Java面向对象学习(六)异常机制与处理
1.异常机制
1)异常例子:用户输入不一定符合程序的要求、程序要打开某个文件但是这个文件却不存在或格式不对、读取数据库但数据库是空的、程序运行的时候内存或硬盘满了等
2)Exception,为了让程序作出合理的处理而不至于程序崩溃,我们要处理异常
3)异常类型
(1).检查型异常:代码逻辑没有错误,但可能会引起的异常,例如打开一个文件,但这个文件不存在的异常,Java编译器和虚拟机都会进行检查,编译器一般会给出错误提示,提醒你去处理这个可能发现的异常。
(2).运行时异常(RuntimeException):是代码逻辑的的问题,是可以避免的,在编译时可以被忽略,程序运行会报的异常,是不检查异常,程序中可以选择捕获也可以不处理
(3).错误Error:由JVM虚拟机生成并抛出,与代码编写无关。例如在JVM试图执行应用时,产生Java虚拟机运行错误(Virtual MachineError)、类定义错误(NoClassDefFoundError)等。这些错误是不可查的,因为它们在应用程序的控制和处理能力之外,而且绝大多数是程序运行时不允许出现的状况。对于设计合理的应用程序来说,即使确实发生了错误,本质上也不应该试图去处理它所引起的异常状况。
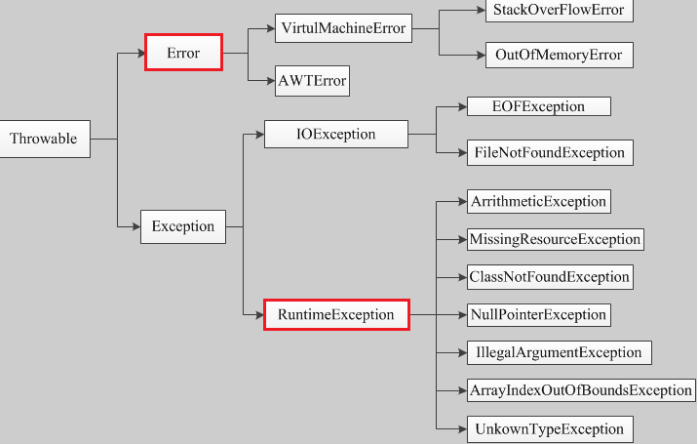
4)在java中,异常被当做对象来处理,java.lang.Throwable是所有异常的超类
2.异常处理:
(1)抛出
int a=0;
public void test(int a){
if (a==0){
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
}
throw抛出: 表示主动抛出了一个异常实例,需要在调用方法时捕获处理。
public void test(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException {
System.out.println(a/b);
}
throws抛出:在方法声明后面,可以写多个异常,告诉方法的调用者,方法中可能会出现这些异常,需要调用者调用方法时处理(捕获/继续抛出)
1 //throw、throws使用 2 3 public class Demo08 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 test1(); 6 try { 7 test2(); //这里test()方法会抛出异常,所以这里也要处理一下这个异常 8 } catch (Exception e) { 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } 11 test3(); 12 } 13 //主动抛出运行时异常 14 public static void test1() { 15 int a =0; 16 if (a==0){ 17 //主动抛出一个运行时异常 18 throw new RuntimeException(); 19 } 20 } 21 //主动抛出运检查异常并用throws解决 22 public static void test2() throws Exception { 23 int a =0; 24 if (a==0){ 25 //主动抛出一个检查异常,这里会报红提示你解决这个检查异常。 26 //throw new Exception();Alt+Enter,选择第一个Add exception to method signatrue 27 throw new Exception(); 28 } 29 } 30 //主动抛出运检查异常并用trycatch解决 31 public static void test3(){ 32 int a =0; 33 if (a==0){ 34 //主动抛出一个检查异常,这里会报红提示你解决这个检查异常。 35 //throw new Exception();Alt+Enter,选择第二个Surround with try/catch 36 try { 37 throw new Exception(); 38 } catch (Exception e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 }
throw和throws区别:
1)throw写在方法内部,
异常抛出后需要进行捕获。
(2)捕获
try {//监控的区域,这里面的代码运行发生的异常
}catch (要捕获的异常 异常名 ){//捕获异常
//如果捕获到了异常,就执行下面的语句
}finally {//可选,无论是否捕获到异常,都会执
}
finally用于处理一些善后工作,比如IO流、资源的关闭
自动生成快捷键:Ctrl+Alt+t,自动生成捕获异常语句,我们也可以在语句中加入退出程序语句等
1 try { 2 System.out.println(a/b); 3 } catch (Exception e) { 4 System.exit(0); //程序结束 5 e.printStackTrace(); //打印错误的栈信息,就是程序报的异常 6 } finally { 7 }
3.实例
1)创建两个变量,a=1,b=0,输出a/b
1 public class demo01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int a=1; 4 int b=0; 5 System.out.println(a/b); //报错java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero 6 } 7 }
程序运行结果为
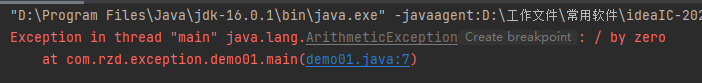
2)可以看到报了一个异常java.lang.ArithmeticException,于是写代码捕获这个异常
