1、Splay树------------------代码讲解都来自董老师,讲的非常非常清楚
复杂度都为O(NlogN)
特点:
(1)允许任意节点旋转到根(经常查询或使用这个数)
(2)当需要分裂和合并的时候非常方便
操作:
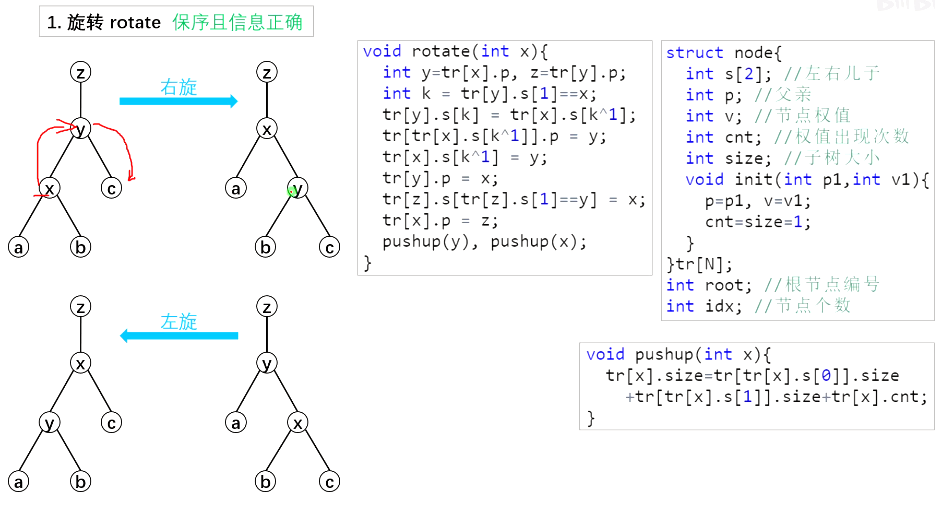
1、旋转:分为左右旋,改变三条边
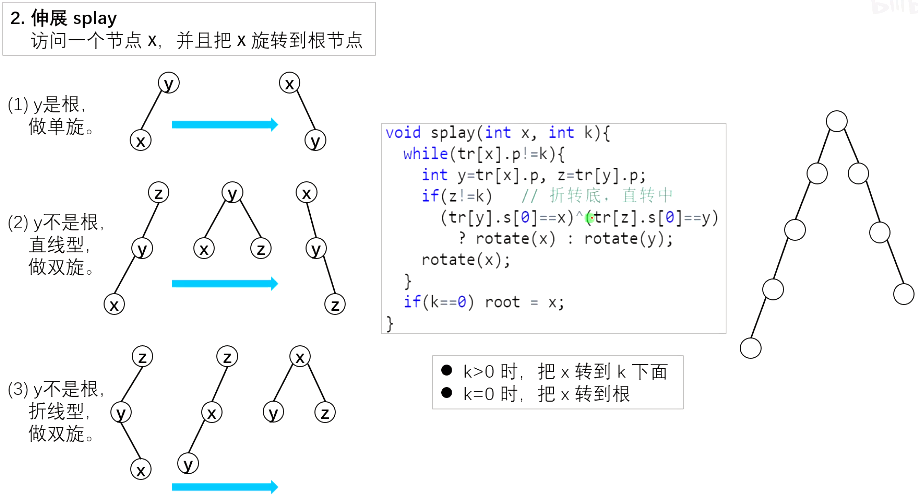
2、提根splay
根据x的位置,可以分为3种类型
1)x的父节点就是根,旋转一次就可以
2)x的父节点,的父节点,三点共线:先旋转x的父节点,在旋转x
3)x的父节点,的父节点,三点不共线:把x按不同的方向旋转2次
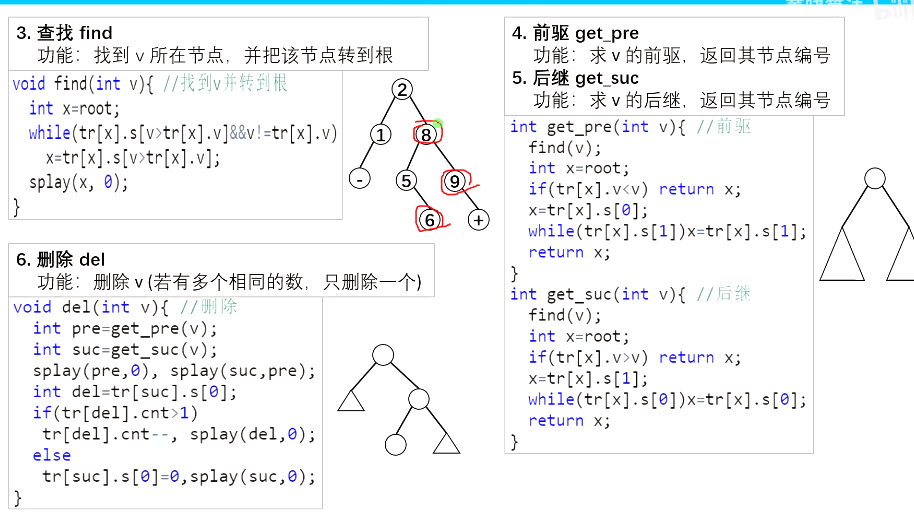
3、查找:找到某个节点,然后splay到根节点
4 and 5、查找某个节点的前驱、后继:把这个节点查找并旋转到根之后,沿着左节点一直往右走找前驱、或者右节点往左右找后继
6、删除:通过找到这个节点的前驱和后继,把他甩到根节点上去,当然要判断这个节点的出现次数做不同的操作
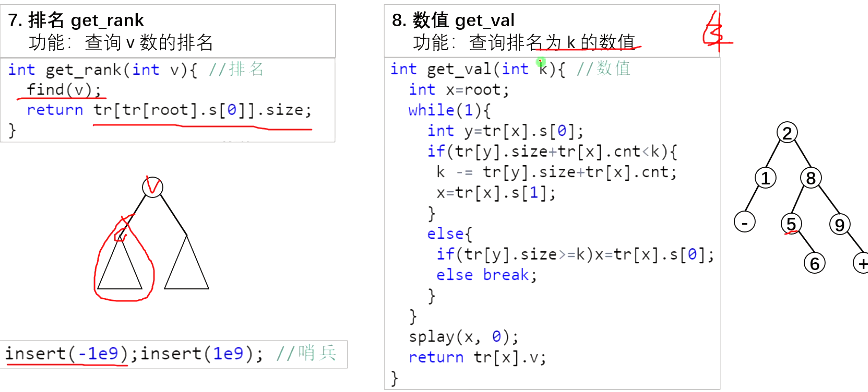
7、查询数v的排名
8、查询排名为k的节点
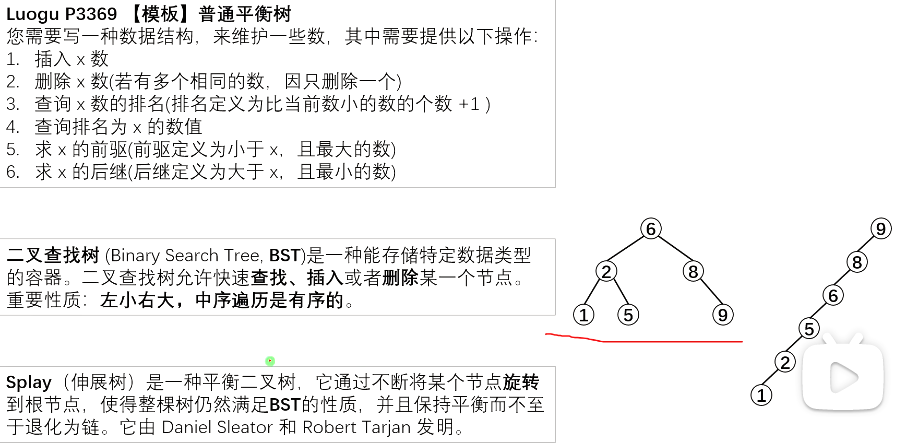
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3369 P3369 【模板】普通平衡树
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100010;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
typedef long long LL;
#define lson(x) tr[x].s[0]
#define rson(x) tr[x].s[1]
int n,m;
int root,idx;
struct node{
int s[2];
int p; //父亲
int v;//节点权值
int cnt;//权值出现次数
int siz;//子树大小
void init(int p1,int v1){
p=p1;v=v1;cnt=siz=1;
}
}tr[maxn];
void pushup(int x){
tr[x].siz=tr[lson(x)].siz+tr[rson(x)].siz+tr[x].cnt;
}
void rotat(int x){ //旋转
int y=tr[x].p,z=tr[y].p; //爸爸、祖父
int k=tr[y].s[1]==x;
tr[z].s[tr[z].s[1]==y]=x; //把儿子和祖父连起来
tr[x].p=z;
tr[y].s[k]=tr[x].s[k^1]; //把儿子的另一个节点换给爸爸
tr[tr[x].s[k^1]].p=y;
tr[x].s[k^1]=y; //把爸爸连到儿子底下
tr[y].p=x;
pushup(y); //先更新底下的
pushup(x); //在更新上面的
}
