【CV】GAN代码解析: networks.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import init
import functools
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
###############################################################################
# Helper Functions
###############################################################################
class Identity(nn.Module):
# 恒等映射层:前向直接返回输入,用于占位(例如 norm_type='none' 时)
def forward(self, x):
return x
def get_norm_layer(norm_type='instance'):
# 这个方法用于构造归一化层,根据norm_type返回一个归一化层,默认的norm_type是instance
"""Return a normalization layer
Parameters:
norm_type (str) -- the name of the normalization layer: batch | instance | none
For BatchNorm, we use learnable affine parameters and track running statistics (mean/stddev).
For InstanceNorm, we do not use learnable affine parameters. We do not track running statistics.
"""
# 这里用 functools.partial 保存构造参数(affine/track_running_stats),方便后续直接调用 norm_layer(num_features)
if norm_type == 'batch':
norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, affine=True, track_running_stats=True) # BN:可学习仿射 + 跟踪均值方差
elif norm_type == 'instance':
norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, affine=False, track_running_stats=False) # IN:无仿射 + 不跟踪统计量
elif norm_type == 'none':
# 若不使用归一化层,则返回一个函数,构造时放置 Identity()
def norm_layer(x):
return Identity()
else:
# 未知类型时报错
raise NotImplementedError('normalization layer [%s] is not found' % norm_type)
return norm_layer
def get_scheduler(optimizer, opt):
# 根据 命令行参数的opt.lr_policy 创建学习率调度器
# 此方法会返回一个调度器对象
"""Return a learning rate scheduler
Parameters:
optimizer -- the optimizer of the network
opt (option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions.
opt.lr_policy is the name of learning rate policy: linear | step | plateau | cosine
For 'linear', we keep the same learning rate for the first <opt.n_epochs> epochs
and linearly decay the rate to zero over the next <opt.n_epochs_decay> epochs.
For other schedulers (step, plateau, and cosine), we use the default PyTorch schedulers.
See https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html for more details.
"""
if opt.lr_policy == 'linear':
# 线性衰减:前 n_epochs 维持初始 lr,之后在 n_epochs_decay 内线性衰减到 0
def lambda_rule(epoch):
lr_l = 1.0 - max(0, epoch + opt.epoch_count - opt.n_epochs) / float(opt.n_epochs_decay + 1)
return lr_l
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda_rule)
elif opt.lr_policy == 'step':
# 固定步长衰减:每 lr_decay_iters 个 epoch 将 lr 乘以 0.1
scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=opt.lr_decay_iters, gamma=0.1)
elif opt.lr_policy == 'plateau':
# 监控指标停滞时衰减:factor=0.2, patience=5
scheduler = lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.2, threshold=0.01, patience=5)
elif opt.lr_policy == 'cosine':
# 余弦退火:在 T_max=n_epochs 内从初始 lr 退火到 eta_min=0
scheduler = lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=opt.n_epochs, eta_min=0)
else:
# 注意:这里返回了一个 NotImplementedError 对象而非抛出,一般应当 `raise NotImplementedError(...)`
return NotImplementedError('learning rate policy [%s] is not implemented', opt.lr_policy)
return scheduler
def init_weights(net, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02):
# 遍历模块,对 Conv/Linear/BatchNorm2d 等层的参数进行特定初始化
"""Initialize network weights.
Parameters:
net (network) -- network to be initialized
init_type (str) -- the name of an initialization method: normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonal
init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
We use 'normal' in the original pix2pix and CycleGAN paper. But xavier and kaiming might
work better for some applications. Feel free to try yourself.
