(二十一)JSP基础
- 定义
JSP全称是Java Server Pages,它和servle技术一样,都是SUN公司定义的一种用于开发动态web资源的技术。
JSP这门技术的最大的特点在于,写jsp就像在写html,但它相比html而言,html只能为用户提供静态数据,而Jsp技术允许在页面中嵌套java代码,为用户提供动态数据。
- 原理
浏览器向服务器发请求,不管访问的是什么资源,其实都是在访问Servlet,所以当访问一个jsp页面时,其实也是在访问一个Servlet,服务器在执行jsp的时候,首先把jsp翻译 成一个Servlet,所以我们访问jsp时,其实不是在访问jsp,而是在访问jsp翻译过后的那个Servlet。
在jsp中编写的java代码和html代码都会被翻译到_jspService方法中去,在jsp中编写的java代码会原封不动地翻译成java代码,如<%out.print("Hello Jsp");%>直接翻译成out.print("Hello Jsp");,而HTML代码则会翻译成使用out.write("<html标签>\r\n");的形式输出到浏览器。在jsp页面中编写的html排版标签都是以out.write("<html标签>\r\n");的形式输出到浏览器,浏览器拿到html代码后才能够解析执行html代码。
-
Web服务器在调用jsp时,会给jsp提供一些什么java对象?
Web服务器在调用jsp时,会给Jsp提供如下的8个java对象
1 PageContext pageContext;
2 HttpSession session;
3 ServletContext application;
4 ServletConfig config;
5 JspWriter out;
6 Object page = this;
7 HttpServletRequest request,
8 HttpServletResponse response
其中page对象,request和response已经完成了实例化,而其它5个没有实例化的对象通过下面的方式实例化
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,null, true, 8192, true);
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
- jsp的应用场景
servlet只负责响应请求产生数据,并把数据通过转发技术带给jsp,数据的显示jsp来做。
-
初步应用:
1 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 2 <% 3 String path = request.getContextPath(); 4 String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; 5 %> 6 7 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> 8 <html> 9 <head> 10 <base href="<%=basePath%>"> 11 12 <title>First Jsp</title> 13 14 </head> 15 16 <body> 17 <h>我是时钟!!!!</h> 18 19 <%! void aaa(){ 20 System.out.print("function()"); 21 } 22 %> 23 24 <% 25 aaa(); 26 out.print("aaaa"); 27 %> 28 </body> 29 </html>
结果:
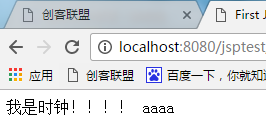
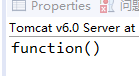 解析:aaa()方法里不能用out.print()输出,因为<%! %>声明的是成员方法和成员变量,out是在jspService()方法里声明的。
解析:aaa()方法里不能用out.print()输出,因为<%! %>声明的是成员方法和成员变量,out是在jspService()方法里声明的。
当我们通过浏览器访问index.jsp时,服务器首先将index.jsp翻译成一个index_jsp.class,在Tomcat服务器的C:\Users\Administrator\workspace\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core\tmp0\work\Catalina\localhost\jsptest\org\apache\jsp目录下可以看到index_jsp.class的源代码文件index_jsp.java,index_jsp.java的代码如下:
package org.apache.jsp;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
import java.util.*;
public final class index_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent {
void aaa(){
System.out.print("function()");
}
private static final JspFactory _jspxFactory = JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
private static java.util.List _jspx_dependants;
private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private org.apache.AnnotationProcessor _jsp_annotationprocessor;
public Object getDependants() {
return _jspx_dependants;
}
public void _jspInit() {
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
_jsp_annotationprocessor = (org.apache.AnnotationProcessor) getServletConfig().getServletContext().getAttribute(org.apache.AnnotationProcessor.class.getName());
}
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
public void _jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, ServletException {
PageContext pageContext = null;
HttpSession session = null;
ServletContext application = null;
ServletConfig config = null;
JspWriter out = null;
Object page = this;
JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write('\r');
out.write('\n');
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">\r\n");
out.write("<html>\r\n");
out.write(" <head>\r\n");
out.write(" <base href=\"");
out.print(basePath);
out.write("\">\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <title>First Jsp</title>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" </head>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" <body>\r\n");
out.write(" <h>我是时钟!!!!</h>\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" ");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(" \r\n");
out.write(" ");
aaa();
out.print("aaaa");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(" </body>\r\n");
out.write("</html>");
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (!(t instanceof SkipPageException)){
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try { out.clearBuffer(); } catch (java.io.IOException e) {}
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
else log(t.getMessage(), t);
}
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
}
- 在jsp中编写的java代码和html代码都会被翻译到_jspService方法中去,在jsp中编写的java代码会原封不动地翻译成java代码,如<%out.print("Hello Jsp");%>直接翻译成out.print("Hello Jsp");,而HTML代码则会翻译成使用out.write("<html标签>\r\n");的形式输出到浏览器。在jsp页面中编写的html排版标签都是以out.write("<html标签>\r\n");的形式输出到浏览器,浏览器拿到html代码后才能够解析执行html代码。
-
Web服务器在调用jsp时,会给jsp提供一些什么java对象?
查看_jspService方法可以看到,Web服务器在调用jsp时,会给Jsp提供如下的8个java对象
1 PageContext pageContext;
2 HttpSession session;
3 ServletContext application;
4 ServletConfig config;
5 JspWriter out;
6 Object page = this;
7 HttpServletRequest request,
8 HttpServletResponse response
其中page对象,request和response已经完成了实例化,而其它5个没有实例化的对象通过下面的方式实例化
1 pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,null, true, 8192, true);
2 application = pageContext.getServletContext();
3 config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
4 session = pageContext.getSession();
5 out = pageContext.getOut();
这8个java对象在Jsp页面中是可以直接使用的,如下所示:
1 <%
2 session.setAttribute("name", "session对象");//使用session对象,设置session对象的属性
3 out.print(session.getAttribute("name")+"<br/>");//获取session对象的属性
4 pageContext.setAttribute("name", "pageContext对象");//使用pageContext对象,设置pageContext对象的属性
5 out.print(pageContext.getAttribute("name")+"<br/>");//获取pageContext对象的属性
6 application.setAttribute("name", "application对象");//使用application对象,设置application对象的属性
7 out.print(application.getAttribute("name")+"<br/>");//获取application对象的属性
8 out.print("Hello Jsp"+"<br/>");//使用out对象
9 out.print("服务器调用index.jsp页面时翻译成的类的名字是:"+page.getClass()+"<br/>");//使用page对象
10 out.print("处理请求的Servlet的名字是:"+config.getServletName()+"<br/>");//使用config对象
11 out.print(response.getContentType()+"<br/>");//使用response对象
12 out.print(request.getContextPath()+"<br/>");//使用request对象
13 %>






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号