void splay(int x,int k){ //把x转到k底下,k=0就是转到根底下
while(tr[x].p!=k){
int y=tr[x].p,z=tr[y].p;
if(z!=k)
(lson(y)==x)^(lson(z)==y)? rotat(x):rotat(y); //直线型或弯曲
rotat(x);
}
if(k==0) root=x;
}
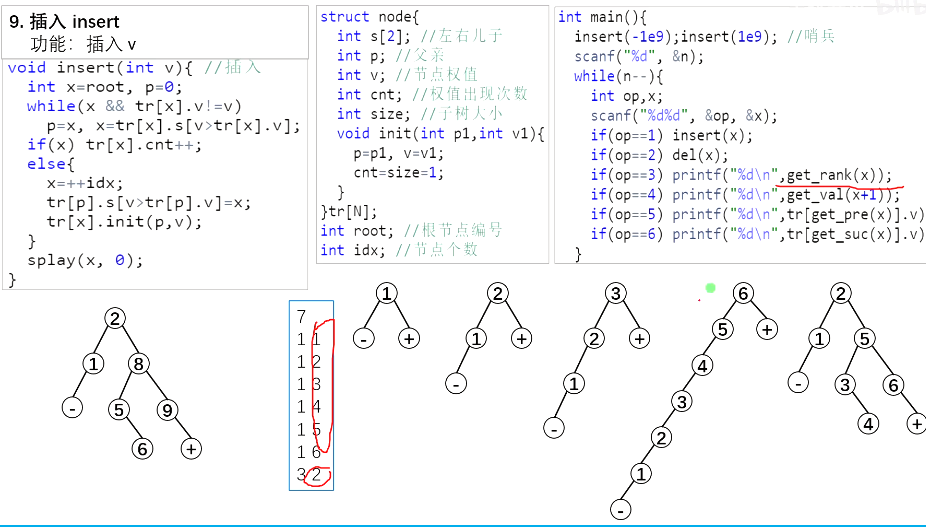
void inser(int v){ //插入
int x=root,p=0;
while(x&&tr[x].v!=v){
p=x;x=tr[x].s[v>tr[x].v];
}
if(x) tr[x].cnt++;
else{
x=++idx;
tr[p].s[v>tr[p].v]=x;
tr[x].init(p,v);
}
splay(x,0);
}
void findd(int v){ //找到v并转到根
int x=root;
while(tr[x].s[v>tr[x].v]&&v!=tr[x].v) x=tr[x].s[v>tr[x].v];
splay(x,0);
}
int getpre(int v){//前驱
findd(v);
int x=root;
if(tr[x].v<v) return x; //不存在也可以找到前驱
x=lson(x);
while(rson(x)) x=rson(x);
return x;
}
int getnex(int v){//后继
findd(v);
int x=root;
if(tr[x].v>v) return x;
x=rson(x);
while(lson(x)) x=lson(x);
return x;
}
void del(int v){ //删除
int pre=getpre(v);
int suc=getnex(v);
splay(pre,0);
splay(suc,pre); //把节点弄成叶子结点
int dell=tr[suc].s[0];
if(tr[dell].cnt>1) {
tr[dell].cnt--;
splay(dell,0);
}
else {
tr[suc].s[0]=0;
splay(suc,0);
}
}
int getrank(int v){ //排名
findd(v);
return tr[tr[root].s[0]].siz; //因为还有个负无穷,所以不加1
}
int getval(int k){ //排第k的
int x=root;
while(1){
int y=lson(x);
if(tr[y].siz+tr[x].cnt<k){
k-=tr[y].siz+tr[x].cnt;
x=rson(x); //要往右子树找
}
else if(tr[y].siz>=k) x=y;
else break; //找到了,因为左右子树都不能走了
}
splay(x,0);
return tr[x].v;
}
int main(){
inser(-INF);
inser(INF); //塞这个进去的目的是确保都找得到前驱、后继
