java object多大 java对象内存模型 数组有多长(二)偏移
1
使用http://www.javamex.com/中提供的classmexer.jar来计算对象的大小。
2
org.openjdk.jol.info.ClassLayout
Shallow
org.openjdk.jol.info.GraphicLayout
retained
3 自写
https://www.cnblogs.com/hubaoxi/p/15993625.html
long/double –> int/float –> short/char –> byte/boolean –> Reference
http://java-performance.info/memory-introspection-using-sun-misc-unsafe-and-reflection/
arrayBaseOffset,获取数组第一个元素的偏移地址
arrayIndexScale返回数组中的每一个元素的内存地址换算因子
使用Unsafe要注意以下几个问题:
1、Unsafe有可能在未来的Jdk版本移除或者不允许Java应用代码使用,这一点可能导致使用了Unsafe的应用无法运行在高版本的Jdk。
2、Unsafe的不少方法中必须提供原始地址(内存地址)和被替换对象的地址,偏移量要自己计算,一旦出现问题就是JVM崩溃级别的异常,会导致整个JVM实例崩溃,表现为应用程序直接crash掉。
3、Unsafe提供的直接内存访问的方法中使用的内存不受JVM管理(无法被GC),需要手动管理,一旦出现疏忽很有可能成为内存泄漏的源头。
暂时总结出以上三点问题。Unsafe在JUC(java.util.concurrent)包中大量使用(主要是CAS),在netty中方便使用直接内存,还有一些高并发的交易系统为了提高CAS的效率也有可能直接使用到Unsafe。
4
instrument的getObjectSize(obj)
Shallow Size
5 https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/345655?utm_source=zhihu&utm_medium=bbs-ex&utm_campaign=other&utm_content=content
5.1
jdk.nashorn.internal.ir.debug.ObjectSizeCalculator only for jdk 1.8,, and只算压缩指针,不能响应压缩指针参数变化
5.2
org.apache.lucene.RamUsageEstimator.sizeOf 准确(1.8 and java 11 pratice),但是不能适时截断递归 ,这也是自写程序的意义;
比如Double/Integer是我们通常关心的,需要retained size,而大多数自定义类型的指针,则不需要
jdk 1.8
no padding
| ClassLayout | my | 5.1 | 5.2 | ||
| 1 | int i; | 16 | 16 | ||
| 2 | int i=7; | 16 | 16 | ||
| 3 | Integer i; | 16 | 16 | ||
| 4 | Integer i=7; | 16 | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| 5 | Integer i=127; | 16 | 32 | 32 | 32 |
|
6 |
Integer i=127; Integer i2=127; |
24 | 36 | 40 | 40 |
|
7 |
Integer i=128; Integer i2=128; |
24 |
52 12+8+Integer(12+4) + Integer(12+4) |
56 | 56 |
| 8 | String str; | 16 | 16 | ||
| 9 | String str="xxxxxxx"; | 16 |
66 (12+4+String(12+4+4+byte[](16+2*7)) |
72 | 72 |
|
padding below |
|||||
|
|
6 |
24 |
40 |
40 | 40 |
|
|
7 |
24 |
56 |
56 | 56 |
| 8 | 16 |
72 |
72 | 72 | |
9 |
static ObjectB bb = new ObjectB(); |
16 *1 |
32 | 32 | |
10 |
//12+4+4=20=24 String xxx = "c";//20(24)+(16+2)(24) 48 |
88 *2 |
96 | 96 | |
11 |
static byte b; |
232 | 256 | 256 | |
| below add yuming's fix | |||||
9 |
32 | 32 | 32 | ||
10 |
96 | 96 | 96 | ||
12 |
static ObjectB bb = new ObjectB(); |
16 | 16 | 16 | |
