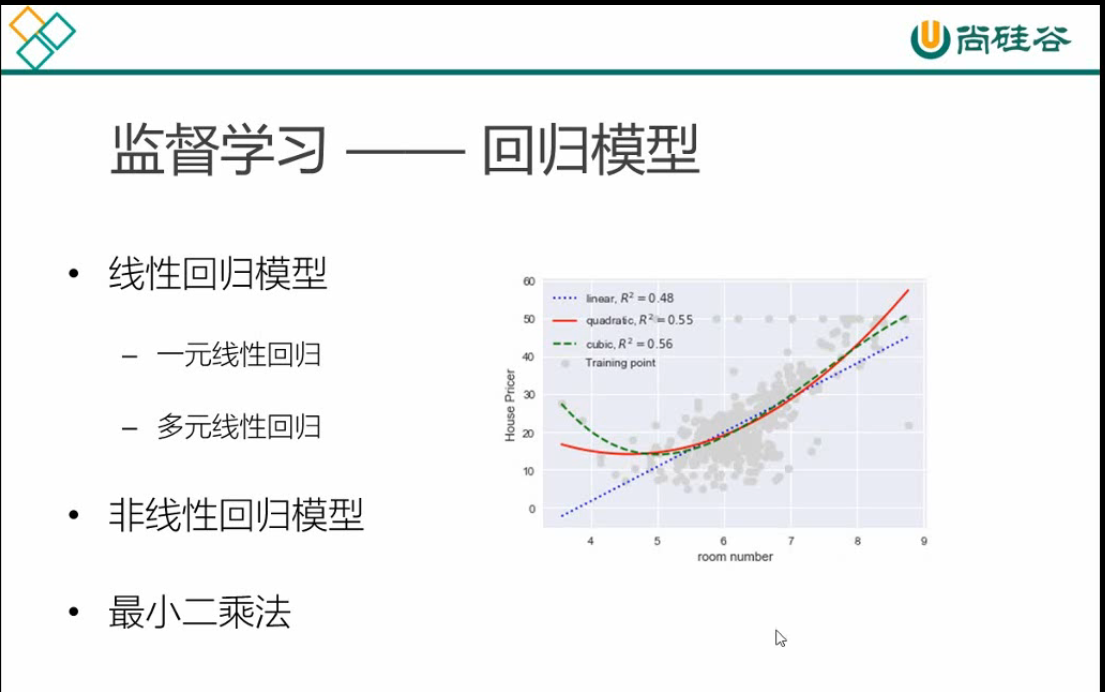
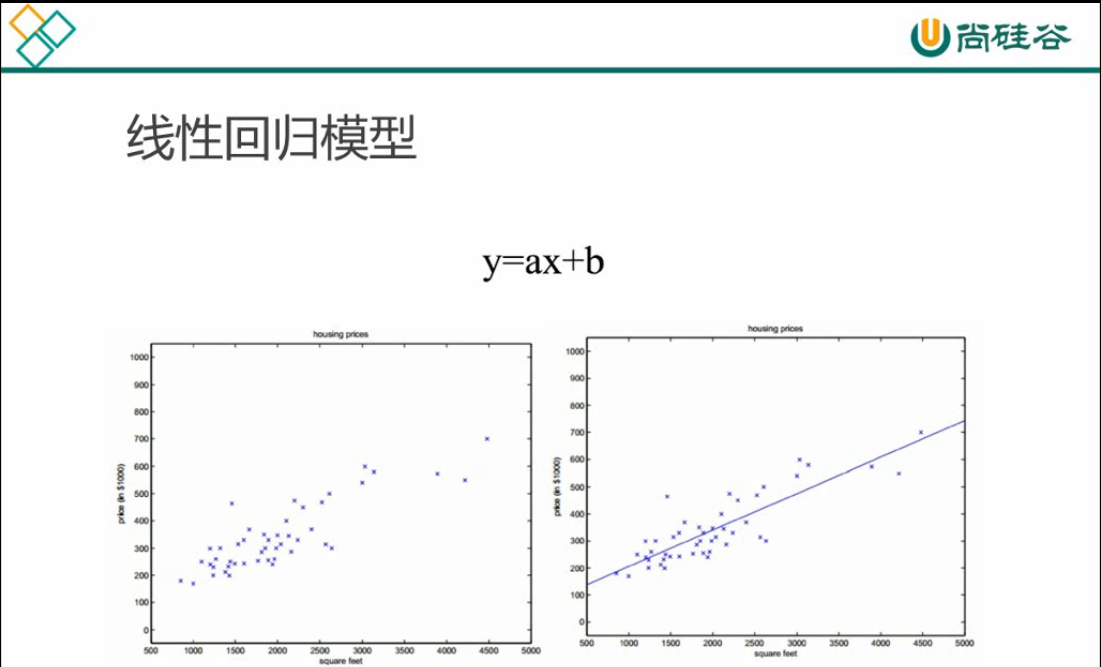
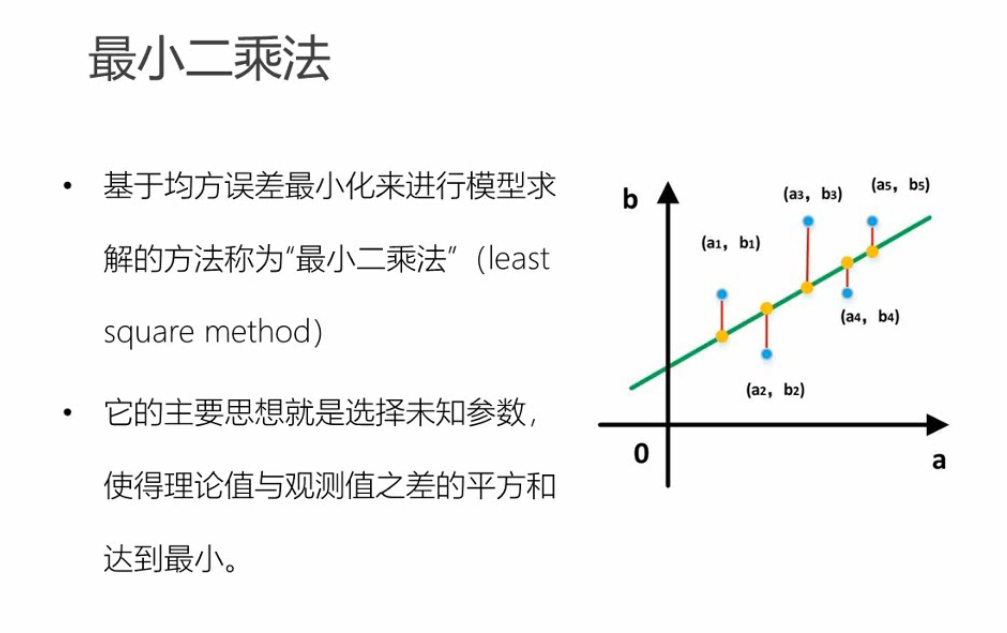
机器学习模型和算法 -----监督学习,线性回归算法,最小二乘法





Python 代码实现:
#导入numpy 和 matplotlib.pyplot 画图工具
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入数据 data.csv (关于学习时间和学习成绩的向量数据)
points = np.genfromtxt('data.csv',delimiter=',') x = points[:, 0] # python 可以直接使用[x,y]取得一组, 切片操作[a:b:c] 所以[:, 0]表示取所有行的第一列 y = points[:, 1] # [:, 0]表示取所有行的第二列
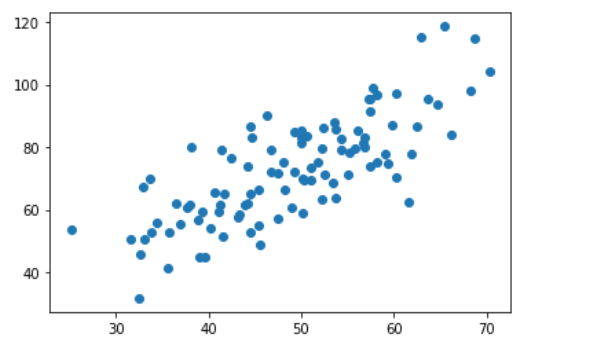
plt.scatter(x, y)# 散点图
plt.show() # 查看散点图
# 定义损失函数
def compute_cost(w, b, points): total_cost = 0 M = len(points) #逐点计算平方损失误差,然后求平均数 for i in range(M): x = points[i, 0] y = points[i, 1] total_cost += (y - w * x -b) ** 2 return total_cost/M
