Day03-流程控制
1. 用户交互scanner
-
之前我们学的基本语法中我们并没有。。。
-
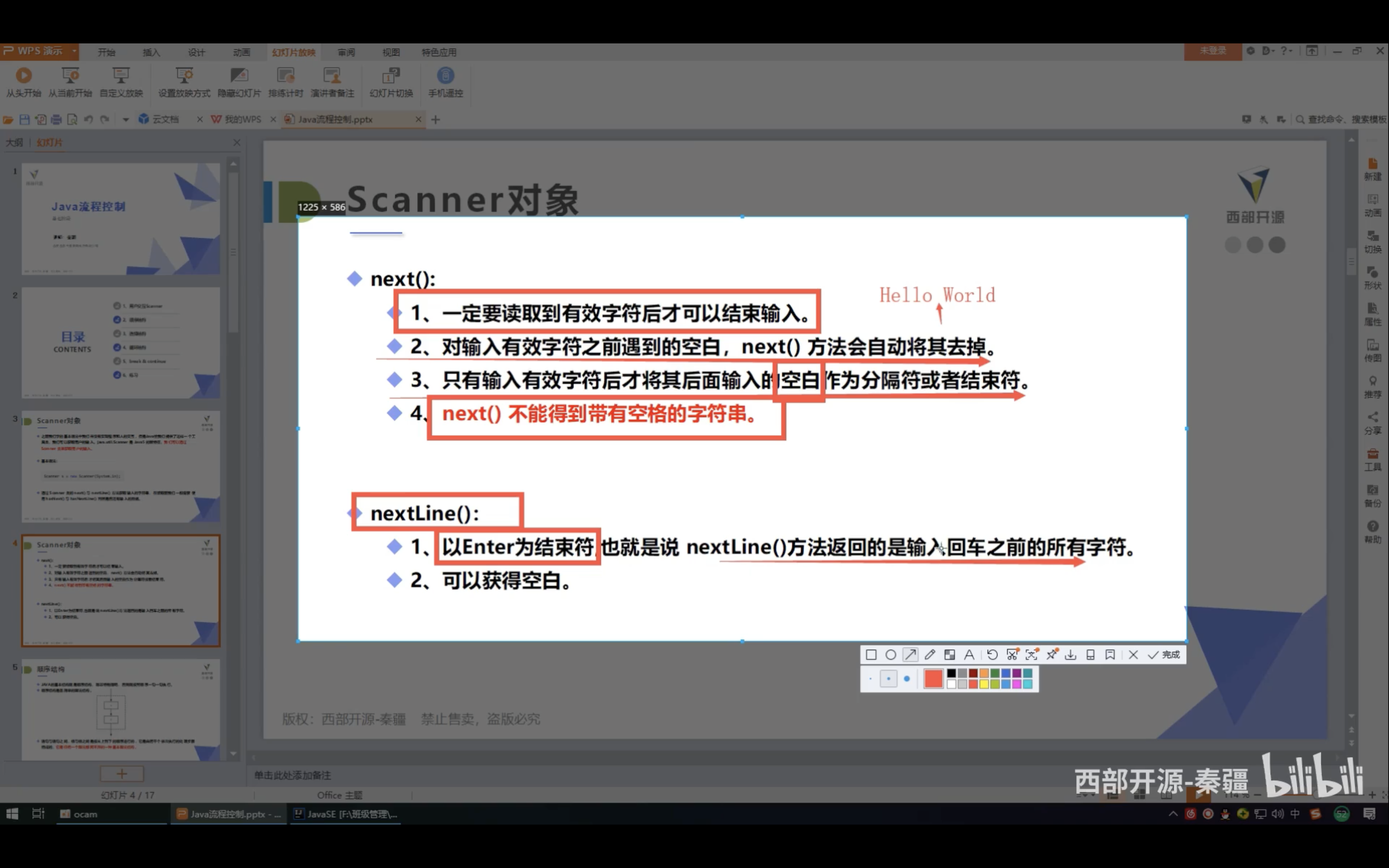
hasNext()//还是否有下一个 hasNext()//还是否有下一行
-
基本语法
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); -
通过Scanner类的next()与nextLine()。。。
next:
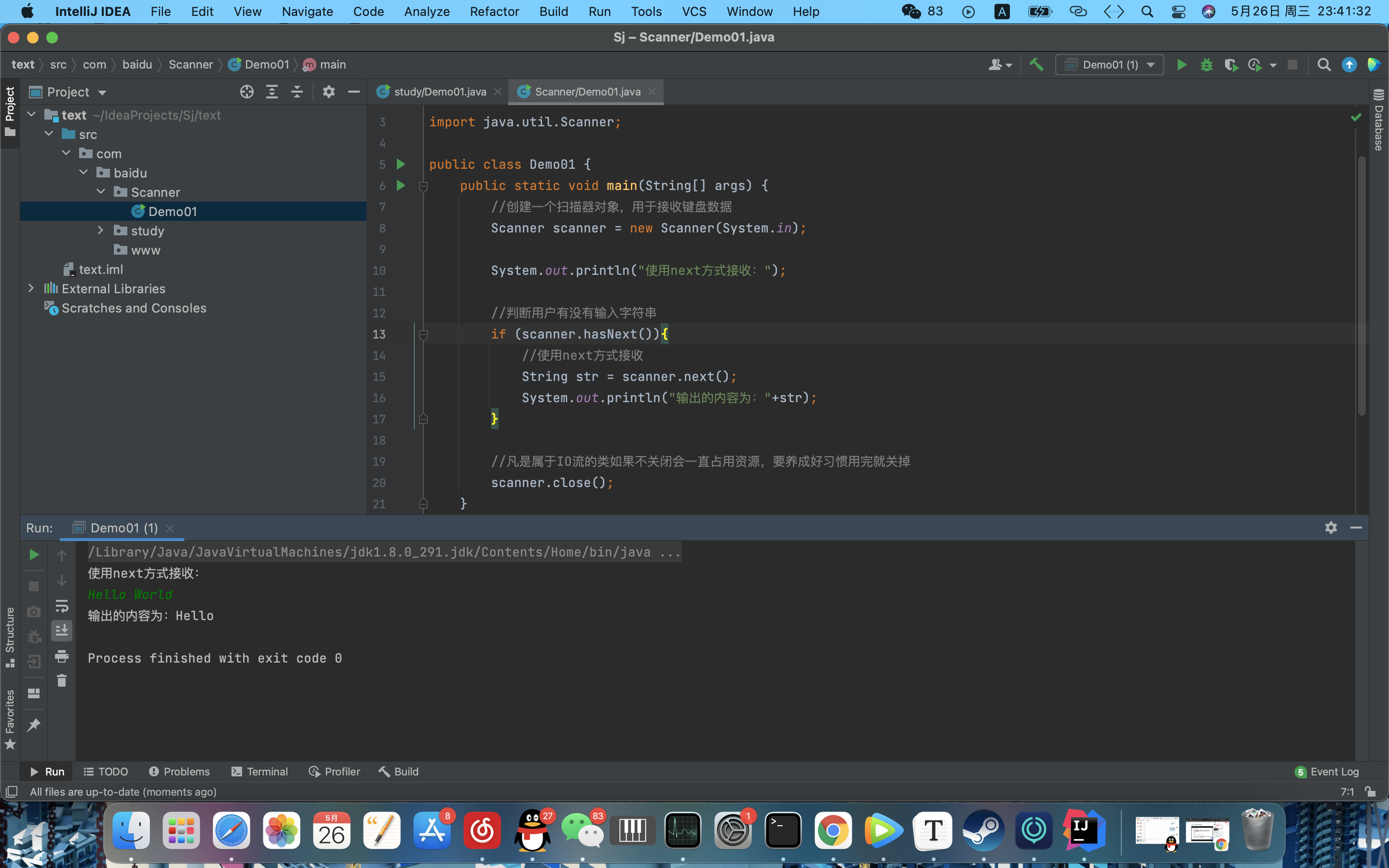
package com.baidu.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描器对象,用于接收键盘数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用next方式接收:");
//判断用户有没有输入字符串
if (scanner.hasNext()){
//使用next方式接收
String str = scanner.next(); //程序会等待用户输入完毕
System.out.println("输出的内容为:"+str);
}
//凡是属于IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成好习惯用完就关掉
scanner.close();
}
}
nextLine:
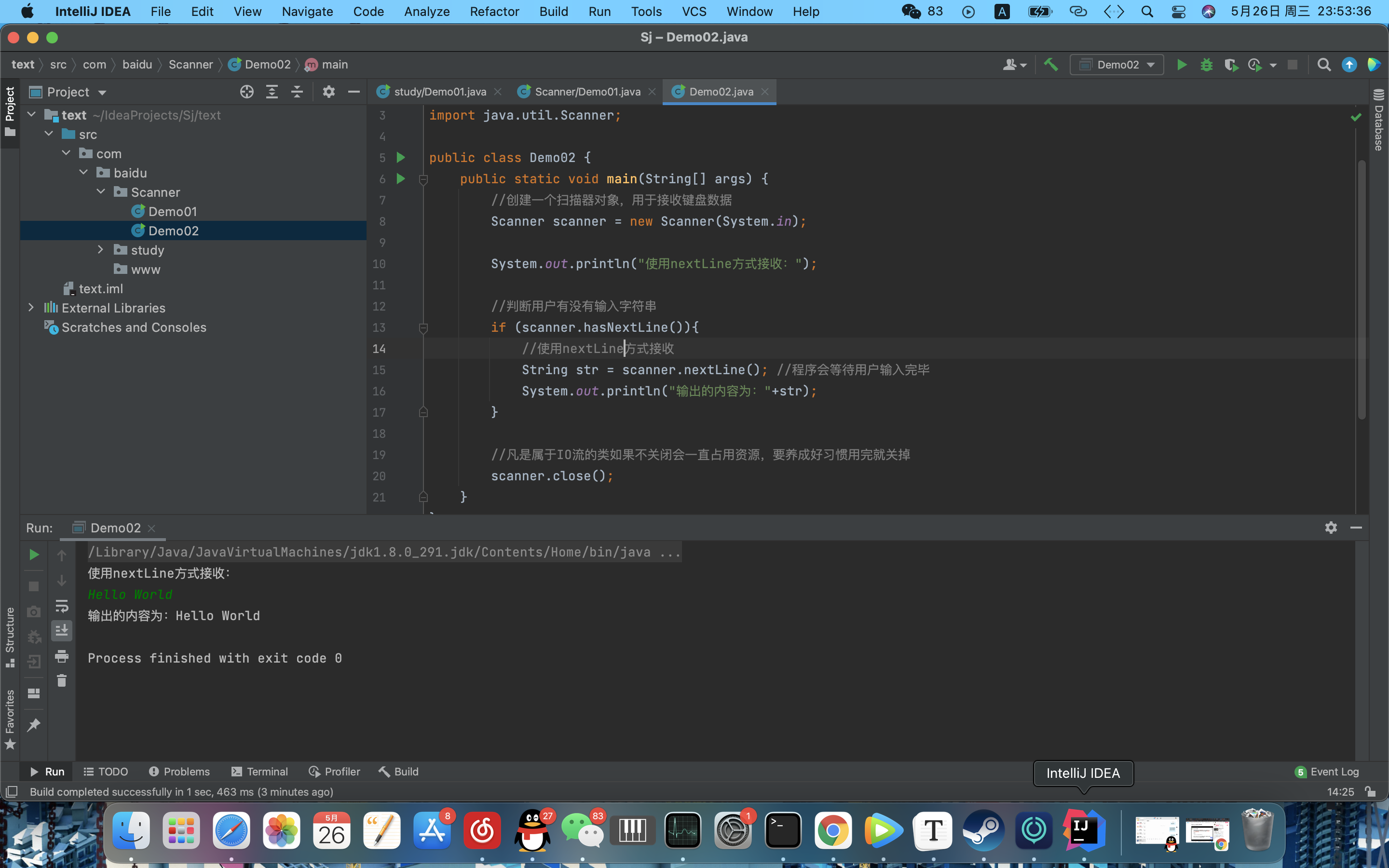
package com.baidu.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个扫描器对象,用于接收键盘数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用nextLine方式接收:");
//判断用户有没有输入字符串
if (scanner.hasNextLine()){
//使用nextLine方式接收
String str = scanner.nextLine(); //程序会等待用户输入完毕
System.out.println("输出的内容为:"+str);
}
//凡是属于IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成好习惯用完就关掉
scanner.close();
}
}
next与nextLine区别:![截屏2021-05-26 下午11.55.38]()
