Spring Boot 集成 Redis 全方位详解 - 指南
文章目录
一、Redis 与 Spring Boot 集成概述
1.1 Redis 简介
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server)是一个开源的、高性能的键值对存储数据库,它以其出色的性能、丰富的数据结构和灵活的使用方式,在现代软件开发中占据了重要地位。
Redis 具有以下核心特性:
- 基于内存存储,读写速度极快,单机每秒可处理数十万次操作
- 支持多种数据结构,包括字符串(String)、哈希(Hash)、列表(List)、集合(Set)、有序集合(ZSet)等
- 支持数据持久化,可将内存中的数据定期写入磁盘,避免数据丢失
- 支持主从复制、哨兵模式和集群模式,保证高可用性和扩展性
- 提供丰富的功能,如事务、Lua 脚本、发布 / 订阅、过期策略等
1.2 Spring Boot 集成 Redis 的优势
Spring Boot 作为当前流行的 Java 开发框架,简化了 Java 应用的开发配置过程。将 Spring Boot 与 Redis 集成,具有以下优势:
- 自动配置:Spring Boot 提供了 Redis 自动配置模块,减少手动配置工作
- 模板化操作:通过 RedisTemplate 等模板类,简化 Redis 操作
- 缓存支持:无缝集成 Spring 缓存抽象,轻松实现数据缓存
- 连接池管理:内置连接池支持,优化 Redis 连接性能
- 与 Spring 生态完美融合:可与 Spring MVC、Spring Data 等组件无缝协作
1.3 应用场景
Spring Boot 集成 Redis 后,可应用于多种场景:
- 数据缓存:减轻数据库压力,提高数据访问速度
- 会话存储:分布式系统中共享会话信息
- 计数器:实现访问量、下载量等计数功能
- 分布式锁:解决分布式系统中的并发问题
- 消息队列:基于发布 / 订阅功能实现简单的消息通信
- 排行榜:利用 ZSet 数据结构实现实时排行榜
二、环境准备与搭建
2.1 环境要求
- JDK:1.8 及以上版本
- Spring Boot:2.x 或 3.x 版本(本文以 2.7.10 为例)
- Redis:5.x 及以上版本
- Maven:3.6 及以上版本(或 Gradle 7.0 及以上)
2.2 Redis 安装与配置
2.2.1 Windows 系统安装 Redis
- 访问 Redis 官方网站(https://redis.io/download)下载 Windows 版本的 Redis(可2. 通过 GitHub 上的微软维护版本获取 解压下载的压缩包到指定目录,如 D:\redis
- 打开命令提示符,进入 Redis 目录,执行以下命令启动 Redis 服务器:
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf- 另开一个命令提示符窗口,执行以下命令启动 Redis 客户端:
redis-cli.exe -h 127.0.0.1 -p 63792.2.2 Linux 系统安装 Redis
- 通过包管理器安装(以 Ubuntu 为例):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install redis-server- 启动 Redis 服务:
sudo systemctl start redis-server- 验证 Redis 是否启动成功:
redis-cli ping若返回 “PONG”,则表示 Redis 启动成功。
2.2.3 Redis 基本配置
Redis 的主要配置文件为 redis.conf,常用配置项如下:
- port 6379:默认端口号
- bind 127.0.0.1:绑定的 IP 地址,默认只允许本地访问
- requirepass yourpassword:设置访问密码
- daemonize yes:以守护进程方式运行(Linux 系统)
- maxmemory:设置 Redis 最大使用内存
- maxmemory-policy:内存达到上限时的淘汰策略
修改配置后,需重启 Redis 服务使配置生效。
2.3 创建 Spring Boot 项目
2.3.1 使用 Spring Initializr 创建项目
- 访问 https://start.spring.io/
- 填写项目信息:
Group:com.example
Artifact:springboot-redis-demo
Name:springboot-redis-demo
Description:Demo project for Spring Boot and Redis
Package name:com.example.redisdemo
Type:Maven
Java:8
Spring Boot:2.7.10
- 选择依赖:
Spring Web
Spring Data Redis
Lombok(可选,用于简化代码)
- 点击 “Generate” 按钮下载项目压缩包,解压后导入 IDE(如 IntelliJ IDEA 或 Eclipse)
2.3.2 手动配置 pom.xml
若手动创建项目,需在 pom.xml 中添加以下依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.10</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-redis-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-redis-demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot and Redis</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Web 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Data Redis 依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 连接池依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Lombok 依赖(可选) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>三、Redis 核心配置
3.1 基本配置
Spring Boot 提供了自动配置功能,我们只需在配置文件中添加 Redis 相关配置即可。常用的配置文件格式有两种:application.properties 和 application.yml,这里以 application.yml 为例。
在 src/main/resources 目录下创建 application.yml 文件,添加以下配置:
spring:
redis:
# Redis 服务器地址
host: 127.0.0.1
# Redis 服务器端口
port: 6379
# Redis 服务器密码(若未设置密码,可省略)
password:
# 数据库索引(0-15,默认为 0)
database: 0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
timeout: 3000ms
# Lettuce 连接池配置
lettuce:
pool:
# 最大连接数
max-active: 8
# 最大空闲连接
max-idle: 8
# 最小空闲连接
min-idle: 2
# 最大等待时间(-1 表示无限制)
max-wait: -1ms3.2 集群配置
如果使用 Redis 集群,配置方式如下:
spring:
redis:
password:
timeout: 3000ms
cluster:
# 集群节点列表
nodes:
- 192.168.1.101:6379
- 192.168.1.102:6379
- 192.168.1.103:6379
- 192.168.1.104:6379
- 192.168.1.105:6379
- 192.168.1.106:6379
# 最大重定向次数
max-redirects: 3
