Java常用类
Object类
称为超类、基类,所有类都直接或间接继承Object类
常用方法:
public final Class<?> getClass() //返回此 Object 的运行时类。
public int hashCode() //返回该对象的哈希码值。哈希值是根据对象内存地址或字符串或数字使用hash算法得到的int数值
public String toString() //返回该对象的字符串表示。可根据需求对该方法进行重写
public boolean equals(Object obj)//指示其他某个对象是否与此对象相等,比较的是两个对象的地址
protected void finalize() throws Throwable //当垃圾回收器确定不存在对该对象的更多引用时,由JVM垃圾回收器调用此方法,JVM会自动回收垃圾,也可使用System.gc()进行手动回收
package com.javaclass;
//Object类
public class ObjectTest {
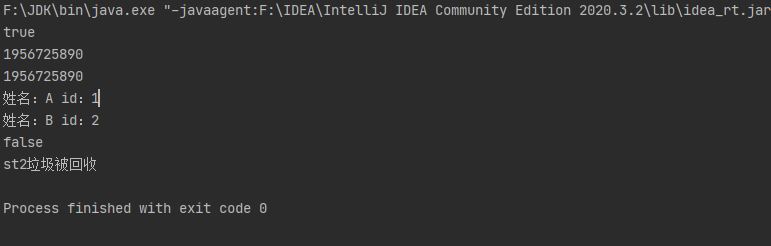
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("A", 1);
Student s2 = new Student("B", 2);
//getClass()方法
Class c1 = s1.getClass();
Class c2 = s2.getClass();
System.out.println(c1 == c2);
//hashCode()方法
int hash1 = c1.hashCode();
int hash2 = c2.hashCode();
System.out.println(hash1);
System.out.println(hash2);
//toString()方法,对Object中的toString方法重写
String string1 = s1.toString();
String string2 = s2.toString();
System.out.println(string1);
System.out.println(string2);
//equals()方法,进行了重写,比较name
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
//finalize()方法,源码未做任何操作
Student st1 = new Student("st1", 3);
new Student("st2", 4);
System.gc();//手动回收垃圾
}
}
class Student {
String name;
int id;
public Student (String name, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
//重写Object中的toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:" + this.name +" id:" + this.id;
}
//重写equals方法,比较两个学生姓名
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof Student) {
Student s1 = (Student) obj;
return s1.name.equals(this.name);
}
return false;
}
//对finalize方法进行重写
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println(this.name + "垃圾被回收");
}
}
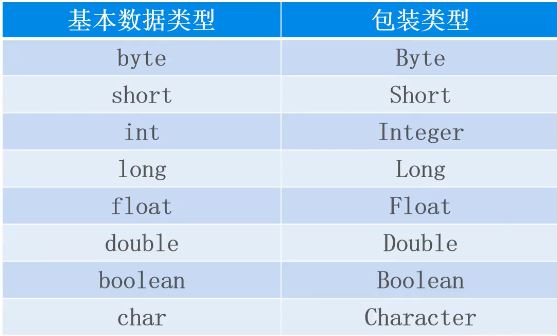
包装类
基本数据类型存储在栈空间中,引用数据类型存储在堆空间中
包装类指的是基本数据类型所对应的引用数据类型,默认值为null。包装类在java.lang包中
类型转化与装箱、拆箱
类型转换指的是基本数据类型和包装类之间的转换
装箱指的是将栈空间的数据转换到堆空间中,即基本数据类型转换为引用数据类型
拆箱与装箱相反,指的是将堆空间中的数据转换到栈空间中
装箱:
每个包装类都可通过构造方法和valueof对基本数据类型进行装箱
例如:Integer
Integer(int value) //构造方法,构造一个新分配的 Integer 对象,value表示指定的 int 值。
static Integer valueOf(int i) //valueof方法,返回一个表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例。
拆箱:
上述所提的包装类均继承自Number类,根据Java帮助文档,Number类中的方法如intValue可进行拆箱
自JDK1.5后,提供了自动装箱和拆箱,自动装箱其实调用的就是Integer.valueOf,自动拆箱调用的是intValue方法。
Integer integer = 2;
int num = integer;
package com.javaclass;
//类型转换:装箱和拆箱
public class Integer2int {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//装箱
int num = 1;
Integer integer = new Integer(num);
Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(num);
//拆箱
int num1 = integer1.intValue();
//JDK1.5之后,提供自动装箱、拆箱
//自动装箱
int num2 = 2;
Integer integer2 = num2;
//自动拆箱
