SixDay-java Collection集合接口
1、集合
集合不能直接存基本数据类型,也不能直接存储对象,存储的是对象内存地址,基本数据类型进行自动装箱存入集合。
注意:集合在Java中本身是一个容器,是一个对象 集合中任何时候存储的都是引用。
2》在java中每一个不同集合,底层会对应不同的数据结构,往不同的集合中存储数据元素,意味着将数据放到了不同的数据结构中。
数据结构:数据存储的结构就是数据结构,不同的数据结构,存储方式不同。
如:数组,二叉树,链表,哈希表,都是常见的数据结构。
new ArrayList();创建一个集合,底层是数组
new LinkedList();底层是链表
new TreeSet();底层是二叉树 ....
图为B站老师所画
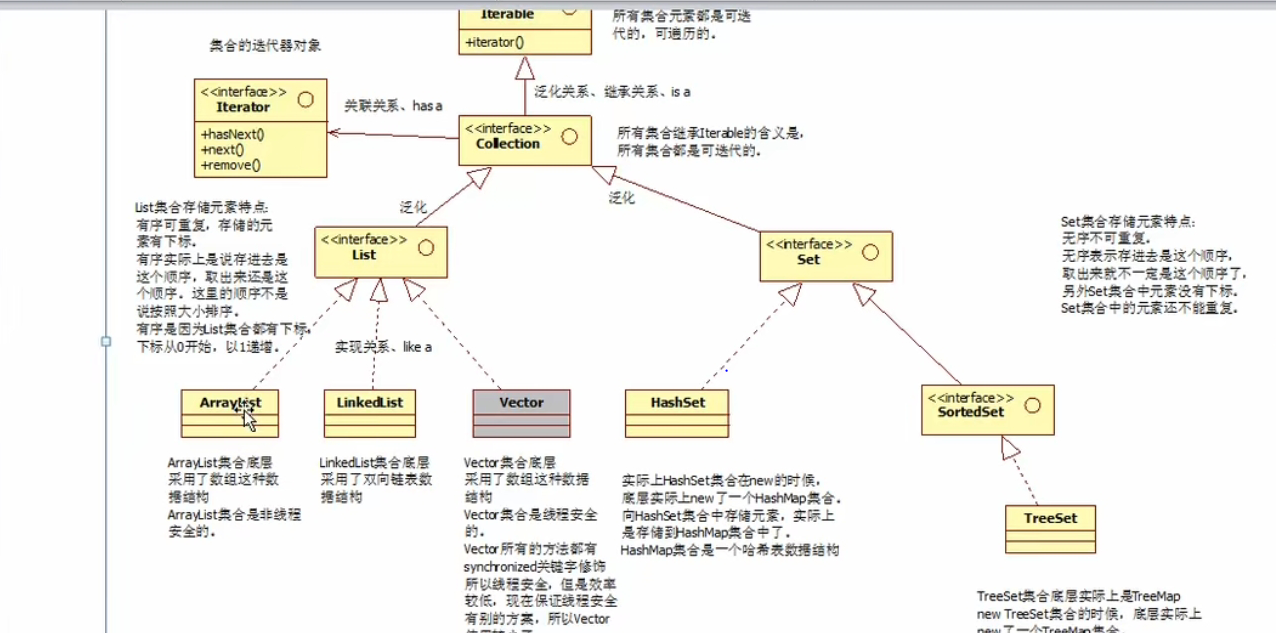
Collection结构图
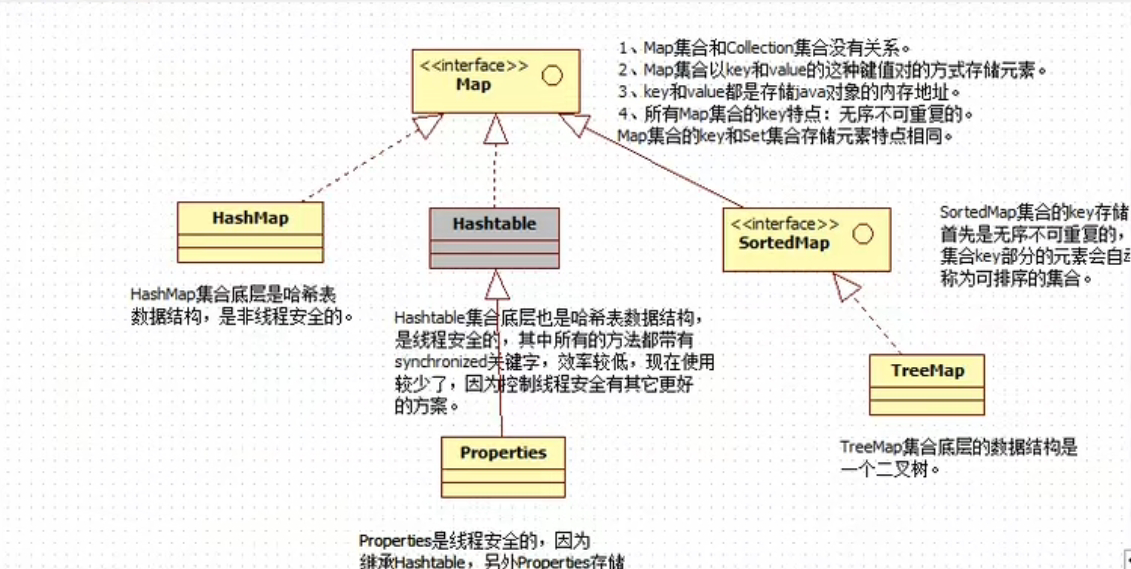
Map接口结构图
2、Collection接口常用方法
总结:
boolean add(E e) 添加元素
void clear() 清除所有元素
int size() 元素的个数
boolean isEmpty() 集合是否为空 为空返回true
boolean contains(Object o) 集合中是否包含元素o,包含返回true
boolean remove(Object o) 删除指定元素,删除成功返回true
Object[] toArray() 把集合转换成数组(了解)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多态
Collection c=new ArrayList();
//add() 添加元素
c.add(123);//自动装箱 Integer i=new Integer(123); 实际放进去的是对象的内存地址
//size() 元素个数
System.out.println(c.size());//1
//清空集合
c.clear();
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
//contains(Object o) 判断是否包含元素0
System.out.println(c.contains("hello"));//true
//isEmpty() 判断元素长度是不是0 是0返回true
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());//false
//remove() 删除指定元素
System.out.println(c.remove("hello"));//true
//集合转成数组
Object[] obj= c.toArray();
for (Object o : obj) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
3、关于集合遍历/迭代
注意:这种迭代方式适用于所有的Collection的接口及实现类,不适用Map集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c=new ArrayList();
