他是SpringFramework创始人,interface21 CEO
Spring 的作者:Rod Johnson

一 :Spring的核心IOC和AOP(本处详解IOC)
IOC:控制反转:(Inverse Of Control)
控制反转(Inversion of Control),是一个重要的面向对象编程的法则来削减计算机程序的耦合问题,也是轻量级的Spring框架的核心,beans。
理解一:将组件对象(业务对象)的控制权从代码本身转移到外部容器()
理解二:IOC控制反转:说的是创建对象实例的控制权从代码控制剥离到IOC容器(spring容器)控制,实际就是你在xml文件控制,侧重于原理。
AOP:面向切面编程; (Aspect Oritend Programming)
提及一下对象间的关系把

案例:
1.下载jar包:
pom文件 节点:
<!--单元测试的依赖 ctrl+shif+/-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--Spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--aop使用的jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId> org.aspectj</groupId >
<artifactId> aspectjweaver</artifactId >
<version> 1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2.一个普通类
package cn.dawn.day01.service;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class DawnService {
private String workInfo;
private Integer age;
public void work(){
System.out.println("info"+workInfo);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DawnService{" +
"workInfo='" + workInfo + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getWorkInfo() {
return workInfo;
}
public void setWorkInfo(String workInfo) {
this.workInfo = workInfo;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3.大配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="service" class="cn.dawn.day01.service.DawnService">
<property name="workInfo" value="第一个Spring程序"></property>
<property name="age" value="12"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4.单测
package cn.dawn.day01;
import cn.dawn.day01.service.DawnService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class test20180303 {
@Test
/*入门案例*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext01.xml");
DawnService service = (DawnService) context.getBean("service");
System.out.println(service);
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
在没有new 的情况下,就拿到了他的实现
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext01.xml");
这行如果不理解我就放一张图
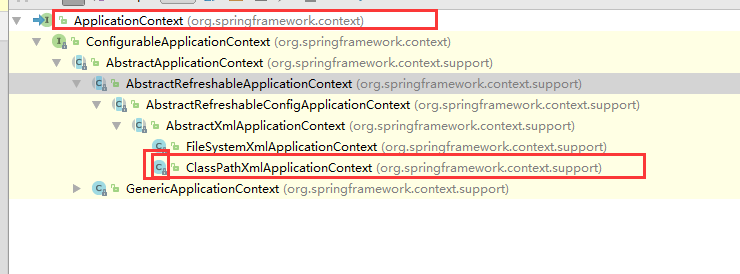
看到ClassPathXmlApplicationContext前面的C吗?在结合这个,表示他是ApplicationContext的实现类,里氏替换,为什么不可以用
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
还记得我提了的IOC吗?我不是说他把创建对象的控制权交给了Spring容器嘛,那么容器在什么时候创建对象呢,是getBean的时候吗?还是。。。。(小实验)
在刚才的那个普通类中,添加一个构造,如下
public DawnService(){
System.out.println("========================DawnService创建=======================");
}
单测方法如下
@Test
/*入门案例*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext01.xml");
/*DawnService service = (DawnService) context.getBean("service");
System.out.println(service);*/
}
运行结果:
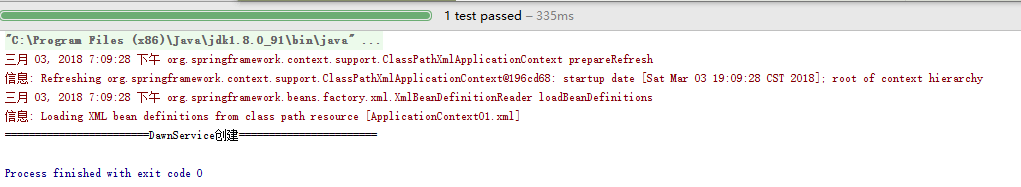
结论就是Spring容器初始化的时候就把bean中的对象实例化了
二 DI:依赖注入
域属性注入:java类
package cn.dawn.day02di;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
//小汽车类
public class Car {
private String type;
private String color;
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
package cn.dawn.day02di;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
//学生类
public class Stu {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Car car;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
}
配置xml中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--汽车-->
<bean id="car" class="cn.dawn.day02di.Car">
<property name="type" value="奔驰"></property>
<property name="color" value="红色"></property>
</bean>
<!--学生-->
<!--这儿的小汽车不能用value,用ref引用上面的那个汽车car-->
<bean id="stu" class="cn.dawn.day02di.Stu">
<property name="name" value="孟六"></property>
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
<property name="car" ref="car"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类
package cn.dawn.day02;
import cn.dawn.day02di.Stu;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class test20180303 {
@Test
/*域属性*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day02.xml");
Stu stu = (Stu) context.getBean("stu");
System.out.println(stu.getName()+"开"+stu.getCar().getType());
}
}
打印机案例先把架构放上来
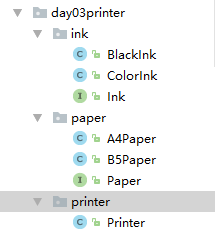
把里面每个类中的代码(code) 放上来
package cn.dawn.day03printer.ink;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*墨盒*/
public interface Ink {
