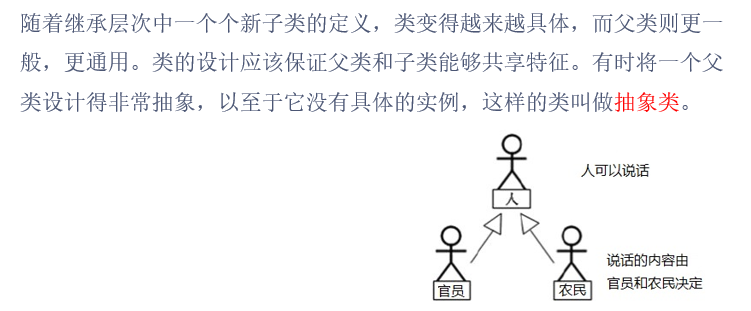
大数据--Java面向对象
abstract关键字的使用
1 /** 2 * 举例1: 3 * abstract class Account{ 4 * double balance; 5 * 6 * //存钱、取钱的方法 7 * } 8 * 9 * class SavingAccount extends Account{ 10 * 11 * } 12 * class CheckAccount extends Account{ 13 * 14 * } 15 * 16 * class Customer{ 17 * Account acct; 18 * public void setAccount(Account acct){ //Account acct = new SavingAccount(); 19 * this.acct = acct; 20 * } 21 * 22 * } 23 * 24 * 1. abstract:抽象的 25 * 2. 可以用来修饰:类、方法 26 * 27 * 3. abstract 来修饰类:抽象类 28 * > 此类就不可以实例化(不能创建对象) ---> 凡是类,内部都有构造器。 29 * -->此时抽象类提供构造器的意义:为了子类对象实例化进行对抽象父类中构造器的调用 30 * > 在开发中,针对于抽象类,我们一定会提供其子类。在实现过程中,创建子类的对象。 31 * 32 * 4. abstract 来修饰方法:抽象方法 33 * > 特点:抽象方法,没有方法体结构。 34 * > 抽象类中可以没有抽象方法;但是,抽象方法所在的类,一定是抽象类。 35 * > 如果抽象类的子类重写了父类中的所有的抽象方法,则此子类可以实例化。 36 * 如果抽象类的子类没有重写父类中所有的抽象方法,则此子类也必须声明为abstract的。 37 * 38 * 39 * 40 * @author shkstart 41 * @create 2020-07-10 9:03 42 */
代码举例
1 public class AbstractTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // Person p1 = new Person(); 5 // p1.eat(); 6 7 Student s1 = new Student(); 8 s1.eat(); 9 10 // Worker w1 = new Worker(); 11 // w1.eat(); 12 13 //提供抽象类的匿名子类的对象 14 Person p2 = new Person(){ 15 16 @Override 17 public void eat() { 18 System.out.println("人:吃饭"); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void walk() { 23 System.out.println("人:走路"); 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public void breath() { 28 System.out.println("人:呼吸"); 29 } 30 }; 31 p2.eat(); 32 33 //创建了BB的匿名子类的对象 34 BB b = new BB(){ 35 36 }; 37 } 38 } 39 40 abstract class BB{ 41 42 } 43 44 abstract class Creature{ 45 46 public abstract void breath(); 47 } 48 49 abstract class Person extends Creature{ 50 String name; 51 int age; 52 53 public Person(){ 54 55 } 56 57 public Person(String name,int age){ 58 this.name = name; 59 this.age = age; 60 } 61 //抽象方法 62 public abstract void eat(); 63 64 //抽象方法 65 public abstract void walk(); 66 } 67 68 class Student extends Person{ 69 String major; 70 71 public Student(){} 72 public Student(String name ,int age ,String major){ 73 super(name, age); 74 this.major = major; 75 } 76 77 public void eat(){ 78 System.out.println("学生:多吃有营养的食物"); 79 } 80 public void walk(){ 81 System.out.println("学生:背着书包上学"); 82 } 83 84 @Override 85 public void breath() { 86 System.out.println("学生应该呼吸新鲜的空气"); 87 } 88 } 89 90 abstract class Worker extends Person{ 91 String skill; 92 93 // public void eat(){ 94 // System.out.println("工人:在工厂吃盒饭"); 95 // } 96 // public void walk(){ 97 // System.out.println("工人:在车间行走"); 98 // } 99 }
举例
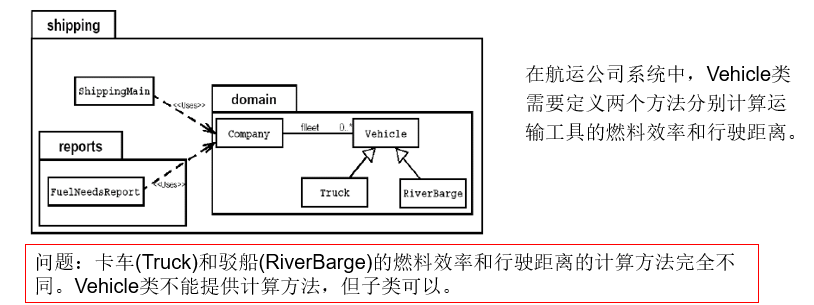
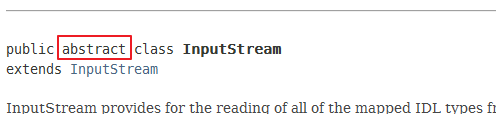
abstract的补充说明
