Apache Curator之InterProcessMutex源码分析(四)
上篇文章通过秒购的例子对InterProcessMutex锁有了初步认识,本文将通过对源码进行分析带你进入分布式锁的世界。
老规矩先上图,为了更清晰的了解获取锁,释放锁的过程,下图简化了一些细节,使整个流程更加通畅。
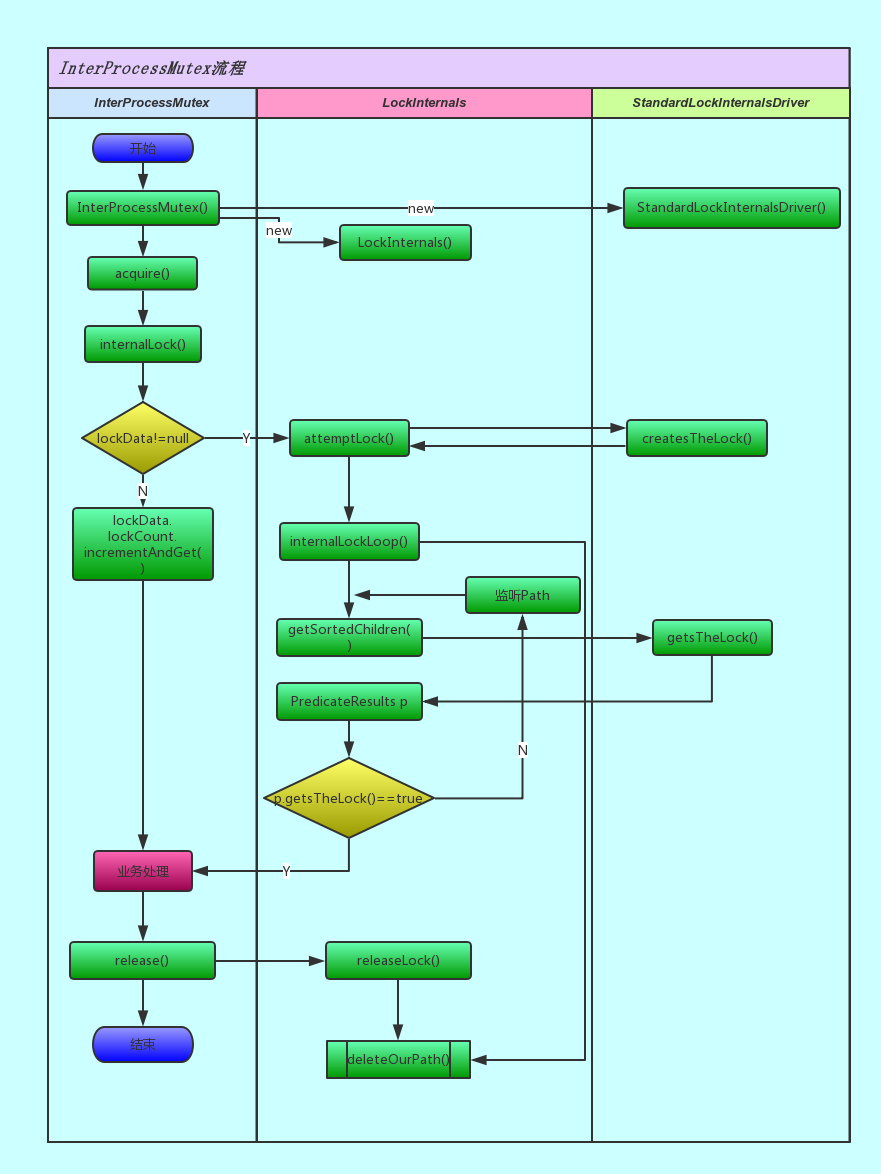
下面将逐个方法去分析。
InterProcessMutex.acquire()
1 @Override
//获得分布式锁,阻塞 2 public void acquire() throws Exception { 3 if (!internalLock(-1, null)) { 4 throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath); 5 } 6 } 7
//获得分布式锁,在指定的时间内阻塞,推荐使用 8 @Override 9 public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { 10 return internalLock(time, unit); 11 }
InterProcessMutex.internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit)
1 private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { 2 3 Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); 4 //获得当前线程的锁对象 5 LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread); 6 if (lockData != null) { 7 // re-entering
//如果锁不为空,当前线程已经获得锁,可重入锁,lockCount++ 8 lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet(); 9 return true; 10 } 11
//获取锁,返回锁的节点路径 12 String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes()); 13 if (lockPath != null) {
//将当前线程的锁对象信息保存起来 14 LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath); 15 threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData); 16 return true; 17 } 18 19 return false; 20 }
LockInternals.attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes)
1 String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception { 2 final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); 3 final Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null;//等待时间,毫秒 4 final byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes; 5 int retryCount = 0; 6 7 String ourPath = null; 8 boolean hasTheLock = false; 9 boolean isDone = false; 10 while (!isDone) { 11 isDone = true; 12 13 try {
//在当前path下创建临时有序节点 14 ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);
//判断是不是序号最小的节点,如果是返回true,否则阻塞等待 15 hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath); 16 } catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) { 17 if (client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper())) { 18 isDone = false; 19 } else { 20 throw e; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 if (hasTheLock) { 26 return ourPath; 27 } 28 29 return null; 30 }
StandardLockInternalsDriver.createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes)
1 @Override 2 public String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception { 3 String ourPath;
//在zookeeper的指定路径上,创建一个临时序列节点。只是纯粹的创建了一个节点,并不是说线程已经持有了锁。 4 if (lockNodeBytes != null) { 5 ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes); 6 } else { 7 ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path); 8 } 9 return ourPath; 10 }
LockInternals.internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath)
1 private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception { 2 boolean haveTheLock = false; 3 boolean doDelete = false; 4 try { 5 if (revocable.get() != null) { 6 client.getData().usingWatcher(revocableWatcher).forPath(ourPath); 7 } 8 9 while ((client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock) {
//获得所有子节点 10 List<String> children = getSortedChildren(); 11 String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash 12 13 PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
//判断是否是最小节点 14 if (predicateResults.getsTheLock()) { 15 haveTheLock = true; 16 } else { 17 String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch(); 18 //同步,是为了实现公平锁 19 synchronized (this) { 20 try {
