Spark SQL
一、Spark SQL概述
Spark SQL是Apache Spark的一个模块,用于处理结构化数据,包括以下几方面:
1、SQL查询与Spark程序进行混合
Spark SQL允许你使用使用SQL或者DataFrame的API在Spark程序中进行结构化数据查询,你可以使用Java、Python、Scala和R语言进行操作。
results = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM people") names = results.map(lambda p: p.name)
2、数据源连接
DataFrame和SQL提供了通用的连接各种数据源的方法,包括Hive,Avro,Parquet,ORC,JSON和JDBC。甚至可以不同源的数据进行连接。
spark.read.json("s3n://...").registerTempTable("json") results = spark.sql( """SELECT * FROM people JOIN json ...""")
3、Hive集成
Spark SQL支持HiveSQL的语法,同时也支持Hive SerDes和UDFs,允许你连接已经存在的数据仓库。也就是说Spark SQL可以使用现有的Hive Metastore,SerDes和UDF。
4、通过JDBC或ODBC
服务模式为商业智能工具提供了行业标准的JDBC或ODBC连接。然后可以通过其它的如BI工具进行数据查询。
所以Spark SQL不仅仅只是操作SQL,它强调的是结构化数据,而非单纯的SQL,它还有一些其它操作数据的方式:
- SQL
- DataFrame API
- Dataset API
二、Spark SQL架构
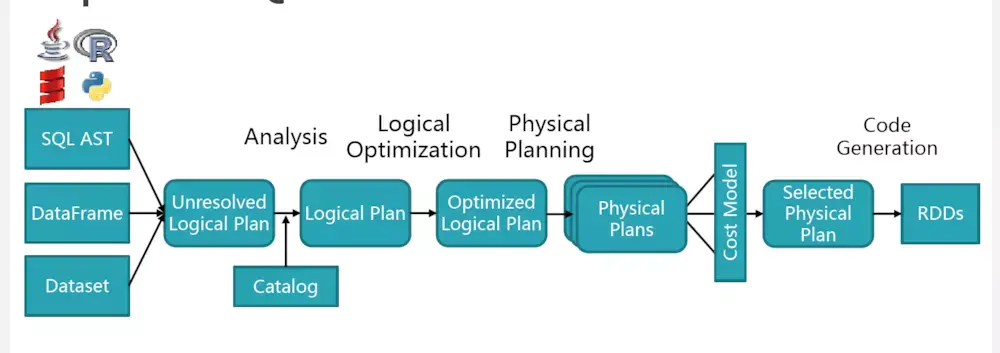
上述过程大概包括:
(1)sql 语句经过 SqlParser 解析成 Unresolved Logical Plan
(2)analyzer 结合 catalog 进行绑定,生成 Logical Plan
(3)optimizer 对 Logical Plan 优化,生成 Optimized LogicalPlan
(4)SparkPlan 将 Optimized LogicalPlan 转换成 Physical Plan
(5)prepareForExecution()将 Physical Plan 转换成 executed Physical Plan
(6)execute()执行可执行物理计划,得到RDD
三、DataFrame详解
一个DataFrame可以理解为一个数据集的很多列组成的。它等效于关系型数据库中的表,但是却对其进行了丰富的优化。DataFrame可以来源于结构化的数据文件,Hive中的表、外部的数据库、或者是已经存在的RDD。
1、DataFrame初体验
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession def handleFile(spark): df = spark.read.json("./people.json") df.show() if __name__ == '__main__': spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("sparksql_test").getOrCreate() #入口点是SparkSession类 handleFile(spark)

{"name":"Michael"}
{"name":"Andy", "age":30}
{"name":"Justin", "age":19}
执行结果为:
+----+-------+ | age| name| +----+-------+ |null|Michael| | 30| Andy| | 19| Justin| +----+-------+
2、DataFrame操作
#df.printSchema() root |-- age: long (nullable = true) |-- name: string (nullable = true) #df.select("age").show() 显示选择的某列 +----+ | age| +----+ |null| | 30| | 19| +----+ #df.select(df["name"],df["age"]+1).show() 选择所有的列,并且age的值+1 +-------+---------+ | name|(age + 1)| +-------+---------+ |Michael| null| | Andy| 31| | Justin| 20| +-------+---------+ #df.filter(df["age"]>20).show() 过滤age列年龄大于20 +---+----+ |age|name| +---+----+ | 30|Andy| +---+----+ #df.groupBy("age").count().show() 对age列进分组,并且统计每一组的个数 +----+-----+ | age|count| +----+-----+ | 19| 1| |null| 1| | 30| 1| +----+-----+
3、SQL操作
上面我们都是进行DataFrame操作,另外可以将DataFrame转成关系型数据库中的表进行操作
