大数据—Java面向对象
1 * 类中方法的声明测试 2 * 1. 之前用过的一些方法: 3 * Scanner类的nextInt() \ next() 4 * Math类的random() \ sqrt(double d) 5 * Arrays类的equals(int[] arr1,int[] arr2) \ toString(int[] arr) \ sort(int[] arr) 6 * \ binarySearch(int[] arr,int value) 7 * 8 * 2. 类中方法声明的格式: 9 * 权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(形参列表){ 10 * 方法体 11 * } 12 * 说明:关于方法中的特殊关键字:static\final\abstract\...暂时先不考虑。 13 * 14 * 3. 方法声明的详细说明: 15 * 3.1 权限修饰符:指名当前方法被调用权限的大小。 16 * 涉及到的权限修饰符有:private 、 缺省 、 protected 、 public。 详细细节见《封装性》 17 * 目前,大家在声明方法时,默认使用public即可。 18 * 3.2 返回值类型 : 19 * > 可以分为:有具体的返回值类型 vs 没有返回值类型:void 20 * > 有具体的返回值类型,可以使用任何的变量类型。比如:基本数据类型、引用数据类型 21 * > 有具体的返回值类型的方法,在调用方法结束后,一定要返回满足要求的返回值类型的变量或常量 22 * 补充:return的使用: 23 * 在有具体返回值类型的方法中,一定需要使用“return + 变量/常量”的方法给方法返回指定的数据。 24 * 如果方法没有返回值类型,也可以使用"return;"结构,表示结束当前方法的执行。 25 * 26 * 3.3 方法名:属于标识符,命名时满足标识符命名的规则和规范。“见名知意” 27 * 3.4 形参列表: 28 * 格式:参数类型1 参数名1,参数类型2,参数名2,... 29 * 方法在声明时,不要给形参列表的变量赋值。当我们调用方法时,才给形参列表赋值:实参。 30 * 3.5 方法体:执行方法时,主要操作的逻辑。 31 32 * 4. 如何确定定义一个方法时,要不要声明返回值类型?要不要声明形参? 33 * ① 看题目要求。 34 * ② 具体问题具体分析。
代码演示
1 public class PersonTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Person p = new Person(); 4 p.printNumber(); 5 int hour = 8; 6 p.sleep(hour); 7 8 System.out.println("##############"); 9 p.eat(); 10 11 } 12 } 13 14 class Person{ 15 String name; 16 int age; 17 Account acct; 18 19 public void printNumber(){ 20 21 for(int i = 0;i < 100;i++){ 22 if(i == 40){ 23 return;//用于结束方法 24 } 25 System.out.println(i); 26 } 27 28 System.out.println("hello!"); 29 } 30 31 public Account getAccount(){ 32 boolean flag = true; 33 if(flag){ 34 return null; 35 } 36 37 return new Account(); 38 39 } 40 41 public int getValue(){ 42 return 1; 43 // return age; 44 } 45 46 public void sleep(int hour){ 47 System.out.println("昨天睡了" + hour + "小时"); 48 } 49 50 public void eat(){ 51 System.out.println("人需要吃饭,补充营养"); 52 System.out.println("name = " + name); 53 54 sleep(10); 55 56 // eat(); 57 58 } 59 60 } 61 62 class Account{//账户 63 64 }
补充说明
* 5. > 可以在当前类的方法中使用当前类定义的属性或其他的方法
* > 方法内不能定义新的方法。
课后练习
1 /** 2 * 2.利用面向对象的编程方法,设计类Circle计算圆的面积。 3 * 4 * @author shkstart 5 * @create 2020-07-01 11:37 6 */ 7 public class CircleTest { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Circle c1 = new Circle(); 11 12 c1.radius = 1.2; 13 //对应方式一 14 // double area = c1.findArea(); 15 // System.out.println("圆的半径为:" + c1.radius + ",面积为:" + area); 16 17 //对应方式二: 18 c1.findArea(); 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 class Circle{//圆 24 double radius;//半径 25 26 //求圆的面积的方法 27 //方式一: 28 // public double findArea(){ 29 // return Math.PI * radius * radius; 30 // } 31 //方式二: 32 public void findArea(){ 33 System.out.println(Math.PI * radius * radius); 34 } 35 36 //错误的: 37 // public double findArea(double r){ 38 // return Math.PI * r * r; 39 // } 40 41 42 }
1 * 1. 什么是方法的重载?同一个类中,相同方法名,不同参数列表的方法之间构成重载。 2 * 3 * “两同一不同”:同一个类,相同方法名;参数个数 或 参数类型不同 4 * 5 * 2. 方法的重载与权限修饰符、返回值类型、形参名没有关系!
