大数据第二周作业
描述性统计分析和相关系数矩阵:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
inputfile = "D:/Jupyter/a/data.csv"
data = pd.read_csv(inputfile)
#描述性统计分析
#依次计算最小值、最大值、均值、标准差
description = [data.min(),data.max(),data.mean(),data.std()]
#将结果存入数据框
description = pd.DataFrame(description,index = ['Min','Max','Mean','STD']).T
print('描述性统计结果:\n',np.round(description,2)) #保留两位小数
描述性统计结果:
Min Max Mean STD
x1 3831732.00 7599295.00 5579519.95 1262194.72
x2 181.54 2110.78 765.04 595.70
x3 448.19 6882.85 2370.83 1919.17
x4 7571.00 42049.14 19644.69 10203.02
x5 6212.70 33156.83 15870.95 8199.77
x6 6370241.00 8323096.00 7350513.60 621341.85
x7 525.71 4454.55 1712.24 1184.71
x8 985.31 15420.14 5705.80 4478.40
x9 60.62 228.46 129.49 50.51
x10 65.66 852.56 340.22 251.58
x11 97.50 120.00 103.30 5.51
x12 1.03 1.91 1.42 0.25
x13 5321.00 41972.00 17273.80 11109.19
y 64.87 2088.14 618.08 609.25
corr = data.corr(method = 'pearson')
print('相关系数矩阵:\n',np.round(corr,2))
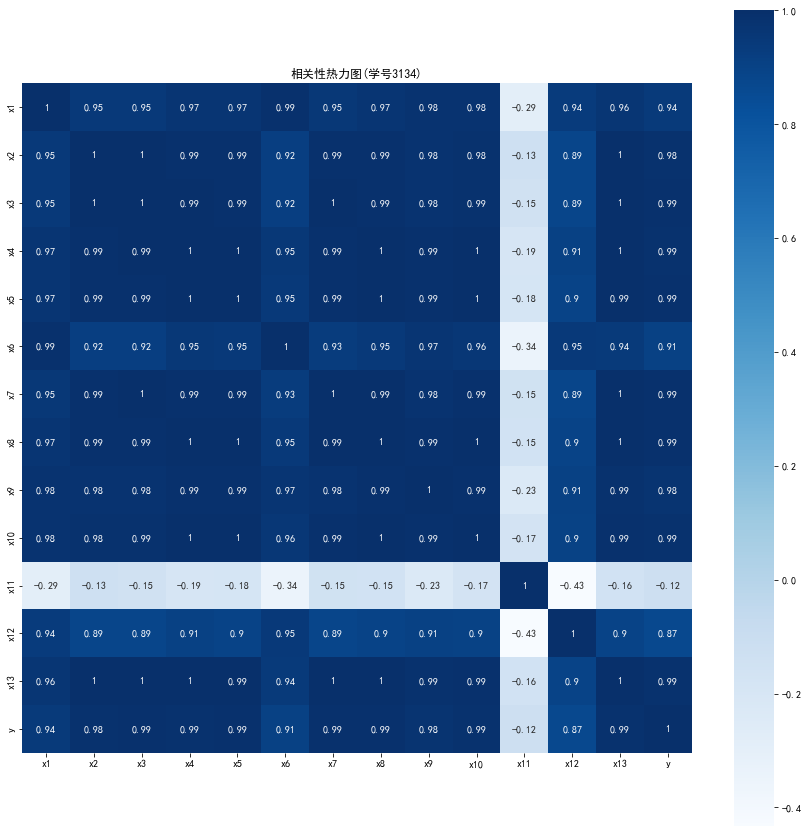
相关系数矩阵:
x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 x7 x8 x9 x10 x11 x12 \
x1 1.00 0.95 0.95 0.97 0.97 0.99 0.95 0.97 0.98 0.98 -0.29 0.94
x2 0.95 1.00 1.00 0.99 0.99 0.92 0.99 0.99 0.98 0.98 -0.13 0.89
x3 0.95 1.00 1.00 0.99 0.99 0.92 1.00 0.99 0.98 0.99 -0.15 0.89
x4 0.97 0.99 0.99 1.00 1.00 0.95 0.99 1.00 0.99 1.00 -0.19 0.91
x5 0.97 0.99 0.99 1.00 1.00 0.95 0.99 1.00 0.99 1.00 -0.18 0.90
x6 0.99 0.92 0.92 0.95 0.95 1.00 0.93 0.95 0.97 0.96 -0.34 0.95
x7 0.95 0.99 1.00 0.99 0.99 0.93 1.00 0.99 0.98 0.99 -0.15 0.89
x8 0.97 0.99 0.99 1.00 1.00 0.95 0.99 1.00 0.99 1.00 -0.15 0.90
x9 0.98 0.98 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.97 0.98 0.99 1.00 0.99 -0.23 0.91
x10 0.98 0.98 0.99 1.00 1.00 0.96 0.99 1.00 0.99 1.00 -0.17 0.90
x11 -0.29 -0.13 -0.15 -0.19 -0.18 -0.34 -0.15 -0.15 -0.23 -0.17 1.00 -0.43
x12 0.94 0.89 0.89 0.91 0.90 0.95 0.89 0.90 0.91 0.90 -0.43 1.00
x13 0.96 1.00 1.00 1.00 0.99 0.94 1.00 1.00 0.99 0.99 -0.16 0.90
y 0.94 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.91 0.99 0.99 0.98 0.99 -0.12 0.87
x13 y
x1 0.96 0.94
x2 1.00 0.98
x3 1.00 0.99
x4 1.00 0.99
x5 0.99 0.99
x6 0.94 0.91
x7 1.00 0.99
x8 1.00 0.99
x9 0.99 0.98
x10 0.99 0.99
x11 -0.16 -0.12
x12 0.90 0.87
x13 1.00 0.99
y 0.99 1.00
相关性热力图:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
plt.subplots(figsize=(15,15)) #设置画面大小
sns.heatmap(corr,annot=True,vmax=1,square=True,cmap="Blues")
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 添加这条可以让图形显示中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 添加这条可以让图形显示负号
plt.title('相关性热力图(学号3134)')
plt.show()
plt.close
<function matplotlib.pyplot.close(fig=None)>
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso
inputfile = "D:/Jupyter/a/data.csv"
data = pd.read_csv(inputfile) #读取数据
lasso = Lasso(1000) #调用Lasso()函数,设置λ的值为1000
lasso.fit(data.iloc[:,0:13],data['y'])
print('相关系数为:',np.round(lasso.coef_,5)) #输出结果,保留五位小数
print('相关系数非零个数为:',np.sum(lasso.coef_ !=0)) #计算相关系数非零的个数