df = spark.read.json("./people.json") #读出的是DataFrame df.createOrReplaceTempView("people") #创建一张临时表 sqlDF = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM `people`") sqlDF.show() +----+-------+ | age| name| +----+-------+ |null|Michael| | 30| Andy| | 19| Justin| +----+-------+

from pyspark.sql import SparkSession def handleFile(spark): df = spark.read.json("./people.json") #读出的是DataFrame df.createOrReplaceTempView("people") #创建一张临时表 sqlDF = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM `people`") sqlDF.show() if __name__ == '__main__': spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("sparksql_test").getOrCreate() handleFile(spark)
四、RDD转换DataFrame
Spark SQL支持有两种方式将RDD转换成DataFrame,分别是:
- 通过反射推断出RDD中包含的Schema(包含对象的类型)
- 通过应用程序接口自己来创建Schema,再应用到RDD上
(一)反射推断Schema
Spark SQL可以将Row对象中的RDD转换成DataFrame对象,推断出数据类型。通过将键值对的列表作为kwargs传递给Row类来构造行,该列表的键作为表的列名,通过对整个数据集的采样来推断出列的类型,类似于对JSON文件的执行判断。
sc = spark.sparkContext #Load a text file and convert each line to a Row. lines = sc.textFile("./people.txt") #RDD Object collect ['Michael, 29', 'Andy, 30', 'Justin, 19'] parts = lines.map(lambda line:line.split(',')) #collect [['Michael', ' 29'], ['Andy', ' 30'], ['Justin', ' 19']] people = parts.map(lambda p:Row(name=p[0],age=p[1])) #collect [Row(age=' 29', name='Michael'), Row(age=' 30', name='Andy'), Row(age=' 19',
name='Justin')] # Infer the schema, and register the DataFrame as a table. schemaPeople = spark.createDataFrame(people) #type DataFrame print(schemaPeople.printSchema()) #inferring schema # root # | -- age: string(nullable=true) # | -- name: string(nullable=true) print(schemaPeople.show()) # +---+-------+ # | age | name | # +---+-------+ # | 29 | Michael | # | 30 | Andy | # | 19 | Justin | # +---+-------+
上面是通过textFile方法读出里面的文件内容,它是一个RDD对象,这与之前读JSON文件不同(读出的直接是DataFrame对象),通过对RDD对象操作,并且构造Row类,然后通过createDataFrame方法将其(PipelinedRDD对象)转成DataFrame对象。
当然,你可以接着将DataFrame对象转成临时表,再进行SQL操作。
... schemaPeople.createOrReplaceTempView("people") # convert table # SQL can be run over DataFrames that have been registered as a table. result = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM `people`") #result type DataFrame print(result.show()) # +---+-------+ # | age | name | # +---+-------+ # | 29 | Michael | # | 30 | Andy | # | 19 | Justin | # +---+-------+ ...
通过createOrReplaceTempView方法将上面的schemaPeople结果注册成临时表people,再进行查询操作,查出的结果其实还是一个DataFrame对象。
上面就是将RDD转成DataFrame的过程,那么是否也可以将DataFrame转成RDD来进行操作呢?当然可以。
... PeopleADD = result.rdd.map(lambda p:"Name:%s;Age:%s"%(p.name,p.age)) print(PeopleADD.collect()) #['Name:Michael;Age: 29', 'Name:Andy;Age: 30', 'Name:Justin;Age: 19'] ...
