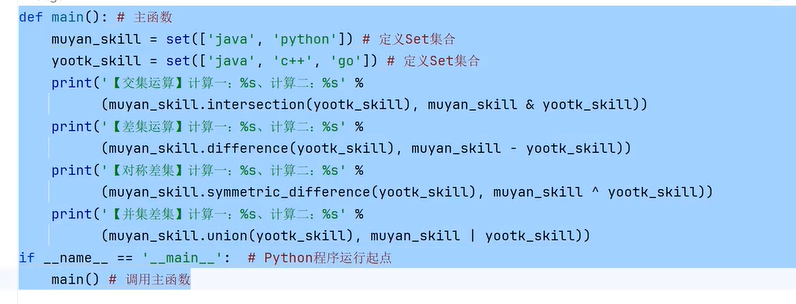
三十、Set集合运算
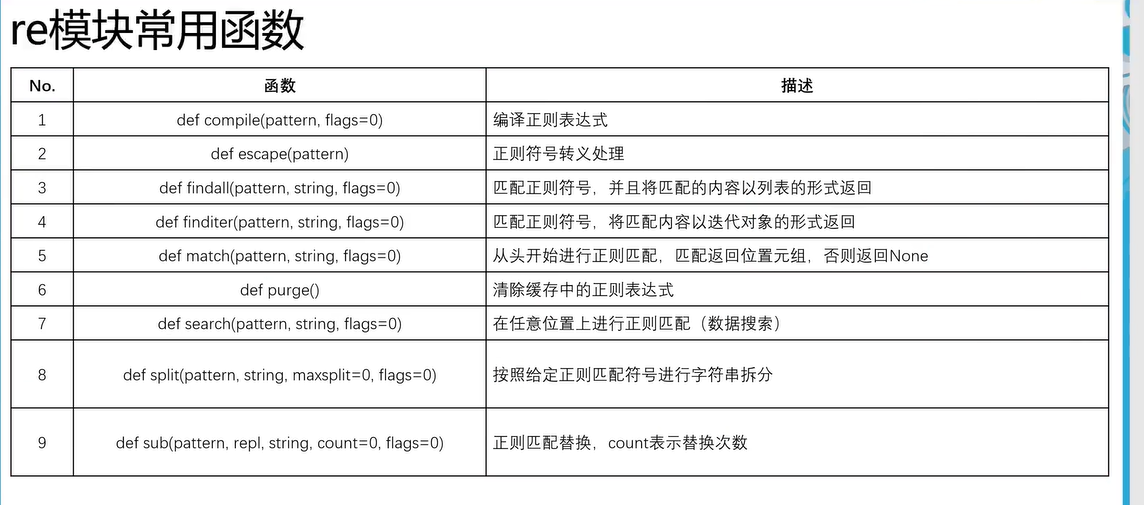
三十一、正则匹配
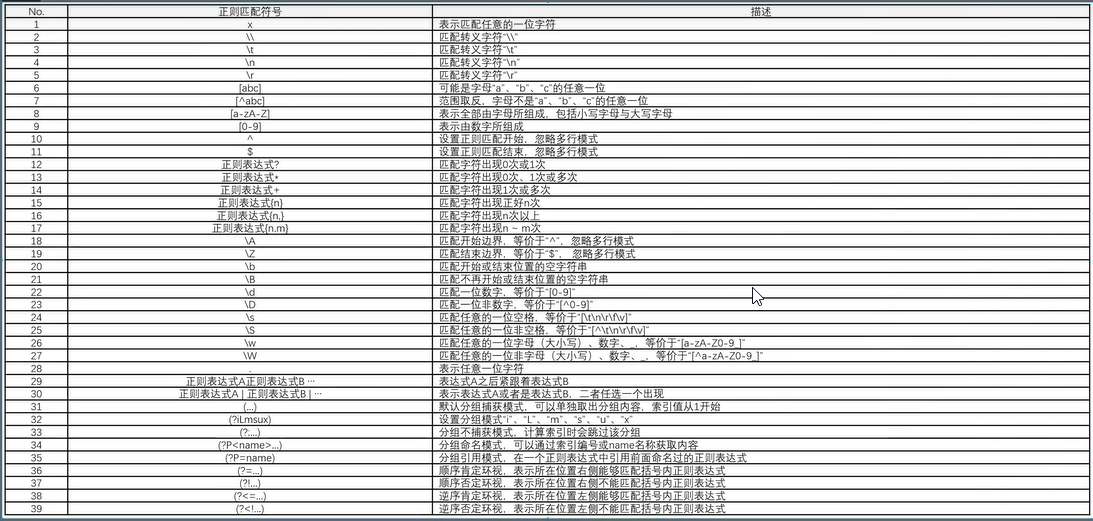

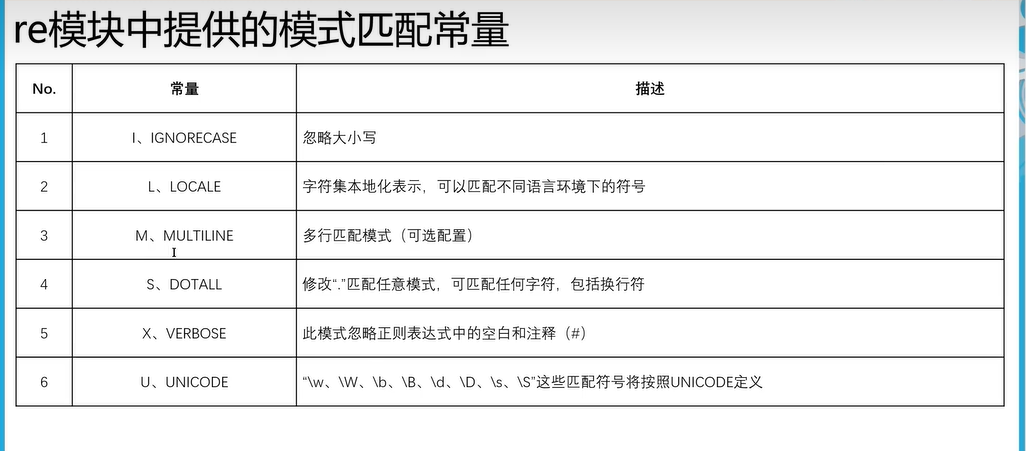


^\w+@\w+\.(cn|com|com\.cn|net|gov){1}$

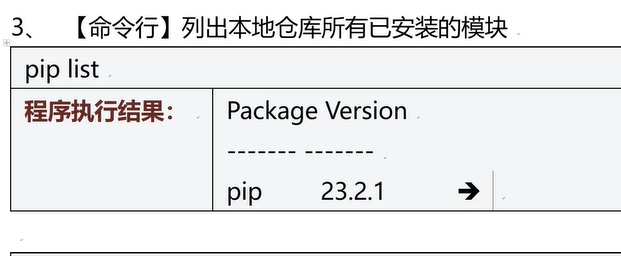
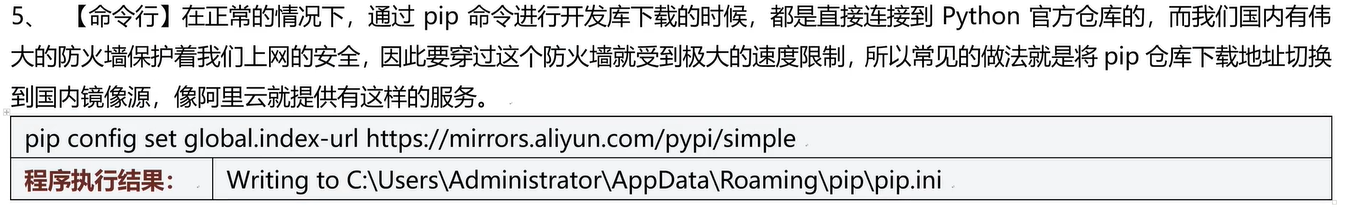
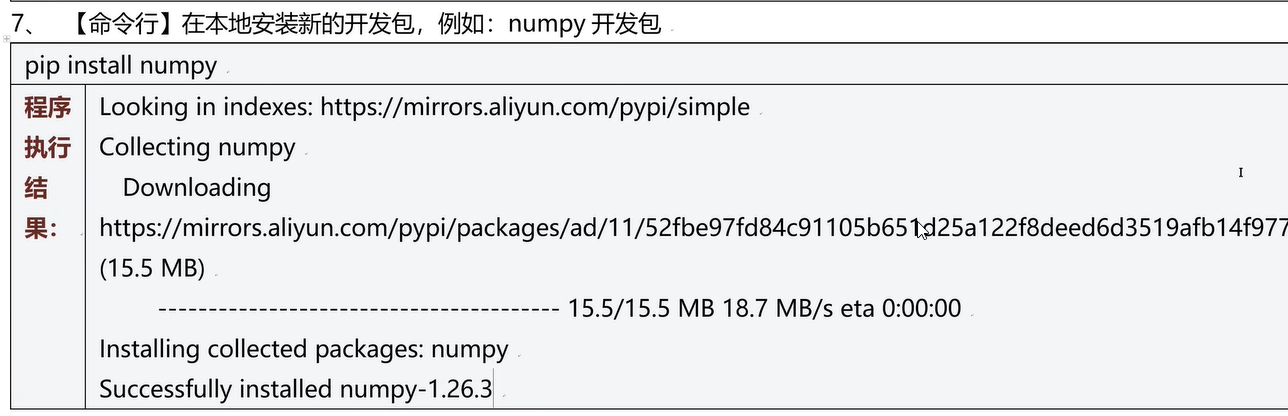
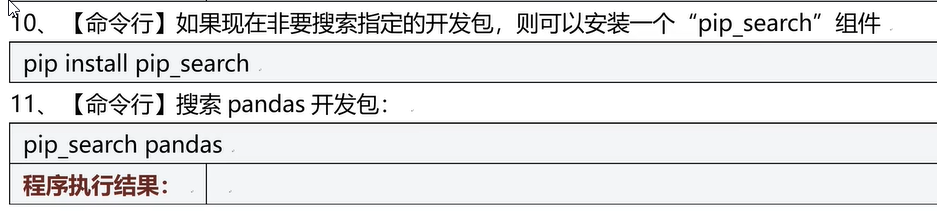
三十二、Pip工具




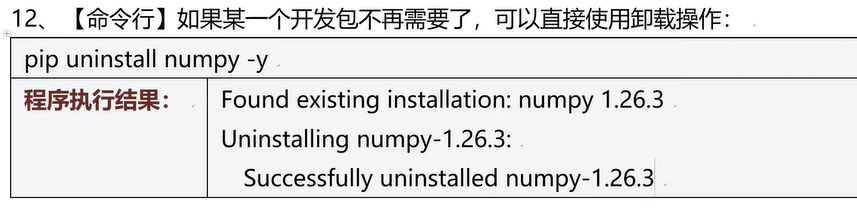
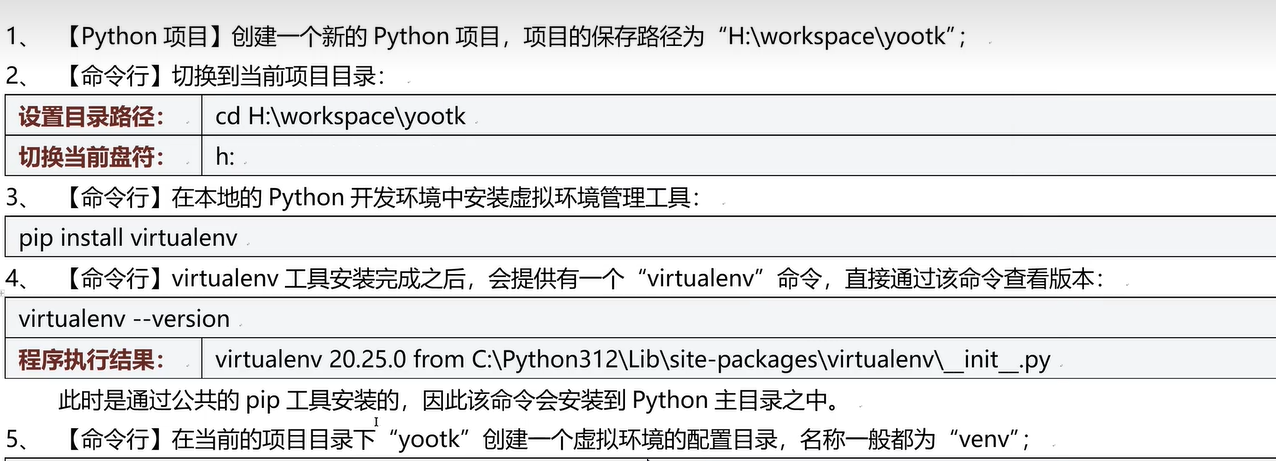
三十三、虚拟环境
- 手动创建python项目虚拟环境
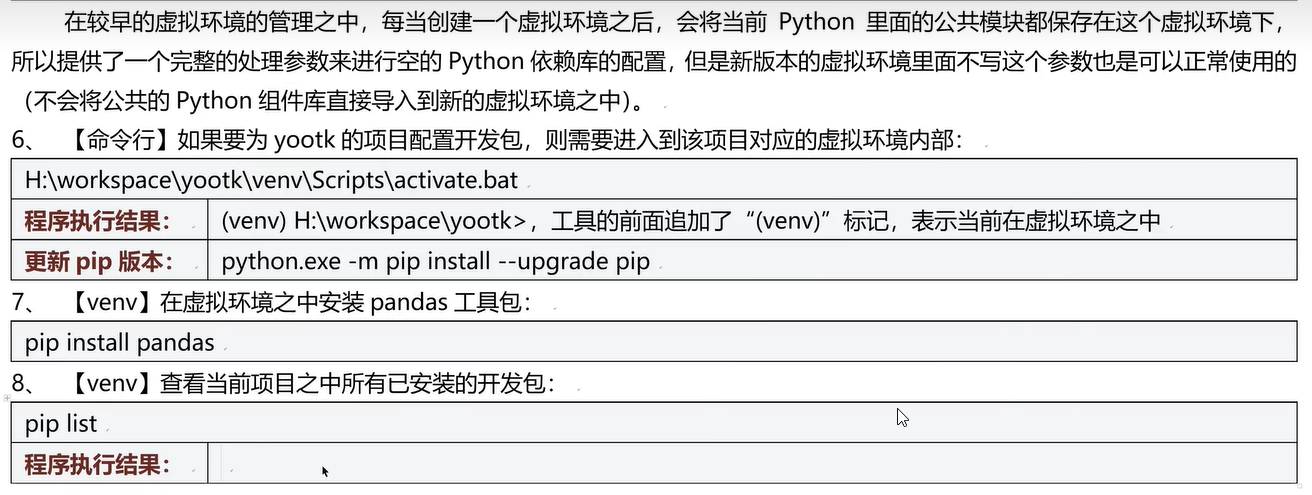
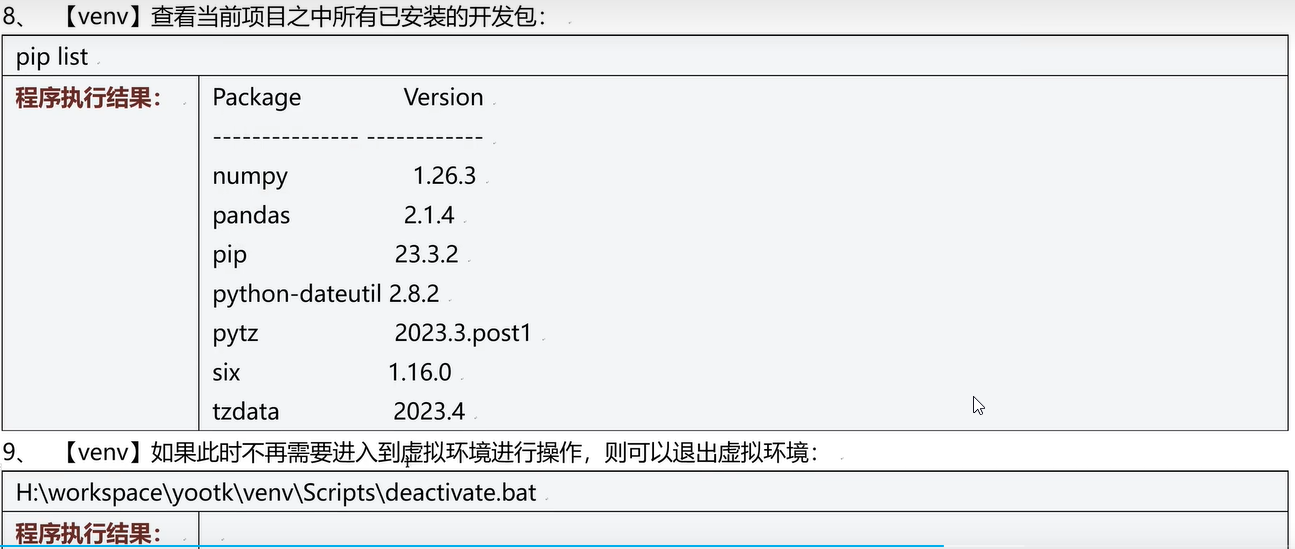
- pycharm每次创建一个项目就会自动创建一个虚拟环境
三十四、python打包
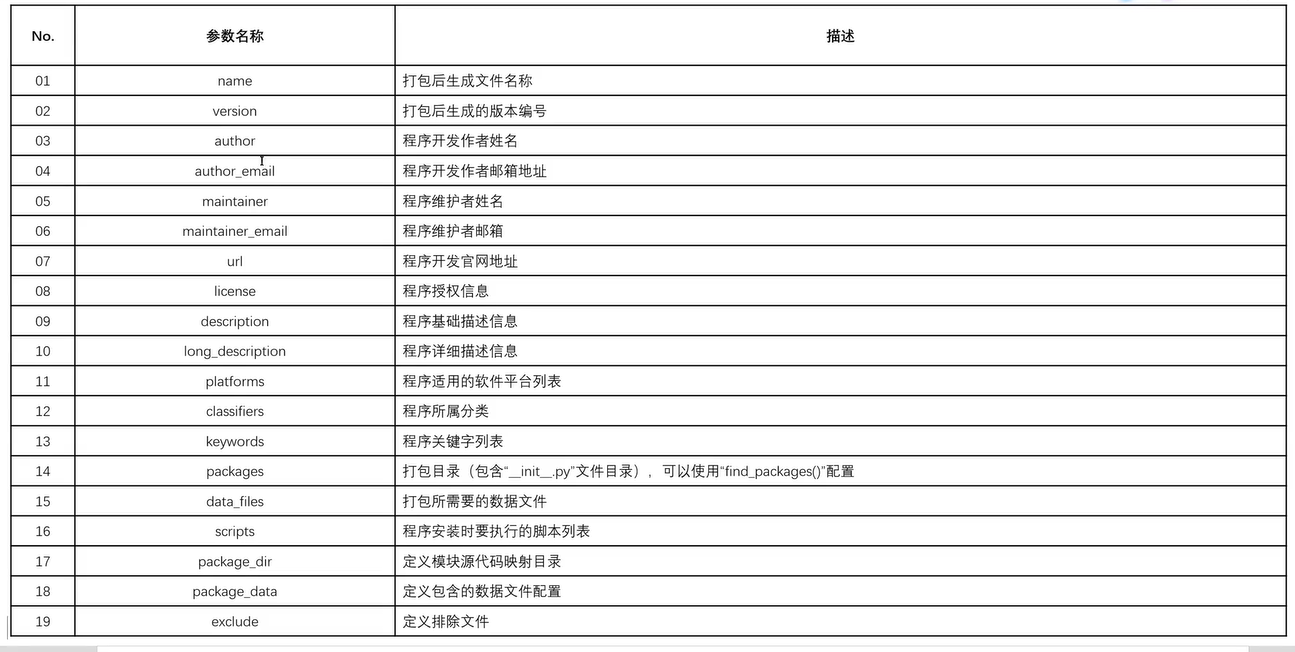