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 4
max-wait: 1000ms3.3 哨兵模式配置
若 Redis 采用哨兵模式,配置如下:
spring:
redis:
password:
timeout: 3000ms
sentinel:
# 主节点名称
master: mymaster
# 哨兵节点列表
nodes:
- 192.168.1.201:26379
- 192.168.1.202:26379
- 192.168.1.203:26379
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 4
max-wait: 1000ms3.4 自定义 RedisTemplate 配置
Spring Boot 自动配置的 RedisTemplate 使用 JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 进行序列化,这种方式会导致存储的数据带有序列化前缀,可读性差且占用空间。因此,通常需要自定义 RedisTemplate,使用 JSON 序列化方式。
创建 Redis 配置类:
package com.example.redisdemo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* 自定义 RedisTemplate,使用 JSON 序列化
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
// 创建 RedisTemplate 实例
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 设置连接工厂
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
// 创建字符串序列化器
StringRedisSerializer stringSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
// 创建 JSON 序列化器
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer jsonSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
// 设置 key 的序列化器
template.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
// 设置 hash key 的序列化器
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
// 设置 value 的序列化器
template.setValueSerializer(jsonSerializer);
// 设置 hash value 的序列化器
template.setHashValueSerializer(jsonSerializer);
// 初始化模板
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}上述配置中,我们使用 StringRedisSerializer 序列化 key,使用 GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 序列化 value。GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 基于 Jackson 库,能够将对象序列化为 JSON 格式,并且在反序列化时能够自动识别对象类型。
3.5 序列化器详解
Redis 序列化器用于将 Java 对象转换为可存储在 Redis 中的字节序列,以及将字节序列转换回 Java 对象。Spring Data Redis 提供了多种序列化器:
- StringRedisSerializer:将对象序列化为字符串,主要用于序列化 key
- JdkSerializationRedisSerializer:使用 JDK 自带的序列化机制,默认的序列化器
- GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer:使用 Jackson 库将对象序列化为 JSON 格式
- Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer:与 GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 类似,但需要指定目标类
- OxmSerializer:使用 Spring O/X 映射功能进行序列化,支持 XML 格式
各种序列化器的优缺点:

在实际开发中,推荐使用 StringRedisSerializer 作为 key 的序列化器,使用 GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 或 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 作为 value 的序列化器。
四、Redis 数据结构操作
Spring Data Redis 提供了 RedisTemplate 和 StringRedisTemplate 两个模板类用于操作 Redis。StringRedisTemplate 是 RedisTemplate 的子类,专门用于处理字符串类型的数据。
4.1 StringRedisTemplate 操作
StringRedisTemplate 的 opsForValue() 方法返回 ValueOperations 对象,用于操作 String 类型的数据。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class StringRedisService {
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/**
* 设置字符串值
*/
public void setString(String key, String value) {
ValueOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value);
}
/**
* 设置字符串值并指定过期时间
*/
public void setStringWithExpire(String key, String value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
ValueOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* 获取字符串值
*/
public String getString(String key) {
ValueOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operations.get(key);
}
/**
* 自增操作
*/
public Long increment(String key, long delta) {
ValueOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operations.increment(key, delta);
}
/**
* 自减操作
*/
public Long decrement(String key, long delta) {
ValueOperations<String, String> operations = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operations.decrement(key, delta);
}
/**
* 删除键
*/
public Boolean delete(String key) {
return stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}4.2 RedisTemplate 操作对象
RedisTemplate 可以操作各种类型的对象,下面以操作用户对象为例进行说明。