| 11 | 256 | 256 | 256 |
*1
static ObjectB bb = new ObjectB();
private static class ObjectA {
private ObjectB objectB = bb;
}
private static class ObjectB {
}
private static class ObjectC {
private ObjectB objectB = bb;
}
由于对象里没有成员,就没有children偏移,所以new ObjectB()被计算为0,实际为12+4(padding)
private long getUnderlyingSize( final boolean isArray )
{
//System.out.println(this.toString());
//long size = 0;
for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
// yuming:原本没有addPaddingSize
size += (yuming?(addPaddingSize(child.arraySize)):child.arraySize) + child.getUnderlyingSize( child.arraySize != 0 );
if ( !isArray && !children.isEmpty() ){
int tempSize = children.get( children.size() - 1 ).offset + children.get( children.size() - 1 ).length;
size += addPaddingSize(tempSize);
}
if( yuming && !visited && !isArray && children.isEmpty() && !cType.isPrimitive() && !contents.equals("null"))
size += addPaddingSize(OBJECT_HEADER);
return size;
}
visited: 防止2个成员变量引用相同的对象重复计算对象头
isArray:array没有这个问题,因为array计算的是里面的引用类型,也就是4(引用类型),到下一级才会计算对象,还会进这个方法
isEmpty:必须children是empty的,否则有成员变量直接拿最大偏移+该偏移的成员大小即可,偏移已包含对象头
isPrimitive:所有primitive的children都是empty的,而且children底部就是基本类型,需排除
contents “null”:防止只有声明没有new的情况,压根没有对象,既然没有对象就无需考虑其对象头
*2
//12+4+4=20=24
String xxx = "c";//20(24)+(16+2)(24) 48
Integer [] ff = new Integer[1];//16+1*4 20=24
其中注释为 "c"和new Integer[1]的大小,他们是独立对象,也应padding
之前对成员变量引用链上的数组对象本身没有pading,则 "c" (String对象)里面的char[1]数组对象为18(属于String对象的数组引用为4),应padding到24,new Integer[1]的大小20,应padding到24,两边相差6+4=10,左边外层对象padding,最终相差8
private long getUnderlyingSize( final boolean isArray )
{
//System.out.println(this.toString());
//long size = 0;
for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
size += (yuming?(addPaddingSize(child.arraySize)):child.arraySize) + child.getUnderlyingSize( child.arraySize != 0 );
if ( !isArray && !children.isEmpty() ){
int tempSize = children.get( children.size() - 1 ).offset + children.get( children.size() - 1 ).length;
size += addPaddingSize(tempSize);
}
if( yuming && !visited && !isArray && children.isEmpty() && !cType.isPrimitive() && !contents.equals("null"))
size += addPaddingSize(OBJECT_HEADER);
return size;
}