![]()
Scanner进阶使用
//接收和判断整数和小数
package com.baidu.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//从键盘接收数据
int i = 0;
float f = 0.0f;
System.out.println("请输入整数:");
//如果。。。那么
if (scanner.hasNextInt()){
i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("整数数据:" + i);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的不是整数数据!");
}
System.out.println("请输入小数:");
//如果。。。那么
if (scanner.hasNextFloat()){
f = scanner.nextFloat();
System.out.println("小数数据:" + f);
}else {
System.out.println("输入的不是小数数据!");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
求和与求平均值:
package com.baidu.Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//我们可以输入多个数字,并求其总和与平均数,每输入一个数字用回车确认,通过输入非数字来结束输入并输出执行结果:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//和
double sum = 0;
//计算输入了多少个数字
int m = 0;
System.out.println("请输入数据:");
//通过循环判断是否还有输入,并在里面对每一次进行求和和统计
while (scanner.hasNextDouble()){
double x = scanner.nextDouble();
m = m + 1; //m++
sum = sum + x;
System.out.println("你输入了第"+m+"个数据,然后当前结果和为"+sum+"当前平均值为"+sum/m);
}
System.out.println(m + "个数的和为:" + sum);
System.out.println(m + "个数的平均值为:" + sum/m);
}
}
2. 顺序结构
package com.baidu.struct;
