Java面向对象学习(三)面向对象三大特性----多态
6.多态
1)先创建一个父类
1 public class Father { 2 3 }
子类
1 public class Son extends Father { 2 3 }
main方法
1 import com.rzd.oop.demo10.Father; 2 import com.rzd.oop.demo10.Son; 3 4 public class Application { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 //当new Son();时,这个对象的实际类型是确定的,是Son类型 7 Son s1 = new Son(); 8 //但是这个对象指向的的引用类型是不确定的,这个对象的引用类型可以是任意一个Son的父类型 9 //这里是父类的引用指向子类 10 Father s2 = new Son(); 11 Object s3 = new Son(); 12 13 } 14 }
这里可以看到一个对象的实际类型,是在new的时候就确定了的,但是它指向的引用类型,可以是任意的实际类型的父类。
2)如果在父类中添加一个run方法
1 public class Father { 2 public void run(){ 3 System.out.println("father run"); 4 } 5 }
在子类中添加一个eat方法
1 public class Son extends Father { 2 public void eat(){ 3 System.out.println("son eat"); 4 } 5 }
在main方法中进行调用
1 import com.rzd.oop.demo10.Father; 2 import com.rzd.oop.demo10.Son; 3 4 public class Application { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Son s1 = new Son(); 7 Father s2 = new Son(); 8 Object s3=new Son(); 9 10 //对象可以调用的方法由它的引用类型决定 11 s1.run(); //s1的引用类型是Son,可以调用父类Father的方法 12 s2.run(); //s2的引用类型是Father,可以调用Father本身的方法 13 //s3.run(); 这里s3的引用类型是Object,是不能调用子类Father的方法的 14 15 s1.eat(); //s1的引用类型是Son,可以调用Son本身的方法 16 //s2.eat(); //同理上面的s3 17 } 18 }
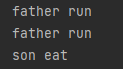
由此可见:一个对象可以调用的方法只能是它的引用类型里面的方法。
3)但是我们如果在子类中重写一个run方法
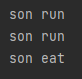
1 public class Son extends Father { 2 public void eat(){ 3 System.out.println("son eat"); 4 } 5 public void run(){ 6 System.out.println("son run"); 7 } 8 }
此时再在main方法中调用的话,就是方法重写,会都调用到子类的方法
小结:
1)多态是方法的多态,与属性无关,重写也是
2)=左边必须是右边的父类,否则会报类型转换异常,ClassCastException
3)多态存在的条件:父子关系、方法重写、父类的引用指向子类 Father f1=new Son()
不能被重写的方法:
1.static修饰的方法,它属于类,不属于实例
2.final修饰的方法:常量
3.private方法:私有的
2.instanceof
X instanceof Y 能否编译通过不报错的前提是X、Y之间有继承关系
结果能是true的前提是X是Y的子类型
1 import com.rzd.oop.demo11.Person; 2 import com.rzd.oop.demo11.Student; 3 import com.rzd.oop.demo11.Teacher; 4 5 public class Application { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //先写个多态 8 Object object = new Student(); //Object是Student的父类,可以写多态 9 10 //Object>Person>Student 11 //Object>Person>Teacher 12 //Object>String 13 14 //由于object是Student类型的,那么object是Student及其父类的类型 15 System.out.println(object instanceof Object); //true 16 System.out.println(object instanceof Student); //true 17 System.out.println(object instanceof Person); //true 18 System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher); //false Student和Teacher是平行的 19 System.out.println(object instanceof String); //false Student和String无关 20 21 System.out.println("=================================="); 22 Person person = new Student(); //这里new出来的person到底是什么类型? 23 24 //person是Person类型的 25 System.out.println(person instanceof Object); //true 26 System.out.println(person instanceof Student); //true 27 System.out.println(person instanceof Person); //true 28 System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher); //false Person是Teacher的父 29 //System.out.println(person instanceof String); //instanceof两边的类型没有继承关系就会编译报错 30 31 System.out.println("=================================="); 32 Student student = new Student(); 33 System.out.println(student instanceof Object); //true 34 System.out.println(student instanceof Student); //true 35 System.out.println(student instanceof Person); //true 36 //System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher); //instanceof两边的类型没有继承关系就会编译报错 37 //System.out.println(student instanceof String); //instanceof两边的类型没有继承关系就会编译报错 38 } 39 }