pip install setuptools #先按照打包模块,然后改下配置类
- 在项目根目录下创建setup.py配置类如下:
import setuptools
setuptools.setup(
name='python_study_XiaoZeng_demo', # 打包文件名称
version='0.0.1', # 打包模块版本号
author= '小曾',
url = 'http://www.baidu.com',
description='这是一个学习Demo代码集',
packages=setuptools.find_packages('src'),
package_dir={'':'src'}, # 打包目录
package_data={'':['*.txt','*.info','*.properties'], '':['data/*.*']}, #配置文件包含的后缀文件
exclude=['*.test','*.test.*','test.*','test'], # 排除所有的配置文件
classifiers=['Environment :: Web Environment',
'Intended Audience :: Developers',
'License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License',
'Operating System :: OS Independent',
'Programming Language :: Python',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 2',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3'])
- 在CMD/WindowPowerShell页面中运行如下命令进行
python setup.py bdist_wheel #python打包命令
-
把生成的程序包让别人执行如下命令,进行安装
![image-20240629172151011]()
pip install F:\pyworkspace\HelloWordDemo\dist\python_study_demo-0.0.1-py3-none-any.whl
- 查看本地模块
pip list
- 在自己的项目中安装自己打包程序
python setup.py install # 第一种方式
# 第二种方式
pip install F:\pyworkspace\HelloWordDemo\dist\python_study_demo-0.0.1-py3-none-any.whl
三十五、项目发布
- 在上传安装包前,先注册pipy远程仓库账号
https://pypi.org/manage/projects/
- 新建token用于上传验证
- 在操作系统的用户目录下创建
.pipyrc文件,可以不用每次输密码上传,类似于git验证
.pipyrc格式如下
[pypi]
username = __token__
password = pypi-AgEIcHlwaS5v....
