图像数据增强 (Data Augmentation in Computer Vision)
1.1 简介
深层神经网络一般都需要大量的训练数据才能获得比较理想的结果。在数据量有限的情况下,可以通过数据增强(Data Augmentation)来增加训练样本的多样性, 提高模型鲁棒性,避免过拟合。
在计算机视觉中,典型的数据增强方法有翻转(Flip),旋转(Rotat ),缩放(Scale),随机裁剪或补零(Random Crop or Pad),色彩抖动(Color jittering),加噪声(Noise)
笔者在跟进视频及图像中的人体姿态检测和关键点追踪(Human Pose Estimatiion and Tracking in videos)的项目。因此本文的数据增强仅使用——翻转(Flip),旋转(Rotate ),缩放以及缩放(Scale)
2.1 裁剪(Crop)
image.shape--([3, width, height])一个视频序列中的一帧图片,裁剪前大小不统一
bbox.shape--([4,])人体检测框,用于裁剪
x.shape--([1,13]) 人体13个关键点的所有x坐标值
y.shape--([1,13])人体13个关键点的所有y坐标值
1 def crop(image, bbox, x, y, length): 2 x, y, bbox = x.astype(np.int), y.astype(np.int), bbox.astype(np.int) 3 4 x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = bbox 5 w, h = x_max - x_min, y_max - y_min 6 7 # Crop image to bbox 8 image = image[y_min:y_min + h, x_min:x_min + w, :] 9 10 # Crop joints and bbox 11 x -= x_min 12 y -= y_min 13 bbox = np.array([0, 0, x_max - x_min, y_max - y_min]) 14 15 # Scale to desired size 16 side_length = max(w, h) 17 f_xy = float(length) / float(side_length) 18 image, bbox, x, y = Transformer.scale(image, bbox, x, y, f_xy) 19 20 # Pad 21 new_w, new_h = image.shape[1], image.shape[0] 22 cropped = np.zeros((length, length, image.shape[2])) 23 24 dx = length - new_w 25 dy = length - new_h 26 x_min, y_min = int(dx / 2.), int(dy / 2.) 27 x_max, y_max = x_min + new_w, y_min + new_h 28 29 cropped[y_min:y_max, x_min:x_max, :] = image 30 x += x_min 31 y += y_min 32 33 x = np.clip(x, x_min, x_max) 34 y = np.clip(y, y_min, y_max) 35 36 bbox += np.array([x_min, y_min, x_min, y_min]) 37 return cropped, bbox, x.astype(np.int), y.astype(np.int)
2.2 缩放(Scale)
image.shape--([3, 256, 256])一个视频序列中的一帧图片,裁剪后输入网络为256*256
bbox.shape--([4,])人体检测框,用于裁剪
x.shape--([1,13]) 人体13个关键点的所有x坐标值
y.shape--([1,13])人体13个关键点的所有y坐标值
f_xy--缩放倍数
1 def scale(image, bbox, x, y, f_xy): 2 (h, w, _) = image.shape 3 h, w = int(h * f_xy), int(w * f_xy) 4 image = resize(image, (h, w), preserve_range=True, anti_aliasing=True, mode='constant').astype(np.uint8) 5 6 x = x * f_xy 7 y = y * f_xy 8 bbox = bbox * f_xy 9 10 x = np.clip(x, 0, w) 11 y = np.clip(y, 0, h) 12 13 return image, bbox, x, y
2.3 翻转(fillip)
这里是将图片围绕对称轴进行左右翻转(因为人体是左右对称的,在关键点检测中有助于防止模型过拟合)
1 def flip(image, bbox, x, y): 2 image = np.fliplr(image).copy() 3 w = image.shape[1] 4 x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max = bbox 5 bbox = np.array([w - x_max, y_min, w - x_min, y_max]) 6 x = w - x 7 x, y = Transformer.swap_joints(x, y) 8 return image, bbox, x, y
翻转前:

翻转后:

2.4 旋转(rotate)
angle--旋转角度
1 def rotate(image, bbox, x, y, angle): 2 # image - -(256, 256, 3) 3 # bbox - -(4,) 4 # x - -[126 129 124 117 107 99 128 107 108 105 137 155 122 99] 5 # y - -[209 176 136 123 178 225 65 47 46 24 44 64 49 54] 6 # angle - --8.165648811999333 7 # center of image [128,128] 8 o_x, o_y = (np.array(image.shape[:2][::-1]) - 1) / 2. 9 width,height = image.shape[0],image.shape[1] 10 x1 = x 11 y1 = height - y 12 o_x = o_x 13 o_y = height - o_y 14 image = rotate(image, angle, preserve_range=True).astype(np.uint8) 15 r_x, r_y = o_x, o_y 16 angle_rad = (np.pi * angle) /180.0 17 x = r_x + np.cos(angle_rad) * (x1 - o_x) - np.sin(angle_rad) * (y1 - o_y) 18 y = r_y + np.sin(angle_rad) * (x1 - o_x) + np.cos(angle_rad) * (y1 - o_y) 19 x = x 20 y = height - y 21 bbox[0] = r_x + np.cos(angle_rad) * (bbox[0] - o_x) + np.sin(angle_rad) * (bbox[1] - o_y) 22 bbox[1] = r_y + -np.sin(angle_rad) * (bbox[0] - o_x) + np.cos(angle_rad) * (bbox[1] - o_y) 23 bbox[2] = r_x + np.cos(angle_rad) * (bbox[2] - o_x) + np.sin(angle_rad) * (bbox[3] - o_y) 24 bbox[3] = r_y + -np.sin(angle_rad) * (bbox[2] - o_x) + np.cos(angle_rad) * (bbox[3] - o_y) 25 return image, bbox, x.astype(np.int), y.astype(np.int)
旋转前:
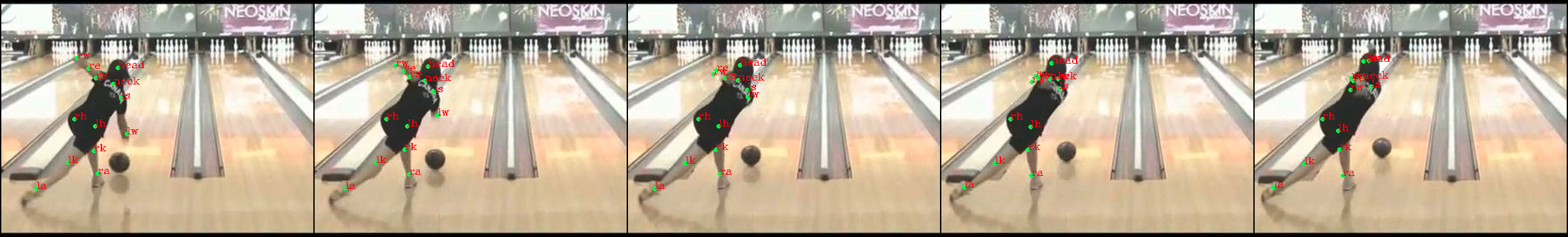
旋转后:

3 结果(output)
数据增强前的原图:
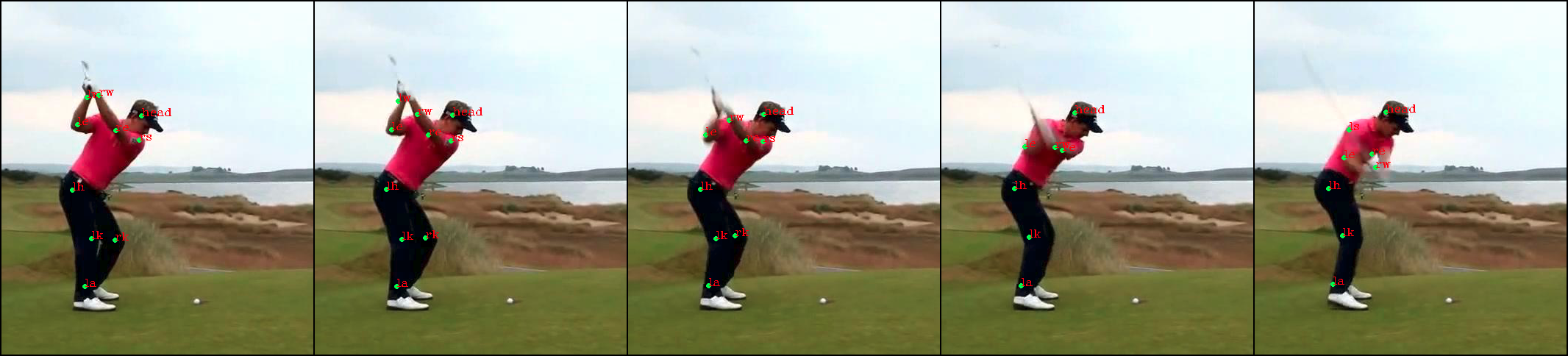

数据增强后:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号