源码分析之Queue(四)LinkedBlockingQueue

数据结构
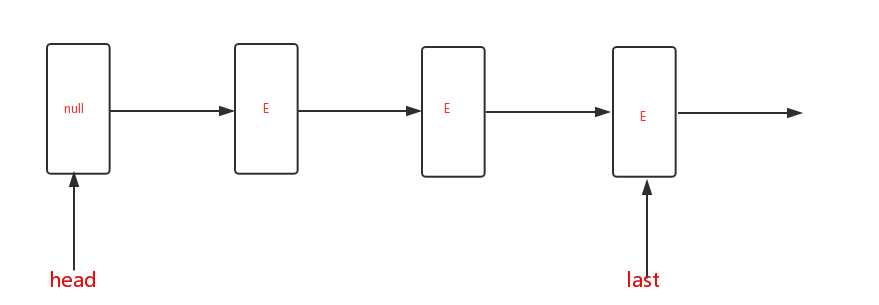
LinkedBlockingQueue是一个底层为单向链表的,有界的,FIFO阻塞队列;访问和移除操作是在队头,添加操作在队尾进行,并且使用不同的锁进行保护。
LinkedBlockingQueue中维持两把锁,一把锁用于入队,一把锁用于出队,这也就意味着,同一时刻,只能有一个线程执行入队,其余执行入队的线程将会被阻塞;同时,可以有另一个线程执行出队,其余执行出队的线程将会被阻塞。换句话说,虽然入队和出队两个操作同时均只能有一个线程操作,但是可以一个入队线程和一个出队线程共同执行,也就意味着可能同时有两个线程在操作队列,那么为了维持线程安全,LinkedBlockingQueue使用一个AtomicInterger类型的变量表示当前队列中含有的元素个数,所以可以确保两个线程之间操作底层队列是线程安全的
源码解析

public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6903933977591709194L; /** * Linked list node class */ static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node(E x) { item = x; } } /** The capacity bound, or Integer.MAX_VALUE if none */ private final int capacity; /** Current number of elements */ private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(); /** * Head of linked list. Invariant: head.item == null */ transient Node<E> head; /** * Tail of linked list.Invariant: last.next == null */ private transient Node<E> last; /** Lock held by take, poll, etc */ private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock(); /** Wait queue for waiting takes */ private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition(); /** Lock held by put, offer, etc */ private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock(); /** Wait queue for waiting puts */ private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition(); /** * Signals a waiting take. Called only from put/offer (which do not * otherwise ordinarily lock takeLock.) //发出一个非空通知,唤醒一个take阻塞线程 */ private void signalNotEmpty() { final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lock(); try { notEmpty.signal(); } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } } /** * Signals a waiting put. Called only from take/poll. //发出一个非满通知,唤醒一个put阻塞线程 */ private void signalNotFull() { final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; putLock.lock(); try { notFull.signal(); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } } /** * Links node at end of queue. 从尾节点入队 * @param node the node */ private void enqueue(Node<E> node) { // assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); // assert last.next == null; last = last.next = node; } /** * Removes a node from head of queue. 从头节点出队 * @return the node */ private E dequeue() { // assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(); // assert head.item == null; Node<E> h = head; Node<E> first = h.next; h.next = h; // help GC head = first; E x = first.item; first.item = null; return x; } /** * Locks to prevent both puts and takes. */ void fullyLock() { putLock.lock(); takeLock.lock(); } /** * Unlocks to allow both puts and takes. */ void fullyUnlock() { takeLock.unlock(); putLock.unlock(); } /** * Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}. */ public LinkedBlockingQueue() { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); } /** * Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed) capacity.*/ public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) { if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.capacity = capacity; last = head = new Node<E>(null); } /** * Creates a {@code LinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}, initially containing the elements of the given collection,*/ public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; putLock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility try { int n = 0; for (E e : c) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if (n == capacity) throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full"); enqueue(new Node<E>(e)); ++n; } count.set(n); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } } /** * Returns the number of elements in this queue. * @return the number of elements in this queue */ public int size() { return count.get(); } /** * Returns the number of additional elements that this queue can ideally accept without blocking*/ public int remainingCapacity() { return capacity - count.get(); } /** * Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if necessary for space to become available. * * @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} */ public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var // holding count negative to indicate failure unless set. int c = -1; Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; final AtomicInteger count = this.count; putLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == capacity) { notFull.await(); } enqueue(node); c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity) notFull.signal(); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0) signalNotEmpty(); } /** * Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if necessary up to the specified wait time for space to become available. * * @return {@code true} if successful, or {@code false} if * the specified waiting time elapses before space is available * @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); int c = -1; final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; final AtomicInteger count = this.count; putLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == capacity) { if (nanos <= 0) return false; nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos); } enqueue(new Node<E>(e)); c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity) notFull.signal(); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0) signalNotEmpty(); return true; } /** * Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue if it is possible to do so immediately without exceeding the queue's capacity * @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null */ public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); final AtomicInteger count = this.count; if (count.get() == capacity) return false; int c = -1; Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; putLock.lock(); try { if (count.get() < capacity) { enqueue(node); c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity) notFull.signal(); } } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0) signalNotEmpty(); return c >= 0; } public E take() throws InterruptedException { E x; int c = -1; final AtomicInteger count = this.count; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == 0) { notEmpty.await(); } x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1) notEmpty.signal(); } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } if (c == capacity) signalNotFull(); return x; } public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { E x = null; int c = -1; long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); final AtomicInteger count = this.count; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == 0) { if (nanos <= 0) return null; nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos); } x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1) notEmpty.signal(); } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } if (c == capacity) signalNotFull(); return x; } public E poll() { final AtomicInteger count = this.count; if (count.get() == 0) return null; E x = null; int c = -1; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lock(); try { if (count.get() > 0) { x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1) notEmpty.signal(); } } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } if (c == capacity) signalNotFull(); return x; } public E peek() { if (count.get() == 0) return null; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lock(); try { Node<E> first = head.next; if (first == null) return null; else return first.item; } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } } /** * Unlinks interior Node p with predecessor trail. 移除P节点,并将p的后续节点指向trail节点 */ void unlink(Node<E> p, Node<E> trail) { p.item = null; trail.next = p.next; if (last == p) last = trail; if (count.getAndDecrement() == capacity) notFull.signal(); } /** * Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,if it is present. * @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present * @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) return false; fullyLock(); try { for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next; p != null; trail = p, p = p.next) { if (o.equals(p.item)) { unlink(p, trail); return true; } } return false; } finally { fullyUnlock(); } } /** * Returns {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element. * More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contains * at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}. * * @param o object to be checked for containment in this queue * @return {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element */ public boolean contains(Object o) { if (o == null) return false; fullyLock(); try { for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) if (o.equals(p.item)) return true; return false; } finally { fullyUnlock(); } } /** * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in proper sequence. * @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue */ public Object[] toArray() { fullyLock(); try { int size = count.get(); Object[] a = new Object[size]; int k = 0; for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) a[k++] = p.item; return a; } finally { fullyUnlock(); } } /** * Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in proper sequence; */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { fullyLock(); try { int size = count.get(); if (a.length < size) a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance (a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); int k = 0; for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) a[k++] = (T)p.item; if (a.length > k) a[k] = null; return a; } finally { fullyUnlock(); } } public String toString() { fullyLock(); try { Node<E> p = head.next; if (p == null) return "[]"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append('['); for (;;) { E e = p.item; sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); p = p.next; if (p == null) return sb.append(']').toString(); sb.append(',').append(' '); } } finally { fullyUnlock(); } } /** * Atomically removes all of the elements from this queue.The queue will be empty after this call returns. */ public void clear() { fullyLock(); try { for (Node<E> p, h = head; (p = h.next) != null; h = p) { h.next = h; p.item = null; } head = last; // assert head.item == null && head.next == null; if (count.getAndSet(0) == capacity) notFull.signal(); } finally { fullyUnlock(); } } /** * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} */ public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) { return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } /** * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} */ public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) { if (c == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if (c == this) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (maxElements <= 0) return 0; boolean signalNotFull = false; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; takeLock.lock(); try { int n = Math.min(maxElements, count.get()); // count.get provides visibility to first n Nodes Node<E> h = head; int i = 0; try { while (i < n) { Node<E> p = h.next; c.add(p.item); p.item = null; h.next = h; h = p; ++i; } return n; } finally { // Restore invariants even if c.add() threw if (i > 0) { // assert h.item == null; head = h; signalNotFull = (count.getAndAdd(-i) == capacity); } } } finally { takeLock.unlock(); if (signalNotFull) signalNotFull(); } } }
总结:
分析LinkedBlockingQueue的源码之后,可以与ArrayBlockingQueue做一个比较。
相同点:
- 不允许元素为null
- 线程安全的队列
不同点:
- ArrayBlockingQueue底层基于定长的数组,所以容量限制了;LinkedBlockingQueue底层基于链表实现队列,所以容量可选,如果不设置,那么容量是int的最大值
- ArrayBlockingQueue内部维持一把锁和两个条件,同一时刻只能有一个线程队列的一端操作;LinkedBlockingQueue内部维持两把锁和两个条件,同一时刻可以有两个线程在队列的两端操作,但同一时刻只能有一个线程在一端操作。
- LinkedBlockingQueue的remove()类似方法时,由于需要对整个队列链表实现遍历,所以需要获取两把锁,对两端加锁。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号