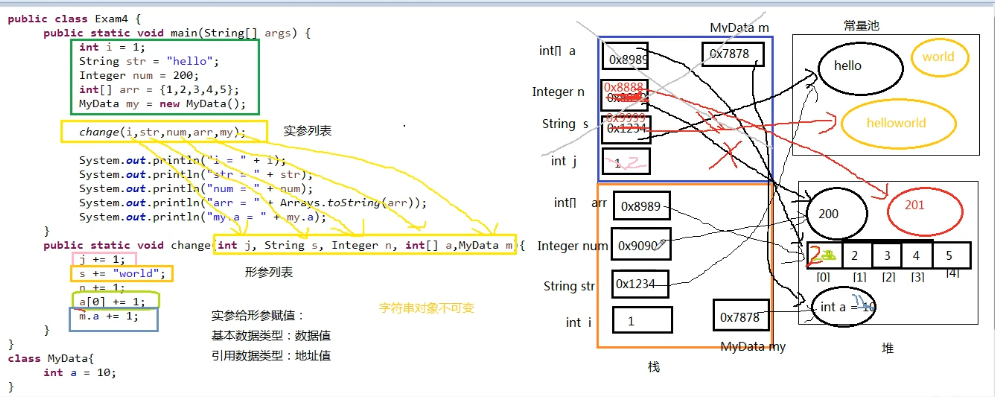
public class DemoTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
String str = "hello";
Integer num = 2; //缓存范围是-128到127 超过缓存范围则存入堆中,没超过就存入栈中 和int一样
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5}; //数组的具体数值也是存入堆中,栈中保存地址
MyData my = new MyData(); //类中定义的变量int 同样存入堆中 my是在栈中的引用地址
change(i,str,num,arr,my);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//2,2,3,4,5
System.out.println(my.a);
}
public static void change(int j,String s,Integer n,int[] a,MyData m){ //参数传递,基本类型传递的是具体值,引用类型传递的是地址
j+=1; // j++;
s+="world"; //s+word
n+=1; // n++;
a[0] +=1;
m.a +=1;
}
}
class MyData{
int a = 10;
}
理解起来挺麻烦。。。。具体参考jvm
![]()
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号