int num3 = integer2;
System.out.println(num3);
}
}
基本数据类型转换为字符串
基本数据类型转换为字符串:
- 使用+号,变量 + “”
- 使用toString方法
字符串转换为基本数据类型
- 使用parexxx方法,例如pareInt方法
package com.javaclass;
public class Integer2String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = 2;
//使用+号
String s1 = n1 + "";
//使用Integer中的toString方法
String s2 = Integer.toString(n1);
String s3 = Integer.toString(20, 16);//将20以16进制的字符串形式输出
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
//字符串转换为基本数据类型
String s4 = "150";
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(s4);//praseInt中的参数必须为数值类型的字符串
boolean b1 = Boolean.parseBoolean("true"); //boolean字符串转换为基本数据类型,"true"(不论大小写)转换为true,其余转换为false
boolean b2 = Boolean.parseBoolean("TRue");
System.out.println(n2);
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(b2);
//
}
}
整数缓冲区
package com.javaclass;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer integer1 = new Integer(1);
Integer integer2 = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(integer1 == integer2);
/*Integer integer3 = 100; //自动装箱其实调用的是Integer.ValueOf方法
Integer integer4 = 100;*/
Integer integer3 = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer integer4 = Integer.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(integer3 == integer4);
/*Integer integer5 = 200;
Integer integer6 = 200;*/
Integer integer5 = Integer.valueOf(200);
Integer integer6 = Integer.valueOf(200);
System.out.println(integer5 == integer6);
}
}
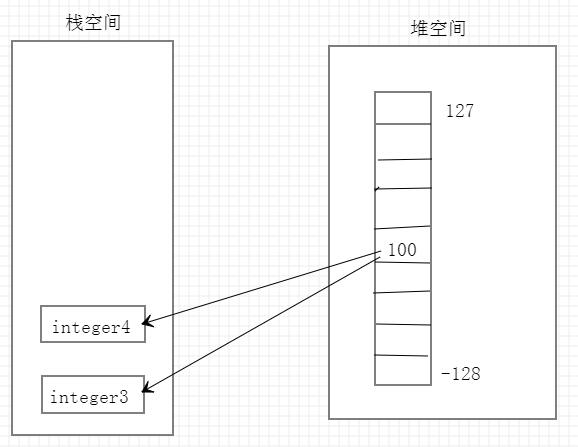
查看valueOf源码
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
再次查看发现,IntegerCache.low = -128,IntegerCache.high = 127,因此当数据为-128到127时,堆空间中数据的地址直接传给栈空间,因此上例的integer3和integer4的地址相同。当数据不在-128到127范围时,从源码看到重新new了内存地址,因此不同。
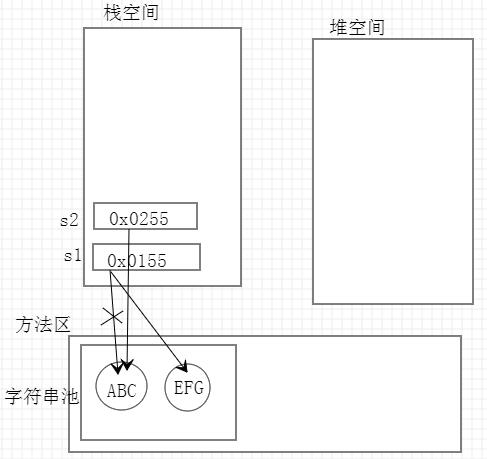
String类
- 字符串的值存储值字符串池中,可以共享
- 字符串是常量,创建后不可改变。不可改变指的是,当改变字符串变量时,该变量内存地址将会重新指向在字符串池中重新开辟的内存空间的地址,字符串池中字符串的值不会改变。字符串池中的内容由JVM自动回收。
package com.javaclass;
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "ABC";//"ABC"存储在字符串池中
s1 = "EFG"; //给字符串赋值时,重新在字符串池中开辟内存空间存储"EFG",栈中的name地址为"EFG"的地址
String s2 = "ABC";
}
}
内存分析
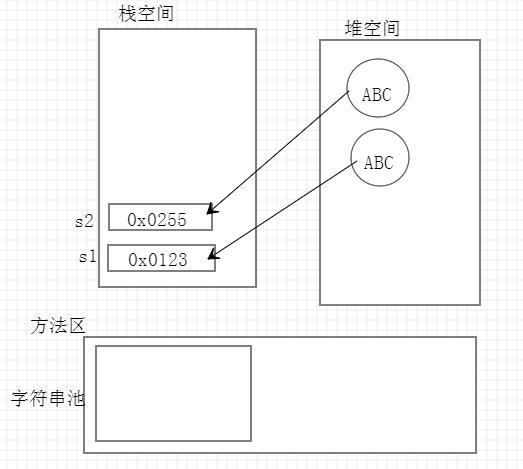
package com.javaclass;
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("ABC");
String s2 = new String("ABC");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
}
}
内存分析
常用方法:
char charAt(int index) //返回指定索引处的 char 值。
boolean contains(CharSequence s) //当且仅当此字符串包含指定的 char 值序列时,返回 true。
int length() //返回此字符串的长度
boolean isEmpty() //当且仅当 length() 为 0 时返回 true。
char[] toCharArray() //将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组。
int indexOf(int ch) //返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