代码演示
1 public class OverLoadTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 OverLoadTest test = new OverLoadTest(); 4 test.show(); 5 6 test.show(1,2); 7 } 8 9 public void show(){ 10 System.out.println("hello"); 11 } 12 public void show(int a){ 13 System.out.println("萨瓦迪卡"); 14 } 15 16 void show(String info){ 17 System.out.println(info); 18 } 19 public int show(int i,int j){ 20 return i + j; 21 } 22 private void show(int i,String info){ 23 24 } 25 public void show(String info,int i){ 26 27 } 28 // public void show(String info1,int j){ 29 // 30 // } 31 32 // public String show(String info,int i){ 33 // return info + i; 34 // } 35 36 37 38 }
重点
1 * 3. 我们在调用类中的方法时,是如何确定调用的是某一个确定的方法呢? 2 * 通过方法名确定 ---> 进一步通过形参列表确定
1 /** 2 * 可变形参方法的使用 3 * 4 * 1. JDK5.0新增的特性。 5 * 2. 格式为:形参类型 ... 形参名 6 * 3. 当调用可变形参的方法时,实参可以为0个,1个,2个,。。。 7 * 4. 可变形参的方法与方法同名的其他方法之间构成重载(排除第5点) 8 * 5. 一个类中,不能同时出现可变形参的方法 和 与其方法名相同且可变形参类型相同的数组的方法。 9 * 6. 如果一个方法中声明有可变形参,则可变形参一定声明在方法参数的最后。 10 * 7. 一个方法的形参中,最多声明一个可变个数的形参结构。 11 * 12 * 13 * @author shkstart 14 * @create 2020-07-01 14:59 15 */ 16 public class ArgsTest { 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 19 // int[] arr = new int[0]; 20 21 ArgsTest test = new ArgsTest(); 22 // test.show(); 23 // test.show("abc"); 24 test.show("abc","123","xyz"); 25 // 26 test.show(new String[]{"abc","def"}); 27 } 28 29 public void show(){ 30 System.out.println("show()"); 31 } 32 public void show(String s){ 33 System.out.println("show(String s)"); 34 } 35 36 public void show(int i){ 37 System.out.println("show(int i)"); 38 } 39 40 public void show(String ... info){ 41 System.out.println("show(String ... info)"); 42 for(int i = 0;i < info.length;i++){ 43 System.out.println(info[i]); 44 } 45 } 46 47 // public void show(String[] info){ 48 // for(int i = 0;i < info.length;i++){ 49 // System.out.println(info[i]); 50 // } 51 // } 52 53 //错误的 54 // public void show(String ... info,String i){ 55 // 56 // } 57 58 59 }
* 1. 如果传递的是基本数据类型的变量,则将变量本身保存的数据值传递过去
* 2. 如果传递的是引用数据类型的变量,则将变量本身保存的地址值传递过去