"""
def init_func(m): # define the initialization function
classname = m.__class__.__name__
# 若层包含 weight,且是卷积或全连接层
if hasattr(m, 'weight') and (classname.find('Conv') != -1 or classname.find('Linear') != -1):
# 按 init_type 选择初始化方法
if init_type == 'normal':
init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, init_gain)
elif init_type == 'xavier':
init.xavier_normal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)
elif init_type == 'kaiming':
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data, a=0, mode='fan_in')
elif init_type == 'orthogonal':
init.orthogonal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('initialization method [%s] is not implemented' % init_type)
# 若存在偏置,置零
if hasattr(m, 'bias') and m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
# 对 BatchNorm2d:权重 ~ N(1, init_gain),偏置=0
elif classname.find('BatchNorm2d') != -1: # BatchNorm Layer's weight is not a matrix; only normal distribution applies.
init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, init_gain)
init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
print('initialize network with %s' % init_type)
net.apply(init_func) # 递归应用到子模块
def init_net(net, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
# 调用上面定义的几个方法,对整个网络进行初始化
"""Initialize a network: 1. register CPU/GPU device (with multi-GPU support); 2. initialize the network weights
Parameters:
net (network) -- the network to be initialized
init_type (str) -- the name of an initialization method: normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonal
gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
Return an initialized network.
"""
# 若指定了 gpu_ids,则将网络放到首个 GPU,并使用 DataParallel 多卡并行
if len(gpu_ids) > 0:
assert(torch.cuda.is_available())
net.to(gpu_ids[0]) # 注意:这里直接传入 int(如 0),在新版本里更推荐传 torch.device('cuda:0')
net = torch.nn.DataParallel(net, gpu_ids) # multi-GPUs
# 初始化网络权重
init_weights(net, init_type, init_gain=init_gain)
return net
def define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, netG, norm='batch', use_dropout=False, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
# 根据各个参数,构造一个生成器对象(就是一个net对象)
# 方法各参数解析:
# input_nc, output_nc 输入和输出通道数
# ngf 最后一层卷积层的滤波器个数
# netG 生成器结构的名字 resnet_9blocks | resnet_6blocks | unet_256 | unet_128
# norm='batch' 归一化层的类别以及默认值
# use_dropout=False 是否使用权重随机丢弃
# init_type='normal' net对象初始化类型
# gpu_ids:gpu设备号
# 为了把生成器放到正确的设备上并(可选)做多卡并行。
# networks.define_G(..., gpu_ids=...) 会把参数传给 init_net
"""Create a generator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
netG (str) -- the architecture's name: resnet_9blocks | resnet_6blocks | unet_256 | unet_128
norm (str) -- the name of normalization layers used in the network: batch | instance | none
use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
init_type (str) -- the name of our initialization method.
init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
Returns a generator
Our current implementation provides two types of generators:
U-Net: [unet_128] (for 128x128 input images) and [unet_256] (for 256x256 input images)
The original U-Net paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597
Resnet-based generator: [resnet_6blocks] (with 6 Resnet blocks) and [resnet_9blocks] (with 9 Resnet blocks)
Resnet-based generator consists of several Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.
We adapt Torch code from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project (https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style).
The generator has been initialized by <init_net>. It uses RELU for non-linearity.
"""
net = None
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm) # 根据 norm 获得归一化层构造器
# 根据 netG 选择具体生成器结构并构造
if netG == 'resnet_9blocks':
net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=9)
elif netG == 'resnet_6blocks':
net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=6)
elif netG == 'unet_128':
net = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 7, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
elif netG == 'unet_256':
net = UnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, 8, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('Generator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netG)
return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids) # 放设备 + 初始化权重 + (可选)多卡
def define_D(input_nc, ndf, netD, n_layers_D=3, norm='batch', init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):
# 用同样的逻辑,构造判别器
"""Create a discriminator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the first conv layer
netD (str) -- the architecture's name: basic | n_layers | pixel
n_layers_D (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator; effective when netD=='n_layers'
norm (str) -- the type of normalization layers used in the network.
init_type (str) -- the name of the initialization method.
init_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.
gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2
Returns a discriminator
Our current implementation provides three types of discriminators:
[basic]: 'PatchGAN' classifier described in the original pix2pix paper.
It can classify whether 70×70 overlapping patches are real or fake.
Such a patch-level discriminator architecture has fewer parameters
than a full-image discriminator and can work on arbitrarily-sized images
in a fully convolutional fashion.
