1.运算符
![]()
package operator;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 25;
int d = 25;
System.out.println(a+b);
System.out.println(a-c);
System.out.println(a*d);
System.out.println(a/(double)b);
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long a = 53215631351631L;
int b = 20;
short c = 10 ;
byte d =15;
System.out.println(a+b+c+d);//long
System.out.println(b+c+d);//int
System.out.println(c+d);//int
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//关系运算符返回的结果,正确,错误 布尔值
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 21;
System.out.println(c%b);//1
System.out.println(a > b);
System.out.println(a < b);
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(a != b);
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//++ -- 自增自减运算符 一元运算符
int a = 3;
int b = a++;//执行完这行代码后,先给b赋值,再自增
int c = ++a;//执行完这行代码后,先自增,再给b赋值
System.out.println(a);//5
System.out.println(b);//3
System.out.println(c);//5
//2^3 很多时候我们会用到数学工具类
double pow = Math.pow(2, 3);//8.0
System.out.println(pow);
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//and(与) or(或) 非(取反)
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
System.out.println("a && b:" + (a&&b));//false 逻辑与运算,两个变量结果都为真,结果才为true
System.out.println("a || b:" + (a||b));//true 逻辑或运算,两个变量有一个为真,结果才为true
System.out.println("!(a && b):" + !(a && b));//true 如果为真,则变为假,如果为假则变为真
//短路运算
int c = 5;
boolean d = (c < 4)&& (c++ < 4);
System.out.println(c);//5
System.out.println(d);//false
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 左移 << *2 右移 >> /2
System.out.println(2<<3);//2左移三位 16
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
a += b;//a = a+b
a -= b;//a = a-b
System.out.println(a);
//字符串连接符 + String
System.out.println(""+a+b);//1020
System.out.println(a+b+"");//30
}
}
package operator;
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//x ? y : z
//如果x == true ,则结果为y,否则结果为z
int score = 80;
String type =score > 60 ? "及格" : "不及格";//必须掌握
System.out.println(type);
}
}
2.包机制
![]()
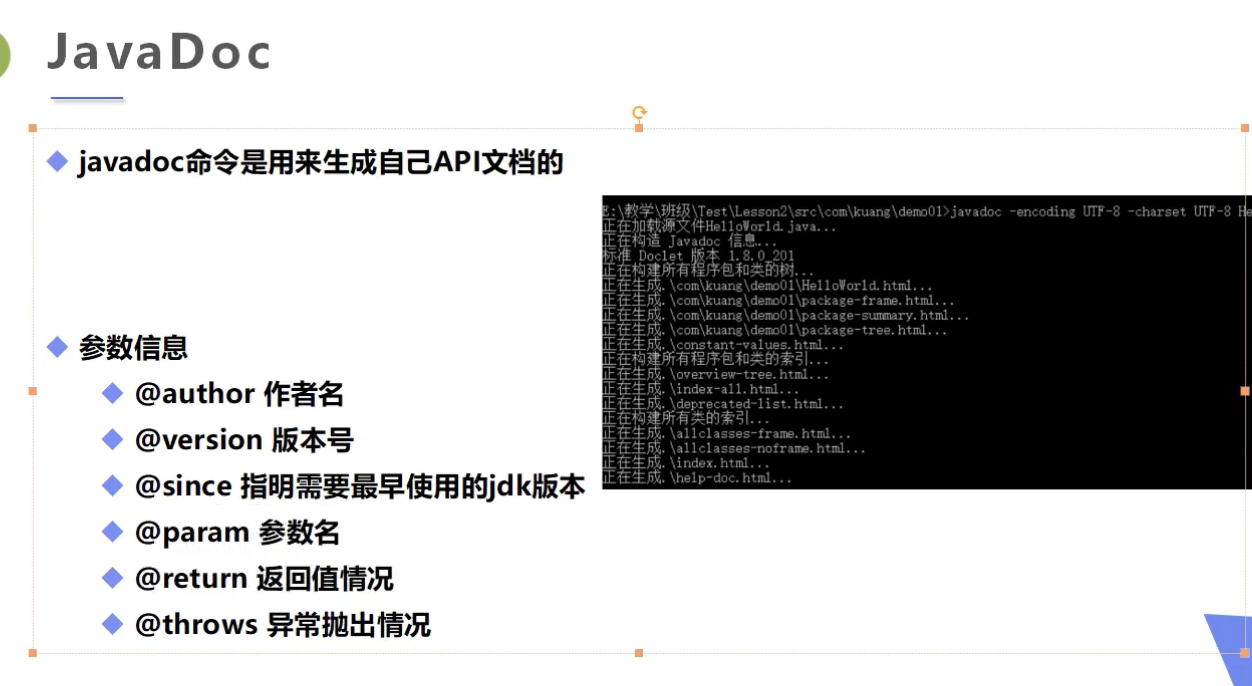
3.JavaDoc
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号