比如String的children char[],当=‘x'时,arraySize = baseOffset (首元素偏移)+ indexScale(单个元素偏移) * Array.getLength(obj);为18,作为一个单独的对象,数组也是对象,应进行padding
*3
应注意到,3个程序都没有像mat那样计算reteined size,B的同一个对象被A 和C同时引用,B的对象仍然计算入A的size
为了定义运行期哪些类我们关心,哪些不关心,比如类A内部一个指向Country对象,Country对象作为基础类对象常驻内存,那么我们就不该统计Country对象,作为A的一部分
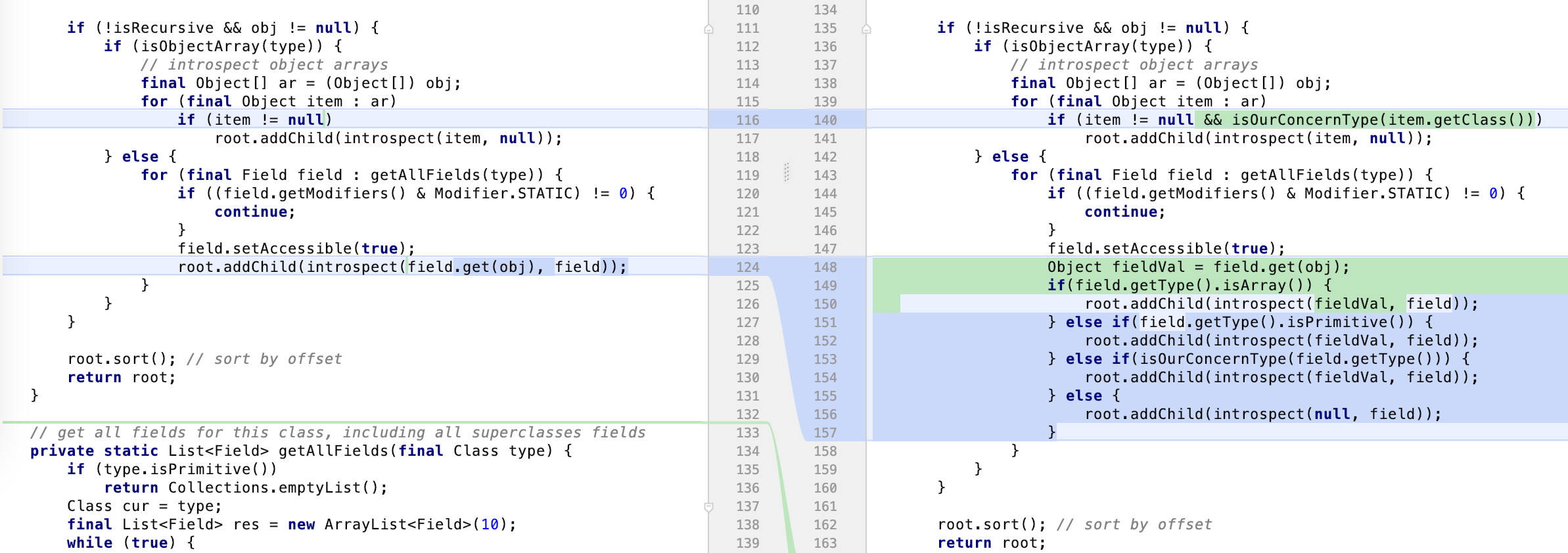
fix版本:
package markdown.memory;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import org.openjdk.jol.info.*;
import jdk.nashorn.internal.ir.debug.ObjectSizeCalculator;
import org.apache.lucene.util.RamUsageEstimator;
import org.openjdk.jol.info.ClassLayout;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
//import sun.misc.Unsafe;
/**
* https://www.cnblogs.com/silyvin/p/17271790.html
* This class could be used for any object contents/memory layout printing.
*/
public abstract class ClassIntrospector {
private static HashSet<Class> set = new HashSet<>();
// 允许不同实例不同配置
private boolean noPadding = false;
private boolean yuming = true;
private int OBJECT_HEADER = 12;
/** Size of any Object reference */
private int objectRefSize;
// 允许不同实例不同配置
abstract protected int getObjectRefSize();
abstract protected int getArrayBaseOffset(Class c);
abstract protected int getArrayIndexScale(Class c);
abstract protected int getObjectFieldOffset(Field field);
abstract protected void sort(ObjectInfo root);
{
objectRefSize = getObjectRefSize();
set.add(Integer.class);
set.add(Short.class);
set.add(Float.class);
set.add(Double.class);
set.add(Character.class);
set.add(Boolean.class);
set.add(Byte.class);
set.add(String.class);
set.add(BigInteger.class);
set.add(BigDecimal.class);
set.add(ObjectB.class);
set.add(TestMemory.CC.class);
}
/** Sizes of all primitive values */
private static final Map<Class, Integer> primitiveSizes;
static {
primitiveSizes = new HashMap<Class, Integer>(10);
primitiveSizes.put(byte.class, 1);
primitiveSizes.put(char.class, 2);
primitiveSizes.put(int.class, 4);
primitiveSizes.put(long.class, 8);
primitiveSizes.put(float.class, 4);
primitiveSizes.put(double.class, 8);
primitiveSizes.put(boolean.class, 1);
}
/**
* Get object information for any Java object. Do not pass primitives to
* this method because they will boxed and the information you will get will
* be related to a boxed version of your value.