public class ShunXuDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello1");
System.out.println("hello2");
System.out.println("hello3");
System.out.println("hello4");
System.out.println("hello5");
}
}
3. 选择结构
if选择结构
-
if单选择结构
if(布尔表达式){
//如果布尔表达式为true将执行的语句
}package com.baidu.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
//if单选择结构
public class IfDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入内容:");
String s =scanner.nextLine();
//equals:判断字符串是否相等
if (s.equals("Hello")){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("End");
scanner.close();
}
}
-
if双选择结构
if(布尔表达式){
//如果布尔表达式为true将执行的语句
}else{
//如果布尔表达式为false将执行的语句
}package com.baidu.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
//if双选择结构
public class IfDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//考试分数大于60就是及格,小于60分就是不及格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
* if 语句至多有1个 else 语句,else 语句在所有的 else if 语句之后。
* if 语句可以有若干个 else if 语句,它们必须在 else 语句之前。
* 一旦其中一个else if 语句检测为 true, 其他的 else if 以及 else 语句都将跳过执行
*/
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score>=60){
System.out.println("及格");
}else {
System.out.println("不及格");
}
scanner.close();
}
} -
if多选择结构
if(布尔表达式1){
//如果布尔表达式1为true将执行的语句
}else if(布尔表达式2){
//如果布尔表达式2为true将执行的语句
}else if(布尔表达式3){
//如果布尔表达式3为true将执行的语句
}else{
//如果以上布尔表达式都不为true将执行的语句
}package com.baidu.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
//if多选择结构
public class IfDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//考试成绩大于60就是及格,小于60分就是不及格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
* if 语句至多有1个 else 语句,else 语句在所有的 else if 语句之后。
* if 语句可以有若干个 else if 语句,它们必须在 else 语句之前。
* 一旦其中一个else if 语句检测为 true, 其他的 else if 以及 else 语句都将跳过执行
*/
System.out.println("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score==100){
System.out.println("恭喜满分");
}else if (score=90){
System.out.println("A级");
}else if (score=80){
System.out.println("B级");
}else if (score=70){
System.out.println("C级");
}else if (score=60){
System.out.println("D级");
}else if (score<60&& score>=0){
System.out.println("成绩不合格");
}else {
System.out.println("成绩不合法");
}
scanner.close();
}
} -
嵌套的if结构
if(布尔表达式 1){
//如果布尔表达式 1为true将执行的语句
if(布尔表达式 2){
//如果布尔表达式 2为true将执行的语句
}
} -
switch多选择结构
Switch多选择结构
1.