1 public class VariableTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int m = 10; 5 //对于基本数据类型变量来说: 6 int n = m; 7 n = 20; 8 System.out.println("m = " + m);//10 9 10 //对于引用数据类型变量来说: 11 Order o1 = new Order(); 12 o1.num = 10; 13 // 14 Order o2 = o1; 15 o2.num = 20; 16 17 System.out.println("o1.num = " + o1.num); 18 19 // 20 int[] array1 = new int[]{2,3,5,7,11}; 21 int[] array2 = array1; 22 array2[0] = 0; 23 System.out.println(array1[0]);//0 24 25 } 26 } 27 class Order{ 28 int num; 29 }
* 1. 形参:方法声明时,小括号内的参数。
* 实参:方法调用时,实际传递给形参的数据
*
* 2. 如果方法的形参是基本数据类型的变量,则将实参保存的数据值传递给形参变量。
* 如果方法的形参是引用数据类型的变量,则将实参保存的地址值传递给形参变量。
基本数据类型
1 public class ValueTransferTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int m = 10; 4 int n = 20; 5 6 System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n); 7 8 //交换两个变量的值 9 // int temp = m; 10 // m = n; 11 // n = temp; 12 ValueTransferTest test = new ValueTransferTest(); 13 test.swap(m,n); 14 15 System.out.println("m = " + m + ", n = " + n); 16 } 17 18 public void swap(int m ,int n){ 19 int temp = m; 20 m = n; 21 n = temp; 22 } 23 }
对应图示
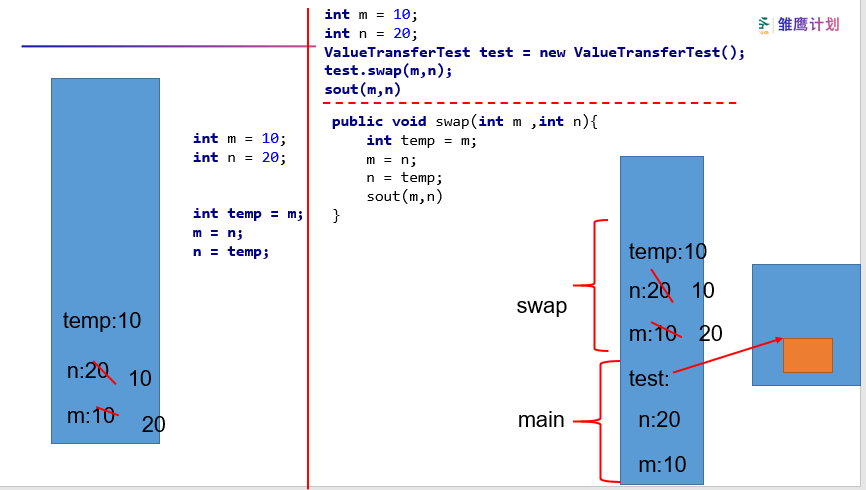
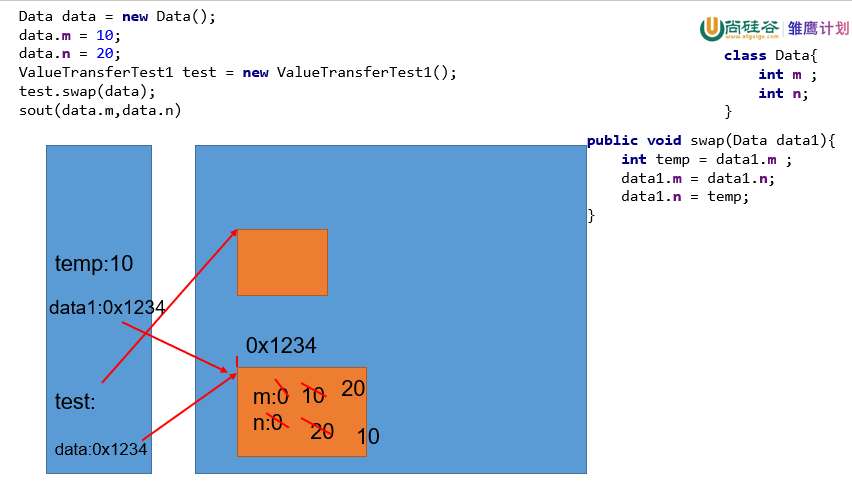
引用数据类型
1 public class ValueTransferTest1 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Data data = new Data(); 5 data.m = 10; 6 data.n = 20; 7 System.out.println("m = " + data.m +", n = " + data.n); 8 9 //交换的操作 10 ValueTransferTest1 test = new ValueTransferTest1(); 11 test.swap(data); 12 System.out.println("m = " + data.m +", n = " + data.n); 13 14 System.out.println(data);//com.atguigu.java1.Data@1540e19d 15 16 // User user = data; 17 } 18 19 public void swap(Data data1){ 20 int temp = data1.m ; 21 data1.m = data1.n; 22 data1.n = temp; 23 } 24 } 25 class Data{ 26 int m ; 27 int n; 28 } 29 30 class User{ 31 32 }
1 /** 2 * @author shkstart 3 * @create 2020-07-01 16:23 4 */ 5 public class ValueTransferTest2 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 int[] arr = new int[]{34, 4, 2, 6, 6, 4, 7, -87, 0, 55, 98}; 10 11 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 12 13 ValueTransferTest2 test = new ValueTransferTest2(); 14 test.sort(arr, "ascend"); 15 16 