*
* @param obj
* Object to introspect
* @return Object info
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
public ObjectInfo introspect(final Object obj)
throws IllegalAccessException {
try {
return introspect(obj, null);
} finally { // clean visited cache before returning in order to make
// this object reusable
m_visited.clear();
}
}
// we need to keep track of already visited objects in order to support
// cycles in the object graphs
private IdentityHashMap<Object, Boolean> m_visited = new IdentityHashMap<Object, Boolean>(
100);
private ObjectInfo introspect(final Object obj, final Field fld)
throws IllegalAccessException {
// use Field type only if the field contains null. In this case we will
// at least know what's expected to be
// stored in this field. Otherwise, if a field has interface type, we
// won't see what's really stored in it.
// Besides, we should be careful about primitives, because they are
// passed as boxed values in this method
// (first arg is object) - for them we should still rely on the field
// type.
boolean isPrimitive = fld != null && fld.getType().isPrimitive();
boolean isRecursive = false; // will be set to true if we have already
boolean visited = false;
// seen this object
if (!isPrimitive) {
if (m_visited.containsKey(obj))
isRecursive = visited = true;
m_visited.put(obj, true);
}
final Class type = (fld == null || (obj != null && !isPrimitive)) ? obj
.getClass() : fld.getType();
int arraySize = 0;
int baseOffset = 0;
int indexScale = 0;
if (type.isArray() && obj != null) {
// type此时数组类型,比如 byte[],而不是byte
baseOffset = getArrayBaseOffset(type);
indexScale = getArrayIndexScale(type);
arraySize = baseOffset + indexScale * Array.getLength(obj);
}
final ObjectInfo root;
if (fld == null) {
root = new ObjectInfo("", type.getCanonicalName(), getContents(obj,
type), 0, getShallowSize(type), arraySize, baseOffset,
indexScale, type, visited);
} else {
final int offset = getObjectFieldOffset(fld);
root = new ObjectInfo(fld.getName(), type.getCanonicalName(),
getContents(obj, type), offset, getShallowSize(type),
arraySize, baseOffset, indexScale, type, visited);
}
if (!isRecursive && obj != null) {
if (isObjectArray(type)) {
// introspect object arrays
final Object[] ar = (Object[]) obj;
for (final Object item : ar)
if (item != null && isOurConcernType(item.getClass()))
root.addChild(introspect(item, null));
} else {
for (final Field field : getAllFields(type)) {
if ((field.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) != 0) {
continue;
}
field.setAccessible(true);
Object fieldVal = field.get(obj);
if(field.getType().isArray()) {
root.addChild(introspect(fieldVal, field));
} else if(field.getType().isPrimitive()) {
root.addChild(introspect(fieldVal, field));
} else if(isOurConcernType(field.getType())) {
root.addChild(introspect(fieldVal, field));
} else {
root.addChild(introspect(null, field));
}
}
}
}
sort(root); // sort by offset
return root;
}
private static boolean isOurConcernType(Class c) {
return set.contains(c);
}
// get all fields for this class, including all superclasses fields
private static List<Field> getAllFields(final Class type) {
if (type.isPrimitive())
return Collections.emptyList();
Class cur = type;
final List<Field> res = new ArrayList<Field>(10);
while (true) {
Collections.addAll(res, cur.getDeclaredFields());
if (cur == Object.class)
break;
cur = cur.getSuperclass();
}
return res;
}
// check if it is an array of objects. I suspect there must be a more
// API-friendly way to make this check.