[n_layers]: With this mode, you can specify the number of conv layers in the discriminator
with the parameter <n_layers_D> (default=3 as used in [basic] (PatchGAN).)
[pixel]: 1x1 PixelGAN discriminator can classify whether a pixel is real or not.
It encourages greater color diversity but has no effect on spatial statistics.
The discriminator has been initialized by <init_net>. It uses Leakly RELU for non-linearity.
"""
net = None
norm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm) # 归一化层构造器
# 选择判别器结构
if netD == 'basic': # default PatchGAN classifier
net = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers=3, norm_layer=norm_layer)
elif netD == 'n_layers': # more options
net = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, norm_layer=norm_layer)
elif netD == 'pixel': # classify if each pixel is real or fake
net = PixelDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, norm_layer=norm_layer)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('Discriminator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netD)
return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids) # 放设备 + 初始化权重 + (可选)多卡
##############################################################################
# Classes
##############################################################################
class GANLoss(nn.Module):
# 定义损失函数
"""Define different GAN objectives.
The GANLoss class abstracts away the need to create the target label tensor
that has the same size as the input.
"""
def __init__(self, gan_mode, target_real_label=1.0, target_fake_label=0.0):
""" Initialize the GANLoss class.
Parameters:
gan_mode (str) - - the type of GAN objective. It currently supports vanilla, lsgan, and wgangp.
target_real_label (bool) - - label for a real image
target_fake_label (bool) - - label of a fake image
Note: Do not use sigmoid as the last layer of Discriminator.
LSGAN needs no sigmoid. vanilla GANs will handle it with BCEWithLogitsLoss.
"""
super(GANLoss, self).__init__()
# 将真实/伪造标签注册为 buffer(随模型保存/加载,且不会被优化)
self.register_buffer('real_label', torch.tensor(target_real_label))
self.register_buffer('fake_label', torch.tensor(target_fake_label))
self.gan_mode = gan_mode
# 根据 gan_mode 选择损失形式
if gan_mode == 'lsgan':
self.loss = nn.MSELoss() # LSGAN 用 MSE
elif gan_mode == 'vanilla':
self.loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() # 原始 GAN:结合 Sigmoid 的 BCE(更稳定,内部带logits)
elif gan_mode in ['wgangp']:
self.loss = None # WGAN-GP 不使用显式目标张量
else:
raise NotImplementedError('gan mode %s not implemented' % gan_mode)
def get_target_tensor(self, prediction, target_is_real):
"""Create label tensors with the same size as the input.
Parameters:
prediction (tensor) - - tpyically the prediction from a discriminator
target_is_real (bool) - - if the ground truth label is for real images or fake images
Returns:
A label tensor filled with ground truth label, and with the size of the input
"""
# 生成与预测同形状的标签张量(展开 broadcast)
if target_is_real:
target_tensor = self.real_label
else:
target_tensor = self.fake_label
return target_tensor.expand_as(prediction)
def __call__(self, prediction, target_is_real):
"""Calculate loss given Discriminator's output and grount truth labels.
Parameters:
prediction (tensor) - - tpyically the prediction output from a discriminator
target_is_real (bool) - - if the ground truth label is for real images or fake images
Returns:
the calculated loss.
"""
# 计算不同 GAN 模式下的损失
if self.gan_mode in ['lsgan', 'vanilla']:
target_tensor = self.get_target_tensor(prediction, target_is_real)
loss = self.loss(prediction, target_tensor)
elif self.gan_mode == 'wgangp':
# WGAN-GP:真实取 -mean,伪造取 +mean
if target_is_real:
loss = -prediction.mean()
else:
loss = prediction.mean()
return loss
# 后面这几个是不同类型的损失函数需要用到的一些方法,先不看了
# 这里也没看懂是什么,写的是WGAN-GP的梯度惩罚项,应该是这种损失函数里的一个正则化项
def cal_gradient_penalty(netD, real_data, fake_data, device, type='mixed', constant=1.0, lambda_gp=10.0):
"""Calculate the gradient penalty loss, used in WGAN-GP paper https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00028
Arguments:
netD (network) -- discriminator network
real_data (tensor array) -- real images
fake_data (tensor array) -- generated images from the generator
device (str) -- GPU / CPU: from torch.device('cuda:{}'.format(self.gpu_ids[0])) if self.gpu_ids else torch.device('cpu')
type (str) -- if we mix real and fake data or not [real | fake | mixed].
