IO流
目录
File
文件和目录路径名的抽象表示形式。
构造方法:
File(String pathname) //通过将给定路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建一个新 File 实例。
常用方法:
boolean canRead()//测试该文件是否可读
boolean canWrite()//测试该文件是否可写
boolean createNewFile()//当且仅当不存在指定文件时,创建新的空的文件
boolean mkdir()//创建指定文件夹
boolean delete()//删除文件或目录。
boolean exists()//测试文件或目录是否存在
long length()//返回文件大小,以字节为单位
String getName()//返回文件名
String getAbsolutePath()//返回绝对路径
String getPath()//返回相对路径
boolean isDirectory()//测试该路径是否是一个目录
File[] listFiles()//返回File数组,为该目录下的所有文件或文件夹
package com.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
//File类测试
public class TestFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("E:\\java.txt");//Windows操作系统下,使用的是“\”,Unix操作系统下,使用是“/“
//创建文件
try {
System.out.println("file创建:" + file.createNewFile());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//创建文件夹
File file1 = new File("E:\\java");
System.out.println("file1创建:" + file1.mkdir());
//创建多级目录
File file2 = new File("E:\\java2\\java\\java");
System.out.println("file2创建:" + file2.mkdirs());
//删除文件
System.out.println("file删除:" + file.delete());
//查询
System.out.println("file是否存在:" + file.exists());
System.out.println("file1是否存在" + file1.exists());
System.out.println("file1大小(字节为单位):" + file1.length());
System.out.println("file1.getAbsolutePath():" + file1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("file1.getPath():" + file1.getPath());
}
}
使用递归查找文件夹下的所有文件
package com.io;
import java.io.File;
//递归查询文件夹下的所有文件
public class TestFile2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TestFile2().showFile("E:\\JavaStudy");
}
public void showFile (String pathName) {
File file1 = new File(pathName);
boolean flag1 = file1.isDirectory(); //判断是文件夹还是文件
if (flag1) { //若为文件夹
File[] file2 = file1.listFiles(); //列出该文件夹下所有内容
//使用传统for循环增强健壮性
for (int i = 0; i < file2.length && file2 != null; i++) {
boolean flag2 = file2[i].isDirectory(); //再次判断是文件夹还是文件
if (flag2) { //若为文件夹,则递归调用
new TestFile2().showFile(file2[i].getAbsolutePath());
} else { //为文件则输出文件名
System.out.println(file2[i].getName() + "---" + file2[i].getPath());
}
}
} else { //为文件则输出文件名
System.out.println(file1.getName() + "---" + file1.getPath());
}
}
}
IO流
字节流
字节流可读取任何文件,包括文本文件,图片,音乐,视频等
字节输入流
外部进入到程序,称为输入流
三要素:
- 数据源
- 铺设管道
- 读取数据
InputStream
- FileInputStream
- BufferedInputStream
FileInputStream
public class FileInputStreamextends InputStream
以字节为单位输入数据
构造方法
FileInputStream(File file)
FileInputStream(String name)
常用方法
int read()//读取一个数据字节。
void close()//关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源
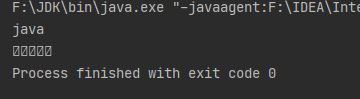
read方法使用,“TestFileInputStream.txt”文档中,内容为java
package com.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestFileInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//铺设管道
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\TestFileInputStream.txt");
//读取数据
int t = 0;//注意:需要使用int变量来接受read()方法的返回值,不可直接强制转换输出
while ((t = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)t);
}
System.out.println();
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("E:\\TestFileInputStream.txt");
while ((fi.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)fis.read());
}
//关闭流
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
因此需要使用int变量来接受read()方法的返回值,不可直接强制转换输出
对于中文来说,UTF-8一个汉字占3个字节,GB2312一个汉字占两个字节,因此当使用FileInputStream读取汉字时,将会乱码
BufferedInputStream
构造方法
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) //size为缓冲区大小
由于FileInputStream继承InputStream,因此可用
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:\\xxx.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
常用方法
int read(byte[] b)//将流中数据读取到数组b中,当读到文件末尾时返回-1
void close()//关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源
package com.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestBufferedInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//铺设管道
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:\\Test.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
String s = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s);
}
//关闭流
bis.close();
is.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字节输出流
三要素
- 铺设管道
- 数据
- 目标文件
FileOutputStream
public class FileOutputStreamextends OutputStream
构造方法
FileOutputStream(File file)
FileOutputStream(String name)
FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)//创建一个向具有指定 name 的文件中写入数据的输出文件流,当append为true时,写入为追加,否则写入为覆盖
常用方法
void write(byte[] b)//将 byte 数组写入此文件输出流中。
void write(int b)//将指定字节写入此文件输出流。
void close() //关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。
package com.io;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestFileOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "java Test";
try {
//铺设管道
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\TestFileOutputStream.txt");
//输出数据