- 在项目虚拟环境下安装twine
pip install twine
- 使用twine上传文件dist目录下安装到pipy远程仓库中,供全球开发者使用。
twine upload dist/*
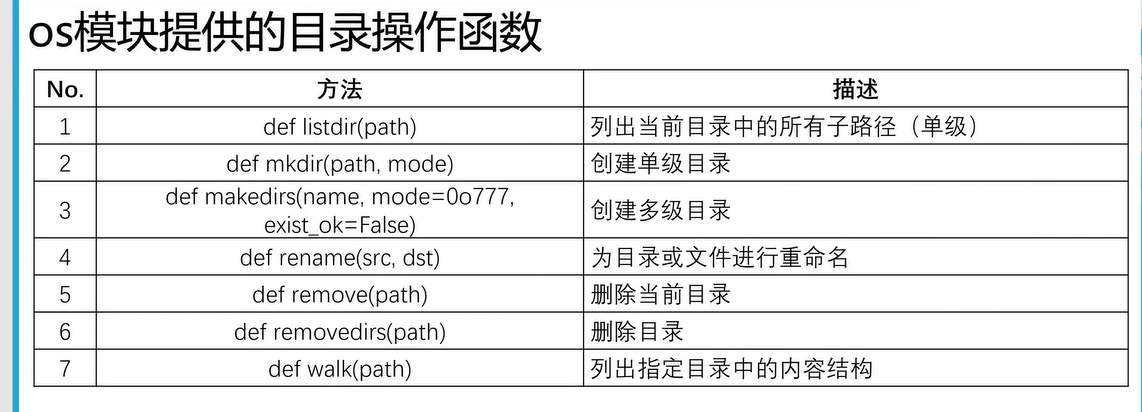
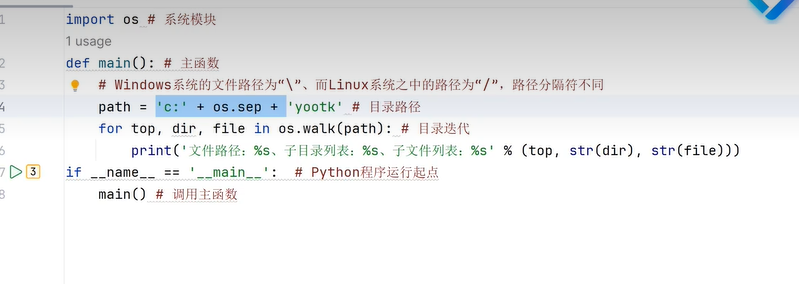
三十六、文件读写





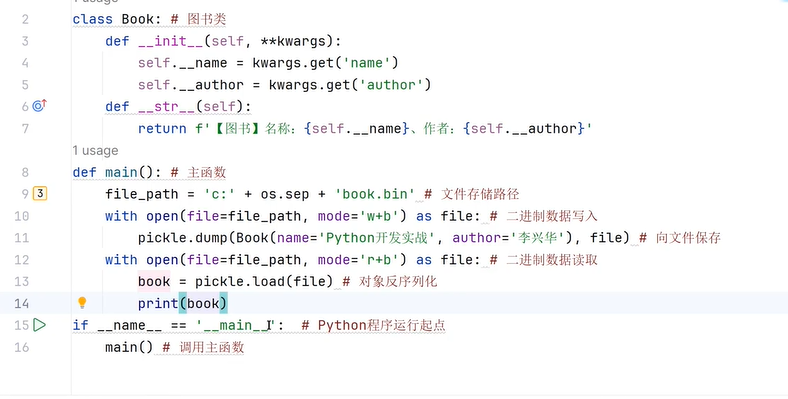
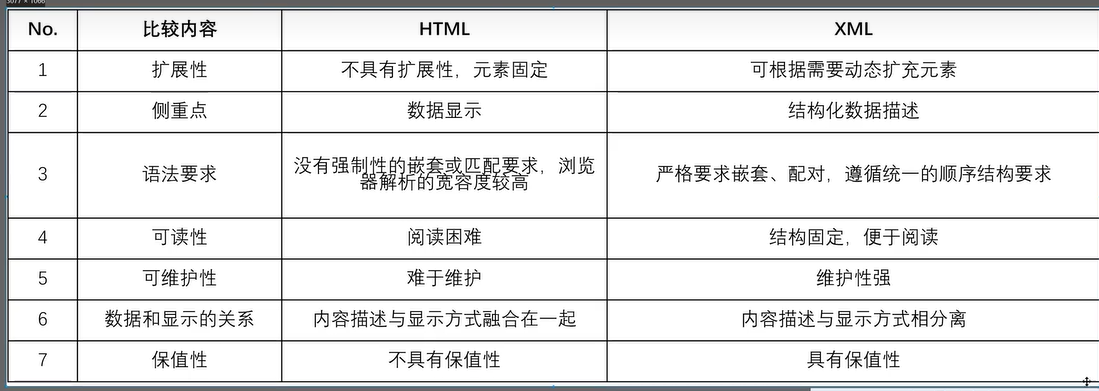
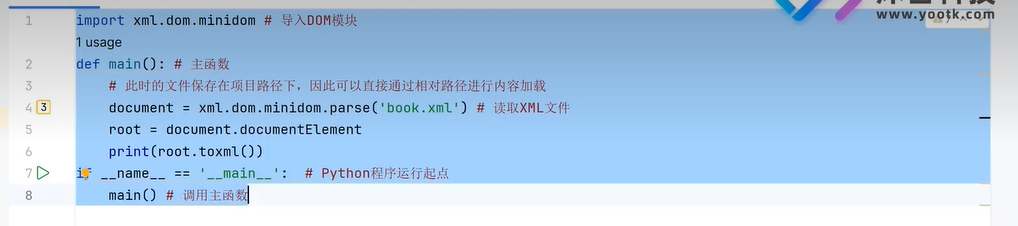
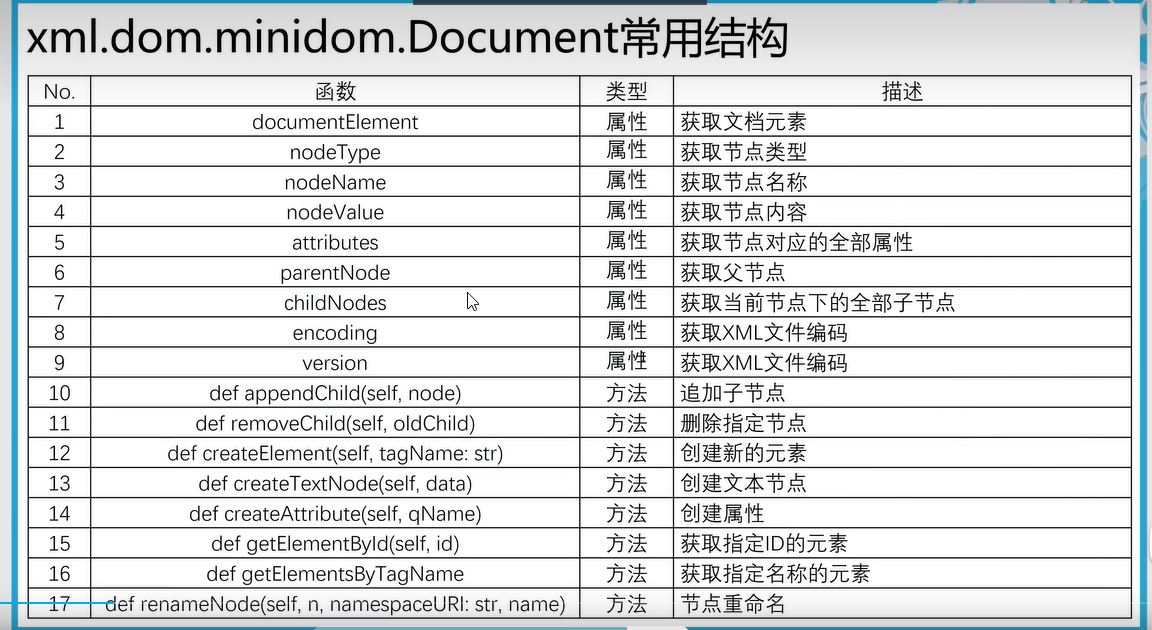
三十七、文本格式(Dom解析)


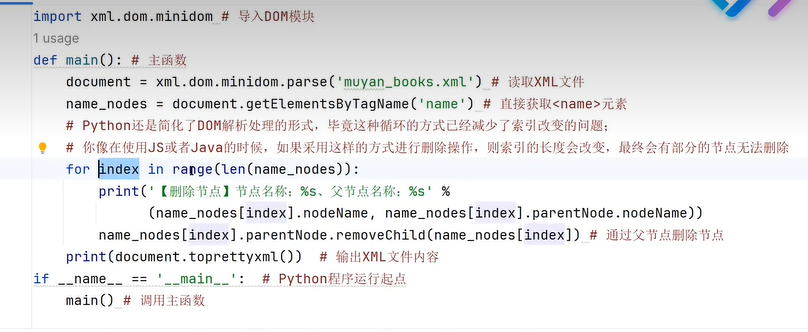