1 public class demo01 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int a=1; 4 int b=0; 5 //System.out.println(a/b); //报错java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero 6 7 //捕获这个异常 8 try {//监控的区域,这里面的代码运行发生的异常 9 System.out.println(a/b); 10 }catch (ArithmeticException e){//catch(要捕获的异常 异常名):捕获异常 11 //如果捕获到了异常,就执行下面的语句 12 System.out.println("除数不能为0"); 13 }finally {//可选,无论是否捕获到异常,都会执行 14 System.out.println("finally"); 15 } 16 } 17 }
程序运行结果为
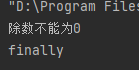
异常消失。
如果将代码中的b改成合法数字1,运行结果为
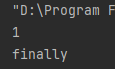
3)捕获多个异常
可以写多条catch来捕获多个异常,异常的顺序必须是从小到大,否则会报错。
1 try { 2 System.out.println(a/b); 3 }catch (Error error){ 4 System.out.println("Error"); 5 }catch (Exception e){ 6 System.out.println("Exception"); 7 }catch (Throwable t){ 8 System.out.println("Throwable"); 9 }finally { 10 System.out.println("finally"); 11 }
4)主动抛出异常
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 int a=1; 3 int b=0; 4 5 new demo01().test(a,b); 6 } 7 //主动抛出异常,一般在方法中使用,用于该方法无法处理这个异常时 8 public void test(int a,int b){ 9 if (b==0){ 10 throw new ArithmeticException(); 11 } 12 }
运行结果为: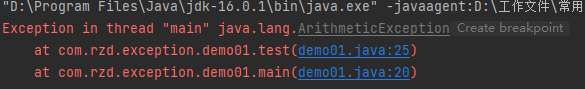
可以看到程序没有运行a/b,但是主动抛出了这个异常
5)使用较多的方式:输出异常信息
1 try {//监控的区域,这里面的代码运行发生的异常 2 System.out.println(a/b); 3 }catch (ArithmeticException e){//catch(要捕获的异常 异常名):捕获异常 4 // 如果捕获到了异常,就执行下面的语句 5 e.printStackTrace();//显示异常的堆栈信息 6 }finally {//可选,无论是否捕获到异常,都会执行 7 System.out.println("finally"); 8 }
多重catch可以用 | 连接
catch (ArithmeticException |NumberFormatException|ArrayStoreException exception)
4.重载和重写中的异常使用(ArithmeticException < Exception)
1)重载:重载的方法之间的异常没有关系
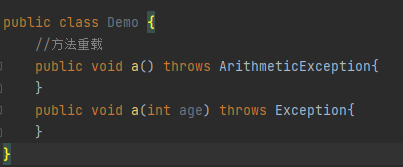
1)重写:子类异常 < 父类异常,否则会报错
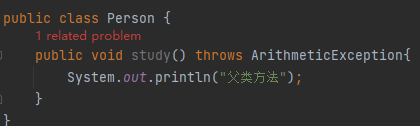
5.自定义异常(用到时再学)
用户自定义异常类,可以继承RuntimeException(运行时异常)或Exception(检查异常)
1)自定义异常继承运行时异常
1 public class MyException extends RuntimeException{ 2 //定义一个无参构造器 3 public MyException(){ 4 5 } 6 //定义一个有参构造器 7 public MyException(String msg){ 8 //调用父类有参构造 9 super(msg); 10 } 11 12 }
编写Test类
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 sex("aaa"); 4 } 5 public static void sex(String sex){ 6 if(sex.equals("男")||sex.equals("女")){ 7 System.out.println(sex); 8 }else{ 9 throw new MyException("性别错误!"); 10 } 11 } 12 }
可以看到运行Test类时,抛出了异常

2)自定义异常继承检查异常
1 public class MyException extends Exception{ 2 //定义一个无参构造器 3 public MyException(){ 4 5 } 6 //定义一个有参构造器 7 public MyException(String msg){ 8 //调用父类有参构造 9 super(msg); 10 } 11 }
在Test里中必须要处理,这里使用try/catch处理
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 sex("aaa"); 4 } 5 public static void sex(String sex){ 6 if(sex.equals("男")||sex.equals("女")){ 7 System.out.println(sex); 8 }else{ 9 try { 10 throw new MyException("性别错误!"); 11 } catch (MyException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 } 15 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号