int lastIndexOf(int ch) //返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引。
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) //返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始。
String trim() //去掉字符串前后空白
String toUpperCase() //将小写转化为大写
String toLowerCase() //将大写转化为小写
boolean startsWith(String prefix) //测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开始
boolean endsWith(String suffix) //测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) //返回一个新的字符串,将字符或字符串转化为新的字符或字符串
String[] split(String regex);//根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串
boolean equals(Object anObject) //将此字符串与指定的对象比较。
int compareTo(String anotherString) //按字典顺序比较两个字符串
String substring(int beginIndex);//返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) //返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。
split方法的使用
package com.javaclass;
public class StringTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "java is ,useful";
String[] strings = s1.split("[ ,]+");
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}
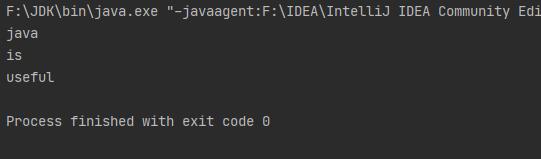
compareTo方法
package com.javaclass;
public class StringTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "ace";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //按字典中字母出现顺序比较大小,若大于则返回1,小于返回-1,相等返回0
String s3 = "abc";
String s4 = "a";
System.out.println(s3.compareTo(s4));//这时比较二者长度
}
}
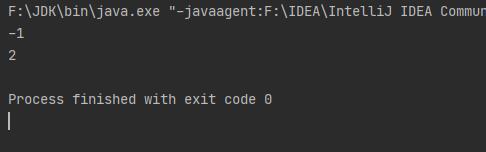
package com.javaclass;
/*
1、获取str中的单词
2、将text转换为practice
3、在text前加easy
4、每个单词首字母大写
*/
public class StringTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "this is a text";
//1、获取str中的单词
String[] s = str.split(" ");
for (String s1 : s) {
System.out.println(s1);
}
//2、将text转换为practice
String s2 = str.replace("text", "practice");
System.out.println(s2);
//3、在text前加easy
String s3 = str.replace("text", "easy text");
System.out.println(s3);
//4、每个单词首字母大写
String s4 = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
char c = Character.toUpperCase(s[i].charAt(0)); //Character.toUpperCase()方法可将小写字符转变为大写字符
s[i] = c + s[i].substring(1);
s4 = s4 + s[i] + " ";
}
s4.trim();
System.out.println(s4);
}
}
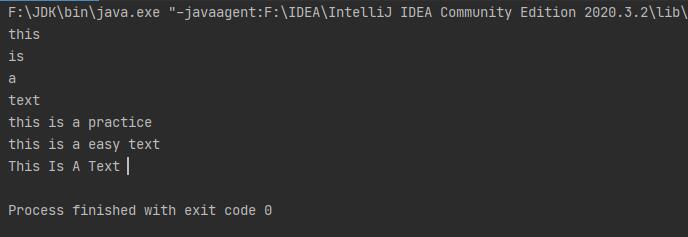
可变字符串
StringBuffer:可变长字符串,效率低,线程安全
StringBuilder:可变长字符串,效率高,线程不安全
比String效率高,节省内存
常用方法:
append(String s) //追加字符串s
insert(int offset, String s) //在offset位置前插入字符串
replace(int start, int end, String s)//将位置start到end换为字符串
delete(int start, int end) //将start到end的元素删除
//清空
s.delete(0, s.length());
验证StringBuilder和String的效率
package com.javaclass;
//验证StringBuilder和String效率
public class StringBuilderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String