package com.baidu.struct;
public class SwitchDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//case 穿透 //switch 匹配一个具体的值
char grade = 'C';
switch (grade){
case 'A':
System.out.println("优秀");
break;//可选
case 'B':
System.out.println("良好");
break;
case 'C':
System.out.println("中等");
break;
case 'D':
System.out.println("及格");
break;
case 'E':
System.out.println("不及格");
break;
default:
System.out.println("未知等级");
break;
}
}
}
2.
package com.baidu.struct;
public class SwitchDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "狂神";
//JDK7的新特性,表达式结果可以是字符串!!!
//字符的本质还是数字
//反编译 java---class (字节码文件)---反编译(IDEA)
switch (name){
case "狂神":
System.out.println("狂神");
break;
case "Asuka":
System.out.println("Asuka");
break;
case "牛哥":
System.out.println("爱喝水");
break;
default:
System.out.println("不喝水");
break;
}
}
}
4. 循环结构
while循环
while(布尔表达式){
//循环内容
}

输出1-100
package com.baidu.struct;
public class WhileDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//输出1-100
int i =0;
while (i<100){
i++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
死循环
package com.baidu.struct;
public class WhileDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//死循坏
while (true){
//等待客户端连接
//定时检查
//。。。。。。
}
}
}
计算1+2+3+...+100=?
package com.baidu.struct;
public class WhileDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//计算1+2+3+...+100=?
//高斯的故事
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
while(i<=100){
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("结果是"+sum);
}
}
do...while循环
do{
//代码语句
}while(布尔表达式);

计算1+2+3+...+100=?
package com.baidu.struct;
public class DoWhileDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//计算1+2+3+...+100=?