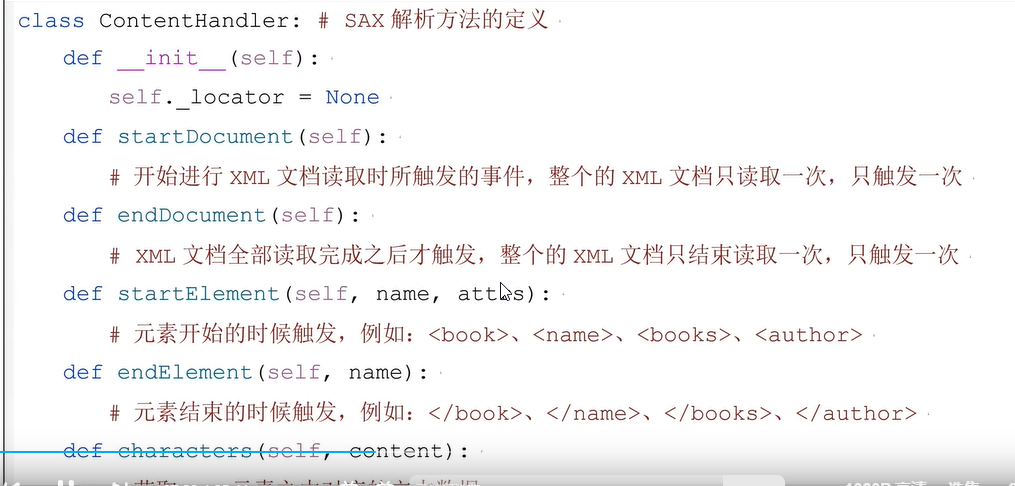
三十七、SAX文件解析
适合大数据量文件开发

import xml.sax
# SAX工具解析xml文件
class Book:
def __init__(self):
pass
def __str__(self):
return f'[图书信息]书名:{self.name},作者:{self.author},isbn:{self.isbn}'
class ContentHandle(xml.sax.ContentHandler):
def startDocument(self): #开始读取xml文档,只执行一次。
# 声明属性
self.__currentBook=None # 当前对象
self.__currentTarge=None # 当前标签
# 读取每个book对象存储在集合中
self.books =[]
def endDocument(self):
print('xml文件读取结束!')
