2022.11.11 函数式接口
5. 函数式接口
5.1 概述
只有一个抽象方法的接口我们称之为函数接口。
JDK的函数式接口都加上了@FunctionalInterface (与重写方法的注解作用类似,校验作用) 注解进行标识。但是无论是否加上该注解只要接口中只有一个抽象方法,都是函数式接口。
5.2 常见函数式接口
-
Consumer 消费接口
![]()
-
Function 计算转换接口
根据其中抽象方法的参数列表和返回值类型知道,我们可以在方法中对传入的参数计算或转换,把结果返回
![]()
-
Predicate 判断接口
根据其中抽象方法的参数列表和返回值类型知道,我们可以在方法中对传入的参数条件判断,返回判断结果
![]()
-
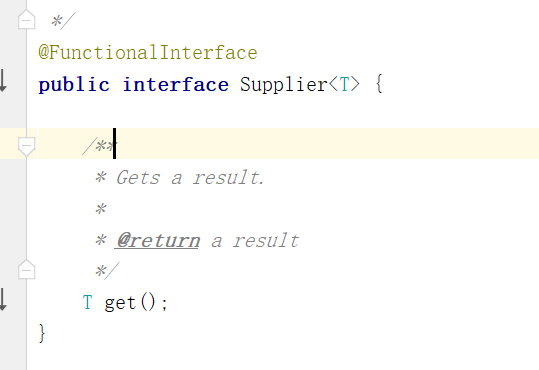
Supplier 生产型接口
根据其中抽象方法的参数列表和返回值类型知道,我们可以在方法中创建对象,把创建好的对象返回
5.3 常用的默认方法
-
and
我们在使用Predicate接口时候可能需要进行判断条件的拼接。而and方法相当于是使用&&来拼接两个判断条件
例如:
打印作家中年龄大于17并且姓名的长度大于1的作家。
1 List<Author> authors = getAuthors(); 2 Stream<Author> authorStream = authors.stream(); 3 authorStream.filter(new Predicate<Author>() { 4 @Override 5 public boolean test(Author author) { 6 return author.getAge()>17; 7 } 8 }.and(new Predicate<Author>() { 9 @Override 10 public boolean test(Author author) { 11 return author.getName().length()>1; 12 } 13 })).forEach(author -> System.out.println(author));
-
or
我们在使用Predicate接口时候可能需要进行判断条件的拼接。而or方法相当于是使用||来拼接两个判断条件。
例如:
打印作家中年龄大于17或者姓名的长度小于2的作家。
1 // 打印作家中年龄大于17或者姓名的长度小于2的作家。 2 List<Author> authors = getAuthors(); 3 authors.stream() 4 .filter(new Predicate<Author>() { 5 @Override 6 public boolean test(Author author) { 7 return author.getAge()>17; 8 } 9 }.or(new Predicate<Author>() { 10 @Override 11 public boolean test(Author author) { 12 return author.getName().length()<2; 13 } 14 })).forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
-
negate
Predicate接口中的方法。negate方法相当于是在判断添加前面加了个! 表示取反
例如:
打印作家中年龄不大于17的作家。
1 // 打印作家中年龄不大于17的作家。 2 List<Author> authors = getAuthors(); 3 authors.stream() 4 .filter(new Predicate<Author>() { 5 @Override 6 public boolean test(Author author) { 7 return author.getAge()>17; 8 } 9 }.negate()).forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getAge()));







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号