首先定义一个 User 实体类:
package com.example.redisdemo.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}然后创建一个服务类,使用 RedisTemplate 操作 User 对象:
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import com.example.redisdemo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class ObjectRedisService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 存储用户对象
*/
public void saveUser(String key, User user) {
ValueOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, user);
}
/**
* 存储用户对象并指定过期时间
*/
public void saveUserWithExpire(String key, User user, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
ValueOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, user, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* 获取用户对象
*/
public User getUser(String key) {
ValueOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
return (User) operations.get(key);
}
/**
* 删除用户对象
*/
public Boolean deleteUser(String key) {
return redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}4.3 操作 Hash 类型
Hash 类型适合存储对象的多个属性,RedisTemplate 的 opsForHash() 方法返回 HashOperations 对象,用于操作 Hash 类型的数据。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
@Service
public class HashRedisService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 向 Hash 中添加一个字段
*/
public void put(String key, String hashKey, Object value) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
operations.put(key, hashKey, value);
}
/**
* 向 Hash 中添加多个字段
*/
public void putAll(String key, Map<String, Object> map) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
operations.putAll(key, map);
}
/**
* 获取 Hash 中指定字段的值
*/
public Object get(String key, String hashKey) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return operations.get(key, hashKey);
}
/**
* 获取 Hash 中所有字段和值
*/
public Map<String, Object> getAll(String key) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return operations.entries(key);
}
/**
* 获取 Hash 中所有字段
*/
public Set<String> getKeys(String key) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return operations.keys(key);
}
/**
* 获取 Hash 中所有值
*/
public Object[] getValues(String key) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return operations.values(key).toArray();
}
/**
* 删除 Hash 中指定字段
*/
public Long delete(String key, String... hashKeys) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return operations.delete(key, hashKeys);
}
/**
* 判断 Hash 中是否存在指定字段
*/
public Boolean hasKey(String key, String hashKey) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return operations.hasKey(key, hashKey);
}
}4.4 操作 List 类型
List 类型是一个有序的字符串列表,RedisTemplate 的 opsForList() 方法返回 ListOperations 对象,用于操作 List 类型的数据。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ListOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class ListRedisService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 从列表左侧插入元素
*/
public Long leftPush(String key, Object value) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.leftPush(key, value);
}
/**
* 从列表左侧插入多个元素
*/
public Long leftPushAll(String key, Object... values) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.leftPushAll(key, values);
}
/**
* 从列表右侧插入元素
*/
public Long rightPush(String key, Object value) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.rightPush(key, value);
}
/**
* 从列表右侧插入多个元素
*/
public Long rightPushAll(String key, Object... values) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.rightPushAll(key, values);
}
/**
* 获取列表指定范围内的元素
*/
public List<Object> range(String key, long start, long end) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.range(key, start, end);
}
/**
* 获取列表长度
*/
public Long size(String key) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.size(key);