# 定义均值函数
def average(data): sum = 0 num = len(data) for i in range(num): sum += data[i] return sum/num # 定义核心拟合合函数 def fit(points): M = len(points) x_bar = average(points[:, 0]) sum_yx = 0 sum_x2 = 0 sum_delta = 0 for i in range(M): x = points[i, 0] y = points[i, 1] sum_yx += y * (x - x_bar) sum_x2 += x ** 2
w = sum_yx / (sum_x2 - M *(x_bar ** 2)) for i in range(M): x = points[i, 0] y = points[i, 1] sum_delta += ( y - w * x ) b = sum_delta / M return w, b
# 调用
w, b = fit(points) print("w is: ", w) print("b is: ", b) cost = compute_cost(w, b, points) print("cost is: ", cost)

画出拟合曲线
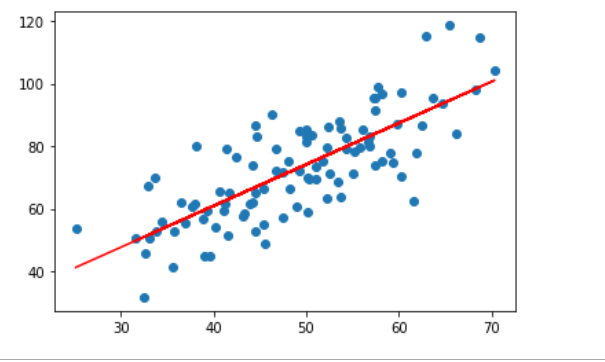
plt.scatter(x, y) pred_y = w * x + b plt.plot(x, pred_y, c='r') plt.show()
hello my world
本文来自博客园,作者:slowlydance2me,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/slowlydance2me/p/16827773.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号