c.add("123");
c.add(23);
c.add(new Object());
//对集合Collection的迭代
//第一步:获取集合迭代器对象Iterator
Iterator t=c.iterator();
//第二步:通过迭代器对象开始遍历集合
while(t.hasNext()){//有下一个吗?true:false
//无论当初存放的是什么类型,取出来都是Object类型
Object obj=t.next();//返回迭代中的下一个元素。
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
4、contains
存放在集合中的类型,必须要重写
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c=new ArrayList();
String s1=new String("asd");
c.add(s1);
String s2=new String("rfv");
c.add(s2);
String x=new String("asd");
/*
虽然表面上是判断是否包含x 的内存地址,但contain底层调用了equals方法
底层有代码:x.equals(s1),String类型调用equals比较的是内容,故此行
输出true!
*/
System.out.println(c.contains(x));//true
}
自定义equals 方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Collection c=new ArrayList();
User user1=new User("lihua");
User user2=new User("lihua");
c.add(user1);
/*
未重写User的equals,User对象调用的是Object的equals方法,用==来比较的
System.out.println(c.contains(user2));//false
*/
//重写equals
System.out.println(c.contains(user2));//true
}
}
class User{
String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o==this) return true;
if(o==null ||!(o instanceof User)) return false;
User user=(User) o;
return this.name==user.name;
}
}
5、remove
结合4中的代码:
//重写equals
System.out.println(c.contains(user2));//true
c.remove(user2);//remove在底层同样调用了equals方法
System.out.println(c.size());//0


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号