constant (float) -- the constant used in formula ( ||gradient||_2 - constant)^2
lambda_gp (float) -- weight for this loss
Returns the gradient penalty loss
"""
# 计算 WGAN-GP 的梯度惩罚项(可在真实/伪造/混合样本上)
if lambda_gp > 0.0:
if type == 'real': # 使用真实样本
interpolatesv = real_data
elif type == 'fake': # 使用伪造样本
interpolatesv = fake_data
elif type == 'mixed': # 使用线性插值的混合样本
alpha = torch.rand(real_data.shape[0], 1, device=device)
# 扩展到与 real_data 同形状:按 batch 展开
alpha = alpha.expand(real_data.shape[0], real_data.nelement() // real_data.shape[0]).contiguous().view(*real_data.shape)
interpolatesv = alpha * real_data + ((1 - alpha) * fake_data)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('{} not implemented'.format(type))
interpolatesv.requires_grad_(True)
# 判别器对插值样本的输出
disc_interpolates = netD(interpolatesv)
# 计算输出对输入的梯度
gradients = torch.autograd.grad(outputs=disc_interpolates, inputs=interpolatesv,
grad_outputs=torch.ones(disc_interpolates.size()).to(device),
create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)
gradients = gradients[0].view(real_data.size(0), -1) # 展平到 (B, -1)
# 计算惩罚项:((||g||_2 - constant)^2).mean() * lambda_gp,加上微小 eps 防止数值问题
gradient_penalty = (((gradients + 1e-16).norm(2, dim=1) - constant) ** 2).mean() * lambda_gp # added eps
return gradient_penalty, gradients
else:
return 0.0, None
接下来这部分比较重要,定义了ResNet 9 blocks类型的生成器的基本结构
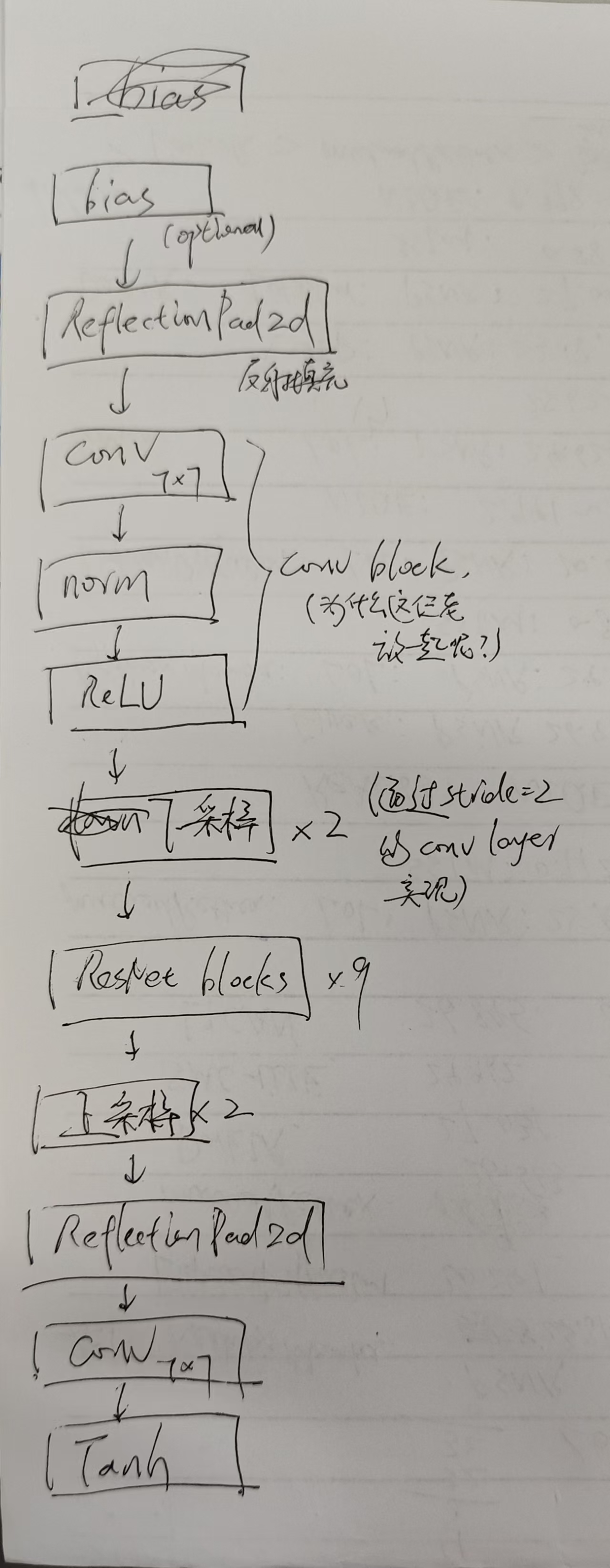
class ResnetGenerator(nn.Module):
"""Resnet-based generator that consists of Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.
We adapt Torch code and idea from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project(https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style)
"""
def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False, n_blocks=6, padding_type='reflect'):
"""Construct a Resnet-based generator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
norm_layer -- normalization layer
use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers
n_blocks (int) -- the number of ResNet blocks
padding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer in conv layers: reflect | replicate | zero
"""
assert(n_blocks >= 0)
super(ResnetGenerator, self).__init__()
# 判断是否需要卷积层 bias:IN 通常需要 bias,BN 通常不需要
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
