iOS - 多线程Notes
多线程
概念 原理 方式
一、概念

二、原理
多线程是通过CPU切换执行的
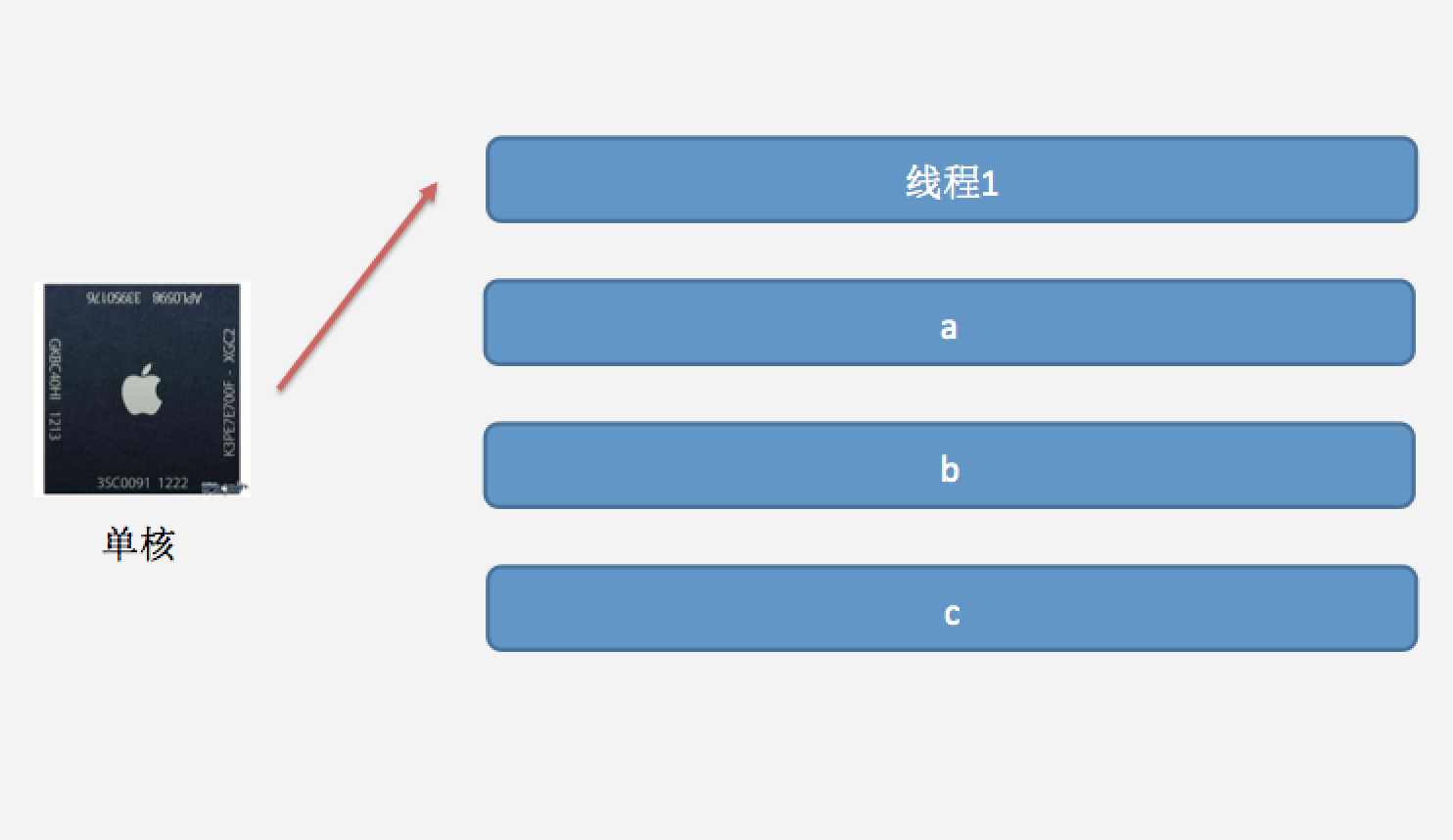
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wendingding/p/3805088.html
三、方式
pthread NSThread GCD NSOperation

