模拟退火算法
算法思想
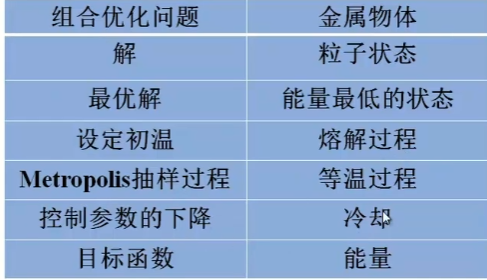
模仿自然界退火现象而得,利用了物理中固体物质的退火过程与一般优化问题的相似性从某一初始温度开始,伴随温度的不断下降,结合概率突跳特性在解空间中随机寻找全局最优解
具体应用
旅行商问题,即TSP问题(Travelling SalesmanProblem)又译为旅行推销员问题、货郎担问题,是数学领域中著名问题之一。
假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。
路径的选择目标是要求得的路径路程为所有路径之中的最小值。
吃今为止,这类问题中没有一个找到有效算法。倾向于接受NP完全问题(NP-Complet或NPC)和NP难题(NP-Hard或NPH)不存在有效算法这一猜想,
认为这类问题的大型实例不能用精确算法求解,必须寻求这类问题的有效的近似算法。
TSP的应用领域
TSP “旅行商问题”的应用领域包括:如何规划最合理高效的道路交通,以减少拥堵;如何更好地规划物流,以减少运营成本;在互联网环境中如何更好地设置节点,以更好地让信息流动等。
代码实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pdb
"旅行商问题 ( TSP , Traveling Salesman Problem )"
coordinates = np.array([[565.0, 575.0], [25.0, 185.0], [345.0, 750.0], [945.0, 685.0], [845.0, 655.0],
[880.0, 660.0], [25.0, 230.0], [525.0, 1000.0], [580.0, 1175.0], [650.0, 1130.0],
[1605.0, 620.0], [1220.0, 580.0], [1465.0, 200.0], [1530.0, 5.0], [845.0, 680.0],
[725.0, 370.0], [145.0, 665.0], [415.0, 635.0], [510.0, 875.0], [560.0, 365.0],
[300.0, 465.0], [520.0, 585.0], [480.0, 415.0], [835.0, 625.0], [975.0, 580.0],
[1215.0, 245.0], [1320.0, 315.0], [1250.0, 400.0], [660.0, 180.0], [410.0, 250.0],
[420.0, 555.0], [575.0, 665.0], [1150.0, 1160.0], [700.0, 580.0], [685.0, 595.0],
[685.0, 610.0], [770.0, 610.0], [795.0, 645.0], [720.0, 635.0], [760.0, 650.0],
[475.0, 960.0], [95.0, 260.0], [875.0, 920.0], [700.0, 500.0], [555.0, 815.0],
[830.0, 485.0], [1170.0, 65.0], [830.0, 610.0], [605.0, 625.0], [595.0, 360.0],
[1340.0, 725.0], [1740.0, 245.0]])
# 得到距离矩阵的函数
def getdistmat(coordinates):
num = coordinates.shape[0] # 52个坐标点
distmat = np.zeros((52, 52)) # 52X52距离矩阵
for i in range(num):
for j in range(i, num):
distmat[i][j] = distmat[j][i] = np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i] - coordinates[j])
return distmat
def initpara():
alpha = 0.99
t = (1, 100)
markovlen = 1000
return alpha, t, markovlen
num = coordinates.shape[0]
distmat = getdistmat(coordinates) # 得到距离矩阵
solutionnew = np.arange(num)
# valuenew = np.max(num)
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy()
valuecurrent = 99000 # np.max这样的源代码可能同样是因为版本问题被当做函数不能正确使用,应取一个较大值作为初始值
# print(valuecurrent)
solutionbest = solutionnew.copy()
valuebest = 99000 # np.max
alpha, t2, markovlen = initpara()
t = t2[1]
result = [] # 记录迭代过程中的最优解
while t > t2[0]:
for i in np.arange(markovlen):
# 下面的两交换和三角换是两种扰动方式,用于产生新解
if np.random.rand() > 0.5: # 交换路径中的这2个节点的顺序
# np.random.rand()产生[0, 1)区间的均匀随机数
while True: # 产生两个不同的随机数
loc1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand() * (num - 1)))
loc2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand() * (num - 1)))
## print(loc1,loc2)
if loc1 != loc2:
break
solutionnew[loc1], solutionnew[loc2] = solutionnew[loc2], solutionnew[loc1]
else: # 三交换
while True:
loc1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand() * (num - 1)))
loc2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand() * (num - 1)))
loc3 = np.int(np.ceil(np.random.rand() * (num - 1)))
if ((loc1 != loc2) & (loc2 != loc3) & (loc1 != loc3)):
break
# 下面的三个判断语句使得loc1<loc2<loc3
if loc1 > loc2:
loc1, loc2 = loc2, loc1
if loc2 > loc3:
loc2, loc3 = loc3, loc2
if loc1 > loc2:
loc1, loc2 = loc2, loc1
# 下面的三行代码将[loc1,loc2)区间的数据插入到loc3之后
tmplist = solutionnew[loc1:loc2].copy()
solutionnew[loc1:loc3 - loc2 + 1 + loc1] = solutionnew[loc2:loc3 + 1].copy()
solutionnew[loc3 - loc2 + 1 + loc1:loc3 + 1] = tmplist.copy()
valuenew = 0
for i in range(num - 1):
valuenew += distmat[solutionnew[i]][solutionnew[i + 1]]
valuenew += distmat[solutionnew[0]][solutionnew[51]]
# print (valuenew)
if valuenew < valuecurrent: # 接受该解
# 更新solutioncurrent 和solutionbest
valuecurrent = valuenew
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy()
if valuenew < valuebest:
valuebest = valuenew
solutionbest = solutionnew.copy()
else: # 按一定的概率接受该解
if np.random.rand() < np.exp(-(valuenew - valuecurrent) / t):
valuecurrent = valuenew
solutioncurrent = solutionnew.copy()
else:
solutionnew = solutioncurrent.copy()
t = alpha * t
result.append(valuebest)
print(t) # 程序运行时间较长,打印t来监视程序进展速度
# 用来显示结果
plt.plot(np.array(result))
plt.ylabel("bestvalue")
plt.xlabel("t")
plt.show()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号