基础进阶
Java Web基础进阶
EL表达式
EL表达式:Expression Language(表达式语言),目的是替换JSP页面中的复杂代码。
EL表达式语法
${变量名} 变量是request域中存储的对象(在servlet中通过request.setAttribute()存储)
代码示例
<form action="/EL/ELServlet">
姓名:<input type="text" name="name" ></br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" ></br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="提交">
</form>
在另一个页面中显示:
姓名:${name}
</br>
年龄:${age}
servlet:
public class ELServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
**//将获取到的数据保存到request域中**
request.setAttribute("name", name);
request.setAttribute("age", age);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/2.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
JSTL标签
JSTL概述
JSTL:(JavaServerPage Standard Tag Library)Java标准标签库
JSTL通常会与EL表达式合作实现JSP页面的编码
使用JSTL,需要在JSP页面中添加taglib指令:
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
为什么要使用JSTL标签
-
在jsp中不建议直接写java代码(规范性问题)
-
EL表达式虽然可以解决不用书写Java代码的问题,但是对于复杂的数据(比如数组、集合等取值会很麻烦
-
使用JSTL标签配合EL表达式能够很好的解决复杂类型数据的问题,简化代码书写
通用标签
set标签:将值保存到指定范围里
<c:set var="username" value="张三" scope="scope" />
将value值存储到范围为scope的变量var中
out标签:将结果输出显示
<c:out value="value" />
remove标签:删除指定域内的数据
<c:remove var="username" scope="session" />
示例代码
<body>
<c:set var="username" value="张三" scope="request" />
<c:out value="${username}" />
<hr>
<c:remove var="username" scope="request" />
<hr>
<c:out value="${username}" />
</body>
条件标签
示例代码
<body>
<!-- if标签 -->
<c:set var="age" value="13" scope="request" />
<c:if test="${age==12 }">
年龄为12岁
</c:if>
hello world
<!-- choose 标签 -->
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${age==12 }">
您的年龄是12岁
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
你的年龄不是12岁
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</body>
迭代标签
示例代码
<body>
<table align="center" border="1">
<tr>
<td>产品</td>
<td>产地</td>
<td>价格</td>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${list}" var="Map">
<tr>
<td>${Map.shopName}</td>
<td>${Map.address}</td>
<td>${Map.price}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</body>
public class JSTLServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Map<String, Object> map1 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map1.put("shopName", "联想笔记本");
map1.put("address", "北京");
map1.put("price", 4999.99);
Map<String, Object> map2 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map2.put("shopName", "神州笔记本");
map2.put("address", "南京");
map2.put("price", 3999.99);
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(map1);
list.add(map2);
request.setAttribute("list", list);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/5.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
}
}
Ajax入门
什么是Ajax
通过在后台与服务器进行少量数据交换,Ajax可以使网页实现异步更新
传统的网页(不使用Ajax)如果需要更新内容的话,必须重载整个网页页面。
Ajax的好处
- 更新时只需要局部刷新,用户体验度好
- 由于只需要刷新局部的数据,对后台服务器的压力较小
Ajax语法总结
- url:请求资源的地址
- type:请求时数据的传递方式(常用的有get/post)