3.1 pthread
3.2 NSThread
https://www.jianshu.com/p/cbaeea5368b1
3.2.1 创建方法
(1).
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTraget:self selector:@selector(task) object:nil];
[thread start];
-(void)task {
NSLog(@"task is running %@",[NSThread currentThread]);
}
//注:创建thread,只是在内存中有了一个thread对象,还需invoke "start",才能运行.
(2). 创建线程后自动启动线程
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(task) toTarget:self withObject:nil];
(3). 隐式创建并启动线程
[self preformSelectorInBackground:@selector(task) withObjcet:nil];
3.2.2 线程的相关方法
- 获得主线程
+(NSThread*)mainThread;
- 判断是否为主线程(对象方法)
-(BOOL)isMainThread;
- 判断是否为主线程(类方法)
+(BOOL)isMainThread;
- 获得当前线程
NSThread *current = [NSThread currentThread];
- 线程的名字-setter方法
-(void)setName:(NSString*)n;
- 线程的名字-getter方法
-(NSString*)name;
3.2.3 线程的状态控制方法
- 启动线程
-(void)start; //线程进入就绪状态 -> 运行状态。当线程任务执行完毕,自动进入死亡状态
- 阻塞(暂停)线程方法
+(void)sleepUnitlDate:(NSDate*)date;
+(void)sleepForTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)ti; //线程进入阻塞状态
- 强制停止线程
+(void)exit; //线程进入死亡状态
3.2.4 线程间的通信
- 在主线程上执行操作
-(void)performSelectorOnMainThread:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
-(void)performSelectorOnMainThread:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)arg watiUntilDone:(BOOL)wait modes:(NSArrsy<NSString *> *)array;
//equivalent to the first method with kCFRunLoopCommonModes
- 在指定线程上执行操作
- (void)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector onThread:(NSThread *)thr withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait modes:(NSArray *)array NS_AVAILABLE(10_5, 2_0);
- (void)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector onThread:(NSThread *)thr withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait NS_AVAILABLE(10_5, 2_0);
- 在当前线程上执行操作,调用NSObjcet的performSelector:相关方法
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector;
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)object;
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)object1 withObject:(id)object2;
3.2.5 线程的生命周期
创建(new)------就绪start-----------运行running-----------阻塞sleep----------死亡dead

//新建状态
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTraget:self selector:@selector(task) object:nil];
//就绪状态
[thread start];
//运行状态(执行task方法)
[self task];
//阻塞状态
NSLog(@"开始睡2秒");
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2]; //1.1
//线程睡眠dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow 下哦那个现在开始到未来的2秒时间段
[NSThread sleepUnitDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:2]]; //1.2
//注:1句话共3个状态切换:运行->阻塞->就绪
NSLog(@"睡醒了");
//手动退出线程
[NSThread exit];
//死亡状态
NSLog(@"我死了");
3.2.6 线程的属性
(1). name(调试使用方便)
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTraget:self selector:@selector(task) object:nil];
thread.name = @"threads";
(2). priority
取值范围:0.0-1.0(1.0最高;默认0.5)
thread.threadPriority = 0.0;
注:优先级高的thread不定比优先级低的thread的先运行,只是有更多的可能性被CPU执行到(只取决CPU的调度算法).
******************************************************************
多线程的基本概念
1.同步:顺序执行
2.异步:同时执行
3.进程:正在运行的程序,一个或多个线程组成
4.线程:最基本组成单元
多线程:线程是切换运行的!!!
主线程:不能在主线程执行耗时操作(易导致卡死)
优点:提升程序的执行效率
适当的提升资源占有率
缺点:线程不是越多越好(切换线程会占用CPU...)
时间成本:大约90ms
空间成本:占用内存512kb
pthread:了解
NSThread:(3种创建对抗)
线程声明周期
1.新建
2.就绪(内存的可调度线程池中)
3.运行
4.阻塞->就绪
5.死亡
常用属性
1.name
2.priority
******************************************************************
3.2.4 多线程共享操作 共享资源问题 一部下载图片 weak&assign 模拟消息循环
******************************************************************
多线程的共享变量
1.互斥锁(同步锁)(掌握(较难))
2.自旋锁
区别:自旋锁.复制方法;互斥锁都可以
自旋锁循环去判断锁的状态(不应锁一个耗时操作);互斥锁休眠安静等待
图片异步下载:
线程间的通信()
子线程下载图片
主线程更新UI
weak&assign
weak:对象释放后,指向0地址。
assign:指针指向地址不变(野指针)
自动释放池:
作用:-延迟对象的释放
什么时候释放: - 消息循环:iOS系统中的执行原理(不断处理用户的事件)
******************************************************************
3.3 GCD
传送门https://www.jianshu.com/p/2d57c72016c6
3.3.1 RunLoop

