概要
本章介绍"简单工厂模式"。内容包括:
简单工厂模式简介
简单工厂模式代码模型
简单工厂模式示例
说明:(01) 本文是在《Java与模式》的学习总结文章! (02) 文章中的UML的相关内容(包括类图说明和绘图工具等),可以参考"UML系列" 文章。
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3526186.html
简单工厂模式简介
简单工厂模式(Simple Factory),又被称为"静态工厂方法模式"。它属于"创建模式"(创建对象的模式),并且是"工厂方法"模式的一种特殊实现。
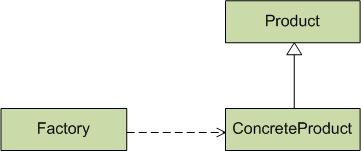
通常,我们利用简单工厂模式来进行类的创建。例如,获取线程池对象,就是通过简单工厂模式来实现的。它的结构图如下所示:
简单工厂模式的结构共包括3个组成部分:工厂(Factory),抽象产品(Product),具体产品(ConcreteProduct)。
1. 工厂 -- 工厂是简单工厂模式的核心,提供了对外接口。客户端或其它程序要获取Product对象,都是通过Factory的接口来获取的。
2. 抽象产品 -- 抽象产品是(许多)不同产品抽象出来的。Product可以是接口或者抽象类。
3. 具体产品 -- 工厂中返回的产品对象,实际上是通过ConcreteProduct来创建的。
简单工厂模式代码模型
public class Factory { public static Product newInstance() { return new ConcreteProduct(); } } public abstract Product { } public class ConcreteProduct extends Product { public ConcreteProduct() {} }
模型的类图
简单工厂模式示例
假设现在有一个水果工厂,能够生成各种各样的水果。目前能生产的水果包括苹果,葡萄和草莓。
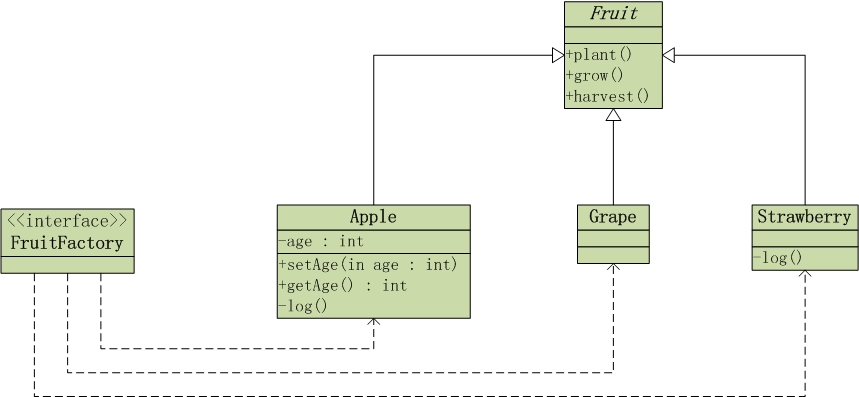
我们通过"简单工厂模式"描述该问题,它的UML类图如下:
1. 工厂类
工厂类是"FruitFactory"。FruitFactory是水果工厂,水果工厂会生成水果。
FruitFactory的源码
1 public class FruitFactory { 2 3 public static Fruit newInstance(String name) 4 throws BadFruitException { 5 // 如果name等于"apple"(忽略大小写),则返回苹果。 6 if ("apple".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) { 7 return new Apple(); 8 // 如果name等于"grape"(忽略大小写),则返回葡萄。 9 } else if ("grape".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) { 10 return new Grape(); 11 // 如果name等于"strawberry"(忽略大小写),则返回草莓。 12 } else if ("strawberry".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) { 13 return new Strawberry(); 14 // 其它情况,则抛出异常。 15 } else { 16 throw new BadFruitException("Bad fruit request!"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
2. 抽象产品类
Product类是"Fruit"。Fruit代表水果,它是抽象类,包含水果的基本特征:生长,种植,收获。
Fruit的源码
1 public abstract class Fruit { 2 abstract void grow(); // 生长 3 abstract void harvest(); // 收获 4 abstract void plant(); // 种植 5 }
3. 具体产品类
具体产品类是"Apple", "Grape"和"Strawberry"。它们是3种具体的水果,分别代表苹果,葡萄和草莓。
Apple的源码
1 // Apple实现Fruit的函数接口,并且Apple中有私有成员age和私有方法log。 2 public class Apple extends Fruit { 3 private int age; 4 5 public void grow() { 6 log("Apple grow()"); 7 } 8 public void harvest() { 9 log("Apple harvest()"); 10 } 11 public void plant() { 12 log("Apple plant()"); 13 } 14 public void setAge(int age) { 15 this.age = age; 16 } 17 public int getAge() { 18 return age; 19 } 20 private void log(String msg) { 21 System.out.println(msg); 22 } 23 }
Grape的源码
1 // Grape仅仅只实现Fruit的函数接口。 2 public class Grape extends Fruit { 3 public void grow() { 4 System.out.println("Grape grow()"); 5 } 6 public void harvest() { 7 System.out.println("Grape harvest()"); 8 } 9 public void plant() { 10 System.out.println("Grape plant()"); 11 } 12 }
Strawberry的源码
1 // Strawberry实现Fruit的函数接口,并且Strawberry中有私有方法log 2 public class Strawberry extends Fruit { 3 4 public void grow() { 5 log("Strawberry grow()"); 6 } 7 public void harvest() { 8 log("Strawberry harvest()"); 9 } 10 public void plant() { 11 log("Strawberry plant()"); 12 } 13 private void log(String msg) { 14 System.out.println(msg); 15 } 16 }
4. 客户端测试程序
客户端是"Client"。
Client的源码
1 public class Client { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 try { 5 Fruit apple = FruitFactory.newInstance("Apple"); 6 apple.plant(); 7 apple.grow(); 8 apple.harvest(); 9 10 Fruit grape = FruitFactory.newInstance("Grape"); 11 grape.plant(); 12 grape.grow(); 13 grape.harvest(); 14 15 Fruit strawberry = FruitFactory.newInstance("strawberry"); 16 strawberry.plant(); 17 strawberry.grow(); 18 strawberry.harvest(); 19 20 Fruit error = FruitFactory.newInstance("error"); 21 error.plant(); 22 error.grow(); 23 error.harvest(); 24 } catch (BadFruitException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 }
运行结果:
Apple plant() Apple grow() Apple harvest() Grape plant() Grape grow() Grape harvest() Strawberry plant() Strawberry grow() Strawberry harvest() BadFruitException: Bad fruit request! at FruitFactory.newInstance(FruitFactory.java:17) at Client.main(Client.java:21)
结果说明:
Client成功创建了Apple, Grape, Strawberry这3个水果对象,并调用了它们的方法;然后创建error时,由于不存在error对应的水果,因此抛出异常。
(01) Fruit,是抽象产品。Fruit中声明了grow(), harvest(), plant()这3个函数接口,它们是水果共用拥有的行为。
(02) Apple, Grape和Strawberry这三个类是具体产品。
Apple -- 实现Fruit的函数接口,并且Apple中有私有成员age和私有方法log。
Grape -- 仅仅只实现Fruit的函数接口。
Strawberry -- 实现Fruit的函数接口,并且Strawberry中有私有方法log
(03) FruitFactory,是工厂类。通过它的newInstance()方法,我们可以获取相应的Fruit对象。若要获取的水果不存在,则抛出BadFruitException异常。BadFruitException是Exception的子类。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号