(二)编程方式指定Schema
如果无法提前定义kwargs的字典参数,那么DataFrame可以通过以下三步来进行创建:
- 从原始的RDD来创建一个元祖或者列表形式的RDD
- 创建Schema的StructType,用于匹配上面元祖或者列表形式的RDD
- 将上面创建的Schema应用于SparkSession提供的createDataFrame方法
sc = spark.sparkContext # Load a text file and convert each line to a Row. lines = sc.textFile("./people.txt") parts = lines.map(lambda line:line.split(",")) print(parts.collect()) #[['Michael', ' 29'], ['Andy', ' 30'], ['Justin', ' 19']] # Each line is converted to a tuple. people = parts.map(lambda p:(p[0],p[1].strip())) print(people.collect()) #[('Michael', '29'), ('Andy', '30'), ('Justin', '19')] # The schema is encoded in a string. schemaString = "name age" fields = [StructField(field_name, StringType(), True) for field_name in schemaString.split()] schema = StructType(fields) # Apply the schema to the RDD. schemaPeople = spark.createDataFrame(people, schema) #DataFrame print(schemaPeople.show()) # +-------+---+ # | name | age | # +-------+---+ # | Michael | 29 | # | Andy | 30 | # | Justin | 19 | # +-------+---+
上面的代码就是通过之前所说的三步,指定Schema来创建对应的DatatFrame,并且将结果进行输出。当然他也可以接着将DataFrame转成临时表,通过SQL进行操作。
... # Creates a temporary view using the DataFrame schemaPeople.createOrReplaceTempView("people") # SQL can be run over DataFrames that have been registered as a table. results = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM `people`") print(results.show()) # +-------+---+ # | name | age | # +-------+---+ # | Michael | 29 | # | Andy | 30 | # | Justin | 19 | # +-------+---+ ...

from pyspark.sql import SparkSession from pyspark.sql.types import StructField,StringType,StructType from pyspark.sql import Row def ProgramSchema(spark): sc = spark.sparkContext # Load a text file and convert each line to a Row. lines = sc.textFile("./people.txt") parts = lines.map(lambda line:line.split(",")) # print(parts.collect()) #[['Michael', ' 29'], ['Andy', ' 30'], ['Justin', ' 19']] # Each line is converted to a tuple. people = parts.map(lambda p:(p[0],p[1].strip())) # print(people.collect()) #[('Michael', '29'), ('Andy', '30'), ('Justin', '19')] # The schema is encoded in a string. schemaString = "name age" fields = [StructField(field_name, StringType(), True) for field_name in schemaString.split()] schema = StructType(fields) # Apply the schema to the RDD. schemaPeople = spark.createDataFrame(people, schema) #DataFrame # print(schemaPeople.show()) # +-------+---+ # | name | age | # +-------+---+ # | Michael | 29 | # | Andy | 30 | # | Justin | 19 | # +-------+---+ # Creates a temporary view using the DataFrame schemaPeople.createOrReplaceTempView("people") # SQL can be run over DataFrames that have been registered as a table. results = spark.sql("SELECT * FROM `people`") print(results.show()) # +-------+---+ # | name | age | # +-------+---+ # | Michael | 29 | # | Andy | 30 | # | Justin | 19 | # +-------+---+ if __name__ == '__main__': spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("sparksql_test").getOrCreate() ProgramSchema(spark)
同理,也可以通过将上述的result(DataFrame类型)转成RDD(通过rdd方法)。
五、操作数据库
可以看到上面都是从文件读入数据的,那么如何从数据库中,比如MySQL中读入数据呢?
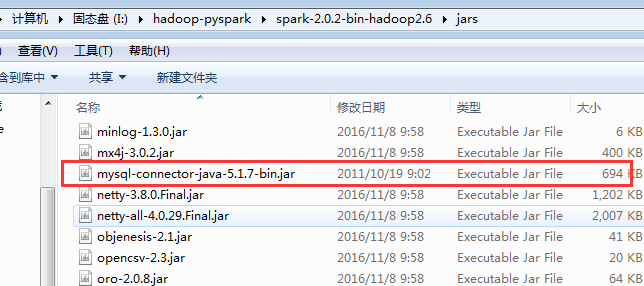
1、安装驱动
使用spark之前,应该先将数据库的驱动进行配置,这里使用的是MySQL数据库,所以将其驱动的jar包下载然后放到I:\hadoop-pyspark\spark-2.0.2-bin-hadoop2.6\jars目录下:
2、连接数据库
jdbcDF = spark.read \ .format("jdbc") \ .option("url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book") \ #数据库 .option("dbtable", "app01_book") \ #数据表 .option("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") \ #驱动 .option("user", "***") \ .option("password", "***") \ .load() print(jdbcDF.show())

from pyspark.sql import SparkSession def ConnectSQL(spark): jdbcDF = spark.read \ .format("jdbc") \ .option("url", "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book") \ .option("dbtable", "app01_book") \ .option("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver") \ .option("user", "root") \ .option("password", "123456") \ .load() print(jdbcDF.show()) if __name__ == '__main__': spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("sparksql_test").getOrCreate() ConnectSQL(spark)
这样返回的数据就是DataFrame类型的数据,接下来的操作与之前一样了。
参考:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号