主线程消息循环:
-(void)demo{
//创建timer
//参数1:间隔时间
//参数2:对象
//参数3:方法
//参数4:自定义
//参数5:是否重复执行
NSTimer *timer = [NSTimer timerWithTimeInterval:1 target:self selector:@selector(task) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
//把定时源加入到当前线程下消息循环中
//参数1:定时源
//参数2:模式
*NSDefaultRunLoopMode 拖动界面,定时源不运行
*NSRunLoopCommonModes 拖动界面不受影响
*没有拖动界面:kCFRunLoopDefaultMode
*拖动界面:UITrackingRunLoopMode
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] addTimer:timer forMode:NSRunLoopCommonModes];
}
-(void)task{
//输出当前循环的模式
NSLog(@"%@",[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop].currentMode);
NSLog(@"task is running");
}
(2).开启消息循环有三种方式:
- 子线程的消息循环
-(void)demo2{
//创建子线程
NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(task2) object:nil];
[thread start];
//往指定线程的消息循环中加入源
//参数1:方法
//参数2:指定线程
//参数3:对象
//参数4:等待方法执行完成
[self performSelector:@selector(addtask) onThread:thread withObject:nil waitUntilDone:NO];
}
-(void)task2{
//NSLog(@"%@",[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop].currentMode);
//输出当前循环的模式
NSLog(@"task2 is running %@",[NSThread currentThread]);
//开启消息循环 使用run方法后无法停止消息循环
//[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run];
- //方法2:指定循环运行时间
//[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runUntilDate:[NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:2]];
- //方法3:apple推荐的方式(了解)
//BOOL shouldKeepRunning = YES; // global
NSRunLoop *theRL = [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop];
while (shouldKeepRunning && [theRL runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]]);
NSLog(@"over");
}
3.3.2 GCD
(1). 剖析
//创建任务
// dispatch_block_t task = ^{
// NSLog(@"task %@",[NSThread currentThread]);
// };
//
// //获取队列
// dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0);
//
// //把任务放到队列里面
// //参数1:队列
// //参数2:任务
// dispatch_async(queue, task);
(2) 一般写法
// //简单写法 工作中常用代码
// dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
//
// });
(3)多任务
//多个任务
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
NSLog(@"task %@ %d",[NSThread currentThread],i);
});
}
//注:会复用创建的线程(eg:上边不一定创建了20个thread).
* 下载图片(GCD)
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
NSString *imgAddr = @"http://img.bimg.126.net/photo/rl0IM2SIJK8jWXgIgxhJsw==/2871889187379358521.jpg";
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:imgAddr];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:url];
//闭包(imgage参数在此方法中,又用到此方法中的方法里)
UIImage *image = [UIImage imageWithData:data];
//线程通信
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
self.testImageView.image = image;
[self.testImageView sizeToFit];
[self.scrollView setContentSize:image.size];
});
});
(4) 主队列
3.4 NSOperation和NSOperationQueue
传送门https://www.jianshu.com/p/4b1d77054b35
3.5多线程与AFN
- 信号量
https://www.jianshu.com/p/efac15d882c7
微信赞赏

支付宝赞赏




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号