mask = lasso.coef_ !=0 #返回一个相关系数是否为零的布尔数组
mask = np.append(mask,True) #将mask的元素补齐到14个
print('相关系数是否为零:',mask)
outputfile = "D:/Jupyter/a/new_reg_data.csv" #输出的数据文件
new_reg_data = data.iloc[:,mask] #返回相关系数非零的数据
new_reg_data.to_csv(outputfile) #存储数据
print('输出数据的维度为:',new_reg_data.shape) #查出输出数据的维度
相关系数为: [-1.8000e-04 -0.0000e+00 1.2414e-01 -1.0310e-02 6.5400e-02 1.2000e-04 3.1741e-01 3.4900e-02 -0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 -4.0300e-02] 相关系数非零个数为: 8 相关系数是否为零: [ True False True True True True True True False False False False True True] 输出数据的维度为: (20, 9)
GM11灰色预测:
import sys
sys.path.append("D:/Jupyter/a/GM11.py")
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from GM11 import GM11 #引入自编的灰色预测函数
inputfile1 = "D:/Jupyter/a/new_reg_data.csv"
inputfile2 = "D:/Jupyter/a/data.csv"
new_reg_data = pd.read_csv(inputfile1) #读取经过属性选择后的数据
data = pd.read_csv(inputfile2) #读取总的数据
new_reg_data.index = range(1994,2014)
new_reg_data.loc[2014] = None
new_reg_data.loc[2015] = None
cols = ['x1','x3','x4','x5','x6','x7','x8','x13']
for i in cols:
f = GM11(new_reg_data.loc[range(1994, 2014),i].values)[0]
new_reg_data.loc[2014,i] = f(len(new_reg_data)-1) #2014年预测结果
new_reg_data.loc[2015,i] = f(len(new_reg_data)) #2015年预测结果
new_reg_data[i] = new_reg_data[i].round(2) #保留两位小数
outputfile = ("D:/Jupyter/a/new_reg_data_GM11.xls") #灰色预测后保存的路径
y = list(data['y'].values) #提取财政收入列,合并至新数据框中
y.extend([np.nan,np.nan])
new_reg_data['y'] = y
new_reg_data.to_excel(outputfile) #结果输出
print('预测结果为:\n',new_reg_data.loc[2014:2015,:]) #预测展示
运行结果:
预测结果为:
Unnamed: 0 x1 x3 x4 x5 x6 \
2014 NaN 8142148.24 7042.31 43611.84 35046.63 8505522.58
2015 NaN 8460489.28 8166.92 47792.22 38384.22 8627139.31
x7 x8 x13 y
2014 4600.40 18686.28 44506.47 NaN
2015 5214.78 21474.47 49945.88 NaN
读取真实值和预测值以及绘图:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVR
inputfile = "D:/Jupyter/a/new_reg_data_GM11.xls" # 灰色预测后保存的路径
data = pd.read_excel(inputfile) # 读取数据
feature = ['x1', 'x3', 'x4', 'x5', 'x6', 'x7', 'x8', 'x13'] # 属性所在列
data.index = range(1994, 2016)
data_train = data.loc[range(1994, 2014)].copy() # 取2014年前的数据建模
data_mean = data_train.mean()
data_std = data_train.std()
data_train = (data_train - data_mean)/data_std # 数据标准化
x_train = data_train[feature].to_numpy() # 属性数据
y_train = data_train['y'].to_numpy() # 标签数据
linearsvr = LinearSVR() # 调用LinearSVR()函数
linearsvr.fit(x_train,y_train)
x = ((data[feature] - data_mean[feature])/data_std[feature]).to_numpy() # 预测,并还原结果。
data['y_pred'] = linearsvr.predict(x) * data_std['y'] + data_mean['y']
outputfile ="D:/Jupyter/a/new_reg_data_GM11_revenue.xls" # SVR预测后保存的结果
data.to_excel(outputfile)
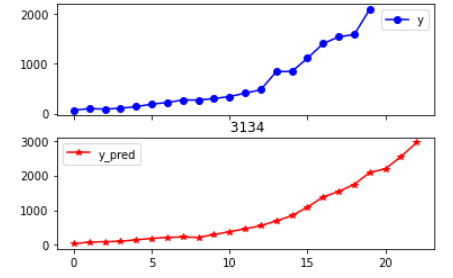
print('真实值与预测值分别为:\n',data[['y','y_pred']])
fig = data[['y','y_pred']].plot(subplots = True, style=['b-o','r-*']) # 画出预测结果图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 添加这条可以让图形显示中文
plt.title('学号3134')
plt.show()
运行结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号