private static boolean isObjectArray(final Class type) {
if (!type.isArray())
return false;
if (type == byte[].class || type == boolean[].class
|| type == char[].class || type == short[].class
|| type == int[].class || type == long[].class
|| type == float[].class || type == double[].class)
return false;
return true;
}
// advanced toString logic
private static String getContents(final Object val, final Class type) {
if (val == null)
return "null";
if (type.isArray()) {
if (type == byte[].class)
return Arrays.toString((byte[]) val);
else if (type == boolean[].class)
return Arrays.toString((boolean[]) val);
else if (type == char[].class)
return Arrays.toString((char[]) val);
else if (type == short[].class)
return Arrays.toString((short[]) val);
else if (type == int[].class)
return Arrays.toString((int[]) val);
else if (type == long[].class)
return Arrays.toString((long[]) val);
else if (type == float[].class)
return Arrays.toString((float[]) val);
else if (type == double[].class)
return Arrays.toString((double[]) val);
else
return Arrays.toString((Object[]) val);
}
return val.toString();
}
// obtain a shallow size of a field of given class (primitive or object
// reference size)
private int getShallowSize(final Class type) {
if (type.isPrimitive()) {
final Integer res = primitiveSizes.get(type);
return res != null ? res : 0;
} else
return objectRefSize;
}
/**
* This class contains object info generated by ClassIntrospector tool
*/
protected class ObjectInfo {
/** Field name */
public final String name;
/** Field type name */
public final String type;
/** Field data formatted as string */
public final String contents;
/** Field offset from the start of parent object */
public int offset;
/** Memory occupied by this field */
public final int length;
/** Offset of the first cell in the array */
public final int arrayBase;
/** Size of a cell in the array */
public final int arrayElementSize;
/** Memory occupied by underlying array (shallow), if this is array type */
public final int arraySize;
/** This object fields */
public final List<ObjectInfo> children;
// 需要,用于对象中new无成员变量类的对象
public final Class cType;
public final boolean visited;
public ObjectInfo(String name, String type, String contents, int offset, int length, int arraySize,
int arrayBase, int arrayElementSize, Class cType, boolean visited)
{
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.contents = contents;
this.offset = offset;
this.length = length;
this.arraySize = arraySize;
this.arrayBase = arrayBase;
this.arrayElementSize = arrayElementSize;
children = new ArrayList<ObjectInfo>( 1 );
this.cType = cType;
this.visited = visited;
}
public void addChild( final ObjectInfo info )
{
if ( info != null )
children.add( info );
}
/**
* Get the full amount of memory occupied by a given object. This value may be slightly less than
* an actual value because we don't worry about memory alignment - possible padding after the last object field.
*
* The result is equal to the last field offset + last field length + all array sizes + all child objects deep sizes
* @return Deep object size
*/
public long getDeepSize()
{
//return length + arraySize + getUnderlyingSize( arraySize != 0 );
return addPaddingSize(arraySize + getUnderlyingSize( arraySize != 0 ));
}
long size = 0;
private long getUnderlyingSize( final boolean isArray )
{
//System.out.println(this.toString());
//long size = 0;
for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
size += (yuming?(addPaddingSize(child.arraySize)):child.arraySize) + child.getUnderlyingSize( child.arraySize != 0 );
if ( !isArray && !children.isEmpty() ){
int tempSize = children.get( children.size() - 1 ).offset + children.get( children.size() - 1 ).length;
size += addPaddingSize(tempSize);
}
if( yuming && !visited && !isArray && children.isEmpty() && !cType.isPrimitive() && !contents.equals("null"))
size += addPaddingSize(OBJECT_HEADER);
return size;
}
private final class OffsetComparator implements Comparator<ObjectInfo>
{
@Override
public int compare( final ObjectInfo o1, final ObjectInfo o2 )
{
return o1.offset - o2.offset; //safe because offsets are small non-negative numbers
}
}
//sort all children by their offset
public void sort()
{
Collections.sort( children, new OffsetComparator() );
}
public void sum() {
if(children.size() == 0)
return;
int sum = 0;
for(ObjectInfo objectInfo : children) {
sum += objectInfo.length;
}
sum = sum + OBJECT_HEADER - children.get( children.size() - 1 ).length;
children.get( children.size() - 1 ).offset = sum;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
toStringHelper( sb, 0 );
return sb.toString();
}
private void toStringHelper( final StringBuilder sb, final int depth )
{
depth( sb, depth ).append("name=").append( name ).append(", type=").append( type )
.append( ", contents=").append( contents ).append(", offset=").append( offset )
.append(", length=").append( length );
if ( arraySize > 0 )
{
sb.append(", arrayBase=").append( arrayBase );
sb.append(", arrayElemSize=").append( arrayElementSize );