1 /** 2 * 不能用abstract修饰变量、代码块、构造器; 3 * 4 * 不能用abstract修饰私有方法、静态方法、final的方法、final的类。 5 * 6 * @author shkstart 7 * @create 2020-07-10 10:11 8 */ 9 public abstract class AbstractTest1 { 10 11 // private abstract void method(); 12 // 13 // public static abstract void method1(); 14 15 } 16 17 class A extends AbstractTest1{ 18 19 }
练习1
1 public abstract class GeometricObject { 2 protected String color;//颜色 3 protected double weight;//权重 4 5 public GeometricObject(String color, double weight) { 6 this.color = color; 7 this.weight = weight; 8 } 9 10 public String getColor() { 11 return color; 12 } 13 14 public void setColor(String color) { 15 this.color = color; 16 } 17 18 public double getWeight() { 19 return weight; 20 } 21 22 public void setWeight(double weight) { 23 this.weight = weight; 24 } 25 26 //返回几何图形的面积 27 public abstract double findArea(); 28 }
练习2
1 package com.atguigu.exer1; 2 3 /** 4 * @author shkstart 5 * @create 2020-07-10 14:28 6 */ 7 public abstract class Employee {//员工类 8 private String name;//姓名 9 private int id;//编号 10 private double salary;//薪水 11 12 public Employee(String name, int id, double salary) {//构造方法 13 this.name = name; 14 this.id = id; 15 this.salary = salary; 16 } 17 18 public abstract void work();//工作方法 19 20 public String getName() { 21 return name; 22 } 23 24 public void setName(String name) { 25 this.name = name; 26 } 27 28 public int getId() { 29 return id; 30 } 31 32 public void setId(int id) { 33 this.id = id; 34 } 35 36 public double getSalary() { 37 return salary; 38 } 39 40 public void setSalary(double salary) { 41 this.salary = salary; 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public String toString() { 46 return 47 "name='" + name + '\'' + 48 ", id=" + id + 49 ", salary=" + salary; 50 } 51 } 52 53 54 package com.atguigu.exer1; 55 56 /** 57 * @author shkstart 58 * @create 2020-07-10 14:35 59 */ 60 public class CommonEmployee extends Employee{//普通员工类 61 62 public CommonEmployee(String name, int id, double salary) {//构造方法 63 super(name, id, salary);//调用父类的构造方法 64 } 65 66 @Override 67 public void work() {//工作方法 68 System.out.println("在工地搬砖"); 69 } 70 71 @Override 72 public String toString() { 73 return "CommonEmployee{ " + super.toString() +"}"; 74 } 75 } 76 77 package com.atguigu.exer1; 78 79 /** 80 * @author shkstart 81 * @create 2020-07-10 14:32 82 */ 83 public class Manager extends Employee { 84 85 private double bonus;//薪水 86 public Manager(String name, int id, double salary) {//构造方法 87 super(name, id, salary);//调用父类的构造方法 88 } 89 90 @Override 91 public void work() {//工作方法 92 System.out.println("在办公室工作"); 93 } 94 95 public double getBonus() { 96 return bonus; 97 } 98 99 public void setBonus(double bonus) { 100 this.bonus = bonus; 101 } 102 103 @Override 104 public String toString() { 105 return "Manager{" + 106 