Java面向对象学习(七)包装类
1.定义:Java中的基本数据类型没有方法和属性,包装类就是将基本数据类型加上方法、属性、构造器之后进行封装,产生一个类,目的是为了使基本数据类型实现对象化交互。
包装类是引用数据类型。
2.对应关系
基本数据类型 包装类 继承关系
byte Byte -->Number-->Object
short Short -->Number-->Object
int Integer -->Number-->Object
long Long -->Number-->Object
float Float -->Number-->Object
double Double -->Number-->Object
char Character -->Object
boolean Boolean -->Object
3.Integer详解
1)查看类的源码可知
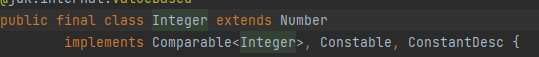
(1)Integer类由final修饰,说明这个类不能被继承
(2)Integer类继承了Number类,Number继承了Object类
(3)Integer里实现了Comparable<Integer>等接口
2)属性

被static修饰的类可以不用自己创建对象,可以通过类名.属性名调用
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 //属性 3 System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); 4 System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); 5 //“物极必反” 6 System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE+1); 7 System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE-1); 8 }
运行结果: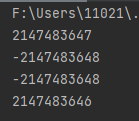
3)构造器:Integer没有空参构造器
查看源码可知,Integer有一个传入int类型参数的构造器,一个传入String类型数据的构造器,但他们最终返回的都是int类型的数据

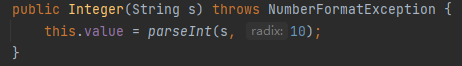
1 //构造器 2 //调用int类型参数构造器:public Integer(int value) {this.value = value;} 3 Integer i1 = new Integer(10); 4 System.out.println(i1); 5 //这里会返回10,因为这个构造器的功能就是将传入的int类型的数据---value=10,传给this.value 6 //调用String类型参数构造器:这个构造器的parseInt()方法的作用是将String类型的数转换为int类型 7 // public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException { 8 // this.value = parseInt(s, 10); //10表示返回的是10进制的数 9 // } 10 Integer i2 = new Integer("15"); 11 System.out.println(i2); 12 //如果传入的是abc这种字符串,就会报如构造器所抛出的异常NumberFormatException 13 Integer i3 = new Integer("abc");
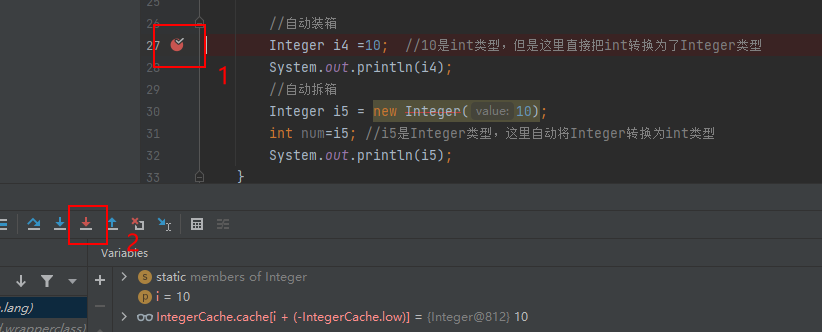
4)自动装箱和自动拆箱:功能是将基本数据类型和包装类进行快速的类型转换
1 //自动装箱 2 Integer i4 =10; //10是int类型,但是这里直接把int转换为了Integer类型 3 System.out.println(i4); 4 //自动拆箱 5 Integer i5 = new Integer(10); 6 int num=i5; //i5是Integer类型,这里自动将Integer转换为int类型 7 System.out.println(i5);
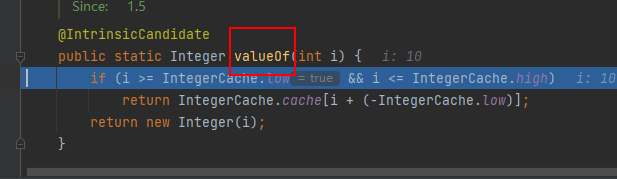
可以通过打断点的方式查看到自动装拆箱其实是调用了Integer类中的valueOf这个方法
5)常用方法
1 package com.rzd.wrapperclass; 2 //包装类:常用方法1 3 public class Demo02 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //常用方法 6 //1.compareTo:在数字上比较两个Integer对象 7 //追溯源码可以看到compareTo调用了compare方法 8 Integer a = new Integer(10); 9 Integer b = new Integer(10); 10 Integer c = new Integer(1); 11 12 System.out.println(a.compareTo(b)); //当a=b,返回0 13 System.out.println(a.compareTo(c)); //当a>b,返回1 14 