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 17 18 } 19 20 public void sort(int[] arr, String sortMethod) { 21 if ("ascend".equals(sortMethod)) {//从小到大 22 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { 23 for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { 24 if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { 25 //最初的写法:正确 26 // int temp = arr[j]; 27 // arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; 28 // arr[j + 1] = temp; 29 //错误的写法 30 // swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]); 31 //正确的写法 32 swap(arr,j,j+1); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 37 } else if ("descend".equals(sortMethod)) {//从大到小 38 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { 39 for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { 40 if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]) { 41 //最初的写法:正确 42 // int temp = arr[j]; 43 // arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; 44 // arr[j + 1] = temp; 45 //错误的写法 46 // swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]); 47 //正确的写法 48 swap(arr,j,j+1); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 } else { 53 System.out.println("排序方式错误!"); 54 } 55 } 56 57 // public void swap(int i,int j){ 58 // int temp = i; 59 // i = j; 60 // j = temp; 61 // } 62 63 public void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) { 64 int temp = arr[i]; 65 arr[i] = arr[j]; 66 arr[j] = temp; 67 } 68 }
1 public class TransferTest3 { 2 public static void main(String args[]) { 3 TransferTest3 test = new TransferTest3(); 4 test.first(); 5 } 6 public void first() { 7 int i = 5; 8 Value v = new Value(); 9 v.i = 25; 10 second(v, i); 11 System.out.println(v.i); 12 } 13 public void second(Value v, int i) { 14 i = 0; 15 v.i = 20; 16 Value val = new Value(); 17 v = val; 18 System.out.println(v.i + " " + i); 19 } 20 } 21 22 class Value { 23 int i = 15; 24 }
对应的图示:
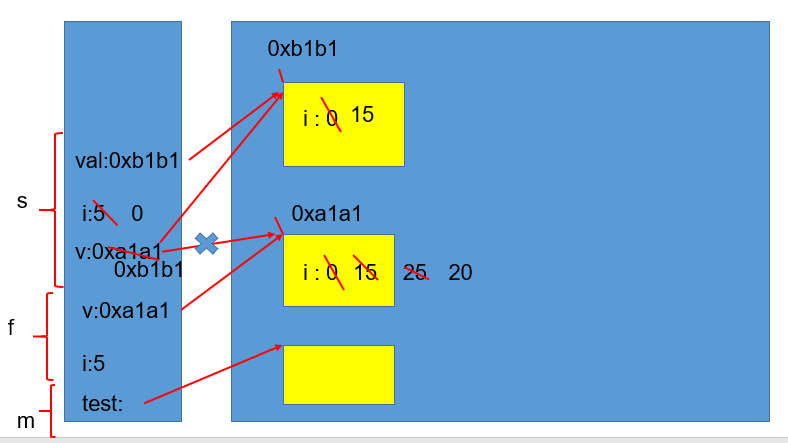