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n--){
int op,x;
scanf("%d %d",&op,&x);
if(op==1) inser(x);
if(op==2) del(x);
if(op==3) printf("%d\n",getrank(x));
if(op==4) printf("%d\n",getval(x+1));
if(op==5) printf("%d\n",tr[getpre(x)].v);
if(op==6) printf("%d\n",tr[getnex(x)].v);
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1890(这个不是裸体,只是利用了旋转功能
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=101000;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
typedef long long LL;
//建树:
//用Splay旋转到根,其左子树的大小即排在左边的个数 ,输出就可以
//翻转左子树:用了线段树的思想:进行标记,而不是直接操作,等splay操作的时候在处理
//标记函数:updat_rev(),
//删除根:根据标记进行子树的翻转
int rev[maxn]; //标记i被翻转
int pre[maxn]; //i的父节点
int size[maxn]; //i的子树上节点的个数
int tree[maxn][2] ; //记录树,0左,1右
int root;
struct node{
int val,id;
bool operator < (const node &a)const{
if(val==a.val) return id<a.id;
else return val<a.val;
}
}nodes[maxn];
void push_up(int x){ //记录以x为根的子树包含的节点
size[x]=size[tree[x][0]]+size[tree[x][1]]+1;
}
//进行旋转
void updata_rev(int x){
if(!x) return; //NULL
swap(tree[x][0],tree[x][1]);
rev[x]^=1; //记录已经更新了
}
void pushdown(int x){
if(rev[x]){ //如果标记了,就旋转,一般用在 rotate和splay
updata_rev(tree[x][0]);
updata_rev(tree[x][1]);
rev[x]=0;
}
}
void Rotate(int x,int c){ //c=0左旋, c=1右旋
int y=pre[x];
pushdown(y);
pushdown(x); //先更新
//然后就是更改和更新信息
//1、改变父子结构
tree[y][!c]=tree[x][c]; //y的儿子
pre[tree[x][c]]=y; //x的儿子重新认爸爸
if(pre[y]){
tree[pre[y]][tree[pre[y]][1]==y]=x; //改变儿子,y的爸爸