sb.append( ", arraySize=").append( arraySize );
}
for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
{
sb.append( '\n' );
child.toStringHelper(sb, depth + 1);
}
}
private StringBuilder depth( final StringBuilder sb, final int depth )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < depth; ++i )
sb.append( "\t");
return sb;
}
private long addPaddingSize(long size){
if(noPadding)
return size;
if(size % 8 != 0){
return (size / 8 + 1) * 8;
}
return size;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InterruptedException {
ObjectInfo res;
ObjectA objectA = new ObjectA();
// 用以测试reteined
ObjectC objectC = new ObjectC();
TestMemory testMemory = new TestMemory();
Object o = (Object)testMemory;
res = new ClassIntrospectorUnsafe().introspect( o );
System.out.println("mycode jdk8-" + res.getDeepSize());
res = new ClassIntrospectorCommon().introspect( o );
System.out.println("mycode jdk11-" + res.getDeepSize());
//System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(objectA).toPrintable());
System.out.println("RamUsageEstimator-" + RamUsageEstimator.humanSizeOf(o));
System.out.println("jdk8ObjectSizeCalculator-" + ObjectSizeCalculator.getObjectSize(o));
// dump
//Thread.sleep(1000000);
}
static ObjectB bb = new ObjectB();
private static class ObjectA {
private ObjectB objectB; // new ObjectB();
}
private static class ObjectB {
}
private static class TestMemory {
static byte b;
byte a ;
Integer integer = 127;
Integer integer2 = 127;
Integer i3;
Integer i4 = 128;
Byte aByte;
Integer i5 = 128;
String xx ;
String xxx = "chhhhhaaaaabbbbbccccc"; // "x" : 20(24)+(16+2)(24) 48
CC cc;
CC ccc = new CC();
byte [] bytes = new byte[0];
Integer [] ff = new Integer[1]; //16+1*4 20=24
Double aDouble;
Float aFloat = 4.3f;
Long [] longs = new Long[7];
long [] longs2 = new long[11];
String [] jfew = {"d", "", "dsfdfff"};
private static class CC {
String xx ;
String xxx = "chhhhhaaaaabbbbbccccc";
Integer i4 = 128;
Byte aByte;
Integer i5 = 128;
byte [] bytes = new byte[0];
Integer [] ff = new Integer[1];
}
}
private static class ObjectC {
private ObjectB objectB = bb;
}
private static class ClassIntrospectorCommon extends ClassIntrospector {
@Override
protected int getObjectRefSize() {
return 4;
}
@Override
protected int getArrayBaseOffset(Class c) {
return 16;
}
@Override
protected int getArrayIndexScale(Class type) {
if(type == byte[].class || type == boolean[].class)
return 1;
else if(type == char[].class || type == short[].class)
return 2;
else if(type == int[].class || type == float[].class)
return 4;
else if(type == double[].class || type == long[].class)
return 8;
else
return 4;
}
@Override
protected int getObjectFieldOffset(Field field) {
return -1;
}
@Override
protected void sort(ObjectInfo root) {
root.sum();
}
}
private static class ClassIntrospectorUnsafe extends ClassIntrospector {
private static Unsafe unsafe = null;
static {
try {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected int getObjectRefSize() {
return unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Object[].class);
}
@Override
protected int getArrayBaseOffset(Class type) {
return unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(type);
}
@Override
protected int getArrayIndexScale(Class type) {
return unsafe.arrayIndexScale(type);
}
@Override
protected int getObjectFieldOffset(Field field) {
return (int) unsafe.objectFieldOffset(field);
}
@Override
protected void sort(ClassIntrospector.ObjectInfo root) {
root.sort();
}
}
}
origin版本:
package test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
/**
* This class contains object info generated by ClassIntrospector tool
*/
public class ObjectInfo {
/** Field name */
public final String name;
/** Field type name */
public final String type;
/** Field data formatted as string */
public final String contents;
/** Field offset from the start of parent object */
public final int offset;
/** Memory occupied by this field */
public final int length;
/** Offset of the first cell in the array */
public final int arrayBase;
/** Size of a cell in the array */
public final int arrayElementSize;
/** Memory occupied by underlying array (shallow), if this is array type */
public final int arraySize;
/** This object fields */
public final List<ObjectInfo> children;
public ObjectInfo(String name, String type, String contents, int offset, int length, int arraySize,
int arrayBase, int arrayElementSize)
{
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.contents = contents;
this.offset = offset;
this.length = length;
this.arraySize = arraySize;
this.arrayBase = arrayBase;
this.arrayElementSize = arrayElementSize;
children = new ArrayList<ObjectInfo>( 1 );
}
public void addChild( final ObjectInfo info )
{
if ( info != null )
children.add( info );
}
/**
* Get the full amount of memory occupied by a given object. This value may be slightly less than
* an actual value because we don't worry about memory alignment - possible padding after the last object field.