//给比自己小的节点设置监听器 21 client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath); 22 if (millisToWait != null) { 23 millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis); 24 startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
//等待超时,超时删除临时节点,超时时间是acquire方法传入的参数 25 if (millisToWait <= 0) { 26 doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node 27 break; 28 } 29 //没有超时,继续等待 30 wait(millisToWait); 31 } else {
//如果等待时间==null,一直阻塞等待 32 wait(); 33 } 34 } catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) { 35 // it has been deleted (i.e. lock released). Try to acquire again 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 } catch (Exception e) { 41 ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e); 42 doDelete = true; 43 throw e; 44 } finally { 45 if (doDelete) { 46 deleteOurPath(ourPath);//如果如果抛出异常或超时,都会删除临时节点 47 } 48 } 49 return haveTheLock; 50 }
LockInternals.getSortedChildren()
1 List<String> getSortedChildren() throws Exception { 2 return getSortedChildren(client, basePath, lockName, driver); 3 } 4 5 public static List<String> getSortedChildren(CuratorFramework client, String basePath, final String lockName, final LockInternalsSorter sorter) throws Exception { 6 try {
//获得basePath下所有子节点,进行排序 7 List<String> children = client.getChildren().forPath(basePath); 8 List<String> sortedList = Lists.newArrayList(children); 9 Collections.sort(sortedList, new Comparator<String>() { 10 @Override 11 public int compare(String lhs, String rhs) { 12 return sorter.fixForSorting(lhs, lockName).compareTo(sorter.fixForSorting(rhs, lockName)); 13 } 14 }); 15 return sortedList; 16 } catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException ignore) { 17 return Collections.emptyList(); 18 } 19 }
StandardLockInternalsDriver.getsTheLock(CuratorFramework c, List<String> child, String nodeName, int max)
1 @Override 2 public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception { 3 int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName); 4 validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex); 5 6 boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases; 7 String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases); 8 9 return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock); 10 }
LockInternals.deleteOurPath(String ourPath)
1 private void deleteOurPath(String ourPath) throws Exception { 2 try { 3 client.delete().guaranteed().forPath(ourPath); 4 } catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) { 5 // ignore - already deleted (possibly expired session, etc.) 6 } 7 }
InterProcessMutex.release()
1 @Override 2 public void release() throws Exception { 3 /* 4 Note on concurrency: a given lockData instance 5 can be only acted on by a single thread so locking isn't necessary 6 */ 7 8 Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); 9 LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
//如果当前线程没有持有锁,不能释放 10 if (lockData == null) { 11 throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("You do not own the lock: " + basePath); 12 } 13
//重入锁计数减一,如果还大于0,不能释放。直到所有重入业务完成,计数为0才能释放 14 int newLockCount = lockData.lockCount.decrementAndGet(); 15 if (newLockCount > 0) { 16 return; 17 } 18 if (newLockCount < 0) { 19 throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("Lock count has gone negative for lock: " + basePath); 20 } 21 try { 22 internals.releaseLock(lockData.lockPath); 23 } finally { 24 threadData.remove(currentThread); 25 } 26 }
LockInternals.release()
1 final void releaseLock(String lockPath) throws Exception { 2 client.removeWatchers();//删除监听 3 revocable.set(null); 4 deleteOurPath(lockPath);//删除Path 5 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号