JDBC
1. 概述
以maven3.6.3+mysql5.7+8.0的驱动包演示(8.0兼容5.7 5.6)
五大步骤
2. 加载并注册驱动
String driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driver);
加载这个类就可以执行静态代码块进行注册:
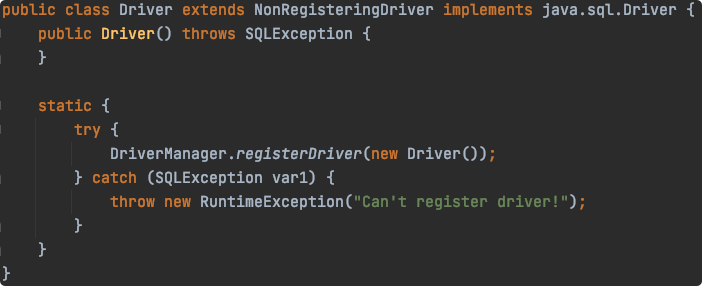
3. 获取数据库连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
4. 操作或访问数据库
Statement
通过调用 Connection 对象的 createStatement() 方法创建该对象。该对象用于执行静态的 SQL 语句,并且返回执行结果
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
Statement 接口中定义了下列方法用于执行 SQL 语句:
int excuteUpdate(String sql):执行更新操作INSERT、UPDATE、DELETEResultSet excuteQuery(String sql):执行查询操作SELECT
ResultSet
ResultSet 对象以逻辑表格的形式封装了执行数据库操作的结果集
ResultSet 对象维护了一个指向当前数据行的游标,初始的时候,游标在第一行之前
常用方法:
- boolean next():移动到下一行
- xxx getXxx(String columnLabel):
columnLabel使用SQL AS子句指定的列标签。如果未指定SQL AS子句,则标签是列名称 - xxx getXxx(int index) :索引从
1开始,针对结果集不针对表
查询示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/girls?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
String driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
// 1.加载驱动并注册
Class.forName(driver);
// 2.获取连接对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 3.1 编写sql
String sql = "select * from `student`";
// 3.2 获取Statement对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4.执行sql
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.print(resultSet.getInt("id"));
System.out.print("\t");
System.out.print(resultSet.getString("name"));
System.out.print("\t");
System.out.print(resultSet.getInt("age"));
System.out.print("\n");
}
// 5.释放资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
PrepatedStatement
可以通过调用 Connection 对象的 preparedStatement(String sql) 方法获取 PreparedStatement 对象。PreparedStatement接口是 Statement 的子接口,它表示一条预编译过的 SQL 语句
方法和Statement一样,只不过没有参数
PrepatedStatement可以解决的问题
- SQL拼接
- SQL注入
- 处理Blob类型数据
插入示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/girls?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai";
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
String driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
// 1.加载驱动并注册
Class.forName(driver);
// 2.获取连接对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 3.1 编写预sql
String sql = "insert into student(`name`,`age`) values(?,?)";
// 3.2 获取PreparedStatement对象
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 3.3 对?进行填充
preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五"); // 从1开始
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 17);
// 4.执行sql
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");
// 5.释放资源
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
CallableStatement
5. 释放资源
Connection、Statement、ResultSet都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接资源,使用后一定要关闭,可以在finally中关闭,按先获取后关闭的原则
事务
需要确保是同一个Connection才有效
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false); // 开启事务
connection.rollback();
connection.commit();
connection.setAutoCommit(true); // 关闭事务
批处理
如果要使用批处理功能,请再url中加参数rewriteBatchedStatements=true
常用方法:
- addBatch():添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或参数
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句;
- clearBatch():清空批处理包的语句
@Test
public void testJDBC3() throws Exception {
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement("insert into `student`(`name`, `age`) values(?,?)");
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
statement.setString(1, "张三" + i);
statement.setInt(2, i);
statement.addBatch();
if (i%1000==0) {
statement.executeBatch();
statement.clearBatch();
}
}
statement.executeBatch();
JDBCUtil.close(connection, null, statement);
}
Blob格式
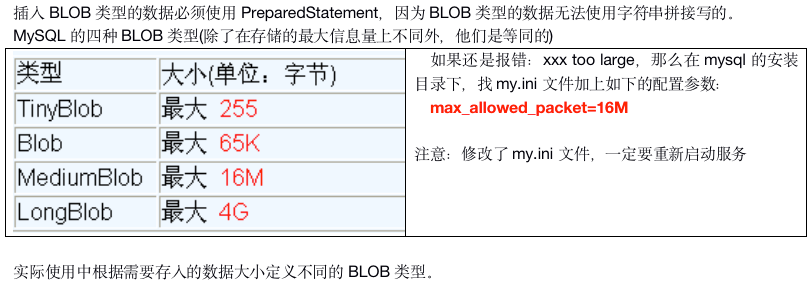
插入
@Test
public void testJDBC4() throws Exception {
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement("insert into `student`(`name`, `age`, `photo`) values(?,?,?)");
statement.setString(1, "张三");
statement.setInt(2, 14);//
// String filePath = JDBCTest.class.getResource("/").getPath() + "动漫头像.jpg";
// statement.setBlob(3, new FileInputStream(filePath));
statement.setBlob(3, getClass().getResourceAsStream("/动漫头像.jpg")); // 放在resources目录下
int i = statement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i > 0 ? "success" : "fail");
JDBCUtil.close(connection, null, statement);
}
读取
@Test
public void testJDBC5() throws Exception {
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from `student` where `id` = ?");
statement.setInt(1, 2);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
resultSet.next();
InputStream is = resultSet.getBinaryStream("photo");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/collin/IdeaProjects/Kuang/JavaWeb02-muti-maven/JDBC/src/test/resources/动漫头像1.jpg");
int len = 0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) {
fos.write(b, 0, len);
}
JDBCUtil.close(connection, resultSet, statement);
is.close();
fos.close();
}
封装JDBC
需要建立jdbc.properties文件和引入BeanUtils包
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
public class JDBCUtil {
private static String DRIVER;
private static String URL;
private static String USERNAME;
private static String PASSWORD;
private static Connection connection;
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(JDBCUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/jdbc.properties"));