super.toString() + 107 ",bonus=" + bonus + 108 "} "; 109 } 110 } 111 112 package com.atguigu.exer1; 113 114 /** 115 * @author shkstart 116 * @create 2020-07-10 14:35 117 */ 118 public class EmployeeTest { 119 120 public static void main(String[] args) { 121 Manager manager = new Manager("马大爷", 1001, 5000); 122 manager.setBonus(10000); 123 System.out.println(manager); 124 manager.work(); 125 126 127 CommonEmployee commonEmployee = new CommonEmployee("杨鹏展", 1002, 500); 128 System.out.println(commonEmployee); 129 commonEmployee.work(); 130 131 } 132 }
练习3
1 package com.atguigu.exer2; 2 3 /** 4 * 编写工资系统,实现不同类型员工(多态)的按月发放工资。如果当月出现某个Employee对象的 5 * 生日,则将该雇员的工资增加100元。 6 * 7 * 实验说明: 8 * (1)定义一个Employee类,该类包含: 9 * private成员变量name,number,birthday,其中birthday 为MyDate类的对象; 10 * abstract方法earnings(); 11 * toString()方法输出对象的name,number和birthday。 12 * 13 * @author shkstart 14 * @create 2020-07-10 14:41 15 */ 16 public abstract class Employee { 17 private String name; 18 private int number; 19 private MyDate birthday; 20 21 public Employee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday) { 22 this.name = name; 23 this.number = number; 24 this.birthday = birthday; 25 } 26 27 public Employee() { 28 } 29 30 public String getName() { 31 return name; 32 } 33 34 public void setName(String name) { 35 this.name = name; 36 } 37 38 public int getNumber() { 39 return number; 40 } 41 42 public void setNumber(int number) { 43 this.number = number; 44 } 45 46 public MyDate getBirthday() { 47 return birthday; 48 } 49 50 public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) { 51 this.birthday = birthday; 52 } 53 54 //abstract方法earnings(); 55 public abstract double earnings(); 56 57 @Override 58 public String toString() { 59 return "name='" + name + '\'' + 60 ", number=" + number + 61 ", birthday=" + birthday.toDateString(); 62 } 63 }
1 package com.atguigu.exer2; 2 3 /** 4 * (2)MyDate类包含: 5 * private成员变量year,month,day ; 6 * toDateString()方法返回日期对应的字符串:xxxx年xx月xx日 7 * 8 * @author shkstart 9 * @create 2020-07-10 14:42 10 */ 11 public class MyDate { 12 private int year; 13 private int month; 14 private int day; 15 16 public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) { 17 this.year = year; 18 this.month = month; 19 this.day = day; 20 } 21 22 public MyDate() { 23 } 24 25 public int getYear() { 26 return year; 27 } 28 29 public void setYear(int year) { 30 this.year = year; 31 } 32 33 public int getMonth() { 34 return month; 35 } 36 37 public void setMonth(int month) { 38 this.month = month; 39 } 40 41 public int getDay() { 42 return day; 43 } 44 45 public void setDay(int day) { 46 this.day = day; 47 } 48 49 public String toDateString(){ 50 return year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日"; 51 } 52 }