String s = "";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取当前系统时间
for (int i = 0; i < 9999; i++) {
s = s + i;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
//StringBuilder
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 9999; i++) {
stringBuilder.append(i);
}
long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end2 - start2);
}
}
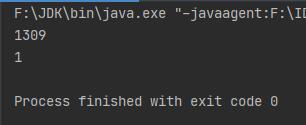
BigDecimal
package com.javaclass;
public class TestBigDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
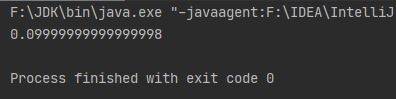
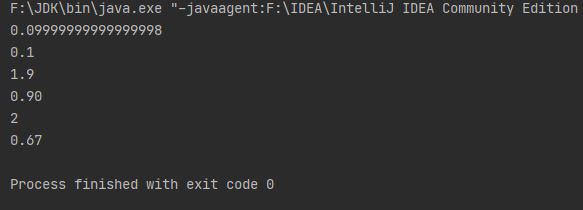
double d1 = 1.0;
double d2 = 0.9;
System.out.println(d1 - d2);
}
}
double 类型在计算机中是近似存储,当要求更高时,需要使用BigDecimal,可精确计算浮点数
package com.javaclass;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class TestBigDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1 = 1.0;
double d2 = 0.9;
System.out.println(d1 - d2);
//使用BigDecimal
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("1.0");//注意为了保证精确,参数必须为字符串
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.9");
//减法
BigDecimal result1 = bd1.subtract(bd2);
System.out.println(result1);
//加法
BigDecimal result2 = bd1.add(bd2);
System.out.println(result2);
//乘法
BigDecimal result3 = bd1.multiply(bd2);
System.out.println(result3);
//除法
BigDecimal result4 = new BigDecimal("1.0").divide(new BigDecimal(0.5));//1.0/0.5
System.out.println(result4);
//当除不尽时
BigDecimal result5 = new BigDecimal("2.0").divide(new BigDecimal("3"), 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);//以四舍五入的方式保留两位小数
System.out.println(result5);
}
}
BigDecimal除法的方法
//divisor为被除数,scale为保留位数,roundingMode为采用保留位数的方式BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP为四舍五入方式
BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode);
Date
类 Date表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒。
//构造方法
Date()// 分配 Date 对象并初始化此对象,以表示分配它的时间(精确到毫秒)。
package com.javaclass;
import java.util.Date;
//Date类的测试
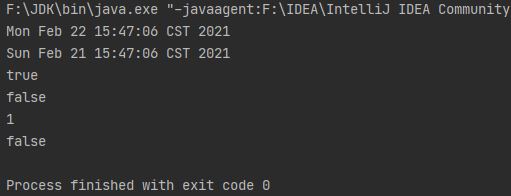
public class TestDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1.toString());
Date date2 = new Date(date1.getTime() - 24*60*60*1000);
System.out.println(date2);
System.out.println(date1.after(date2));
System.out.println(date1.before(date2));
System.out.println(date1.compareTo(date2)); //如果参数 Date 等于此 Date,则返回值 0;如果此 Date 在 Date 参数之前,则返回小于 0 的值;如果此 Date 在 Date 参数之后,则返回大于 0 的值。
System.out.println(date1.equals(date2));
}
}
从 JDK 1.1 开始,应该使用Calendar类实现日期和时间字段之间转换,使用 DateFormat 类来格式化和解析日期字符串。Date中的相应方法已废弃。
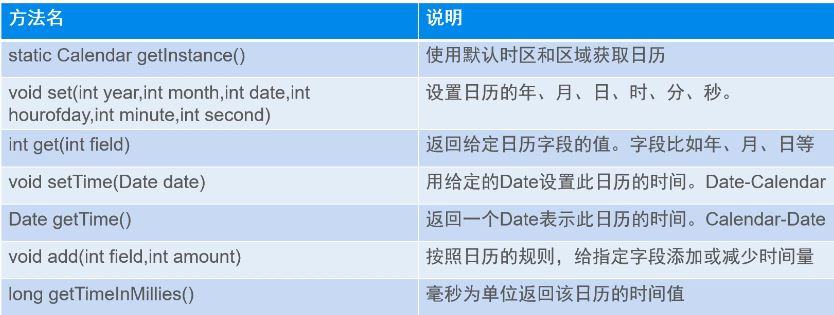
Calendar
构造方法为protected Calendar,无法直接创建对象,