//高斯的故事
int i = 1;
int sum = 0;
do {
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}while (i<=100);
System.out.println("结果是"+sum);
}
}
while与do while 对比
package com.baidu.struct;
public class DoWhileDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0;
//while与do while 对比
while (a<0){
System.out.println(a);
a++;
}
System.out.println("==============");
do {
System.out.println(a);
}while (a<0);
}
}
for循环
for(初始化;布尔表达式;更新){
//代码语句
}
for循环语句是支持迭代的一种通用结构,是最有效、最灵活的循环结构。
package com.baidu.struct;
public class ForDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1; //初始化条件
while (a<=100){//条件判断
System.out.println(a);//循环体
a+=2;//迭代
}
System.out.println("while循环结束!");
//初始化 //条件判断 //迭代
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("for循环结束!");
/*
关于for循环有以下几点说明:
最先执行初始化步骤。可以声明一种类型,但可初始化一个或多个循环控制变量,也可以是空语句。
然后,检测布尔表达式的值。如果为true,循环体被执行。如果为false, 循环终止, 开始执行循环体后面的语句。
执行一次循环后。更新循环控制变量(迭代因子控制循环变量的增减)。
再次检测布尔表达式。循环执行上面的过程。
*/
/*死循环
for (; ; ) {
}
*/
}
}
练习1:计算0到100之间奇数和偶数的和
package com.baidu.struct;
public class ForDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//练习1:计算0到100之间奇数和偶数的和
int oddsum = 0;
int evensum = 0;
for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){
if (i%2!=0){//奇数
oddsum = oddsum + i;//oddsum+=i;
}else {//偶数
evensum = evensum + i;//evensum+=i;
}
}
System.out.println("奇数和="+oddsum);
System.out.println("偶数和="+evensum);
}
}
练习2:用while 或for循环输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出3个
package com.baidu.struct;
public class ForDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//练习2:用while 或for循环输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出3个
for (int i = 0; i <=1000; i++){
if (i%5==0){
System.out.print(i+"\t");//"\t"=空格;"\n"=换行 print与println之间区别:ln代表自动换行
}
if (i%(5*3)==0){//每行3个就换行(第三个数必备15整除)
System.out.println();
//System.out.println("\n");
}
}
//println 输出完会换行
//print 输出完不会换行
}
}
"\t"=空格;"\n"=换行 print与println之间区别:ln代表自动换行
练习3:打印九九乘法口诀表
package com.baidu.struct;
//练习3:打印九九乘法口诀表
//1*1=1
//1*2=2 2*2=4
//1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9
//1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16
//1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
//1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
//1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
//1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
//1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
//
//Process finished with exit code 0