//原来是哪边,现在还是哪边
}
pre[x]=pre[y]; //x也重新仁爸爸
tree[x][c]=y; //儿子
pre[y]=x;
push_up(y);
}
void splay(int x,int goal){ //把节点x作为goal的孩子,如果goal为0,那么就是旋转到跟
pushdown(x);
while(pre[x]!=goal){ //一直旋转,知道成为goal的孩子
//区分三种情况
if(pre[pre[x]]==goal){ //1、父节点是根,直接旋转一次就可以
pushdown(pre[x]);
pushdown(x);
Rotate(x,tree[pre[x]][0]==x); //左孩子:右旋,右孩子:左旋
}
else{ //父节点不是根
pushdown(pre[pre[x]]);
pushdown(pre[x]); //先更新
pushdown(x);
int y=pre[x];
int c=(tree[pre[y]][0]==y); //先判断父节点是左还是右孩子
if(tree[y][c]==x){ //三点不共线!!!! 把x按不同的方向旋转2次
Rotate(x,!c);
Rotate(x,c);
}
else{ //三点共线 先旋转x的父节点,在旋转x
Rotate(y,c);
Rotate(x,c);
}
}
}
push_up(x);
if(goal==0) root=x; //如果goal是0,那么就更新根节点
}
//接下来是删除节点操作
int get_max(int x){
pushdown(x); //更新
while(tree[x][1]) {
x=tree[x][1]; //找前驱:一直在做孩子的右节点找:BST
pushdown(x);
}
return x;
}
void del_node(){
//删除根节点(通过前面的操作,已经把需要删除的节点放在根节点了
if(tree[root][0]==0){ //没有左孩子:没有前驱,而且可以直接删掉
root=tree[root][1];
pre[root]=0;
}
else{
int m=get_max(tree[root][0]); //找到前驱
splay(m,root); //提根
tree[m][1]=tree[root][1]; //右孩子=另一棵树(相当于合并两棵树
pre[tree[root][1]]=m; //更新爸爸
root=m;
pre[root]=0;
push_up(root);
}
}
void newnode(int &x,int fa,int val){ //新建节点
x=val;
pre[x]=fa;
size[x]=1;
rev[x]=0;
tree[x][0]=tree[x][1]=0; //全体初始化
}
void buildtree(int &x,int l,int r,int fa){ //建树
if(l>r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>1; //中间开始建(平衡)
newnode(x,fa,mid); //先按照初始位置建树!!!