# 头部:反射填充 3,7x7 Conv,Norm,ReLU
model = [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3),
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ngf, kernel_size=7, padding=0, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True)]
# 下采样 2 次:每次通道数 *2,stride=2 的 3x3 Conv
n_downsampling = 2
for i in range(n_downsampling): # add downsampling layers
mult = 2 ** i
model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, ngf * mult * 2, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ngf * mult * 2),
nn.ReLU(True)]
# 中间堆叠 ResNet blocks(保持分辨率与通道不变)
mult = 2 ** n_downsampling
# 这里的n_blocks是参数,代表一共堆叠多少层resnet
for i in range(n_blocks): # add ResNet blocks
model += [ResnetBlock(ngf * mult, padding_type=padding_type, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, use_bias=use_bias)]
# for循环构造resnetBlock类,这个类在下面有定义
# 上采样 2 次:ConvTranspose2d 反卷积 + Norm + ReLU
for i in range(n_downsampling): # add upsampling layers
mult = 2 ** (n_downsampling - i)
model += [nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * mult, int(ngf * mult / 2),
kernel_size=3, stride=2,
padding=1, output_padding=1,
bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(int(ngf * mult / 2)),
nn.ReLU(True)]
# 尾部:反射填充 + 7x7 Conv + Tanh 输出到 [-1,1]
model += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3)]
model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf, output_nc, kernel_size=7, padding=0)]
model += [nn.Tanh()]
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, input):
"""Standard forward"""
return self.model(input)
定义resnet blocks类
class ResnetBlock(nn.Module):
"""Define a Resnet block"""
def __init__(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias):
"""Initialize the Resnet block
A resnet block is a conv block with skip connections
We construct a conv block with build_conv_block function,
and implement skip connections in <forward> function.
Original Resnet paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf
"""
super(ResnetBlock, self).__init__()
# 构建“Conv-Norm-ReLU-(Dropout)-Conv-Norm”的子序列
self.conv_block = self.build_conv_block(dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias)
def build_conv_block(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias):
# 构造conv block(注意不是简单的conv层)
"""Construct a convolutional block.