}
/**
* 从列表左侧弹出元素
*/
public Object leftPop(String key) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.leftPop(key);
}
/**
* 从列表右侧弹出元素
*/
public Object rightPop(String key) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.rightPop(key);
}
/**
* 根据索引设置列表元素的值
*/
public void set(String key, long index, Object value) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
operations.set(key, index, value);
}
/**
* 删除列表中指定次数的元素
*/
public Long remove(String key, long count, Object value) {
ListOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return operations.remove(key, count, value);
}
}4.5 操作 Set 类型
Set 类型是一个无序的字符串集合,不允许重复元素,RedisTemplate 的 opsForSet() 方法返回 SetOperations 对象,用于操作 Set 类型的数据。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.Set;
@Service
public class SetRedisService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 向集合中添加元素
*/
public Long add(String key, Object... values) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.add(key, values);
}
/**
* 获取集合中的所有元素
*/
public Set<Object> members(String key) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.members(key);
}
/**
* 判断元素是否在集合中
*/
public Boolean isMember(String key, Object value) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.isMember(key, value);
}
/**
* 获取集合的大小
*/
public Long size(String key) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.size(key);
}
/**
* 从集合中移除元素
*/
public Long remove(String key, Object... values) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.remove(key, values);
}
/**
* 随机从集合中弹出一个元素
*/
public Object pop(String key) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.pop(key);
}
/**
* 计算两个集合的交集
*/
public Set<Object> intersect(String key1, String key2) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.intersect(key1, key2);
}
/**
* 计算两个集合的并集
*/
public Set<Object> union(String key1, String key2) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.union(key1, key2);
}
/**
* 计算两个集合的差集
*/
public Set<Object> difference(String key1, String key2) {
SetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return operations.difference(key1, key2);
}
}4.6 操作 ZSet 类型
ZSet 类型是一个有序的字符串集合,每个元素都关联一个分数(score),RedisTemplate 的 opsForZSet() 方法返回 ZSetOperations 对象,用于操作 ZSet 类型的数据。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.Set;
@Service
public class ZSetRedisService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 向有序集合中添加元素
*/
public Boolean add(String key, Object value, double score) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.add(key, value, score);
}
/**
* 向有序集合中添加多个元素
*/
public Long add(String key, Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> tuples) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.add(key, tuples);
}
/**
* 获取有序集合中元素的分数
*/
public Double score(String key, Object value) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.score(key, value);
}
/**
* 增加有序集合中元素的分数
*/
public Double incrementScore(String key, Object value, double delta) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.incrementScore(key, value, delta);
}
/**
* 获取有序集合的大小
*/
public Long size(String key) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.size(key);
}
/**
* 移除有序集合中的元素
*/
public Long remove(String key, Object... values) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.remove(key, values);
}
/**
* 获取有序集合中指定排名范围的元素(按分数升序)
*/
public Set<Object> range(String key, long start, long end) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.range(key, start, end);
}
/**
* 获取有序集合中指定分数范围的元素(按分数升序)
*/
public Set<Object> rangeByScore(String key, double min, double max) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.rangeByScore(key, min, max);