def characters(self, content): # 获取xml元素中对应的文本数据
# 判断是否有内容
if len(content.strip())>0:
if self.__currentTarge=='author':
self.__currentBook.author=content
elif self.__currentTarge=='isbn':
self.__currentBook.isbn=content
elif self.__currentTarge=='name':
self.__currentBook.name=content
def startElement(self, name, attrs): # 获取<name>开始标签
# 获取当前标签名称
self.__currentTarge=name
# 如果是子标签对象的话就实例化对象
if self.__currentTarge == 'book':
self.__currentBook=Book()
# 把熟悉添加到对象中
self.__currentBook.isbn=attrs.getValue('isbn')
def endElement(self, name): # 获取</name>结束标签
if name=='book':
self.books.append(self.__currentBook)
def main():
# 获取sax解析器对象
sax=xml.sax.make_parser()
# 关闭命名空间检查
sax.setFeature(xml.sax.handler.feature_namespaces, 0)
# 实例化解析
chd = ContentHandle()
sax.setContentHandler(chd) #SAX解析配置
sax.parse('F:\\pyworkspace\\HelloWordDemo\\book.xml')
for book in chd.books:
print('xml文件集合:', book,end='\t\t')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
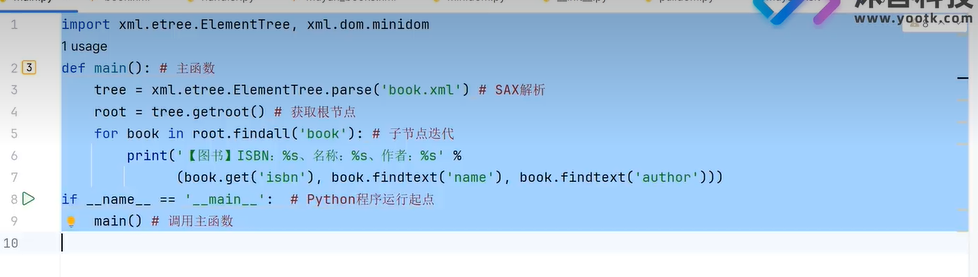
三十八、ElementTree(创建Dom树)
三十九、HTML
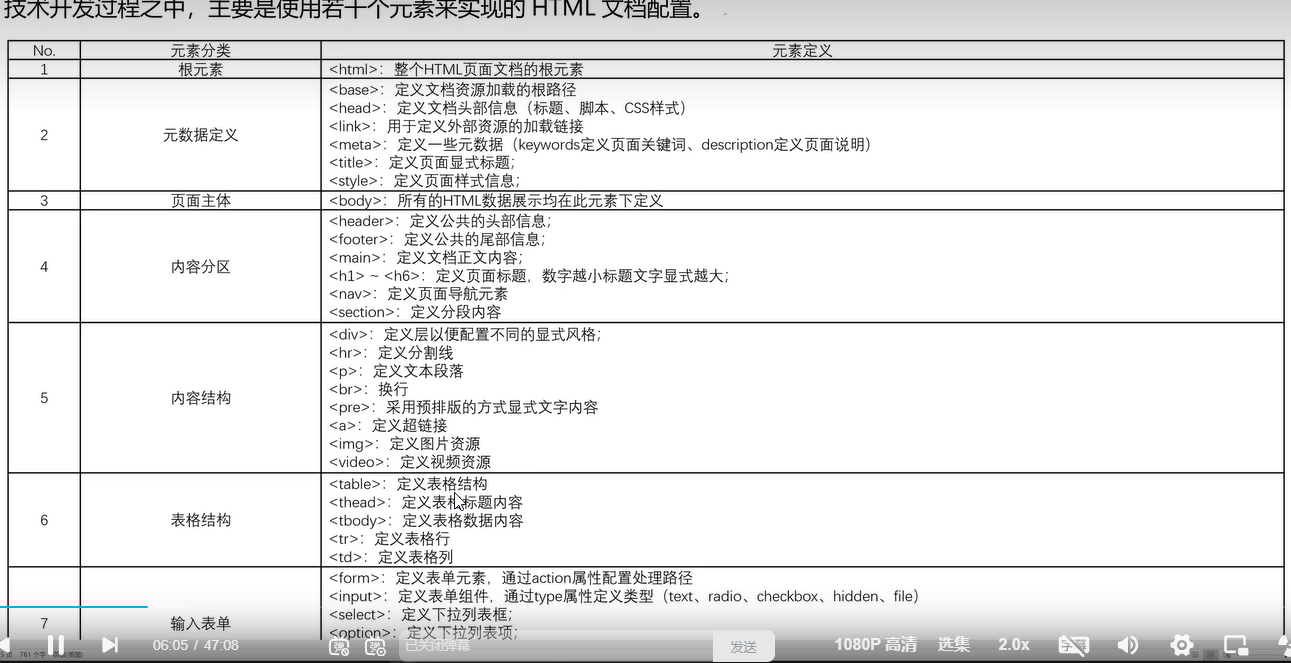
四十、ZIP压缩文件创建
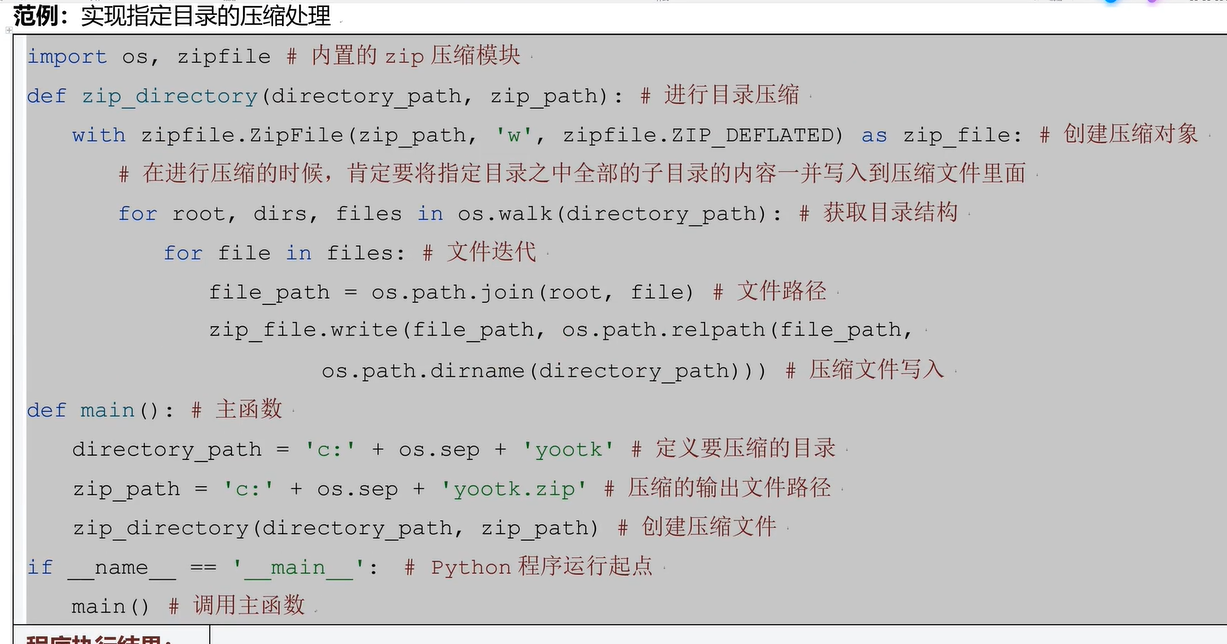

四十一、tar.gz压缩文件文件创建


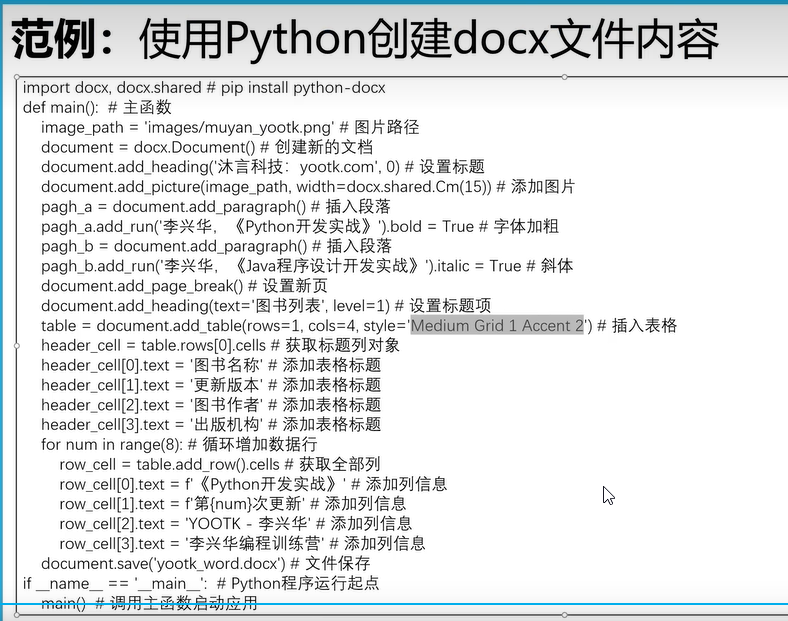
四十二、python操作word
- 安装python依赖包(在虚拟环境下)
pip install python-docx
四十三、python操作excel文件
- 安装依赖库
pip install openpyxl
# 导入依赖 pip install openpyxl
import openpyxl,openpyxl.styles
def main():
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
#获取第一个工作簿
sheet1=wb.active
# 在第一行第二列输入值
sheet1.cell(1,2,'沐言优拓')
sheet1.cell(row=1,column=3,value='李兴华')
# 追加一行数据
sheet1.append(['java','python','go','c++','c','ruby'])
# 设置单元格数据
sheet1['A1']='测试单元格插入数据!'
