java:多线程
创建线程
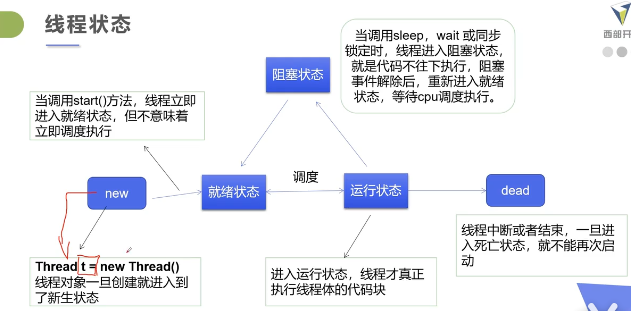
线程状态:
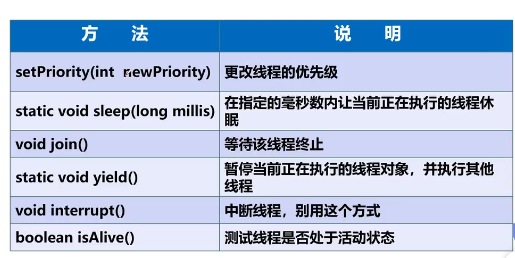
方法:
三种创建方式:1.继承Thread类。2.实现Runnable接口。3.实现Callable接口。
1.继承Thread类
public class StartThread extends Thread { //线程入口点 @Override public void run() { //线程体 } }
StartThread startThread=new StartThread(); startThread.start();//注意是start方法,不是run方法
注:因为单继承的局限性,不推荐使用。
2.实现Runnable接口
public class TestThread implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { //线程体 } }
TestThread testThread=new TestThread(); Thread thread=new Thread(testThread);//注意与继承Thread的不同 thread.start();
注:避免了单继承的局限性,灵活方便,推荐使用。
方便同一个对象被多个线程使用。(一份资源:多个代理)例子如下:
//买火车票的例子(注意:这个例子会出现数据紊乱,原因是多个线程操作同一个对象,数据不安全了) public class TestThread implements Runnable { //票数 private int ticketNums=10; @Override public void run() { while(true) { if(ticketNums<=0) break; try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"拿到了第"+ticketNums+"张票!"); ticketNums--; } } }
TestThread testThread=new TestThread(); new Thread(testThread,"小明").start(); new Thread(testThread,"老师").start(); new Thread(testThread,"黄牛").start();
简单创建
Thread thread=new Thread() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("___________________"); } }; thread.start();
线程停止
推荐线程自己停止下来。建议使用一个标志位进行终止变量:当flag=false,则终止线程运行。
public class StartThread extends Thread { boolean flag=true; @Override public void run() { while(flag) { System.out.println("This thread is running"); } } public void Stop() { flag=false; } }
StartThread startThread=new StartThread(); startThread.start(); startThread.Stop();
线程休眠
sleep(时间)指定当前线程阻塞的毫秒数;
sleep时间达到后线程进入就绪状态;
每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁;
sleep函数最好使用在run方法内部,可以让该线程休眠;
public static void main(String[] args) { int i=0; while(true) { System.out.println(i); i++; if(i>10) break; try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }
线程_yield
礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞。
将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态。
让cpu重新调度,礼让不一定成功。
(java中yiled()方法的作用是:让当前处于运行状态的线程退回到可运行状态,让出抢占资源的机会)
(比喻:三个人塞米赛跑,三人都快跑到90m位置的时候,2号突然被传送到了起点,三人继续跑,这样1号和3号赢的机会就大得多)
public class StartThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行"); Thread.yield(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程停止执行"); } }
线程_join
合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞。
thread.Join把指定的线程加入到当前线程,可以将两个交替执行的线程合并为顺序执行的线程。
test.join()方法阻塞调用此方法的线程(calling thread)进入 TIMED_WAITING 状态,直到线程test完成,此线程再继续;比如在线程B中调用了线程A的Join()方法,直到线程A执行完毕后,才会继续执行线程B。
通常用于在main()主线程内,等待其它线程完成再结束main()主线程。
Join方法实现是通过wait。
public class TestJoin { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread1 = new Thread(new JoinThread());; Thread thread2 = new Thread(new JoinThread()); thread1.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.start(); } static class JoinThread implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { for(int i=0; i<100; i++) { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
注:在主线程中调用了thread1的join方法,就等于将主线程和thread1的执行方式由并行改为了串行,也就是必须当thread1全部执行结束之后,才会调用thread2的方法。
线程状态

线程优先级
TestThread testThread=new TestThread(); Thread tThread=new Thread(testThread); tThread.getPriority();//获取优先级 tThread.setPriority(0);//改变优先级
/** * The minimum priority that a thread can have. */ public static final int MIN_PRIORITY = 1; /** * The default priority that is assigned to a thread. */ public static final int NORM_PRIORITY = 5; /** * The maximum priority that a thread can have. */ public static final int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
2021.09.15



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号