- data:用来传递的数据(建议使用json传递)
- success:与servlet交互成功后要执行的方法
- dataType:ajax接收后台数据的类型(建议使用json)
注意事项
ajax和后台交互的时候,后台是不能直接跳转到其他页面的
代码示例
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1、首先获取jsp页面传递过来的参数信息
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
//2、如果username="15912345678",password="12345678"则登录成功,否则登录失败
JSONObject jsonObject = null;
if("15912345678".equals(username) && "12345678".equals(password)){
System.out.println("username="+username);
System.out.println("password="+password);
jsonObject = new JSONObject("{flag:true}");
}else{
//如果登录失败,则给ajax返回数据
jsonObject = new JSONObject("{flag:false}");
}
response.getOutputStream().write(jsonObject.toString().getBytes("utf-8"));
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request,response);
}
}
jsp页面中的代码
<body style="text-align:center;">
<%-- <form action="<%=basePath%>/LoginServlet" method="post"> --%>
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<span class="c1">欢迎登录</span>
<span class="c2">没有帐号?</span>
<span class="c3">立即注册</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="text" name="username" placeholder="请输入登录邮箱/手机号"><span class="tip" style="color:red;font-size:12px"></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="password" name="password" placeholder="6-16位密码,区分大小写,不能空格"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<!-- <input type="submit" value="登录" id="login"> -->
<input type="button" value="登录" id="login">
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- </form> -->
</body>
<!--这里使用 #login来指示按下登录按钮(id为login)
<script type="text/javascript">
$("#login").click(function(){
//单击登录按钮的时候触发ajax事件
$.ajax({
url:"<%=basePath%>/LoginServlet",
type:"post",
data:{
username:$("input[name=username]").val(),
password:$("input[name=password]").val()
},
dataType:"json",
success:function(result){
var flag = result.flag;
if(flag==true){
//如果登录成功则跳转到成功页面
window.location.href="<%=basePath%>/pages/front/success.jsp";
}else{
//跳回到Index.jsp登录页面,同时在登录页面给用户一个友好的提示
$(".tip").text("您输入的用户名或者密码不正确");
}
}
});
});
</script>
Ajax使用场景
- 百度搜索框
- 地图
过滤器
过滤器概述
作用:实现对web资源请求的拦截,完成特殊的操作,尤其是对请求的预处理(除预处理之外,还有后处理)。
过滤器的应用场景
web资源访问权限控制
请求字符集编码处理
内容敏感字符词汇过滤
响应信息压缩
过滤器工作流程
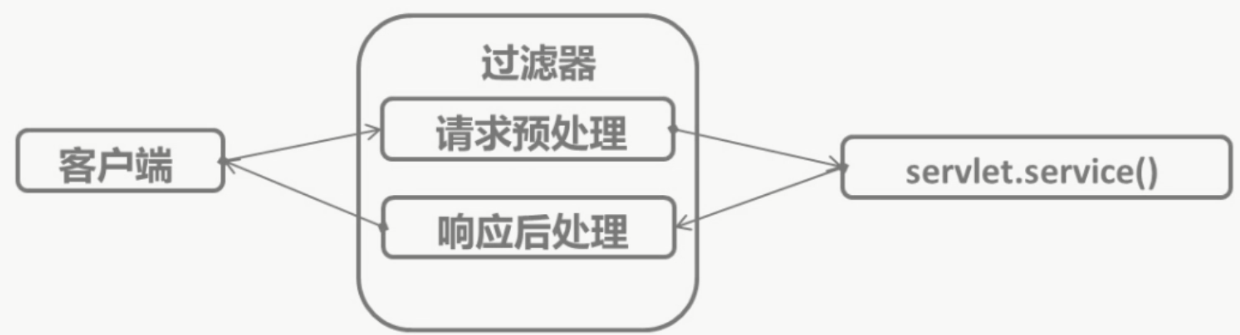
过滤器的生命周期——过滤器的创建和销毁由Web服务器负责
-
web应用程序启动时,web服务器创建Filter的实例对象,以及对象的初始化
-
当请求访问与过滤器关联的web资源时,过滤器拦截请求,完成指定功能。
-
Filter对象创建后会驻留在内存中,在web应用移除或服务器停止时才被销毁。
过滤器的实现步骤
-
编写Java类实现Filter接口,并实现其中的doFilter方法
-
在web.xml中对Filter类进行注册,并设置所拦截的资源
过滤器链
在一个web应用中,多个过滤器组合起来称之为一个过滤器链。
过滤器的调用顺序取决于过滤器在web.xml文件中的注册顺序。
示例:字符集过滤器
web.xml中进行注册:
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.scnb.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
实现Filter类
public class CharacterEncodingFilter implements Filter {
public CharacterEncodingFilter() {
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter destroy ...");
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