public String getInkColor();
}
package cn.dawn.day03printer.ink;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*彩色墨盒*/
public class ColorInk implements Ink {
public String getInkColor() {
return "彩色墨盒";
}
}
package cn.dawn.day03printer.ink;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*黑白墨盒*/
public class BlackInk implements Ink {
public String getInkColor() {
return "黑白墨盒";
}
}
package cn.dawn.day03printer.paper;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*纸张*/
public interface Paper {
public String getPagerSize();
}
package cn.dawn.day03printer.paper;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*B5纸张*/
public class B5Paper implements Paper{
public String getPagerSize() {
return "B5纸";
}
}
package cn.dawn.day03printer.paper;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*A4纸张*/
public class A4Paper implements Paper {
public String getPagerSize() {
return "A4纸";
}
}
package cn.dawn.day03printer.printer;
import cn.dawn.day03printer.ink.Ink;
import cn.dawn.day03printer.paper.Paper;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
/*打印机*/
public class Printer {
/*墨盒*/
private Ink ink;
/*纸张*/
private Paper paper;
/*打印方法*/
public void print(){
System.out.println("我们的喷墨打印机,用"+ink.getInkColor()+"和"+paper.getPagerSize()+"打印出了------》我爱Spring");
}
public Ink getInk() {
return ink;
}
public void setInk(Ink ink) {
this.ink = ink;
}
public Paper getPaper() {
return paper;
}
public void setPaper(Paper paper) {
this.paper = paper;
}
}
配置文件中:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--墨盒-->
<bean id="ink" class="cn.dawn.day03printer.ink.ColorInk"></bean>
<!--纸张-->
<bean id="paper" class="cn.dawn.day03printer.paper.A4Paper"></bean>
<!--打印机-->
<bean id="printer" class="cn.dawn.day03printer.printer.Printer">
<property name="ink" ref="ink"></property>
<property name="paper" ref="paper"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
单测方法
package cn.dawn.day03;
import cn.dawn.day02di.Stu;
import cn.dawn.day03printer.printer.Printer;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class test20180303 {
@Test
/*打印机案例*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day03.xml");
Printer printer = (Printer) context.getBean("printer");
printer.print();
}
}
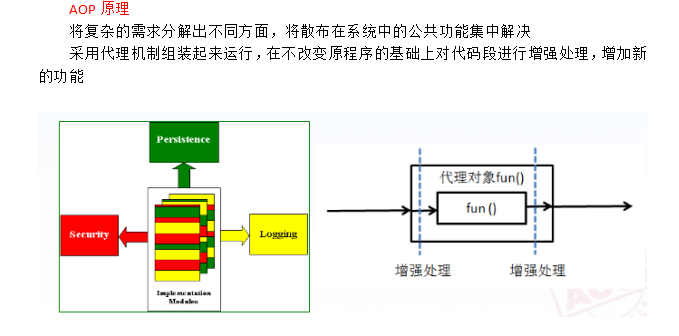
三 AOP:面向切面编程
AOP的主要作用:
加上双引号的意思:所谓业务,是指他的核心,各行业中需要处理的核心事务,核心啊
AOP的思想:

AOP的原理
入门案例:DAO层(一个接口,一个他的实现类,模拟操作修改数据库)
package cn.dawn.day04aop.dao;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
/*dao层接口*/
public interface IHellowDAO {
/*aop入门案例*/
public void doSome();
}
package cn.dawn.day04aop.dao.impl;
import cn.dawn.day04aop.dao.IHellowDAO;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
/*dao层实现类*/
public class HellowDAOImpl implements IHellowDAO{
public void doSome() {
System.out.println("数据已经成功写入到DB");
}
}
service层
package cn.dawn.day04aop.service;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
/*service层接口*/
public interface IHellowService {
/*aop入门案例*/
public void doSome();
}
package cn.dawn.day04aop.service.impl;
import cn.dawn.day04aop.dao.IHellowDAO;
import cn.dawn.day04aop.service.IHellowService;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
/*service层实现类 */
public class HellowServiceImpl implements IHellowService {
IHellowDAO dao;
public void doSome() {
dao.doSome();
}
public IHellowDAO getDao() {
return dao;
}
public void setDao(IHellowDAO dao) {
this.dao = dao;
}
}
新开多的一层,叫aop层,他就存放了增强的操作(也就是交叉业务,例如日志记录等),此处我放了俩个类,一个执行前置增强,一个后置增强
需要实现MethodBeforeAdvice
package cn.dawn.day04aop.aop;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
/*前置增强*/
public class LoggerBefore implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("日志记录");
}
}
需要实现AfterReturningAdvice
package cn.dawn.day04aop.aop;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
/*后置增强*/
public class LoggerAfter implements AfterReturningAdvice {
public void afterReturning(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, Object o1) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("===============after==================");
