26.虚函数示例理解
Eg1.都没虚函数
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
class Father{
public:
Father(){
cout <<"this is the Father constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Father is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
void say(){
cout <<"Father is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
class Son :public Father{
public:
Son(){
cout <<"this is the Son constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Son is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
void say(){
cout <<"Son is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
int main(){
Father* fa = new Son();
fa->watchTv();
fa->say();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果
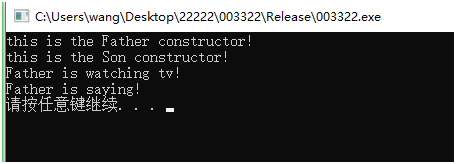
解析:因为是Father类型的指针直接调用Father类函数
Eg2.子类有虚函数
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
class Father{
public:
Father(){
cout <<"this is the Father constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Father is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
void say(){
cout <<"Father is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
class Son :public Father{
public:
Son(){
cout <<"this is the Son constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Son is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
virtualvoid say(){
cout <<"Son is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
int main(){
Father* fa = new Son();
fa->watchTv();
fa->say();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
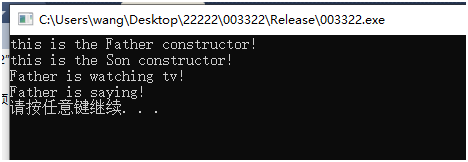
解析:也是直接调用父类函数
Eg3.子类有虚函数
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
class Father{
public:
Father(){
cout <<"this is the Father constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Father is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
virtualvoid say(){
cout <<"Father is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
class Son :public Father{
public:
Son(){
cout <<"this is the Son constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Son is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
void say(){
cout <<"Son is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
int main(){
Father* fa = new Son();
fa->watchTv();
fa->say();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果

解析:Father* fa = new Son()表示在son上Father类型指针,父类有虚函数,就会产生一个虚表,指向该函数,子数也会产生同样一个虚表,不过是指向父类,当主函数执行到fa->say();同于子类重写,父类也跟着重写了,所以是
。
Eg4.子类有虚函数
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
class Father{
public:
Father(){
cout <<"this is the Father constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Father is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
virtualvoid say(){
cout <<"Father is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
class Son :public Father{
public:
Son(){
cout <<"this is the Son constructor!"<< endl;
}
void watchTv(){
cout <<"Son is watching tv!"<< endl;
}
virtualvoid say(){
cout <<"Son is saying!"<< endl;
}
};
int main(){
Father* fa = new Son();
fa->watchTv();
fa->say();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
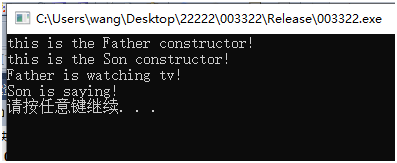
解析:
同eg3一样
全总结:父类和了类,一般都是先运行父类再运行子数,虚函数只改写子类。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号