buildtree(tree[x][0],l,mid-1,x);
buildtree(tree[x][1],mid+1,r,x);
push_up(x);
}
void inti(int n){
root=0;
tree[root][0]=tree[root][1]=pre[root]=size[root]=0;
buildtree(root,1,n,0);
}
int main(){
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n){
inti(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&nodes[i].val);
nodes[i].id=i;
}
sort(nodes+1,nodes+1+n);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ //只进行n-1次操作
splay(nodes[i].id,0); //第i次旋转:把第i大的节点旋转到根
updata_rev(tree[root][0]); //左子树需要旋转
printf("%d ",i+size[tree[root][0]]);
//第i个被翻转的数的左边的数,就是左子树的个数
del_node();
}
printf("%d\n",n);
}
return 0;
}
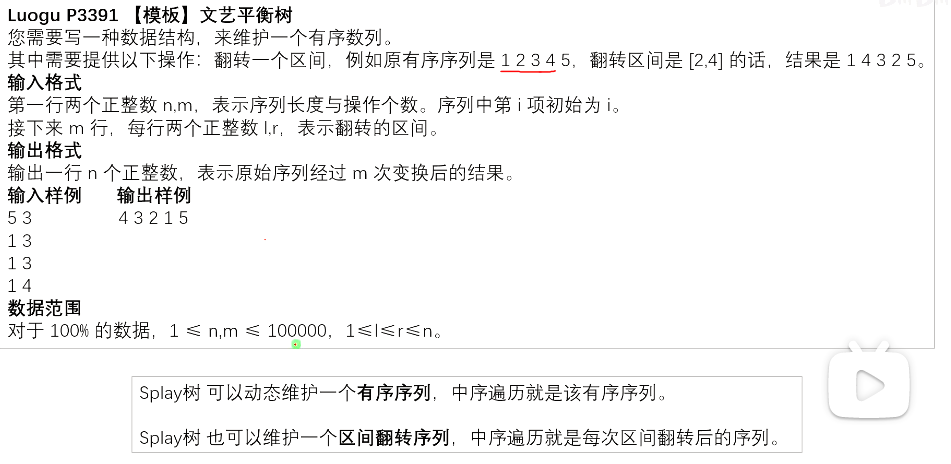
文艺平衡树
1、注意上传pushup和下传pushdown 的时机
2、夹挤区间的技巧
3、注意::::使用了线段树的技巧:tag标记,而且这个题目很合适,重复翻转等于不翻转,等到遇到了再去做翻转
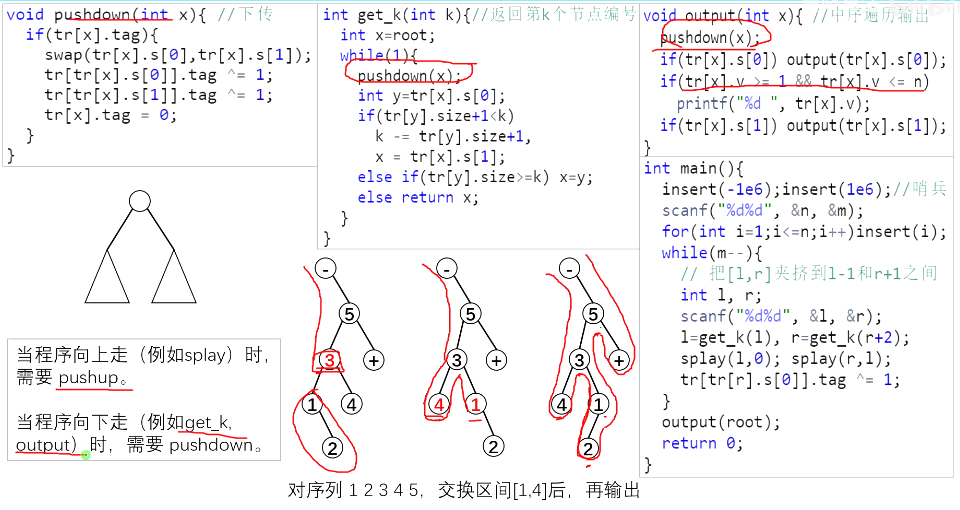
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3391 P3391 【模板】文艺平衡树
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100010;
const int INF=0x3fffffff;
int n,m;
struct node{
int s[2],p,v;
int siz,tag; //有了懒标记
void init(int p1,int v1){
p=p1;v=v1;siz=1;
}
}tr[maxn];
int root,idx;
void pushup(int x){
tr[x].siz=tr[tr[x].s[0]].siz+tr[tr[x].s[1]].siz+1;
}
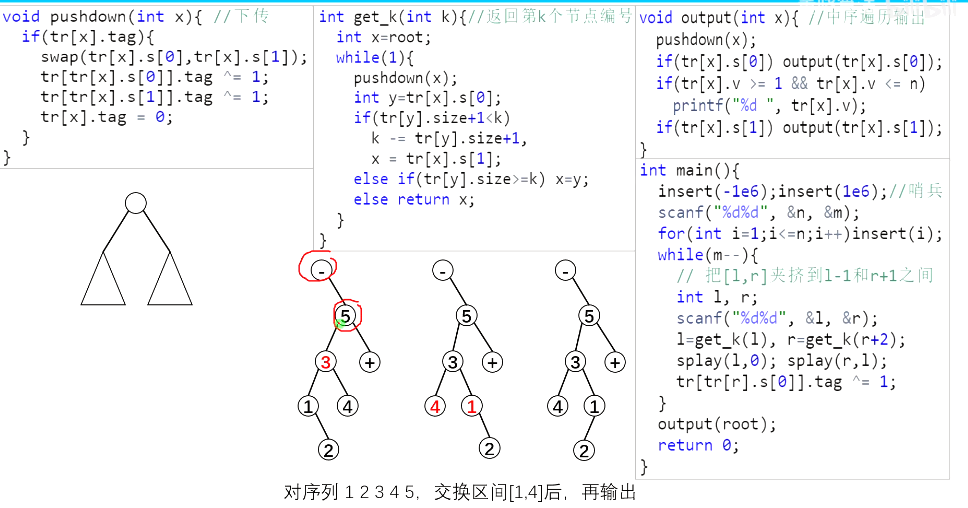
void pushdown(int x){
if(tr[x].tag){ //下传标记
swap(tr[x].s[0],tr[x].s[1]);