1 package com.atguigu.exer2; 2 3 /** 4 * 定义SalariedEmployee类继承Employee类,实现按月计算工资的员工处理。 5 * 该类包括:private成员变量monthlySalary; 6 * 实现父类的抽象方法earnings(),该方法返回monthlySalary值; 7 * toString()方法输出员工类型信息及员工的name,number,birthday。 8 * 9 * 10 * @author shkstart 11 * @create 2020-07-10 14:46 12 */ 13 public class SalariedEmployee extends Employee { 14 15 private double monthlySalary;//月工资 16 17 public SalariedEmployee(double monthlySalary) { 18 this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary; 19 } 20 21 public SalariedEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double monthlySalary) { 22 super(name, number, birthday); 23 this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary; 24 } 25 26 public SalariedEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday) { 27 super(name, number, birthday); 28 } 29 30 public double getMonthlySalary() { 31 return monthlySalary; 32 } 33 34 public void setMonthlySalary(double monthlySalary) { 35 this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary; 36 } 37 38 @Override 39 public double earnings() { 40 return monthlySalary; 41 } 42 43 //toString()方法输出员工类型信息及员工的name,number,birthday 44 @Override 45 public String toString() { 46 return "SalariedEmployee{" + super.toString() + "}"; 47 } 48 }
1 package com.atguigu.exer2; 2 3 /** 4 * (4)参照SalariedEmployee类定义HourlyEmployee类,实现按小时计算工资的员工处理。 5 * 该类包括: 6 * private成员变量wage和hour; 7 * 实现父类的抽象方法earnings(),该方法返回wage*hour值; 8 * toString()方法输出员工类型信息及员工的name,number,birthday。 9 * 10 * 11 * @author shkstart 12 * @create 2020-07-10 14:50 13 */ 14 public class HourlyEmployee extends Employee { 15 16 private int hour;//小时数 17 private int wage;//单位小时的工资 18 19 20 @Override 21 public double earnings() { 22 return hour * wage; 23 } 24 25 public HourlyEmployee() { 26 } 27 28 public HourlyEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday) { 29 super(name, number, birthday); 30 } 31 32 public HourlyEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, int hour, int wage) { 33 super(name, number, birthday); 34 this.hour = hour; 35 this.wage = wage; 36 } 37 38 public int getHour() { 39 return hour; 40 } 41 42 public void setHour(int hour) { 43 this.hour = hour; 44 } 45 46 public int getWage() { 47 return wage; 48 } 49 50 public void setWage(int wage) { 51 this.wage = wage; 52 } 53 54 //toString()方法输出员工类型信息及员工的name,number,birthday。 55 @Override 56 public String toString() { 57 return "HourlyEmployee{" + super.toString() + "}"; 58 } 59 }
