03-树3 Tree Traversals Again
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
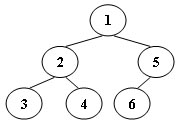
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
1 //Push的顺序是先序遍历的顺序,Pop的顺序的中序遍历的顺序 2 //三个序列中,知道中序和随意另一个,即可确定一棵树 3 #include<stdio.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #define null -1 6 7 struct SNode{ 8 int *Data; 9 int Top; 10 int Maxsize; 11 }; 12 typedef struct SNode *stack; 13 14 //建空堆栈 15 stack BuildStack(int n){ 16 stack S = (stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode)); 17 S->Data = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n); 18 S->Top = null; 19 S->Maxsize = n; 20 return S; 21 } 22 23 //判断堆栈是否满 24 bool IsFull(stack S){ 25 return S->Top == S->Maxsize-1; 26 } 27 28 //将元素入栈 29 void Push(stack S, int data){ 30 if(!IsFull(S)){ 31 S->Data[++(S->Top)] = data; 32 } 33 } 34 35 //将元素出栈,没有写判断栈空的函数,这题不会超出堆栈范围的,其实判断栈满的函数也不用写(当然这样的习惯不好🤐) 36 int Pop(stack S){ 37 return S->Data[(S->Top--)]; 38 } 39 40 //递归求后序序列 41 void Posttraversal(int *pre, int *mid, int root, int left, int right) { 42 //root是pre中根节点的位置,left、right是这段序列在mid中的范围 43 //这段写的很难看,可是我也不知道怎么改好一点,我知道了会回来改的🙃 44 if(left>right){ 45 return; 46 } 47 else if(left==right){ 48 printf("%d ", mid[left]); 49 return; 50 } 51 int i, L=0; 52 for(i=left; i<=right; i++){ //在mid中找到根的位置,以此确定左右子树 53 if(mid[i]==pre[root]){ 54 break; 55 } 56 } 57 L = i-left; //求出左子树的个数,用这个去求递归右子树时pre中根节点的位置,将左子树为空的情况考虑进去 58 Posttraversal(pre, mid, root+1, left, i-1); //递归遍历左子树 59 Posttraversal(pre, mid, root+L+1, i+1, right); //递归遍历右子树 60 if(root == 0) 61 printf("%d\n", pre[0]); //后序序列整棵树的根结点在最后,单独拿出来处理格式 62 else 63 printf("%d ", pre[root]); 64 } 65 66 int main( ){ 67 int N; 68 scanf("%d", &N); 69 int data, pre[N], mid[N]; 70 stack S = BuildStack(N); 71 for(int i=0, j=0, k=0; i<2*N; i++){ 72 char c, str[5]; 73 scanf("\n"); 74 for(int m=0; m<5; m++){ 75 scanf("%c", &c); 76 if(c=='\n') 77 break; 78 else str[m] = c; 79 } 80 if(str[1]=='u'){ 81 scanf("%d", &data); 82 pre[j++] = data; 83 Push(S, data); 84 } 85 else if(str[1]=='o'){ 86 mid[k++] = Pop(S); 87 } 88 } 89 // for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { 90 // printf("%d %d\n", pre[i], mid[i]); 91 // } 92 if(N==1) 93 printf("%d\n", pre[0]); 94 else 95 Posttraversal(pre, mid, 0, 0, N-1); 96 return 0; 97 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号