二叉树模型
基本结点
public class Node {
Object data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(Object data, Node leftChild, Node rightChild) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
}
二叉树接口
//二叉树接口
public interface Tree {
public int size();
public boolean isEmpty();
public int getHeight();
public void preTraversal();
public void middleTraversal();
public void postTraversal();
//借助队列实现层次遍历
public void orderByQueue();
//借助栈实现非递归遍历二叉树,使用先序进行遍历
public void preTraByStack();
//借助栈实现非递归遍历二叉树,使用中序进行遍历
void inOrderByStack();
//借助栈实现非递归遍历二叉树,使用后序进行遍历
void postTraByStack();
}
接口实现
public class LinkedBinaryTree implements Tree {
private Node root;
private Node node;
public LinkedBinaryTree() {
}
public LinkedBinaryTree(Node root) {
this.root = root;
}
@Override
public int size() {
System.out.print("树的大小:");
return this.size(root);
}
private int size(Node node) {
if (null == node) {
return 0;
} else {
//获取左子树的size
int ln = this.size(node.leftChild);
//获取右子树的size
int rn = this.size(node.rightChild);
//左子树+右子树的size+1
return ln + rn + 1;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null ? true : false;
}
@Override
public int getHeight() {
System.out.print("Tree的高度:");
return this.getHeight(root);
}
private int getHeight(Node node) {
if (null == node) {
return 0;
} else {
//获取左子树的高度
int ln = this.getHeight(node.leftChild);
//获取右子树的高度
int rn = this.getHeight(node.rightChild);
//取较大的值并加上根高度
return ln > rn ? ln + 1 : rn + 1;
}
}
@Override
public void preTraversal() {
System.out.print("前序遍历:");
this.preTraversal(root);
}
private void preTraversal(Node node) {
if (null != node) {
//输出根节点值
System.out.print(node.data + ",");
//对左子树先序遍历
this.preTraversal(node.leftChild);
//对右子树先序遍历
this.preTraversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
@Override
public void middleTraversal() {
System.out.print("\n中序遍历:");
this.middleTraversal(root);
}
private void middleTraversal(Node node) {
if (null != node) {
//对左子树先序遍历
this.middleTraversal(node.leftChild);
//输出根节点值
System.out.print(node.data + ",");
//对右子树先序遍历
this.middleTraversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
@Override
public void postTraversal() {
System.out.print("\n后序遍历:");
this.postTraversal(root);
}
private void postTraversal(Node node) {
if (null != node) {
//对左子树先序遍历
this.postTraversal(node.leftChild);
//对右子树先序遍历
this.postTraversal(node.rightChild);
//输出根节点值
System.out.print(node.data + ",");
}
}
@Override
public void orderByQueue() {
System.out.print("\n通过队列实现遍历二叉树:");
if (null == root) return;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.add(root);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
int len = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node temp = queue.poll();
System.out.print(temp.data + ",");
if (null != temp.leftChild) queue.add(temp.leftChild);
if (null != temp.rightChild) queue.add(temp.rightChild);
}
}
}
@Override
public void preTraByStack() {
System.out.print("\n通过栈实现先序遍历二叉树:");
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<Node>();
Node current = root;
while (null != current || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (null != current) {
System.out.print(current.data + ",");
stack.push(current);
current = current.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
current = stack.pop();
current = current.rightChild;
}
}
}
@Override
public void inOrderByStack() {
System.out.print("\n通过栈实现中序遍历二叉树:");
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<Node>();
Node current = root;
while (null != current || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (null != current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
current = stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.data + ",");
current = current.rightChild;
}
}
}
@Override
public void postTraByStack() {
System.out.print("\n通过栈实现后序遍历二叉树:");
//新建栈,先进后出,将根结点入栈,双端队列
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<>();
//新建一个list,记录结点的状态是否已经被访问过
ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
Node node = root;
int flag;
//首先检查完树的左子树,再右子树,最后将根节点输出
while (node != null || stack.size() > 0) {
//将最左子树添加完毕
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.leftChild;
}
//和中序遍历相似,为先输出左结点,但是做结点输出完毕之后,不能直接将根结点弹出,而是必 Binary Tree须先将右结点弹出,
//最后再将根结点弹出来,就会牵扯到一个根结点的访问状态的问题,是否已经被遍历过了
//利用一个list集合记录已将被遍历过的根结点,防止产生死循环
if (stack.size() > 0) {
Node peek = stack.peek();
if (peek.rightChild != null) {
boolean con = list.contains(peek);
if (con == true) {
Node pop = stack.pop();
System.out.print(pop.data + ",");
} else {
list.add(peek);
node = peek.rightChild;
}
} else {
Node pop = stack.pop();
System.out.print(pop.data + ",");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public Node findKey(int key) {
return this.findKey(root, key);
}
private Node findKey(Node root, Object key) {
if (null == root) {
return null;
} else if (null != root && key == root.data) {
return root;
} else {
Node node1 = this.findKey(root.leftChild, key);
Node node2 = this.findKey(root.rightChild, key);
if (null != node1 && key == node1.data) {
return node1;
}
if (null != node2 && key == node2.data) {
return node2;
}
return null;
}
}
main方法
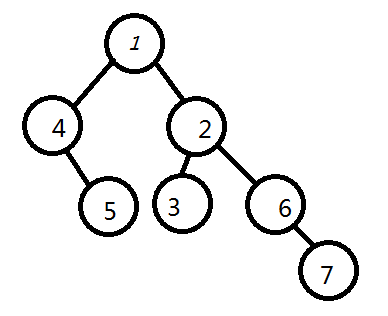
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node5 = new Node(5, null, null);
Node node4 = new Node(4, null, node5);
Node node3 = new Node(3, null, null);
Node node7 = new Node(7, null, null);
Node node6 = new Node(6, null, node7);
Node node2 = new Node(2, node3, node6);
Node root = new Node(1, node4, node2);
LinkedBinaryTree link = new LinkedBinaryTree(root);
link.preTraversal();
link.middleTraversal();
link.postTraversal();
System.out.print(link.getHeight());
System.out.println(link.size());
System.out.print("查找到的结点:"+link.findKey(6));
link.preTraByStack();
link.inOrderByStack();
link.postTraByStack();
}
结果
前序遍历:1,4,5,2,3,6,7,
中序遍历:4,5,1,3,2,6,7,
后序遍历:5,4,3,7,6,2,1,
Tree的高度:4
树的大小:7
查找到的结点:Node{data=6, leftChild=null, rightChild=Node{data=7, leftChild=null, rightChild=null}}
通过队列实现遍历二叉树:1,4,2,5,3,6,7,
通过栈实现先序遍历二叉树:1,4,5,2,3,6,7,
通过栈实现中序遍历二叉树:4,5,1,3,2,6,7,
通过栈实现后序遍历二叉树:5,4,3,7,6,2,1,


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号