}
/**
* 获取元素在有序集合中的排名(按分数升序)
*/
public Long rank(String key, Object value) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.rank(key, value);
}
/**
* 获取元素在有序集合中的排名(按分数降序)
*/
public Long reverseRank(String key, Object value) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return operations.reverseRank(key, value);
}
}五、Spring 缓存抽象集成
Spring 提供了缓存抽象,可以通过注解的方式轻松实现数据缓存功能。Spring Boot 与 Redis 集成后,可以将 Redis 作为缓存的存储介质。
5.1 开启缓存支持
要使用 Spring 缓存抽象,需要在配置类或启动类上添加 @EnableCaching 注解开启缓存支持。
package com.example.redisdemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching // 开启缓存支持
public class RedisDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RedisDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}5.2 配置缓存管理器
Spring Boot 会自动配置 RedisCacheManager,但我们可以根据需要自定义缓存管理器,设置缓存过期时间、序列化方式等。
package com.example.redisdemo.config;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
/**
* 自定义 RedisCacheManager
*/
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
// 全局默认缓存配置
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
// 设置 key 序列化器
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
// 设置 value 序列化器
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()))
// 默认过期时间 30 分钟
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
// 不缓存 null 值
.disableCachingNullValues();
// 针对不同缓存名称设置不同的过期时间
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> configMap = new HashMap<>();
// 用户缓存过期时间 1 小时
configMap.put("userCache", defaultConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1)));
// 商品缓存过期时间 10 分钟
configMap.put("productCache", defaultConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10)));
// 订单缓存过期时间 5 分钟
configMap.put("orderCache", defaultConfig.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(5)));
// 创建缓存管理器
return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(defaultConfig) // 设置默认缓存配置
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(configMap) // 设置自定义缓存配置
.build();
}
}5.3 缓存注解详解
Spring 缓存抽象提供了多个注解用于实现缓存功能:
- @Cacheable:用于查询操作,方法执行前先查询缓存,如果缓存中存在,则直接返回缓存结果,不执行方法;如果缓存中不存在,则执行方法,并将方法返回值存入缓存。
主要属性:- value/cacheNames:缓存名称,必填,用于指定缓存的存储位置
- key:缓存的 key,可以使用 SpEL 表达式,默认为方法参数组合
- condition:缓存条件,满足条件才进行缓存
- unless:排除条件,满足条件则不进行缓存
- @CachePut:用于更新操作,方法执行后将返回值存入缓存,无论缓存中是否已存在该 key。
主要属性与 @Cacheable 相同。 - @CacheEvict:用于删除操作,方法执行后删除缓存中的指定数据。
主要属性:- value/cacheNames:缓存名称,必填
- key:要删除的缓存 key
- allEntries:是否删除缓存中的所有数据,默认为 false
- beforeInvocation:是否在方法执行前删除缓存,默认为 false
- @Caching:用于组合多个缓存注解,可以同时指定 @Cacheable、@CachePut 和 @CacheEvict。
- @CacheConfig:用于类级别,统一配置该类中所有缓存注解的公共属性,如 value、keyGenerator 等。
5.4 缓存注解使用示例
下面以用户服务为例,展示缓存注解的使用:
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import com.example.redisdemo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class UserCacheService {
// 模拟数据库存储用户信息
private static final Map<Long, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
// 初始化一些用户数据
userMap.put(1L, new User(1L, "张三", 20, "zhangsan@example.com"));
userMap.put(2L, new User(2L, "李四", 25, "lisi@example.com"));
userMap.put(3L, new User(3L, "王五", 30, "wangwu@example.com"));
}
/**
* 根据 ID 查询用户
* 使用 @Cacheable 注解,缓存名称为 userCache,key 为 "user:" + id
*/
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "'user:' + #id")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
System.out.println("从数据库查询用户,id=" + id);
return userMap.get(id);
}
/**
* 添加用户
* 使用 @CachePut 注解,将新添加的用户存入缓存
*/
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "'user:' + #result.id")
public User addUser(User user) {
System.out.println("向数据库添加用户,user=" + user);
userMap.put(user.getId(), user);
return user;
}
/**
* 更新用户
* 使用 @CachePut 注解,更新缓存中的用户信息
*/
