# P4667 [BalticOI 2011] Switch the Lamp On 电路维修 (Day1)
P4667 [BalticOI 2011] Switch the Lamp On 电路维修 (Day1)
题目描述
Casper 正在设计电路。有一种正方形的电路元件,在它的两组相对顶点中,有一组会用导线连接起来,另一组则不会。有 $N\times M$ 个这样的元件,你想将其排列成 $N$ 行,每行 $M$ 个。 电源连接到板的左上角。灯连接到板的右下角。只有在电源和灯之间有一条电线连接的情况下,灯才会亮着。为了打开灯,任何数量的电路元件都可以转动 90°(两个方向)。
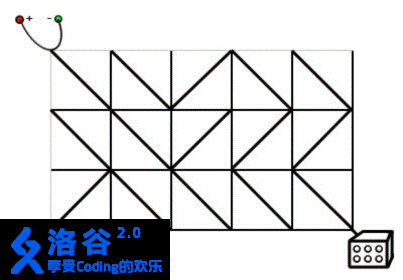
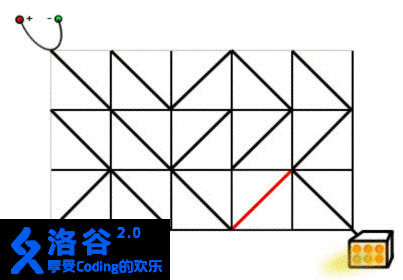
在上面的图片中,灯是关着的。如果右边的第二列的任何一个电路元件被旋转 90°,电源和灯都会连接,灯被打开。现在请你编写一个程序,求出最小需要多少旋转多少电路元件。
输入格式
输入的第一行包含两个整数 $N$ 和 $M$,表示盘子的尺寸。 在以下 $N$ 行中,每一行有 $M$ 个符号 \ 或 /,表示连接对应电路元件对角线的导线的方向。
输出格式
如果可以打开灯,那么输出只包含一个整数,表示最少转动电路元件的数量。
如果不可能打开灯,输出 NO SOLUTION。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
3 5
\\/\\
\\///
/\\\\
输出 #1
1
说明/提示
对于 $40%$ 的数据,$1 \le N \le 4$,$1 \le M \le 5$。
对于所有数据,$1 \le N,M \le 500$。
这是一个bfs0-1的题目,也就是说边的权值只有0和1两种
我们将边权为 0 的路径 插入队头(front),边权为 1 的路径 插入队尾(rear),这样可以确保更小代价的路径先被扩展,维护一个严格的最短路径队列。
来看这个题目
这个题目核心的地方在于这个路线的联通问题上,怎么来处理
点击查看代码
int dx[] = {1, 1, -1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 1, -1};
int gx[] = {0, 0, -1, -1};
int gy[] = {0, -1, 0, -1};
char expected[] = {'\\', '/', '/', '\\'};
点击查看代码
还有就是联通路径的处理
//如果下一条电路与预期的一致则说明联通了,否则就需要进行一次旋转操作
int cost = (map[gx0][gy0] == expected[d]) ? 0 : 1;
int new_step = now.step + cost;
点击查看代码
以及**bfs0-1的关键思想** ``` if (cost == 0) queue[--front] = next;//如果无需旋转优先入队,目的是寻找最短路径 else queue[rear++] = next; ```完整代码如下
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXN 502
#define INF 1e9
typedef struct {
int x, y,step;
}Node;
int n,m;
int map[MAXN][MAXN];
int visited[MAXN][MAXN];
int dx[] = {1, 1, -1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 1, -1};
int gx[] = {0, 0, -1, -1};
int gy[] = {0, -1, 0, -1};
char expected[] = {'\\', '/', '/', '\\'};
int BFS() {
Node queue[MAXN * MAXN * 2];
int front = 0, rear = 0;
queue[rear++] = (Node) {0, 0, 0};
visited[0][0] = 1;
while (front < rear) {
Node now = queue[front++];
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = now.x + dx[d];
int ny = now.y + dy[d];
int gx0 = now.x + gx[d];
int gy0 = now.y + gy[d];
//确保没有越界
if (nx < 0 || nx > n || ny < 0 || ny > m)
continue;
if (gx0 < 0 || gx0 >= n || gy0 < 0 || gy0 >= m)
continue;
//如果下一条电路与预期的一致则说明联通了,否则就需要进行一次旋转操作
int cost = (map[gx0][gy0] == expected[d]) ? 0 : 1;
int new_step = now.step + cost;
if (visited[nx][ny] > new_step) {
visited[nx][ny] = new_step;
Node next = {nx, ny, new_step};
if (cost == 0)
queue[--front] = next;//如果无需旋转优先入队,目的是寻找最短路径
else
queue[rear++] = next;
}
}
return 1;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%s", map[i]);
// 初始化 visited 数组
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
visited[i][j] = INF;
}
}
int result = BFS();



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号