request.setCharacterEncoding(this.config.getInitParameter("charset"));
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
public void init(FilterConfig fConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("CharacterEncodingFilter init ...");
}
}
示例:用户登录控制
web.xml中:
<filter>
<filter-name>SessionFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.scnb.filter.SessionFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>SessionFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/message.jsp</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
public class SessionFilter implements Filter {
public void destroy() {
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest)request;
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse)response;
String loginUser = (String)req.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if (loginUser == null) {
resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp?flag=1");
}else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
}
public void init(FilterConfig fConfig) throws ServletException {
}
}
监听器
监听器定义
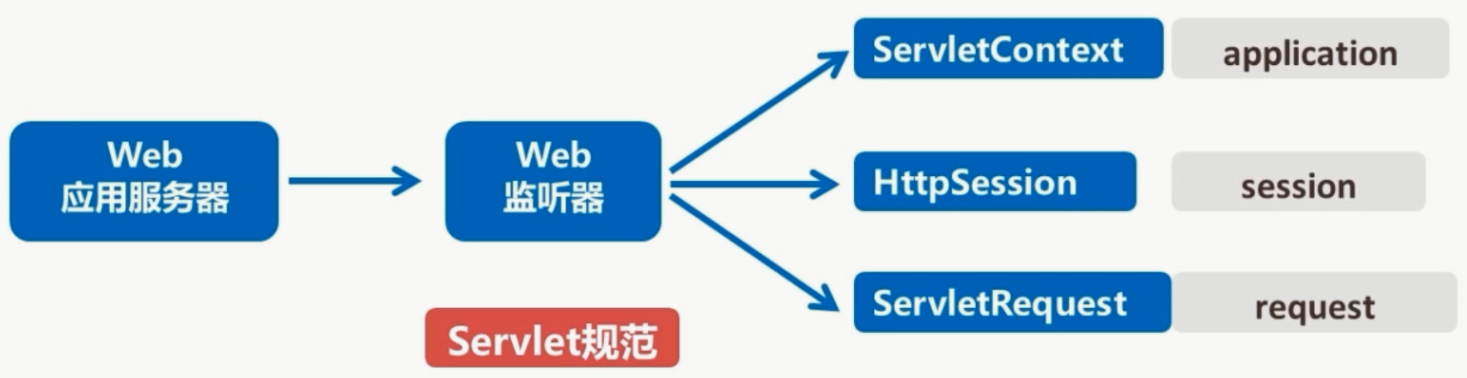
- 是Servlet规范定义的一种特殊类。
- 用于监听ServletContext、HttpSession、ServletRequest等域对象的创建、销毁及其属性修改发生变化的事件。
- 监听器可以在事件发生前后进行一些必要的处理操作。
常见应用场景
-
统计在线人数
-
页面访问量的统计
-
应用启动时完成信息初始化工作
-
与spring结合
-
监听器的实现步骤
-
编写java类实现监听器接口,并实现其接口方法
-
在web.xml文件中对实现的监听器类进行注册
监听器的基本实现
<listener>
<listener-class>com.scnb.listener.MyFirstListener</listener-class>
</listener>
public class MyFirstListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("context destroy...");
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("context init...");
}
}
多监听器的启动顺序

即按照在web.xml中定义的顺序来执行
监听器的分类
按监听对象
- ServletContext对象监听器
- HttpSession对象监听器:主要监听会话对象
- ServletRequest对象监听器:主要监听请求对象
按监听事件
- 域对象自身的创建和销毁事件监听器
- 域对象中属性的创建、替换和清除事件监听器
- 绑定到session中的某个对象的状态事件监听器
ServletContextListener
代码示例:
<context-param>
<param-name>version</param-name>
<param-value>1.0</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>com.scnb.listener.MyServletContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener {
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
String appName = (String)sce.getServletContext().getAttribute("app_name");
String version = (String)sce.getServletContext().getAttribute("version");
System.out.println("context destroy appName = " + appName + " version = " + version);
}
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
String appName = sce.getServletContext().getInitParameter("app_name");
String version = sce.getServletContext().getInitParameter("version");
sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("app_name", appName);
sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("version", version);
System.out.println("context init appName = " + appName + " version = " + version);
}
}
SessionListener