Parameters:
dim (int) -- the number of channels in the conv layer.
padding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer: reflect | replicate | zero
norm_layer -- normalization layer
use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
use_bias (bool) -- if the conv layer uses bias or not
Returns a conv block (with a conv layer, a normalization layer, and a non-linearity layer (ReLU))
"""
# 包含卷积层,归一化层,ReLU非线性层
conv_block = []
# 定义一个列表变量
p = 0
# 第一层的“等效 padding”:可用反射/复制 padding 模块,或使用 zero padding(p=1)
if padding_type == 'reflect':
conv_block += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'replicate':
conv_block += [nn.ReplicationPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'zero':
p = 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)
# Conv + Norm + ReLU
conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias), norm_layer(dim), nn.ReLU(True)]
if use_dropout:
conv_block += [nn.Dropout(0.5)]
# 第二层前的 padding 选择与第一层一致
p = 0
if padding_type == 'reflect':
conv_block += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'replicate':
conv_block += [nn.ReplicationPad2d(1)]
elif padding_type == 'zero':
p = 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)
# Conv + Norm(无激活,便于残差相加前保留线性变换)
conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias), norm_layer(dim)]
return nn.Sequential(*conv_block)
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward function (with skip connections)"""
out = x + self.conv_block(x) # 残差连接:F(x) + x
return out
uNet架构的生成器
可以看出,在uNet架构生成器里,ngf(尾部卷积层滤波器个数)对于网络结构有很大用处
class UnetGenerator(nn.Module):
"""Create a Unet-based generator"""
def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, num_downs, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False):
"""Construct a Unet generator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
output_nc (int) -- the number of channels in output images
num_downs (int) -- the number of downsamplings in UNet. For example, # if |num_downs| == 7,
image of size 128x128 will become of size 1x1 # at the bottleneck
ngf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
norm_layer -- normalization layer
We construct the U-Net from the innermost layer to the outermost layer.
It is a recursive process.
"""
super(UnetGenerator, self).__init__()
# 自底向上地搭建 U-Net(先最内层,再逐层包裹),最后外层接 Tanh 输出
# 最内层 block(innermost=True)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=None, norm_layer=norm_layer, innermost=True) # add the innermost layer
# 若 num_downs 较大,中间堆叠多个(通道 ngf*8 不变),可选 dropout
for i in range(num_downs - 5): # add intermediate layers with ngf * 8 filters
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout)
# 逐步减小通道:ngf*8 → ngf*4 → ngf*2 → ngf
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 4, ngf * 8, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 2, ngf * 4, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer)
unet_block = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf, ngf * 2, input_nc=None, submodule=unet_block, norm_layer=norm_layer)
# 这里是一个逐渐递归的构建过程,以上一层的基础再往上加新的层
# 构建过程通过UnetSkipConnectionBlock类的构造函数实现
# 这里用到的UnetSkipConnectionBlock类再后面有定义
# 最外层:指定 input_nc / output_nc,并且 outermost=True(最后接 Tanh)
self.model = UnetSkipConnectionBlock(output_nc, ngf, input_nc=input_nc, submodule=unet_block, outermost=True, norm_layer=norm_layer) # add the outermost layer
def forward(self, input):
"""Standard forward"""
return self.model(input)
class UnetSkipConnectionBlock(nn.Module):
"""Defines the Unet submodule with skip connection.
X -------------------identity----------------------
|-- downsampling -- |submodule| -- upsampling --|
"""
def __init__(self, outer_nc, inner_nc, input_nc=None,
submodule=None, outermost=False, innermost=False, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False):
"""Construct a Unet submodule with skip connections.
Parameters:
outer_nc (int) -- the number of filters in the outer conv layer
inner_nc (int) -- the number of filters in the inner conv layer
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images/features
submodule (UnetSkipConnectionBlock) -- previously defined submodules
outermost (bool) -- if this module is the outermost module
innermost (bool) -- if this module is the innermost module
norm_layer -- normalization layer
use_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.