public class ForDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.我们先打印第一列,这个大家应该都会
//2.我们把固定的1再用一个循环抱起来
//3.去掉重复项,就 j <= i;
for (int i = 1; i<=9; i++){
for (int j = 1; j<=i;j++){
System.out.print(j+"*"+i+"="+ (i*j)+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
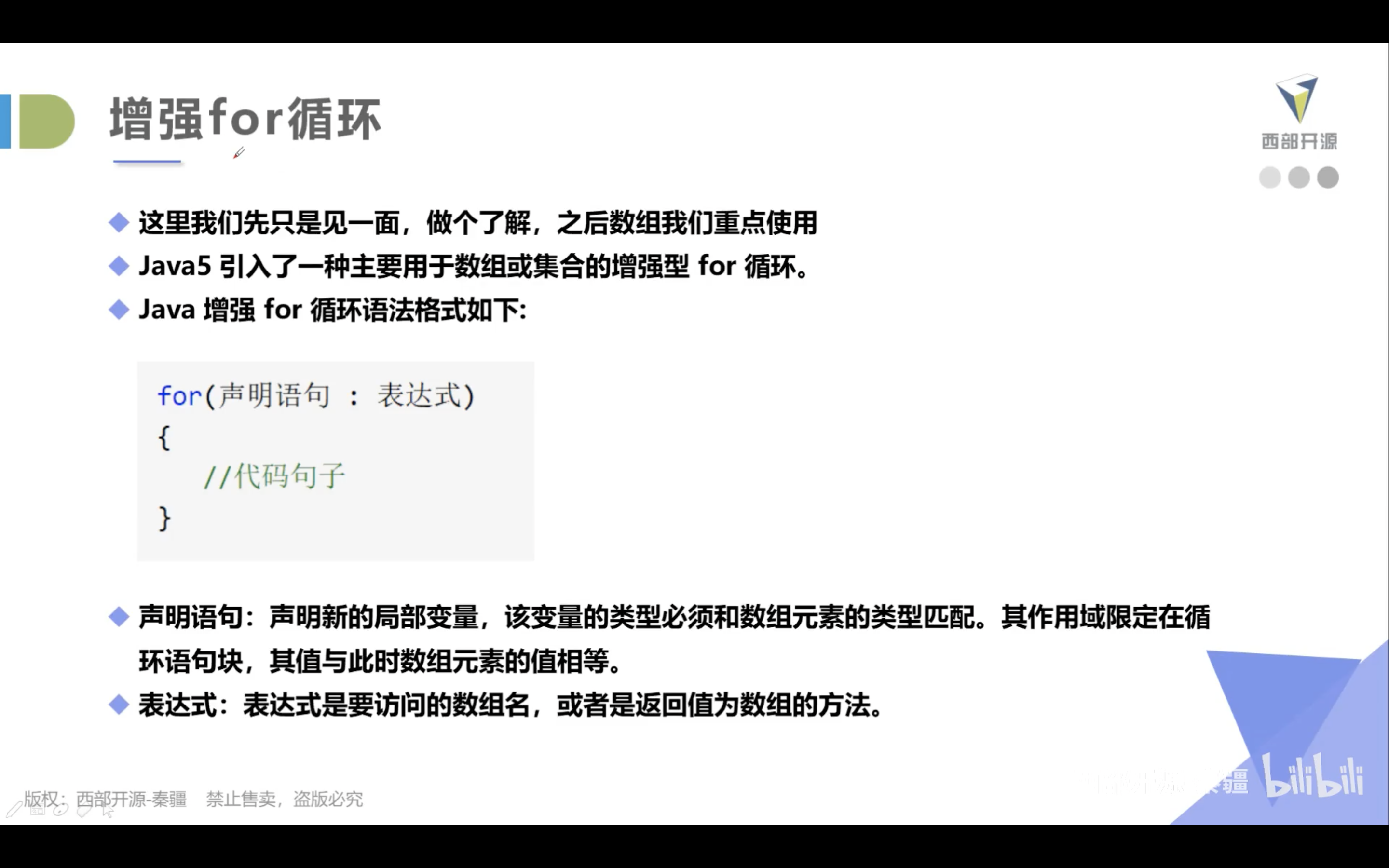
在Java5中引入了一种主要用于数组的增强型for循环
for(声明语句 : 表达式)
{
//代码句子
}
package com.baidu.struct;
public class ForDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] numbers = {10,20,30,40,50};//定义一个数组
for (int i = 0;i<5;i++){ //上下方法作用相同
System.out.println(numbers[i]);
}
System.out.println("==================");
//遍历数组元素
for (int x: numbers){
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
5. break & continue & goto
break:
package com.baidu.struct;
public class BreakDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i<100){
i++;
System.out.println(i);
if (i==30){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("123");
}
}
continue:
package com.baidu.struct;
public class ContinueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i<100){
i++;
if (i%10==0){
System.out.println();
continue;
}
System.out.print(i);
}
//break在任何循环语句的主体部分, 均可用break控制循环的流程。
//break用于强行退出循环, 不执行循环中剩余的语句。(break语句也在switch语句中使用)
//
//continue 语句用在循环语句体中, 用于终止某次循环过程,即跳过循环体中尚未执行的语句, 接着进行下一次是否执行循环的判定。
System.out.println("123");
}
}
goto:
package com.baidu.struct;
public class LabelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印101-105之间所有的质数
//质数是指在大于1的自然数中, 除了1和它本身以外不再有其他因素的自然数。
/*标签:outer:
代码
continue outer;
*/
int count = 0;
outer:for (int i = 101;i<150;i++){
for (int j = 2; j<i/2;j++){
if (i % j == 0){
continue outer;
}
}
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
6. 练习
打印三角形及Debug
package com.baidu.struct;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印三角形 5行
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 5;j >=i; j--){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 1;j <= i; j++ ){
System.out.print("*");
}
for (int j = 1;j < i; j++ ){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
判断季节
package com.baidu.study;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String jijie = scanner.nextLine();
switch (jijie){
case "春":
System.out.println("1-3");
break;
case "夏":
System.out.println("4-6");
break;
case "秋":
System.out.println("6-9");
break;
case "冬":
System.out.println("10-12");
break;
default:
System.out.println("您输入的数据不符合");
}
scanner.close();
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号