@CachePut(value = "userCache", key = "'user:' + #user.id")
public User updateUser(User user) {
System.out.println("更新数据库中的用户,user=" + user);
userMap.put(user.getId(), user);
return user;
}
/**
* 删除用户
* 使用 @CacheEvict 注解,删除缓存中的用户信息
*/
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", key = "'user:' + #id")
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("从数据库删除用户,id=" + id);
userMap.remove(id);
}
/**
* 清空所有用户缓存
* 使用 @CacheEvict 注解,allEntries = true 表示删除缓存中的所有数据
*/
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache", allEntries = true)
public void clearUserCache() {
System.out.println("清空所有用户缓存");
}
}5.5 SpEL 表达式在缓存中的应用
在缓存注解中,key、condition、unless 等属性支持使用 SpEL 表达式,使缓存配置更加灵活。
常用的 SpEL 表达式:
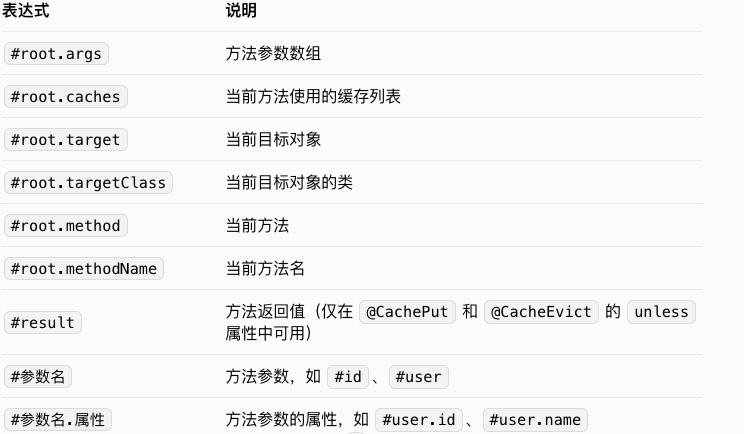
示例:
// 使用方法参数作为 key
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }
// 使用方法参数的属性作为 key
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#user.id")
public User getUserByUser(User user) { ... }
// 组合多个参数作为 key
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#name + ':' + #age")
public List<User> getUsersByNameAndAge(String name, Integer age) { ... }
// 根据条件进行缓存
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id", condition = "#id > 10")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }
// 根据返回值决定是否缓存
@Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }六、Redis 高级特性
6.1 分布式锁
在分布式系统中,多个进程可能同时操作共享资源,为了保证数据一致性,需要使用分布式锁。Redis 可以通过 setIfAbsent 方法(即 SET NX 命令)实现分布式锁。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class RedisDistributedLockService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
// 锁的前缀
private static final String LOCK_PREFIX = "lock:";
/**
* 获取分布式锁
*
* @param lockKey 锁的 key
* @param value 锁的 value,用于标识锁的持有者
* @param expireTime 锁的过期时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return 是否获取到锁
*/
public boolean tryLock(String lockKey, String value, long expireTime, TimeUnit unit) {
String key = LOCK_PREFIX + lockKey;
// 使用 setIfAbsent 方法实现分布式锁,该方法是原子操作
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value, expireTime, unit));
}
/**
* 释放分布式锁
*
* @param lockKey 锁的 key
* @param value 锁的 value,用于验证是否为锁的持有者
*/
public void unlock(String lockKey, String value) {
String key = LOCK_PREFIX + lockKey;
try {
// 获取锁的 value
Object currentValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 验证是否为锁的持有者
if (currentValue != null && currentValue.equals(value)) {
// 释放锁
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}上述实现存在一个问题:如果持有锁的进程在释放锁之前崩溃,可能导致锁无法释放。为了解决这个问题,可以给锁设置过期时间,确保锁最终会被释放。
更完善的分布式锁实现可以使用 Redisson 框架,它提供了更可靠的分布式锁实现,支持自动续期、公平锁等功能。
6.2 发布 / 订阅
Redis 提供了发布 / 订阅功能,可以实现简单的消息通信。Spring Data Redis 对 Redis 的发布 / 订阅功能进行了封装,使用起来更加方便。
6.2.1 消息发布者
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class RedisMessagePublisher {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 发布消息
*
* @param channel 频道
* @param message 消息内容
*/
public void publish(String channel, Object message) {
redisTemplate.convertAndSend(channel, message);
}
}6.2.2 消息订阅者
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.Message;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.MessageListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class RedisMessageSubscriber implements MessageListener {
/**
* 接收消息
*
* @param message 消息
* @param pattern 模式
*/
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) {
// 获取消息内容
String content = new String(message.getBody());
// 获取频道
String channel = new String(message.getChannel());
// 处理消息
System.out.println("收到来自频道 " + channel + " 的消息:" + content);
}
}6.2.3 配置消息监听容器
package com.example.redisdemo.config;
import com.example.redisdemo.service.RedisMessageSubscriber;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.PatternTopic;