1 package com.atguigu.exer2; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 /** 6 * 定义PayrollSystem类,创建Employee变量数组并初始化,该数组存放各类雇员对象的引用。 7 * 利用循环结构遍历数组元素,输出各个对象的类型,name,number,birthday,以及该对象生日。 8 * 当键盘输入本月月份值时,如果本月是某个Employee对象的生日,还要输出增加工资信息。 9 * 10 * @author shkstart 11 * @create 2020-07-10 14:55 12 */ 13 public class PayrollSystem { 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 Employee[] emps = new Employee[2]; 16 17 emps[0] = new SalariedEmployee("杨超宇",1001,new MyDate(1994,4,02),20000); 18 emps[1] = new HourlyEmployee("闫宏浩",1002,new MyDate(1988,7,10),240,100); 19 20 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 21 System.out.println("请输入当前的月份:"); 22 int month = scanner.nextInt(); 23 24 for (int i = 0; i < emps.length; i++) { 25 System.out.println(emps[i]); 26 double monthlyMoney = emps[i].earnings(); 27 if(month == emps[i].getBirthday().getMonth()){ 28 monthlyMoney += 200; 29 } 30 System.out.println("月工资为:" + monthlyMoney); 31 } 32 } 33 }
1 /** 2 * interface关键字的使用 3 * 1. 我们使用interface来声明一个接口。 4 * 接口与类,是Java中并列关系的两个结构。 5 * 6 * 2. 接口,可以理解为特定功能的封装。通过类实现接口的方法,进而体现功能的扩充。同时,还不 7 * 影响此类单继承父类的情况。 8 * 而且,一个类可以实现多个接口。 9 * 3. 格式:class SubClass extends SuperClass implements 接口1,接口2,... 10 * 11 * 4. 关于接口的使用: 12 * JDK 7及之前:只能定义全局常量 和 抽象方法 13 * > 全局常量使用:public static final 修饰。也可以省略不写 14 * > 抽象方法使用:public abstract 修饰。也可以省略不写 15 * 16 * JDK 8: 增加了对静态方法、默认方法的定义。 17 * JDK 9: 增加了对私有方法的定义。 18 * 19 * 5. 实现类在实现了接口之后,必须要实现接口中的所有抽象方法,方可实例化。 20 * 否则,实现类如果没有实现接口中的所有抽象方法,则此实现类仍为抽象类。 21 * 22 * 6. 接口中不能定义构造器的。也就是说,接口不能实例化。 23 * 24 * 7. 类与接口之间是实现关系,而且是可以多实现的。 25 * 接口与接口之间是继承关系,而且是可以多继承的。 26 * 27 * 28 * 补充说明: 29 * 类继承类的关系:is - a 30 * 类实现接口的关系: like - a 31 * 类及其属性的关系: has - a 32 * 33 * @author shkstart 34 * @create 2020-07-10 10:30 35 */
代码演示
1 public class InterfaceTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println(Flyable.MAX_SPEED); 4 // Flyable.MAX_SPEED = 8000; 5 } 6 } 7 8 interface Flyable{ 9 //全局常量 10 public static final int MIN_SPEED = 1; 11 int MAX_SPEED = 7900; 12 //抽象方法 13 public abstract void fly(); 14 15 void stop(); 16 } 17 interface AttackAble{ 18 19 void attack();//攻击 20 21 } 22 23 abstract class Plane implements Flyable{ 24 25 @Override 26 public void fly() { 27 28 } 29 30 // @Override 31 // public void stop() { 32 // 33 // } 34 } 35 36 class Bullet implements Flyable,AttackAble{ 37 38 @Override 39 public void fly() { 40 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public void stop() { 45 46 } 47 48 @Override 49 public void attack() { 50 51 } 52 } 53 54 55 56 57 interface AA{ 58 59 } 60 61 interface CC{ 62 63 64 } 65 interface DD extends AA,CC{ 66 67 }
体会接口作为标准、规范的存在
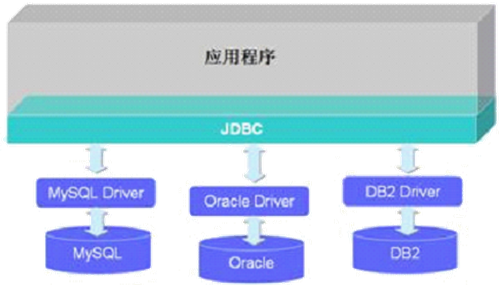
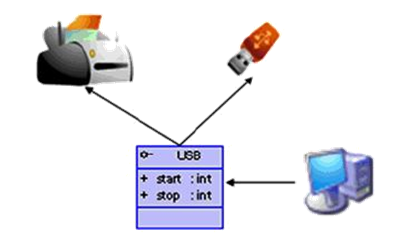