package com.javaclass;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class TestCalendar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(calendar.getTime().toLocaleString());
//获取时间信息
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONDAY) + 1); //calendar.get(Calendar.MONDAY)返回值从0-11
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR));//12小时
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));//12小时
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND));
//设置时间
calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR, 2020);
System.out.println(calendar.getTime().toLocaleString());
calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR, 1);
System.out.println(calendar.getTime().toLocaleString());
//获取当前字段最大值
System.out.println(calendar.getActualMaximum(Calendar.MONTH) + 1);
System.out.println(calendar.getActualMinimum(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));
}
}
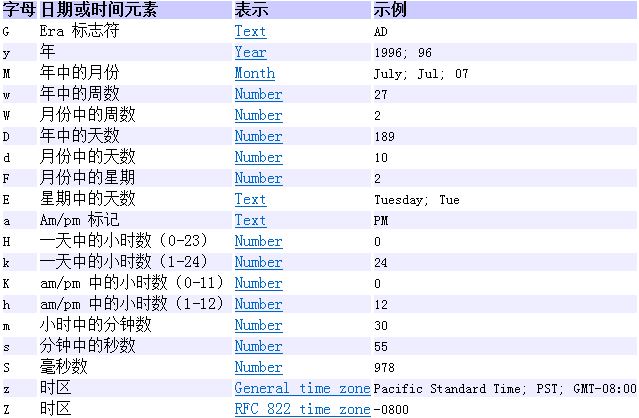
SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat 是一个以与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类。它允许进行格式化(日期 -> 文本)、解析(文本 -> 日期)和规范化。
package com.javaclass;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
//SimpleDateFormat测试
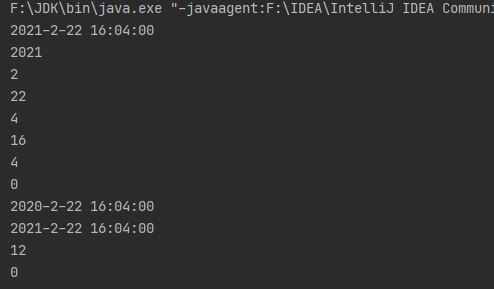
public class TestSimpleDateFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH-mm-ss");
Date date = new Date();
//格式化,Date->String
String str = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(str);
//解析,String->Date
Date date1 = sdf.parse("2020-2-2 5-10-5");
System.out.println(date1.toString());
//和Calendar类结合
System.out.println(sdf.format(Calendar.getInstance().getTime()));
}
}
System
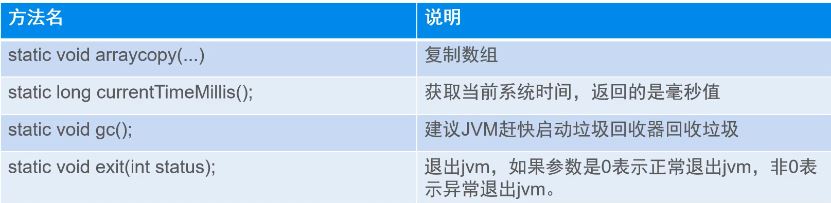
在System 类提供的方法中,有标准输入、标准输出和错误输出流;对外部定义的属性和环境变量的访问;加载文件和库的方法;还有快速复制数组的一部分的实用方法。 System中的方法均为静态方法,System类不能被实例化
static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)//src,源数组;srcPos,源数组复制开始位置;dest,目标数组;destPos,目标数组开始位置;length,复制长度
//通常用System.currentTimeMillis()来计算代码执行时间
System.gc()//内存回收方法见前文Object类
package com.javaclass;
//System测试
public class TestSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] res = {1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 5};
int[] tag = new int[5];
//src,源数组;srcPos,源数组复制开始位置;dest,目标数组;destPos,目标数组开始位置;length,复制长度
System.arraycopy(res, 1, tag, 1, 3); //native方法,效率很高
for (int i : tag) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
//通常用System.currentTimeMillis()来计算代码执行时间
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); //从1970年1月1日到现在的毫秒数
System.exit(0); //0表示正常退出
System.out.println("程序已退出");
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号