DRIVER = properties.getProperty("driver");
URL = properties.getProperty("url");
USERNAME = properties.getProperty("username");
PASSWORD = properties.getProperty("password");
// 注册驱动
Class.forName(DRIVER);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
return DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
}
return connection;
}
public static void beginTransaction() throws SQLException {
getConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
}
public static void commitTransaction() throws SQLException {
getConnection().commit();
getConnection().setAutoCommit(true);
}
public static void rollBackTransaction() throws SQLException {
getConnection().rollback();
getConnection().setAutoCommit(true);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement) throws SQLException {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement) throws SQLException {
close(null, resultSet, statement);
}
public static void close(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
close(null, null, statement);
}
public static void closeConnection(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
close(connection, null, null);
}
public static int update(String sqlStr, Object... params) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
preparedStatement = getConnection().prepareStatement(sqlStr);
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
}
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw e;
} finally {
close(preparedStatement);
}
}
public static List<Map<String, Object>> queryForMap(String querySql, Object... params) throws SQLException {
List<Map<String, Object>> result = new ArrayList<>();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
preparedStatement = getConnection().prepareStatement(querySql);
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, params[i]); //Statement的参数下标从1
}
rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData resultMeta = rs.getMetaData(); // 获取结果集元信息
while (rs.next()) {
Map<String, Object> record = new HashMap<>();
// 把结果集的一条记录封装到Map中,key-字段名, value-字段值
for (int i = 1; i <= resultMeta.getColumnCount(); i++) {
record.put(resultMeta.getColumnName(i), rs.getObject(i));
}
result.add(record);
}
return result;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw e;
} finally {
close(rs, preparedStatement);
}
}
public static <T> List<T> queryForBean(String querySql, Class<T> beanClass, Object... params) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
preparedStatement = getConnection().prepareStatement(querySql);
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, params[i]); //Statement的参数下标从1
}
rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData resultMeta = rs.getMetaData();
while (rs.next()) { // 循环封装数据
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= resultMeta.getColumnCount(); i++) {
map.put(resultMeta.getColumnName(i).toLowerCase(), rs.getObject(i));
}
T obj = beanClass.newInstance();
BeanUtils.populate(obj, map); // 反射创建实体对象,需要引入BeanUtils包
result.add(obj);
}
return result;
} catch (SQLException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
throw e;
} finally {
close(rs, preparedStatement);
}
}
}
Druid数据源
当数据库访问结束后,程序还是像以前一样关闭数据库连接:conn.close();但conn.close()并没有关闭数据库的物理连接,它仅仅把数据库连接释放,归还给了数据库连接池。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>
Properties:
url=jdbc:mysql://47.106.64.90:3306/girls?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username=root
password=root
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initialSize=10
maxActive=20
maxWait=1000
filters=wall
@Test
public void testJDBC6() throws Exception {
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.load(getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection); // com.alibaba.druid.proxy.jdbc.ConnectionProxyImpl@5e57643e
}
DBUtils
Apache 组织提供的一个开源 JDBC工具类库,它是对JDBC的简单封装
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-dbutils/commons-dbutils -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
<version>1.7</version>
</dependency>
QueryRunner
该类封装了SQL的执行,是线程安全的
更新
插入
批处理
查询
@Test
public void testJDBC7() throws Exception {
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.load(getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(pro);
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(dataSource);
String sql = "select * from student";
List<Student> studentList = queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Student.class));
for (Student student : studentList) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
ResultSetHandler
该接口有如下常用实现类可以使用:
- BeanHandler:将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中
- BeanListHandler:将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个对应的JavaBean实例中,存放到List里
- ColumnListHandler:将结果集中某一列的数据存放到List中
- MapHandler:将结果集中的第一行数据封装到一个Map里,key是列名,value就是对应的值
- MapListHandler:将结果集中的每一行数据都封装到一个Map里,然后再存放到List
- ScalarHandler:查询单个值
本文来自博客园,作者:神乐g,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/shenleg/p/14267204.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号