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.RedisMessageListenerContainer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.adapter.MessageListenerAdapter;
@Configuration
public class RedisMessageConfig {
/**
* 配置消息监听适配器
*/
@Bean
public MessageListenerAdapter messageListenerAdapter(RedisMessageSubscriber subscriber) {
return new MessageListenerAdapter(subscriber);
}
/**
* 配置消息监听容器
*/
@Bean
public RedisMessageListenerContainer redisMessageListenerContainer(
RedisConnectionFactory factory, MessageListenerAdapter adapter) {
RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer();
container.setConnectionFactory(factory);
// 订阅 "news" 频道
container.addMessageListener(adapter, new PatternTopic("news"));
// 可以订阅多个频道
container.addMessageListener(adapter, new PatternTopic("notice"));
return container;
}
}6.3 管道操作
Redis 管道(Pipeline)允许客户端一次性发送多个命令,减少网络往返次数,提高批量操作的效率。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class RedisPipelineService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 批量设置键值对
*
* @param keys 键列表
* @param values 值列表
* @return 操作结果
*/
public List<Object> batchSet(List<String> keys, List<Object> values) {
if (keys.size() != values.size()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("keys 和 values 的大小必须相等");
}
// 使用管道进行批量操作
return redisTemplate.executePipelined((RedisCallback<Object>) connection -> {
for (int i = 0; i < keys.size(); i++) {
String key = keys.get(i);
Object value = values.get(i);
// 序列化 key 和 value
byte[] keyBytes = redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize(key);
byte[] valueBytes = redisTemplate.getValueSerializer().serialize(value);
// 设置键值对
connection.set(keyBytes, valueBytes);
}
return null;
});
}
/**
* 批量获取值
*
* @param keys 键列表
* @return 值列表
*/
public List<Object> batchGet(List<String> keys) {
// 使用管道进行批量操作
return redisTemplate.executePipelined((RedisCallback<Object>) connection -> {
for (String key : keys) {
// 序列化 key
byte[] keyBytes = redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize(key);
// 获取值
connection.get(keyBytes);
}
return null;
}, redisTemplate.getValueSerializer());
}
}6.4 事务
Redis 支持事务,可以将多个命令打包成一个事务,一次性执行,要么全部执行,要么全部不执行。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SessionCallback;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class RedisTransactionService {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 执行 Redis 事务
*/
public List<Object> executeTransaction() {
// 使用 SessionCallback 执行事务
return redisTemplate.execute((SessionCallback<List<Object>>) session -> {
// 开启事务
session.multi();
// 向事务中添加命令
session.opsForValue().set("name", "张三");
session.opsForValue().set("age", 20);
session.opsForHash().put("user", "id", 1);
session.opsForHash().put("user", "name", "张三");
// 执行事务
return session.exec();
});
}
/**
* 带条件的事务(使用 Watch 命令)
*/
public List<Object> executeTransactionWithCondition(String key, Object expectedValue) {
// 使用 SessionCallback 执行事务
return redisTemplate.execute((SessionCallback<List<Object>>) session -> {
// 监视 key
session.watch(key);
// 获取当前值
Object currentValue = session.opsForValue().get(key);
// 判断当前值是否与预期值一致
if (expectedValue.equals(currentValue)) {
// 开启事务
session.multi();
// 向事务中添加命令
session.opsForValue().set(key, "new value");
session.opsForValue().set("otherKey", "other value");
// 执行事务
return session.exec();
} else {
// 取消监视
session.unwatch();
return null;
}
});
}
}七、实战案例
7.1 缓存用户信息
下面实现一个用户信息管理系统,使用 Redis 缓存用户信息,提高查询效率。
7.1.1 控制器
package com.example.redisdemo.controller;
import com.example.redisdemo.entity.User;
import com.example.redisdemo.service.UserCacheService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