tr[tr[x].s[0]].tag^=1;
tr[tr[x].s[1]].tag^=1;
tr[x].tag=0;
}
}
void rotat(int x){
int y=tr[x].p, z=tr[y].p;
int k = tr[y].s[1]==x;
tr[z].s[tr[z].s[1]==y] =x;
tr[x].p = z;
tr[y].s[k] = tr[x].s[k^1];
tr[tr[x].s[k^1]].p = y;
tr[x].s[k^1] = y;
tr[y].p = x;
pushup(y);pushup(x);
}
void splay(int x,int k){
while(tr[x].p!=k){
int y=tr[x].p, z=tr[y].p;
if(z!=k) // 折转底,直转中
(tr[y].s[0]==x)^(tr[z].s[0]==y)? rotat(x) : rotat(y);
rotat(x);
}
if(k==0) root=x;
}
void inser(int v){
int x=root,p=0;
while(x){
p=x;
x=tr[x].s[v>tr[x].v];
}
x=++idx;
tr[p].s[v>tr[p].v]=x;
tr[x].init(p,v);
splay(x,0);
}
int get_k(int k){
int x=root;
while(1){
pushdown(x);
int y=tr[x].s[0];
if(tr[y].siz+1<k){
k -= tr[y].siz+1;
x = tr[x].s[1];
}
else if(tr[y].siz>=k) x=y;
else return x;
}
}
void output(int x){
pushdown(x); //需要往下更新的时候
if(tr[x].s[0]) output(tr[x].s[0]);
if(tr[x].v>=1&&tr[x].v<=n) printf("%d ",tr[x].v); //过滤最大值最小值
if(tr[x].s[1]) output(tr[x].s[1]);
}
int main(){
inser(-INF);
inser(INF);
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) inser(i);
while(m--){
int l,r;
scanf("%d %d",&l,&r);
l=get_k(l);
r=get_k(r+2); //因为有最小值,所有往右偏移1
splay(l,0);// 把[l,r]夹挤到l-1和r+1之间
splay(r,l);
tr[tr[r].s[0]].tag^=1;
}
output(root);
return 0;
}


 posted on
posted on

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号