}
}
大配置xml文件(idea)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--aop入门案例起-->
<!--dao-->
<bean id="dao" class="cn.dawn.day04aop.dao.impl.HellowDAOImpl"></bean>
<!--service-->
<bean id="service" class="cn.dawn.day04aop.service.impl.HellowServiceImpl">
<property name="dao" ref="dao"></property>
</bean>
<!--通知-->
<bean id="afterAdvice" class="cn.dawn.day04aop.aop.LoggerAfter"></bean>
<bean id="beforeAdvice" class="cn.dawn.day04aop.aop.LoggerBefore"></bean>
<!--aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--切点-->
<aop:pointcut id="mypointcut" expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))"></aop:pointcut>
<!--<aop:pointcut id="mypointcut" expression="execution(public void cn.dawn.day04aop.service.IHellowService.doSome())"></aop:pointcut>-->
<!--<aop:pointcut id="mypointcut" expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))">-->
<!--顾问,织入-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"></aop:advisor>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
<!--aop入门案例完毕-->
</beans>
切点pointcut:expression的属性:

单测方法:
package cn.dawn.day04aop;
import cn.dawn.day03printer.printer.Printer;
import cn.dawn.day04aop.service.IHellowService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class test20180305 {
@Test
/*aop入门案例*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day04aop.xml");
IHellowService service = (IHellowService) context.getBean("service");
service.doSome();
}
}
结果如下:
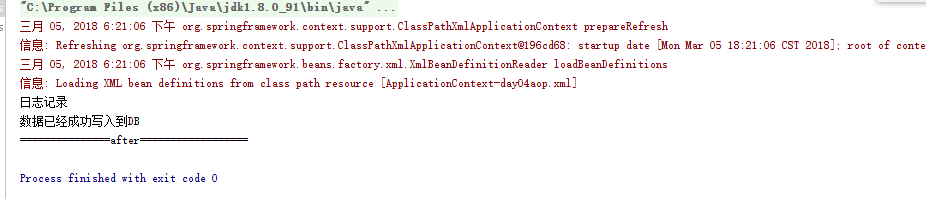
四 DI和IOC相比,DI更偏向于实现
在实体类中(有俩个实体类,我做了关联关系)
package cn.dawn.day05diup;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
public class Car {
private String color;
private String type;
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
package cn.dawn.day05diup;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
//student类
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Car car;
//带参构造
public Student(String name, Integer age, Car car) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.car = car;
}
//无参构造
public Student() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
}
在大配置xml文件中
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd ">
<bean id="car" class="cn.dawn.day05diup.Car">
<property name="color" value="黑色"></property>
<property name="type" value="奥迪"></property>
</bean>
<!--di构造注入--> index索引从0开始,对应的是那个带参构造的index
<!--<bean id="student" class="cn.dawn.day05diup.Student">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="孟六"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="20"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2" ref="car"></constructor-arg>
</bean>-->
<!--p命名注入-->
<bean id="student" class="cn.dawn.day05diup.Student" p:name="孟小六" p:age="8" p:car-ref="car"></bean>
</beans>
单测方法:
@Test
/*diP命名注入*/
public void t02(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day05diup.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("学生"+student.getName()+"开着"+student.getCar().getColor()+"的"+student.getCar().getType());
}
@Test
/*di构造注入*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day05diup.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("学生"+student.getName()+"开着"+student.getCar().getColor()+"的"+student.getCar().getType());
}
集合注入:数组,List,Set,Map,Properties
实体类
package cn.dawn.day05diup;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
public class MyCollection {
private String[] array;
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String,String> map;
private Properties properties;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyCollection{" +
"array=" + Arrays.toString(array) +
", list=" + list +
", set=" + set +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
public String[] getArray() {
return array;
}
public void setArray(String[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
}
大配置中的bean节点
<!--di的集合注入-->
<bean id="mycollection" class="cn.dawn.day05diup.MyCollection">
<!--数组注入-->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>孟六</value>
<value>孟六十六</value>