# 给单元格设置字体
sheet1.cell(row=3,column=1,value='样式内容').font =(
# 字体类型 字体大小 是否加粗 字体颜色 是否倾斜
openpyxl.styles.Font(name='微软雅黑',size=12,bold=True,color='00FF00',italic=True))
# 设置文本左对齐
sheet1.cell(3,2,'文本左对齐').alignment=openpyxl.styles.Alignment(horizontal='left')
#底色填充
sheet1.cell(3,3,'底色填充').fill=openpyxl.styles.PatternFill(fill_type='solid',start_color='ffeb9c')
# 单元格边框
sheet1.cell(3,4,'单元格边框').border=openpyxl.styles.Border(left=openpyxl.styles.Side(border_style='double',color='FF0000'),right=openpyxl.styles.Side(border_style='double',color='00FF00'))
# 受保护的单元格
sheet1.cell(4,4,'受保护单元格').protection=openpyxl.styles.Protection()
# 数值文本格式化
sheet1.cell(4,5,0.9).number_format=openpyxl.styles.numbers.FORMAT_PERCENTAGE
wb.save('test2.xlsx')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 函数处理
import openpyxl,openpyxl.styles
def main():
workbook=openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet1=workbook.active
sheet1.title='图书销售情况'
sheet1.append(('图书名称','图书作者','出版机构','图书印刷量','图书销售量','图书破损量','图书库存量'))
book_name=['Mysql开发实战','Redis开发实战','ElasticSearch开发实战','PostgreSQL开发实战','MongDB开发实战']
prints=[5000,8000,7000,5000,3000] # 印刷量
sales=[4500,7200,5300,3500,1800] # 销售量
breaks=[213,239,131,231,89]
for index in range(len(book_name)):
sheet1.cell(row=index+2,column=1,value=book_name[index])
sheet1.cell(row=index + 2, column=2, value='李兴华')
sheet1.cell(row=index + 2, column=3, value='沐言优拓')
sheet1.cell(row=index+2,column=4,value=prints[index])
sheet1.cell(row=index+2, column=5,value=sales[index])
sheet1.cell(row=index+2, column=6,value=breaks[index])
sheet1.cell(row=index+2, column=7,value=prints[index]-sales[index]-breaks[index])
# 为表头添加数据筛选功能
sheet1.auto_filter.ref='A1:G1'
sheet1['D7']='=SUM(D2:D6)'
sheet1['E7']='=SUM(E2:E6)'
workbook.save('test3.xlsx')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 生成Excel柱状图
import openpyxl,openpyxl.styles,openpyxl.chart
def main():
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
vals=[('季度','python','c','c++','java','golang','ruby')
,(1,1232,4536,1254,7865,3456,4567)
,(2,4567,2356,7986,2567,9876,5687)
,(3,3456,8790,2365,1789,9867,1456)
,(4,1456,7896,1456,4578,2567,8967)]
for row in vals:
sheet.append(row)
# 柱状图
# bar = openpyxl.chart.BarChart()
# 折线图
bar=openpyxl.chart.LineChart()
bar.title='编程语言使用统计'
bar.x_axis.title='季度'
bar.y_axis.title='使用量'
chart_data=openpyxl.chart.Reference(sheet,min_col=2,max_col=7,min_row=1,max_row=5)
chart_catelog=openpyxl.chart.Reference(sheet,min_col=1,min_row=2,max_row=5)
# 设置统计数据
bar.set_categories(chart_catelog)
bar.add_data(chart_data,titles_from_data=True)
# 柱状图展示的位置
sheet.add_chart(bar,'H9')