"""
super(UnetSkipConnectionBlock, self).__init__()
self.outermost = outermost # 记录是否为最外层(影响 forward 合并方式)
# 确定是否需要 bias(与 IN/BN 选择相关)
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
# 若未显式给 input_nc,则默认与 outer_nc 相同(便于递归堆叠)
if input_nc is None:
input_nc = outer_nc
# 下采样:4x4/stride=2 的卷积
downconv = nn.Conv2d(input_nc, inner_nc, kernel_size=4,
stride=2, padding=1, bias=use_bias)
# 基本组件:LeakyReLU/BN/ReLU 等
downrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
downnorm = norm_layer(inner_nc)
uprelu = nn.ReLU(True)
upnorm = norm_layer(outer_nc)
if outermost:
# 最外层:上采样不接 BN,最后接 Tanh 输出到 [-1,1]
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1)
down = [downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv, nn.Tanh()]
model = down + [submodule] + up
elif innermost:
# 最内层:下采样后直接上采样并接 BN(无子模块)
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=use_bias)
down = [downrelu, downconv]
up = [uprelu, upconv, upnorm]
model = down + up
else:
# 中间层:下采样 + 子模块 + 上采样,可能附加 Dropout
upconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1, bias=use_bias)
down = [downrelu, downconv, downnorm]
up = [uprelu, upconv, upnorm]
if use_dropout:
model = down + [submodule] + up + [nn.Dropout(0.5)]
else:
model = down + [submodule] + up
self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)
def forward(self, x):
if self.outermost:
# 最外层:不做 skip 相加/拼接,直接返回
return self.model(x)
else: # add skip connections
# 其它层:与输入在通道维度拼接,实现 U-Net 的跳接(cat([x, F(x)], dim=1))
return torch.cat([x, self.model(x)], 1)
NLayerDiscriminator类定义patchGAN类型的判别器结构

class NLayerDiscriminator(nn.Module):
"""Defines a PatchGAN discriminator"""
def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
"""Construct a PatchGAN discriminator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
n_layers (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator
norm_layer -- normalization layer
"""
super(NLayerDiscriminator, self).__init__()
# 与上文相同逻辑:IN 时使用 bias,BN 时不使用
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial: # no need to use bias as BatchNorm2d has affine parameters
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
kw = 4 # 卷积核大小 4x4
padw = 1 # padding=1 保持特定空间尺寸变化
# 第一层:不接 BN(经验上判别器首层不加 BN)
sequence = [nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)]
nf_mult = 1
nf_mult_prev = 1
# 中间层:逐层通道倍增(最多到 *8),stride=2 下采样
for n in range(1, n_layers): # gradually increase the number of filters
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
# 倒数第二层:stride=1,进一步提取局部判别特征
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)
sequence += [
nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)
]
# 最后一层:输出 1 通道的“Patch 级”真伪图(无需 Sigmoid,交由损失函数处理)
sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)] # output 1 channel prediction map
self.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)
def forward(self, input):
"""Standard forward."""
return self.model(input)
定义一个像素级别的判别器
根据上面的定义可以知道,patchGAN最终的判别图的尺寸有很多种
当判别图尺寸为1×1时,即为像素级别的判别器
class PixelDiscriminator(nn.Module):
"""Defines a 1x1 PatchGAN discriminator (pixelGAN)"""
def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):
"""Construct a 1x1 PatchGAN discriminator
Parameters:
input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input images
ndf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layer
norm_layer -- normalization layer
"""
super(PixelDiscriminator, self).__init__()
# 同样的 bias 逻辑(取决于是否使用 IN)
if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial: # no need to use bias as BatchNorm2d has affine parameters
use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2d
else:
use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d
# PixelGAN:全使用 1x1 卷积,仅对颜色分布进行逐像素判别(不建模空间结构)
self.net = [
nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=use_bias),
norm_layer(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True),
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, 1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=use_bias)]
self.net = nn.Sequential(*self.net)
# 备注:PixelDiscriminator 鼓励颜色多样性,但不对空间统计(纹理/结构)建模
def forward(self, input):
"""Standard forward."""
return self.net(input)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号