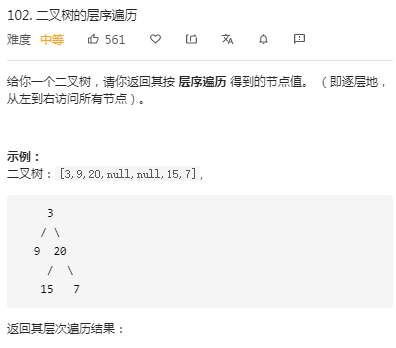

方法一:本文采用BFS进行层序遍历,具体分析参见https://www.cnblogs.com/sbb-first-blog/p/13259728.html
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * struct TreeNode *left; 6 * struct TreeNode *right; 7 * }; 8 */ 9 #define MAX_RETURN_NUM 1000 10 11 /** 12 * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. 13 * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. 14 * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). 15 */ 16 int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){ 17 int **ret=(int**)calloc(MAX_RETURN_NUM,sizeof(int *)); //分配一个二维数组 18 *returnColumnSizes=(int*)calloc(MAX_RETURN_NUM,sizeof(int)); //分配空间 19 *returnSize=0; 20 struct TreeNode *queue[10000]; 21 int outIndex=0; 22 int inIndex=0; 23 24 //判断异常输入,进入while循环之前初始化 25 if(root==NULL) return NULL; 26 queue[inIndex++]=root; 27 int levelcount=inIndex-outIndex; //记录每层的个数 28 int count=0,i; 29 30 //bfs 31 while(levelcount>0) 32 { 33 count++; 34 ret[*returnSize]=(int *)calloc(levelcount,sizeof(int)); 35 (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize]=levelcount; 36 //对每一层进行处理 37 for(i=0;i<levelcount;i++) 38 { 39 if(queue[outIndex]->left!=NULL) 40 { 41 queue[inIndex++]=queue[outIndex]->left; 42 } 43 if(queue[outIndex]->right!=NULL) 44 { 45 queue[inIndex++]=queue[outIndex]->right; 46 } 47 ret[*returnSize][i]=queue[outIndex]->val; 48 outIndex++; 49 } 50 //进入下一层的操作 51 (*returnSize)++; //在returnSize所指向的数据上加1, 52 levelcount=inIndex-outIndex; 53 } 54 return ret; 55 56 }
方法二:链表加BFS
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * struct TreeNode *left; 6 * struct TreeNode *right; 7 * }; 8 */ 9 10 11 /** 12 * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. 13 * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. 14 * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). 15 */ 16 typedef struct queue{ 17 int front; 18 int rear; 19 struct TreeNode *data[1009]; 20 }QUEUE; 21 int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){ 22 *returnSize=0; 23 if(root==NULL) 24 { 25 return NULL; 26 } 27 QUEUE q; 28 q.front=0; 29 q.rear=1; 30 q.data[0]=root; 31 int levelcount=q.rear-q.front; 32 int **res=(int **)malloc(sizeof(int *)*1009); //给二维数组分配空间 33 int n=-1; 34 while(q.front!=q.rear) 35 { 36 res[*returnSize]=(int *)malloc(1009*sizeof(int)); 37 (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize]=levelcount; 38 for(int i=0;i<levelcount;i++) 39 { 40 if(q.data[(q.front)]->left) 41 { 42 q.data[(q.rear)++]=q.data[q.front]->left; 43 } 44 if(q.data[(q.front)]->right) 45 { 46 q.data[(q.rear)++]=q.data[q.front]->right; 47 } 48 res[*returnSize][i]=q.data[q.front]->val; 49 q.front++; 50 } 51 levelcount=q.rear-q.front; 52 (*returnSize)++; 53 } 54 // *returnSize=n; 55 return res; 56 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号