1 /** 2 * 1. 接口的本质是契约,标准,规范 3 * 4 * 2. 接口的使用:实现了多态性。 5 * 6 * 3. 匿名实现类的理解 7 * 8 * @author shkstart 9 * @create 2020-07-10 11:24 10 */ 11 public class USBTest { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 Computer com = new Computer(); 14 //1.创建了接口的实现类的对象printer 15 Printer printer = new Printer(); 16 com.transferData(printer); 17 18 //2.创建了接口的实现类的匿名对象 19 com.transferData(new Flash()); 20 21 //3. 创建接口的匿名实现类的对象 22 USB camera = new USB(){ 23 @Override 24 public void start() { 25 System.out.println("照相机开始工作"); 26 } 27 28 @Override 29 public void stop() { 30 System.out.println("照相机结束工作"); 31 } 32 }; 33 34 com.transferData(camera); 35 36 //4. 创建接口的匿名实现类的匿名对象 37 com.transferData(new USB(){ 38 @Override 39 public void start() { 40 System.out.println("mp3开始工作"); 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public void stop() { 45 System.out.println("mp3结束工作"); 46 } 47 }); 48 } 49 } 50 51 class Computer{ 52 53 public void transferData(USB usb){ //体现了多态性。 54 55 usb.start(); //虚方法调用 56 57 System.out.println("========具体的数据传输细节======="); 58 59 usb.stop(); 60 } 61 62 } 63 interface USB{ 64 void start(); 65 66 void stop(); 67 } 68 69 class Printer implements USB{ //打印机 70 71 @Override 72 public void start() { 73 System.out.println("打印机开始工作"); 74 } 75 76 @Override 77 public void stop() { 78 System.out.println("打印机结束工作"); 79 } 80 } 81 82 class Flash implements USB{//U盘 83 84 @Override 85 public void start() { 86 System.out.println("U盘开始工作"); 87 } 88 89 @Override 90 public void stop() { 91 System.out.println("U盘结束工作"); 92 } 93 }
java8中接口的新特性
1 package com.atguigu.java2; 2 3 import java.net.SocketTimeoutException; 4 5 /** 6 * @author shkstart 7 * @create 2020-07-10 15:37 8 */ 9 public interface CompareA { 10 11 public static void method1() { 12 System.out.println("CompareA:北京"); 13 } 14 15 public default void method2() { 16 System.out.println("CompareA:上海"); 17 18 } 19 20 default void method3() { 21 System.out.println("CompareA:广州"); 22 } 23 24 public default void method4(){ 25 System.out.println("CompareA:深圳"); 26 } 27 28 } 29 30 package com.atguigu.java2; 31 32 /** 33 * @author shkstart 34 * @create 2020-07-10 15:50 35 */ 36 public interface CompareB { 37 public default void method2() { 38 System.out.println("CompareB:上海"); 39 } 40 } 41 package com.atguigu.java2; 42 43 /** 44 * @author shkstart 45 * @create 2020-07-10 15:46 46 */ 47 public class SuperClass { 48 49 public void method4(){ 50 System.out.println("SuperClass:深圳"); 51 } 52 } 53 54 55 package com.atguigu.java2; 56 57 /** 58 * @author shkstart 59 * @create 2020-07-10 15:39 60 */ 61 public class SubClass extends SuperClass implements CompareA,CompareB { 62 public void method3() { 63 System.out.println("SubClass:广州"); 64 } 65 66 public void method4(){ 67 System.out.println("SubClass:深圳"); 68 } 69 70 public void method2() { 71 System.out.println("SubClass:上海"); 72 } 73 74 public void method(){ 75 //6. 如何在子类(或实现类)中调用父类或接口中被重写的方法 76 //调用父类的方法: 77 super.method4(); 78 //调用接口中的方法: 79 CompareA.super.method2(); 80 CompareB.super.method2(); 81 82 } 83 }