3)类型转换
类型转换:(1)多态----父类引用子类的对象
(2)子类转换为父类---低转高,是向上转型,直接转换;父类转换为子类---高转低,是向下转型,强制转换。
(3)与基本类型强制转换会丢失精度一样,引用类型强制转换会丢失方法
类型转换的作用:方便方法的调用,减少重复的代码
先写三个空的Person、Student、Teacher方法
在main方法中输入
1 import com.rzd.oop.demo11.Person; 2 import com.rzd.oop.demo11.Student; 3 import com.rzd.oop.demo11.Teacher; 4 5 public class Application { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 //先写个多态 8 Object object = new Student(); //Object是Student的父类,可以写多态 9 10 //Object>Person>Student 11 //Object>Person>Teacher 12 //Object>String 13 14 //由于object是Student类型的,那么object是Student及其父类的类型 15 System.out.println(object instanceof Object); //true 16 System.out.println(object instanceof Student); //true 17 System.out.println(object instanceof Person); //true 18 System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher); //false Student和Teacher是平行的 19 System.out.println(object instanceof String); //false Student和String无关 20 21 System.out.println("=================================="); 22 Person person = new Student(); //这里new出来的person到底是什么类型? 23 24 //person是Person类型的 25 System.out.println(person instanceof Object); //true 26 System.out.println(person instanceof Student); //true 27 System.out.println(person instanceof Person); //true 28 System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher); //false Person是Teacher的父 29 //System.out.println(person instanceof String); //false instanceof两边的类型没有继承关系就会编译报错 30 31 Student student = new Student(); 32 System.out.println(student instanceof Object); //true 33 System.out.println(student instanceof Student); //true 34 System.out.println(student instanceof Person); //true 35 //System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher); //false instanceof两边的类型没有继承关系就会编译报错 36 //System.out.println(student instanceof String); //false instanceof两边的类型没有继承关系就会编译报错 37 38 } 39 }
在多态中,父类要想使用子类的方法,要进行类型转换
基本类型转换:64位>32>16>8 低转高直接转换,高转低需要强制转换
引用类型转换:父--->子 强制转换 子--->父,直接转换
先在子类中写一个方法study()
1 public class Student extends Person{ 2 public void study(){ 3 System.out.println("Student在学习"); 4 } 5 }
在main方法中创建一个父类的obj对象,使用子类的方法
1 //类型转换 2 Person obj = new Student(); //将student类的oj转换为Person类,子--->父,低--->高,是直接转换 3 obj.study();//这行无法运行,报错。 4 // 这里表示,obj本来是Student,是子类,被转换成了父类之后,不能调用本身的study方法了,说明子类转换为父类会丢失自己本来的方法
当子类转换成父类时,会丢失方法。
所以父类使用子类本身的方法, 需要强制转换,将父类转换为子类
1 public class Application { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //类型转换 4 Person obj = new Student(); //将student类的oj转换为Person类,子--->父,低--->高,是直接转换 5 obj.study();//这行无法运行,报错。 6 // 这里表示,obj本来是Student,是子类,被转换成了父类之后,不能调用本身的study方法了,说明子类转换为父类会丢失自己本来的方法 7 8 //父类要想使用子类的方法,还需要类型转换.obj现在是是Person类型,要转换为Student类型,高转低,要强制转换 9 //先输入(Student)obj;,Alt+回车,选择第二个。 10 //这里就是用一个Student类型的对象student1来接收被强制转换为Student类型的对象obj 11 Student student1 = (Student) obj; 12 //然后student1就可以使用Student的方法 13 student1.study(); 14 //上面两行可以简化成 15 ((Student) obj).study(); 16 } 17 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号