<value>孟六百六十六</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--list集合注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>奥迪</value>
<value>奥小迪</value>
<value>奥迪迪</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--set集合注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>set1</value>
<value>set2</value>
<value>set3</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--map集合注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="姓名">
<value>孟五</value>
</entry>
<entry key="年龄">
<value>555</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--properties-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="key1">v1</prop>
<prop key="key2">v2</prop>
<prop key="key3">v3</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
单测
@Test
/*di集合注入*/
public void t03(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day05diup.xml");
MyCollection mycollection = (MyCollection) context.getBean("mycollection");
System.out.println(mycollection);
}
五 自动注入byType方式
案例:实体类:
package cn.dawn.day06autowire;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
//student类
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Car car;
//带参构造
public Student(String name, Integer age, Car car) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.car = car;
}
//无参构造
public Student() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
}
package cn.dawn.day06autowire;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
public class Car {
private String color;
private String type;
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
在配置文件中:
<!--汽车的bean-->
<bean id="car" class="cn.dawn.day06autowire.Car">
<property name="color" value="黑色"></property>
<property name="type" value="奥迪"></property>
</bean>
<!--装配student-->
<bean id="student" class="cn.dawn.day06autowire.Student" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="马云"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
单测方法:
package cn.dawn.day06autowire;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class test20180306 {
@Test
/*di自动注入*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day06autowire.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("学生"+student.getName()+"开着"+student.getCar().getColor()+"的"+student.getCar().getType());
}
}
单测后可以正常执行
byType结果是不行的,它报错的解释是,不能自动装配,所以,引出了另外一种方式byName
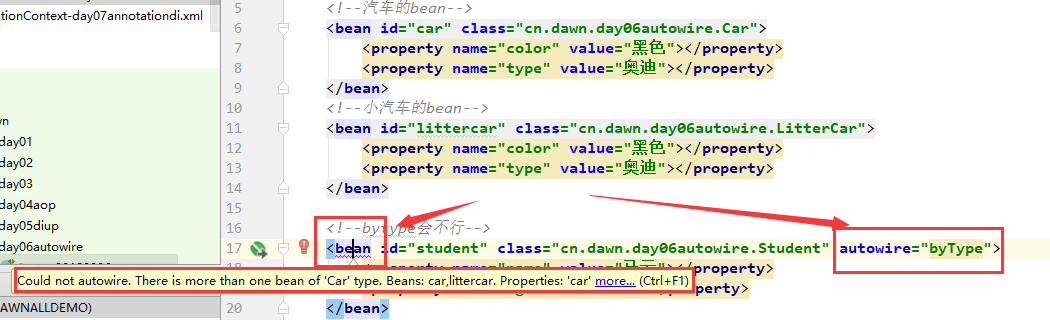
byName
<bean id="student" class="cn.dawn.day06autowire.Student" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="马云"></property>
<property name="age" value="18"></property>
</bean>
六 注解:@Overried,@Test,@Param等等
Car类
package cn.dawn.day07annotationdi; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5. */ @Component("car")//表示这个生成的对象的名字 public class Car { @Value("红色") //用于给属性赋值 private String color; @Value("奔驰") private String type; public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } }
Student类
package cn.dawn.day07annotationdi;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/5.
*/
//student类
@Component("student")
public class Student {
@Value("老胡小子,呵呵哒")
private String name;
@Value("20")
private Integer age;
//@Resource(name = "car")//这个是javax包下的注解,可以实现域属性的注入,下面还有一种方式,@AutoWried
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "car") //这两行联用,他是spring的注解,也是给对象的域属性赋值
private Car car;
//带参构造
public Student(String name, Integer age, Car car) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.car = car;
}
//无参构造
public Student() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
}
在Spring的配置文件中首先导入命名空间context,和注解的包扫描器(idea)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.dawn.day07annotationdi">
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
单测方法
package cn.dawn.day07annotationdi;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Dawn on 2018/3/3.
*/
public class test20180306 {
@Test
/*di注解注入*/
public void t01(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ApplicationContext-day07annotationdi.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("学生"+student.getName()+"开"+student.getCar().getType());
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号