private final UserCacheService userCacheService;
public UserController(UserCacheService userCacheService) {
this.userCacheService = userCacheService;
}
/**
* 根据 ID 查询用户
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userCacheService.getUserById(id);
}
/**
* 添加用户
*/
@PostMapping
public User addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userCacheService.addUser(user);
}
/**
* 更新用户
*/
@PutMapping
public User updateUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userCacheService.updateUser(user);
}
/**
* 删除用户
*/
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
userCacheService.deleteUser(id);
}
/**
* 清空用户缓存
*/
@DeleteMapping("/cache")
public void clearUserCache() {
userCacheService.clearUserCache();
}
}7.1.2 测试
- 启动应用后,可以使用 Postman 或 curl 等工具测试接口:
- 查询用户:GET http://localhost:8080/users/1
- 添加用户:POST http://localhost:8080/users,请求体为 JSON 格式的用户信息
- 更新用户:PUT http://localhost:8080/users,请求体为 JSON 格式的用户信息
- 删除用户:DELETE http://localhost:8080/users/1
- 清空缓存:DELETE http://localhost:8080/users/cache
7.2 实现分布式计数器
使用 Redis 的自增操作实现一个分布式计数器,可用于统计网站访问量、下载量等。
package com.example.redisdemo.service;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class DistributedCounterService {
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/**
* 增加计数器的值
*
* @param key 计数器 key
* @param delta 增加的值
* @return 增加后的值
*/
public Long increment(String key, long delta) {
return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, delta);
}
/**
* 减少计数器的值
*
* @param key 计数器 key
* @param delta 减少的值
* @return 减少后的值
*/
public Long decrement(String key, long delta) {
return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(key, delta);
}
/**
* 获取计数器的值
*
* @param key 计数器 key
* @return 计数器的值
*/
public Long getCount(String key) {
String value = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
return value == null ? 0 : Long.parseLong(value);
}
/**
* 重置计数器的值
*
* @param key 计数器 key
*/
public void reset(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
/**
* 设置计数器的过期时间
*
* @param key 计数器 key
* @param timeout 过期时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return 是否设置成功
*/
public Boolean expire(String key, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);
}
}八、问题排查与最佳实践
8.1 常见问题及解决方案
- 连接超时
- 检查 Redis 服务器是否启动
- 检查 Redis 服务器地址和端口是否正确
- 检查防火墙是否允许连接 Redis 端口
- 检查网络是否通畅
- 密码错误
- 检查 Redis 配置的密码是否正确
- 检查应用配置中的密码是否与 Redis 配置一致
- 序列化异常
- 确保使用的序列化器能够正确序列化和反序列化对象
- 对于自定义对象,确保其具有无参构造函数
- 检查对象是否实现了序列化接口(如果使用 JDK 序列化)
- 缓存与数据库不一致
- 确保更新数据库后及时更新或删除缓存
- 考虑使用事务保证缓存和数据库操作的原子性
- 对于并发场景,可使用分布式锁保证数据一致性
- Redis 内存溢出
- 合理设置缓存过期时间
- 配置 Redis 的内存淘汰策略
- 定期清理无用缓存
8.2 最佳实践
- 合理设置过期时间
- 根据业务需求为缓存设置合适的过期时间,避免 Redis 内存溢出
- 对于热点数据,可以适当延长过期时间
- 对于变化频繁的数据,应缩短过期时间
- 选择合适的序列化方式
- 推荐使用 StringRedisSerializer 作为 key 的序列化器
- 对于 value 的序列化,推荐使用 JSON 序列化器,如 GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer
- 避免使用 JDK 序列化器,除非有特殊需求
- 使用连接池
- 配置合理的连接池参数,提高连接复用率
- 根据业务并发量调整最大连接数、最大空闲连接数等参数
- 缓存穿透防护
- 对于不存在的 key,也进行缓存(缓存 null 值)
- 使用布隆过滤器过滤不存在的 key
- 缓存击穿防护
- 对于热点 key,设置永不过期或延长过期时间
- 使用互斥锁防止缓存击穿
- 缓存雪崩防护
- 为不同的 key 设置随机的过期时间,避免大量缓存同时过期
- 使用熔断降级机制,当 Redis 不可用时,直接访问数据库
- 部署 Redis 集群,提高可用性
- 监控与告警
- 监控 Redis 的内存使用情况、连接数、命中率等指标
- 设置告警阈值,当指标超过阈值时及时告警
- 数据备份与恢复
- 配置 Redis 持久化机制(RDB 或 AOF)
- 定期备份 Redis 数据,确保数据可恢复
九、总结
本文详细介绍了 Spring Boot 集成 Redis 的全过程,包括环境搭建、核心配置、数据结构操作、缓存注解使用、高级特性及实战案例。通过本文的学习,读者可以掌握 Spring Boot 与 Redis 集成的基本方法和最佳实践。
Redis 作为一款高性能的缓存数据库,在现代软件开发中有着广泛的应用。Spring Boot 提供了简洁的配置和丰富的模板类,使得集成 Redis 变得非常简单。在实际开发中,应根据业务需求合理使用 Redis 的各种功能,充分发挥其高性能的优势,同时注意解决缓存一致性、分布式锁等问题,确保系统的稳定运行。
随着业务的发展,还可以进一步学习 Redis 集群、哨兵模式、Redisson 框架等高级内容,以应对更高的并发和更复杂的业务场景。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号