wb.save('test4.xlsx')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 生成Excel柱状图
import openpyxl,openpyxl.styles,openpyxl.chart
def main():
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
vals=[('季度','python','c','c++','java','golang','ruby')
,(1,1232,4536,1254,7865,3456,4567)
,(2,4567,2356,7986,2567,9876,5687)
,(3,3456,8790,2365,1789,9867,1456)
,(4,1456,7896,1456,4578,2567,8967)]
for row in vals:
sheet.append(row)
# 面积图
bar=openpyxl.chart.AreaChart()
bar.title='编程语言使用统计'
bar.x_axis.title='季度'
bar.y_axis.title='使用量'
chart_data=openpyxl.chart.Reference(sheet,range_string='sheet!B1:G5')
chart_catelog=openpyxl.chart.Reference(sheet,range_string='sheet!A2:A5')
# 设置统计数据
bar.set_categories(chart_catelog)
bar.add_data(chart_data,titles_from_data=True)
# 柱状图展示的位置
sheet.add_chart(bar,'H9')
wb.save('test5.xlsx')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
import openpyxl
def main():
# 加载Excel中的数据
content=openpyxl.load_workbook('test.xlsx')
# 获取sheet列表
print('sheet名字列表',content.sheetnames)
# 获取名称获取表格信息
sheet1=content['图书销售总量']
for item in range(2025,2027):
# 复制单元表 并改名
sheet1_copy=content.copy_worksheet(sheet1)
sheet1_copy.title = 'Sheet1'
sheet1_copy.sheet_properties_tabcolor='ba7f57'
# 删除工作簿
content.remove(sheet1_copy)
content.save('test1.xlsx')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 处理excel
import openpyxl
def main():
# 创建多个sheet
program=['python','java','sql','go']
# 获取wordbook对象
workbook=openpyxl.Workbook()
#创建默认的sheet
sheet1=workbook.active
sheet1.title='图书销售总量'
for item in program:
workbook.create_sheet(f'{item}图书销售')
workbook.save('test.xlsx')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
四十四、CSV格式使用
import csv
def main():
with open('test.csv', 'r+', newline='',encoding='UTF-8') as csvfile:
csv_file=csv.reader(csvfile)
# 获取标题
csv_header=next(csv_file)
print(csv_header) # 以列表显示
# 读取每行数据
for row in csv_file:
print(row) # 以列表显示
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
import csv
def main():
# 以空格换行
with open('test.csv', 'r+', newline='',encoding='UTF-8') as csvfile:
# 以字典读取
csv_file=csv.DictReader(csvfile)
print(next(csv_file)) # 迭代输出字典
# 读取每行数据
for row in csv_file:
print(row.get('图书名称'),row.get('图书作者')) # 以列表显示
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
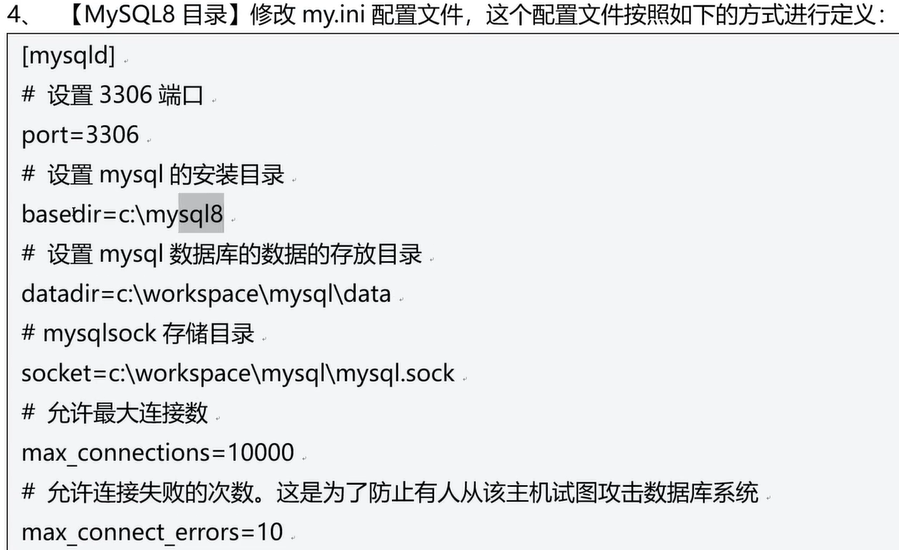
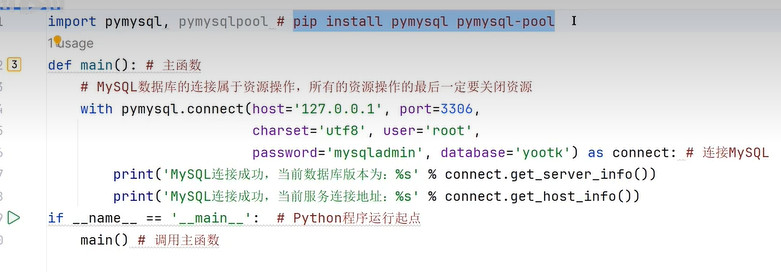
四十五、连接MySQL







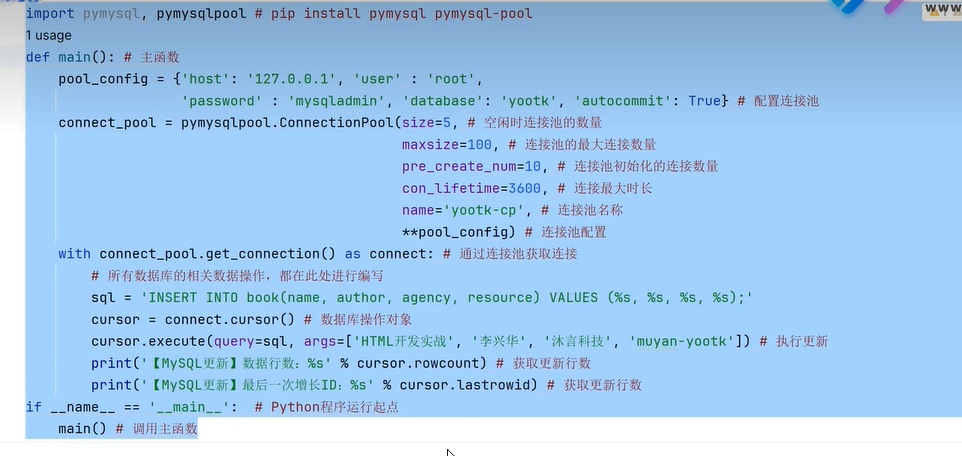


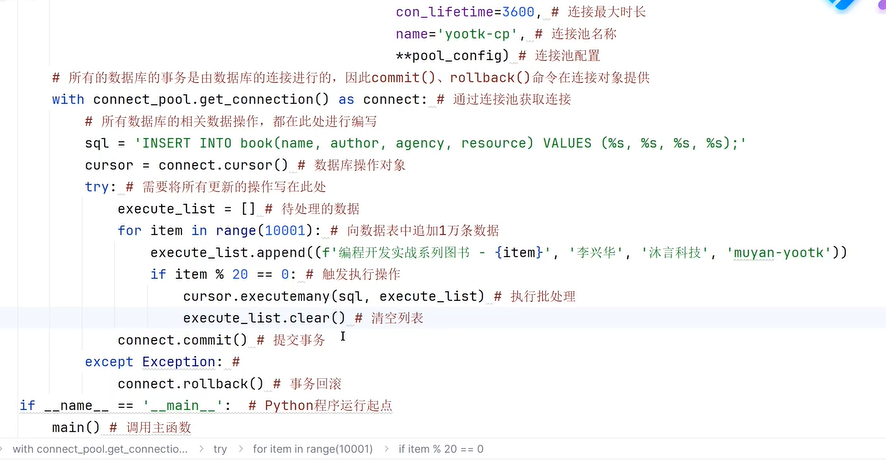
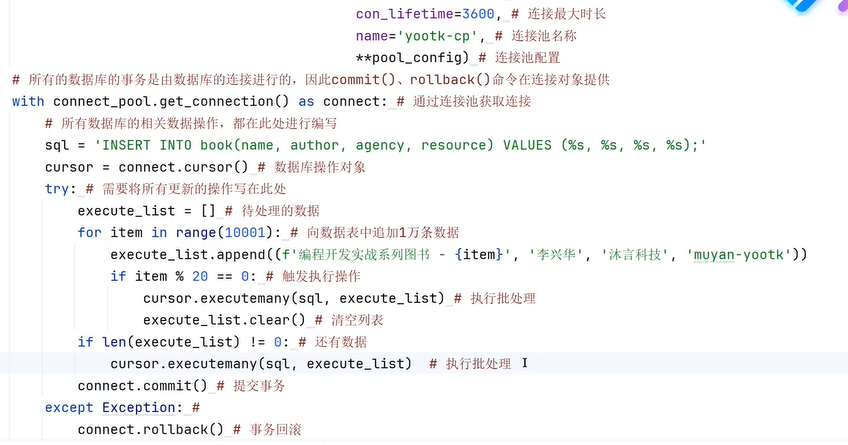


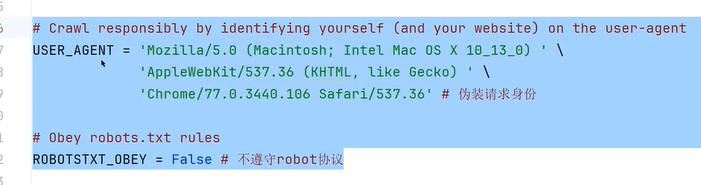
四十六、scrapy框架爬虫



本文来自博客园,作者:戴莫先生Study平台,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/smallzengstudy/p/18924851


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号