<listener>
listener-class>com.scnb.listener.MyHttpSessionListener</listener-class>
</listener>
public class MyHttpSessionListener implements javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener {
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent hse) {
String sessionId = hse.getSession().getId();
Date createTime = new Date(hse.getSession().getCreationTime());
System.out.println("session id = " + sessionId + ", createTime = " + createTime);
}
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent hse) {
String sessionId = hse.getSession().getId();
System.out.println("session id = " + sessionId);
}
}
ServletRequestListener
用户每发出一次请求操作,都会创建一个请求对象。
配置好请求对象监听器,就可以监听到用户发出的请求对象,从而得到请求对象中所有的内容。
示例代码:
<listener>
<listener-class>com.scnb.listener.MyServletRequestListener</listener-class>
</listener>
public class MyServletRequestListener implements ServletRequestListener {
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("request listener destroy...");
}
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {
System.out.println("request listener init...");
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest)sre.getServletRequest();
String path = req.getRequestURI();
String age = req.getParameter("age");
System.out.println("path = " + path + ", age = " + age);
}
}
<body>
首页
ServletRequestListener测试 <a href="servlet_request.jsp?age=12">点击测试</a>
</body>
域事件监听器
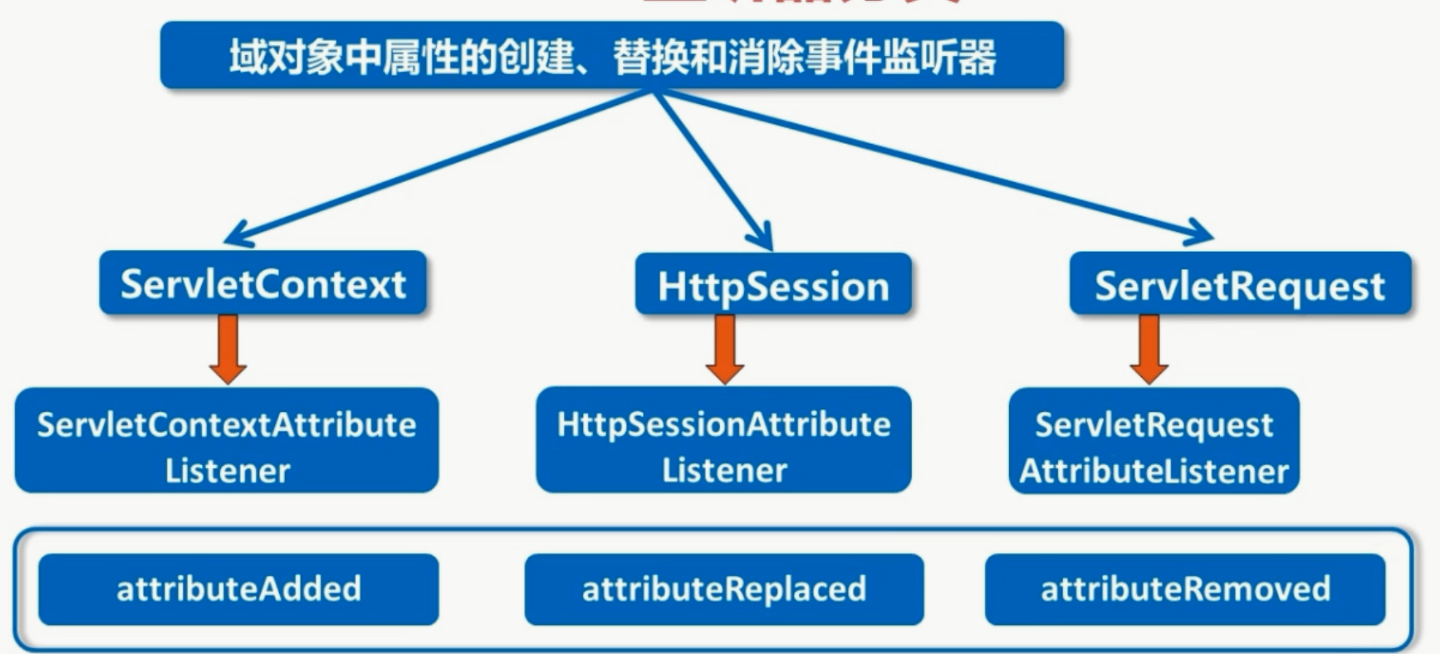
示例代码:
<listener>
<listener-class>com.scnb.listener.MyServletContextAttributeListener</listener-class>
</listener>
public class MyServletContextAttributeListener implements ServletContextAttributeListener {
public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent scae) {
System.out.println("ServletContext#attAdded#name:" + scae.getName() + "#value:" + scae.getValue());
}
public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent scae) {
System.out.println("ServletContext#attRemove#name:" + scae.getName() + "#value:" + scae.getValue());
}
public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent scae) {
System.out.println("ServletContext#attReplace#name:" + scae.getName() + "#value:" + scae.getValue());
}
}
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<label>
ServletRequestListener测试
</br>
<a href="servlet_request.jsp?age=12">点击测试</a>
</br>
</br>
</label>
</hr>
<label>
AttributeListener测试
</br>
<a href="attribute_init.jsp">属性初始化</a>
<a href="attribute_replace.jsp">属性修改</a>
<a href="attribute_remove.jsp">属性删除</a>
</label>
</body>
HttpSessionBindingListener
绑定到session中的某个对象的状态事件监听器
该监听器比较特殊,不需要在web.xml中注册。
实现两个方法:
-
valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event):当监听对象绑定至Http会话时调用
-
valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event):当监听对象从Http会话内被修改、移除或者会话被销毁时调用
getName():返回发生绑定和取消绑定的对象的名字




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号