System.out.println(c.compareTo(a)); //当a<b,返回-1 15 16 //2.equals:比较两个对象 17 System.out.println(a==b);//==比较的是地址,所以一定会返回false 18 System.out.println(a.equals(b)); 19 //返回了true,说明重写了Object类中的equals方法,重写为比较两个对象的数字值 20 21 //上面是new创建对象,现在通过自动装箱方式创建对象 22 Integer d1=10; 23 Integer e1=10; 24 System.out.println(d1.equals(e1)); //返回了true 25 System.out.println(d1 == e1); //这里会返回true 26 27 Integer d2=130; 28 Integer e2=130; 29 System.out.println(d2 == e2); //这里会返回false 30 /* 这里可以看到,当自动装箱的值为10时,==比较返回的时true,也就是说比较的是数值。 31 如果自动装箱的值为130,那么返回false,也就是比较的是对象的地址。 32 因为用Integer自动装箱创建的对象,其实是调用了valueOf方法,这里打断点对valueOf源码进行分析。 33 */ 34 35 36 } 37 }
valueOf的源码分析:
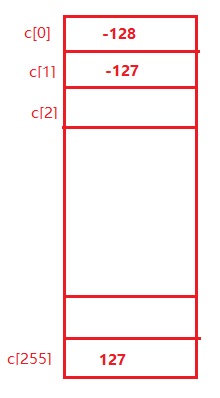
1 //1.从alueOf方法跳到IntegerCache类,IntegerCache是Integer的一个内部类 2 public static Integer valueOf(int i) { 3 /*6.如果传进来的值在low和high之间,也就是在-128~127之间,就返回cache[]数组里的某一个值。 4 这里假如传入的是i=10,那么返回的就是cache[10+(-(-128))]--->cache[138],也就是返回的是一个数。 5 如果i不在-128~127之间,就不走if语句,直接走return new Integer(i);,也就是将i封装为对象。 6 */ 7 if (i >= Integer.IntegerCache.low && i <= Integer.IntegerCache.high) 8 return Integer.IntegerCache.cache[i + (-Integer.IntegerCache.low)]; 9 return new Integer(i); 10 } 11 12 13 private static class IntegerCache { 14 static final int low = -128; 15 static final int high; 16 static final Integer[] cache; 17 static Integer[] archivedCache; 18 19 //sttic代码块先执行 20 static { 21 int h = 127; 22 high = h; 23 int size = (high - low) + 1; 24 //2.上面三行可以看到low=-128,high=127,size也就是数组cache的长度为256 25 26 if (archivedCache == null || size > archivedCache.length) { 27 //3.定义一个数组c[],长度为256,然后给他赋值 28 Integer[] c = new Integer[size]; 29 int j = low; j=-128 30 for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) { 31 c[i] = new Integer(j++); 32 /*4.赋值为: 33 第一次,i=0,c[0]=-128; 34 第二次,i=1,c[1]=-127; 35 第三次,i=2,c[2]=-126; 36 最后,当i=255,c[255]=127;也就是如下图的一个数组。 37 */ 38 } 39 archivedCache = c; 40 } 41 cache = archivedCache;//5.cache[]=archivedCache[]=c[] 42 } 43 }
还有一些类型转换的方法:
1 package com.rzd.wrapperclass; 2 //包装类:常用方法2 3 public class Demo03 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //3.intvalue():将Integer类型转换为int类型 6 Integer i1=110; 7 System.out.println(i1); 8 int i= i1.intValue(); 9 System.out.println(i); 10 11 //4.parseInt():将String类型转换为int类型 12 int i2=Integer.parseInt("123"); 13 System.out.println(i2); 14 15 //5.toString(): 16 Integer i3=120; 17 System.out.println(i3.toString()); 18 } 19 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号