1 /** 2 * 关于面向对象内容中的NullPointerException的说明: 3 * 凡是引用数据类型的变量(对象、数组),如果取值为null时,通过此变量调用其内部结构的话,一定就是 4 * NullPointerException的异常。 5 * 6 * @author shkstart 7 * @create 2020-07-01 9:15 8 */ 9 public class NullPointerExceptionTest { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 User u1 = new User(); 12 // u1 = null; 13 // u1.name = "孔江江"; 14 // u1.show(); 15 System.out.println(u1.name); 16 // System.out.println(u1.name.toString()); 17 } 18 } 19 20 class User{ 21 String name; 22 int age; 23 public void show(){ 24 String str = null; 25 System.out.println("我是一个用户"); 26 } 27 }
1 /** 2 * 定义类Student,包含三个属性:学号number(int),年级state(int),成绩score(int)。 3 * 创建20个学生对象,学号为1到20,年级和成绩都由随机数确定。 4 * 问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。 5 * 问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息 6 * 7 * 提示: 8 * 1) 生成随机数:Math.random(),返回值类型double; 9 * 2) 四舍五入取整:Math.round(double d),返回值类型long。 10 * 11 * @author shkstart 12 * @create 2020-07-01 11:56 13 */ 14 public class StudentArrayTest { 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 int[] arr = new int[10]; 17 String[] arr1 = new String[10]; 18 19 // 创建20个学生对象 20 Student[] stus = new Student[20];//虚位以待 21 for (int i = 0; i < stus.length; i++) { 22 stus[i] = new Student(); 23 //给每一个学生的属性赋值 24 //学号 25 stus[i].number = i + 1; 26 //年级:1-6 27 stus[i].state = (int)(Math.random() * 6 + 1); 28 //成绩:0-100 29 stus[i].score = (int)(Math.random() * 101); 30 } 31 32 //问题一:打印出3年级(state值为3)的学生信息。 33 // for (int i = 0; i < stus.length; i++) { 34 // if(stus[i].state == 3){ 35 // stus[i].info(); 36 // } 37 // } 38 //问题二:使用冒泡排序按学生成绩排序,并遍历所有学生信息 39 for(int i = 0;i < stus.length - 1;i++){ 40 for(int j = 0;j < stus.length - 1 - i;j++){ 41 if(stus[j].score > stus[j + 1].score){ 42 Student temp = stus[j]; 43 stus[j] = stus[j + 1]; 44 stus[j + 1] = temp; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 for (int i = 0; i < stus.length; i++) { 50 stus[i].info(); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 class Student{ 56 int number;//学号 57 int state;//年级 58 int score;//成绩 59 60 public void info(){ 61 System.out.println("number : " + number + ", state : " + state + ", score : " + score); 62 } 63 }
对应的内存解析
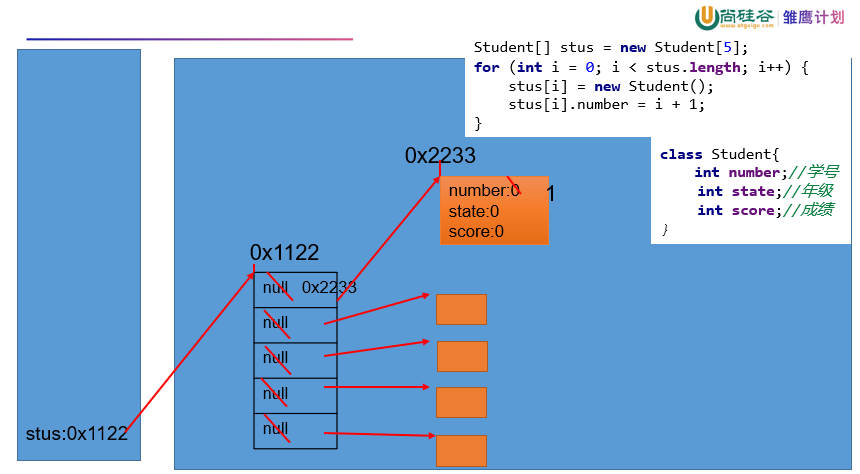



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号