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes);
//关闭流
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BufferedOutputStream
构造方法
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) //size为缓冲区大小
常用方法
void flush()//迫使所有缓冲的输出字节被写出到底层输出流中
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) //将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此缓冲的输出流。
void write(byte[] b)//使用这种方法最后一次写入可能会导致多余的字节写入
package com.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestBufferedOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//铺设管道
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\Test2.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
bytes = "Java Test".getBytes();
bos.write(bytes);
//关闭流
bos.flush();
bos.close();
os.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件复制
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream方法
package com.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\Test.txt");
//输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\TestCopy.txt");
int ch = 0;
while ((ch = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(ch);
}
//关闭流
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream方法
package com.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestCopy2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:\\Test.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
//输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:\\Copy2.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(b)) != -1) {
bos.write(b, 0, len);
}
//关闭流
bos.flush();
bos.close();
os.close();
bis.close();
is.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符流
字符流可读取文本文件,可解决乱码问题(注意文档使用UTF-8编码),不可读取音乐、图片、视频等。字符流中的很多方法和字节流中类似
字符输入流
FileReader
public class FileReader extends InputStreamReader
public class InputStreamReader extends Reader
构造方法
FileReader(File file)
FileReader(String fileName)
常用方法
int read()
void close()
package com.io;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestFileReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//铺设管道
FileReader fr = new FileReader("E:\\Test.txt");
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(ch)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(ch, 0, len)); //文档使用UTF-8编码
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
BufferedReader
public class BufferedReaderextends Reader
构造方法
BufferedReader(Reader in)
BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz)
常用方法
void close()//关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有资源。
int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) //将字符读入数组的某一部分。
String readLine() //读取一个文本行。
package com.io;
import java.io.*;
public class TestBufferedReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//管道
Reader reader = new FileReader("E:\\Test.txt");
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(reader);
char ch[] = new char[1024];
int len;
System.out.println(bf.readLine());//接下来读的是下一行之后的内容
while ((len = bf.read(ch)) != -1) {
String str = new String(ch, 0, len);
System.out.println(str);
}
//关闭流
bf.close();
reader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符输出流
FileWriter
public class FileWriterextends OutputStreamWriter
public class OutputStreamWriterextends Writer
构造方法
FileWriter(File file)
FileWriter(File file, boolean append)
FileWriter(String fileName)
FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) //append的为true时为追加
常用方法
void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
void write(String str)
void flush()
void close()
package com.io;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestFileWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
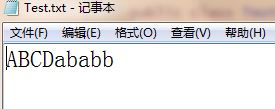
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("E:\\Test.txt");
fw.write("ABCD");
fw.write("ababb".toCharArray());
fw.flush();
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
因此,在单次写入中,写的内容是追加的。
BufferedWriter
public class BufferedWriterextends Writer
构造方法
BufferedWriter(Writer out)
BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz)
常用方法
void close()
void flush()
void write(String s, int off, int len)
void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
void newLine()// 写入一个行分隔符
文本文档复制
package com.io;
import java.io.*;
//使用字符流实现文本文档的复制,有中文时文档应使用UTF-8编码
public class TestBufferedWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Reader r = new FileReader("E:\\Test.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(r);
Writer w = new FileWriter("E:\\Test2.txt");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(w);
char[] ch = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = br.read(ch)) != -1) {
bw.write(ch, 0, len);
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
w.close();
br.close();
r.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号