*
* The result is equal to the last field offset + last field length + all array sizes + all child objects deep sizes
* @return Deep object size
*/
public long getDeepSize()
{
//return length + arraySize + getUnderlyingSize( arraySize != 0 );
return addPaddingSize(arraySize + getUnderlyingSize( arraySize != 0 ));
}
long size = 0;
private long getUnderlyingSize( final boolean isArray )
{
//long size = 0;
for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
size += child.arraySize + child.getUnderlyingSize( child.arraySize != 0 );
if ( !isArray && !children.isEmpty() ){
int tempSize = children.get( children.size() - 1 ).offset + children.get( children.size() - 1 ).length;
size += addPaddingSize(tempSize);
}
return size;
}
private static final class OffsetComparator implements Comparator<ObjectInfo>
{
@Override
public int compare( final ObjectInfo o1, final ObjectInfo o2 )
{
return o1.offset - o2.offset; //safe because offsets are small non-negative numbers
}
}
//sort all children by their offset
public void sort()
{
Collections.sort( children, new OffsetComparator() );
}
@Override
public String toString() {
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
toStringHelper( sb, 0 );
return sb.toString();
}
private void toStringHelper( final StringBuilder sb, final int depth )
{
depth( sb, depth ).append("name=").append( name ).append(", type=").append( type )
.append( ", contents=").append( contents ).append(", offset=").append( offset )
.append(", length=").append( length );
if ( arraySize > 0 )
{
sb.append(", arrayBase=").append( arrayBase );
sb.append(", arrayElemSize=").append( arrayElementSize );
sb.append( ", arraySize=").append( arraySize );
}
for ( final ObjectInfo child : children )
{
sb.append( '\n' );
child.toStringHelper(sb, depth + 1);
}
}
private StringBuilder depth( final StringBuilder sb, final int depth )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < depth; ++i )
sb.append( "\t");
return sb;
}
private long addPaddingSize(long size){
if(size % 8 != 0){
return (size / 8 + 1) * 8;
}
return size;
}
}
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
/**
* This class could be used for any object contents/memory layout printing.
*/
public class ClassIntrospector {
private static final Unsafe unsafe;
/** Size of any Object reference */
private static final int objectRefSize;
static {
try {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) field.get(null);
objectRefSize = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Object[].class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/** Sizes of all primitive values */
private static final Map<Class, Integer> primitiveSizes;
static {
primitiveSizes = new HashMap<Class, Integer>(10);
primitiveSizes.put(byte.class, 1);
primitiveSizes.put(char.class, 2);
primitiveSizes.put(int.class, 4);
primitiveSizes.put(long.class, 8);
primitiveSizes.put(float.class, 4);
primitiveSizes.put(double.class, 8);
primitiveSizes.put(boolean.class, 1);
}
/**
* Get object information for any Java object. Do not pass primitives to
* this method because they will boxed and the information you will get will
* be related to a boxed version of your value.
*
* @param obj
* Object to introspect
* @return Object info
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
public ObjectInfo introspect(final Object obj)
throws IllegalAccessException {
try {
return introspect(obj, null);
} finally { // clean visited cache before returning in order to make
// this object reusable
m_visited.clear();
}
}
// we need to keep track of already visited objects in order to support
// cycles in the object graphs
private IdentityHashMap<Object, Boolean> m_visited = new IdentityHashMap<Object, Boolean>(
100);
private ObjectInfo introspect(final Object obj, final Field fld)
throws IllegalAccessException {
// use Field type only if the field contains null. In this case we will
// at least know what's expected to be
// stored in this field. Otherwise, if a field has interface type, we
// won't see what's really stored in it.
