2022.8.21 CAS与原子引用(解决CAS的ABA问题)
什么是CAS
1 package com.xing.cas; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 4 // 原子类的底层用的cas 5 public class CASDemo { 6 //compareAndSet比较并交换 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);//原子类 9 /* 10 期望 更新 11 public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) { 12 return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update); 13 } 14 */ 15 //如果和期望的值相同就更新,CAS是CPU的并发原语 16 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021)); 17 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // 2021 18 19 // 上面已经修改为了2021 所以这个失败 20 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 20201)); 21 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());//2021 22 } 23 } 24 25
AtomicInteger的getAndIncrement方法源码
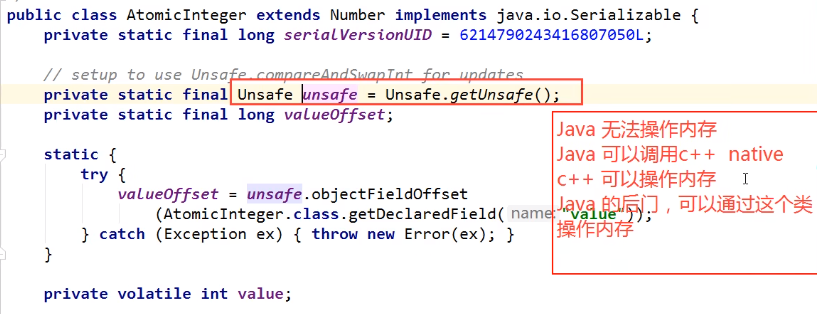
unsafe类
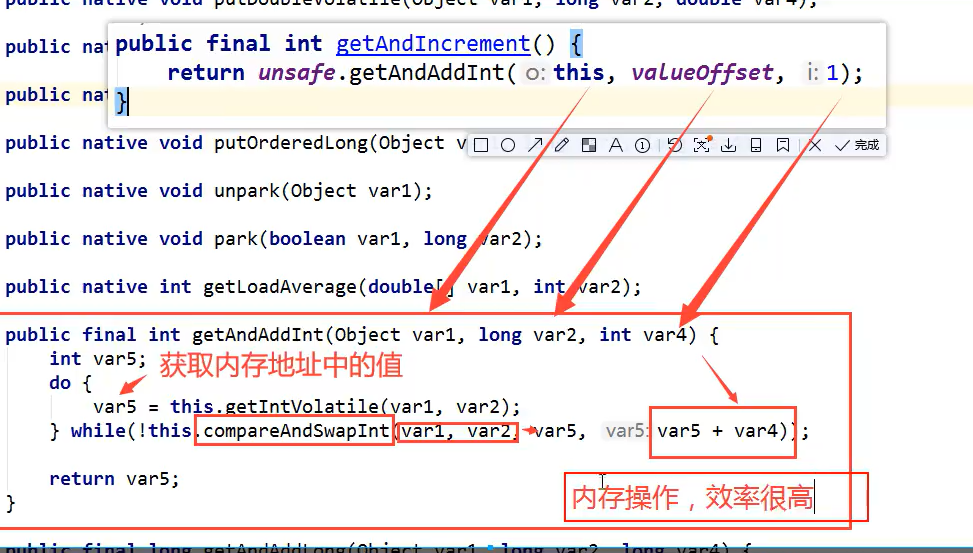
精髓!!!!:var1对象等于var2内存地址偏移值,对应如果这个值还是我们希望的var5,那么我们就让这个值加一
总结:CAS: 比较当前工作内存中的值,若果这个值是期望中的,那么执行该操作 ,如果不是会一直循环因为底层是do while会一直循环
缺点:
-
循环耗时
-
一次性只能保证一个共享变量的共享性
-
ABA问题
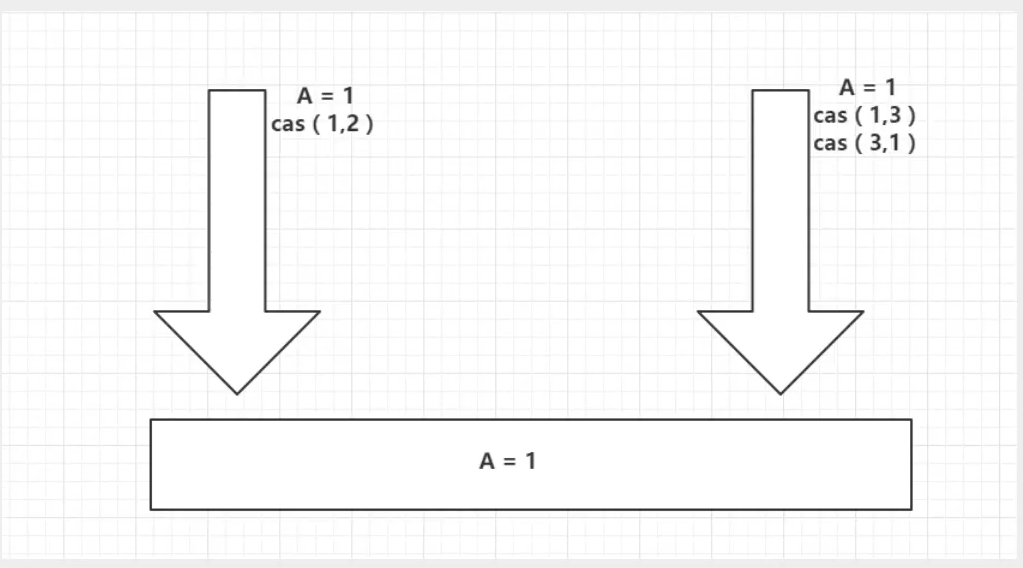
ABA问题(狸猫换太子)别人改了又改回去,但是使用的人不知道
1 package com.xing.cas; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 4 5 public class CASDemo { 6 //比较并交换 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2020);//原子类 9 /* 10 期望 更新 11 public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) { 12 return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update); 13 } 14 */ 15 //对我们写平时写的sql:乐观锁 16 //如果和期望的值相同就更新,CAS是CPU的并发原语 17 //*******捣乱的线程********** 18 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021)); 19 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // 2021 20 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021, 2020)); 21 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); // 2020 22 //********期望的线程********* 23 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2020, 2021)); 24 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());//2021 25 } 26 }