1 package com.atguigu.java2; 2 3 /** 4 * @author shkstart 5 * @create 2020-07-10 15:40 6 */ 7 public class SubClassTest { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 10 //1. 接口中静态方法的调用:只能使用接口本身来调用,其实现类不可以调用。 11 CompareA.method1(); 12 // SubClass.method1(); 13 14 //2. 可以通过实现类的对象,调用接口中的默认方法 15 SubClass sub1 = new SubClass(); 16 sub1.method2(); 17 //3.实现类可以重写接口中的默认方法。 18 sub1.method3(); 19 20 //4.如果子类(或实现类)继承的父类和实现的接口中声明了同名同参数的方法,则子类在没有 21 //重写此方法的情况下,默认调动的是父类中声明的方法。--->类优先原则 22 //补充:如果子类(或实现类)重写了上述的方法,则调用的就是自己重写的方法。 23 sub1.method4(); 24 25 //5.如果实现类实现了多个接口,且多个接口中声明了同名同参数的方法。则 26 //子类必须重写此方法。否则,编译不通过。 --->接口冲突。 27 sub1.method2(); 28 29 //6. 见SubClass内 30 sub1.method(); 31 } 32 }
1 /** 2 * 类的成员之五:内部类 3 * 4 * 1. 分类: 5 * 成员内部类:直接声明在外部类的内部。 6 * 7 * 局部内部类:声明在方法内、代码块内等的内部类。 8 * 9 * 2. 关于成员内部类的使用: 10 * 2.1 作为外部类的一个成员: 11 * > 可以使用4种不同的权限进行修饰 12 * > 可以使用static进行修饰 13 * > 可以在内部类中调用外部类的成员 14 * 15 * 2.2 作为类的: 16 * > 可以在内部声明属性、方法、构造器、代码块、内部类.... 17 * > 可以被abstract、final修饰。 18 * 19 * 20 * 21 * 3. 学习内部类需要掌握的三个知识点 22 * ① 如何创建成员内部类的对象 23 * ② 如何在成员内部类中调用外部类的属性、方法 24 * ③ 熟悉局部内部类的基本使用: 见 InnerClassTest1.java 25 * 26 * @author shkstart 27 * @create 2020-07-10 16:19 28 */
代码举例
外部类的使用
1 public class InnerClassTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //创建静态的成员内部类 4 Person.Bird bird = new Person.Bird(); 5 //创建非静态的成员内部类 6 Person p = new Person(); 7 Person.Dog dog = p.new Dog(); 8 9 dog.info(); 10 dog.show("旺财"); 11 } 12 } 13 14 15 class Person{ 16 String name = "小明"; 17 int age = 1; 18 //静态的成员内部类 19 static class Bird{ 20 21 } 22 //非静态的成员内部类 23 class Dog{ 24 String name = "小花"; 25 26 public void info(){ 27 //直接调用外部类的属性和方法 28 System.out.println(age); 29 Person.this.eat(); 30 } 31 32 public void show(String name){ 33 System.out.println(name); 34 System.out.println(this.name); 35 System.out.println(Person.this.name); 36 } 37 38 public void eat(){ 39 System.out.println("狗吃骨头"); 40 } 41 } 42 43 public void eat(){ 44 System.out.println("人吃饭"); 45 } 46 47 }
内部类的使用
1 package com.atguigu.java3; 2 3 /** 4 * 体会局部内部类的使用 5 * 6 * @author shkstart 7 * @create 2020-07-10 16:40 8 */ 9 public class InnerClassTest1 { 10 11 //此种方式使用局部内部类:不常见 12 public void method(){ 13 //声明一个局部内部类 14 class A{ 15 16 } 17 } 18 19 //常见如下的操作: 20 public Comparable getComparable(){ 21 //方式一: 22 /*//内部声明一个接口的实现类 23 class MyComparable implements Comparable{ 24 25 @Override 26 public int compareTo(Object o) { 27 return 0; 28 } 29 } 30 31 return new MyComparable();*/ 32 33 //方式二:创建了接口的匿名实现类的匿名对象 34 return new Comparable(){ 35 36 @Override 37 public int compareTo(Object o) { 38 return 0; 39 } 40 }; 41 } 42 43 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号