// Besides, we should be careful about primitives, because they are
// passed as boxed values in this method
// (first arg is object) - for them we should still rely on the field
// type.
boolean isPrimitive = fld != null && fld.getType().isPrimitive();
boolean isRecursive = false; // will be set to true if we have already
// seen this object
if (!isPrimitive) {
if (m_visited.containsKey(obj))
isRecursive = true;
m_visited.put(obj, true);
}
final Class type = (fld == null || (obj != null && !isPrimitive)) ? obj
.getClass() : fld.getType();
int arraySize = 0;
int baseOffset = 0;
int indexScale = 0;
if (type.isArray() && obj != null) {
baseOffset = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(type);
indexScale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(type);
arraySize = baseOffset + indexScale * Array.getLength(obj);
}
final ObjectInfo root;
if (fld == null) {
root = new ObjectInfo("", type.getCanonicalName(), getContents(obj,
type), 0, getShallowSize(type), arraySize, baseOffset,
indexScale);
} else {
final int offset = (int) unsafe.objectFieldOffset(fld);
root = new ObjectInfo(fld.getName(), type.getCanonicalName(),
getContents(obj, type), offset, getShallowSize(type),
arraySize, baseOffset, indexScale);
}
if (!isRecursive && obj != null) {
if (isObjectArray(type)) {
// introspect object arrays
final Object[] ar = (Object[]) obj;
for (final Object item : ar)
if (item != null)
root.addChild(introspect(item, null));
} else {
for (final Field field : getAllFields(type)) {
if ((field.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) != 0) {
continue;
}
field.setAccessible(true);
root.addChild(introspect(field.get(obj), field));
}
}
}
root.sort(); // sort by offset
return root;
}
// get all fields for this class, including all superclasses fields
private static List<Field> getAllFields(final Class type) {
if (type.isPrimitive())
return Collections.emptyList();
Class cur = type;
final List<Field> res = new ArrayList<Field>(10);
while (true) {
Collections.addAll(res, cur.getDeclaredFields());
if (cur == Object.class)
break;
cur = cur.getSuperclass();
}
return res;
}
// check if it is an array of objects. I suspect there must be a more
// API-friendly way to make this check.
private static boolean isObjectArray(final Class type) {
if (!type.isArray())
return false;
if (type == byte[].class || type == boolean[].class
|| type == char[].class || type == short[].class
|| type == int[].class || type == long[].class
|| type == float[].class || type == double[].class)
return false;
return true;
}
// advanced toString logic
private static String getContents(final Object val, final Class type) {
if (val == null)
return "null";
if (type.isArray()) {
if (type == byte[].class)
return Arrays.toString((byte[]) val);
else if (type == boolean[].class)
return Arrays.toString((boolean[]) val);
else if (type == char[].class)
return Arrays.toString((char[]) val);
else if (type == short[].class)
return Arrays.toString((short[]) val);
else if (type == int[].class)
return Arrays.toString((int[]) val);
else if (type == long[].class)
return Arrays.toString((long[]) val);
else if (type == float[].class)
return Arrays.toString((float[]) val);
else if (type == double[].class)
return Arrays.toString((double[]) val);
else
return Arrays.toString((Object[]) val);
}
return val.toString();
}
// obtain a shallow size of a field of given class (primitive or object
// reference size)
private static int getShallowSize(final Class type) {
if (type.isPrimitive()) {
final Integer res = primitiveSizes.get(type);
return res != null ? res : 0;
} else
return objectRefSize;
}
}
public class ClassIntrospectorTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
final ClassIntrospector ci = new ClassIntrospector();
ObjectInfo res;
res = ci.introspect( new ObjectA() );
System.out.println( res.getDeepSize() );
}
private static class ObjectA {
String str; // 4
int i1; // 4
byte b1; // 1
byte b2; // 1
int i2; // 4
ObjectB obj; //4
byte b3; // 1
}
private static class ObjectB {
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号