虽然最终期望确实完成可但是我们不希望数据被人动过了还不知道下面来解决这个问题
如何解决这个问题?原子引用
我们使用另外一个 AtomicStampedReference 原子类 带有版本号时间戳,可以每次记录加一类似于乐观锁
20、原子引用(解决CAS的ABA问题)
带版本号的原子操作
1 package com.xing.cas; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference; 5 6 public class CASDemo { 7 //比较并交换 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 10 //注意,如果泛型是一个包装类,注意对象的引用问题 正常业务中,泛型中都是对象 11 //Integer 使用了对象缓存机制,默认范围是 -128 ~ 127 ,推荐使用静态工厂方法 valueOf 获取对象实例,而不是 new,因为 valueOf 使用缓存,而 new 一定会创建新的对象分配新的内存空间; 12 AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicInteger = new AtomicStampedReference<>(1,1);//初始值,版本号时间戳 13 new Thread(()->{ 14 int stamp = atomicInteger.getStamp();//获得版本号 15 System.out.println("A = >" + stamp); 16 try { 17 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 //最后两个参数,拿到最新的版本号,把版本号+1 期望值 更新值 期望时间戳 新时间戳 22 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(1, 2, atomicInteger.getStamp(), atomicInteger.getStamp() + 1)); 23 System.out.println("A2 = >"+atomicInteger.getStamp()); 24 //把这个值该回去 25 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2, 1, atomicInteger.getStamp(), atomicInteger.getStamp() + 1)); 26 System.out.println("A3 = >"+atomicInteger.getStamp()); 27 28 },"a").start(); 29 30 31 new Thread(()->{ 32 int stamp = atomicInteger.getStamp();//获得版本号 33 System.out.println("B = >" + stamp); 34 35 try { 36 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 37 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 System.out.println(atomicInteger.compareAndSet(1, 3, stamp, stamp + 1)); 41 42 System.out.println("b2 = >" +atomicInteger.getStamp()); 43 },"b").start(); 44 } 45 } 46

注意:Integer 使用了对象缓存机制,默认范围是 -128 ~ 127 ,推荐使用静态工厂方法 valueOf 获取对象实例,而不是 new,因为 valueOf 使用缓存,而 new 一定会创建新的对象分配新的内存空间;每一次的2020都是一个新的值
阿里巴巴手册





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号