实验3
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include <windows.h> #define N 80 void printText(int line, int col, char text[]); void printSpaces(int n); void printBlankLines(int n); int main() { int line,col,i; char text[N] = "hi, May~"; srand(time(0)); for(i=1;i<=10;++i) { line = rand()%25; col = rand()%80; printText(line, col, text); Sleep(1000); } return 0; } void printSpaces(int n) { int i; for(i=1;i<=n;++i) printf(" "); } void printBlankLines(int n) { int i; for(i=1;i<=n;++i) printf("\n"); } void printText(int line, int col,char text[]) { printBlankLines(line-1); printSpaces(col-1); printf("%s", text); }
功能:在屏幕上随机打印出10个“hi, May~”的弹幕
task2.1:
源代码:
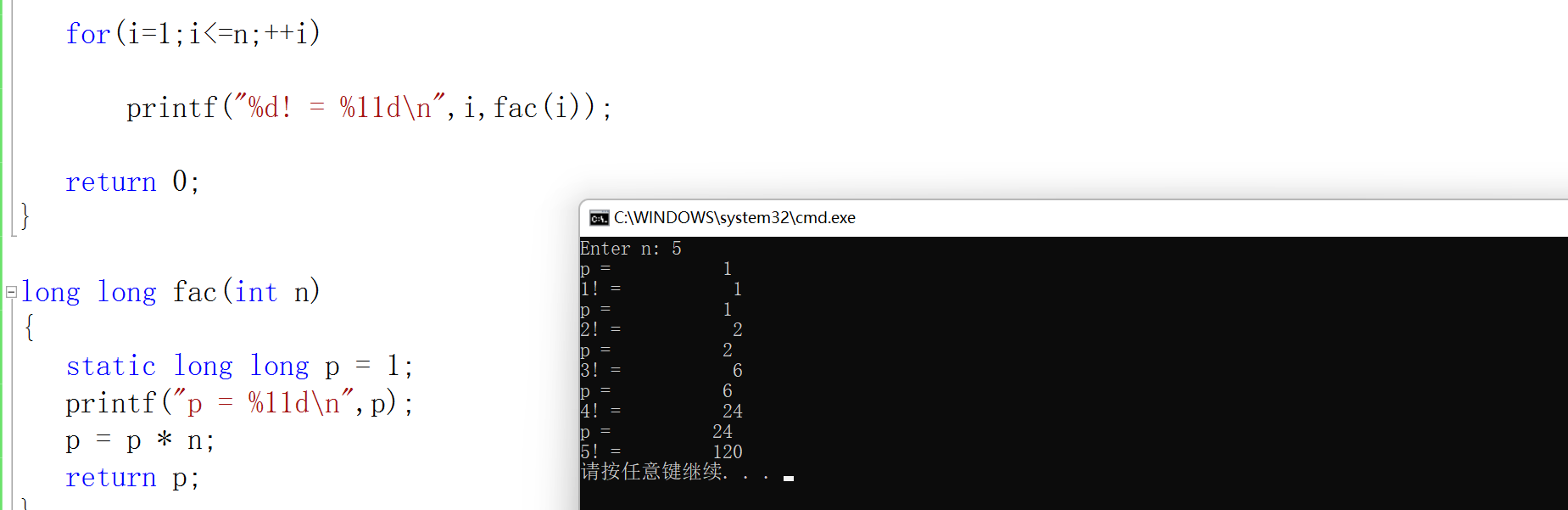
#include <stdio.h> long long fac(int n); int main() { int i, n; printf("Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=1;i<=n;++i) printf("%d! = %11d\n",i,fac(i)); return 0; } long long fac(int n) { static long long p = 1; p = p * n; return p;
增加代码后运行截图:
task2_2:
预测结果:8,17
源代码:
#include <stdio.h> int func(int, int); int main() { int k = 4,m = 1,p1,p2; p1 = func(k,m); p2 = func(k,m); printf("%d,%d\n",p1,p2); return 0; } int func(int a,int b) { static int m = 0,i = 2; i+=m + 1; m = i + a +b; return m; }
运行截图:

(与预期结果一致)
static变量的特性是:函数运行结束后,变量的值保存不变,且与其他函数中的相同字母表示的变量无关,再次运行该函数时,可以继续使用上次的结果继续运行。
task3:
#include <stdio.h> long long fun(int n); int main() { int n; long long f; while (scanf("%d",&n) != EOF) { f = fun(n); printf("n = %d,f = %11d\n",n,f); } return 0; } long long fun(int n) { int i; long long f; if(n==1) f=1; else f=2*(fun(n-1)+1)-1; return f; }
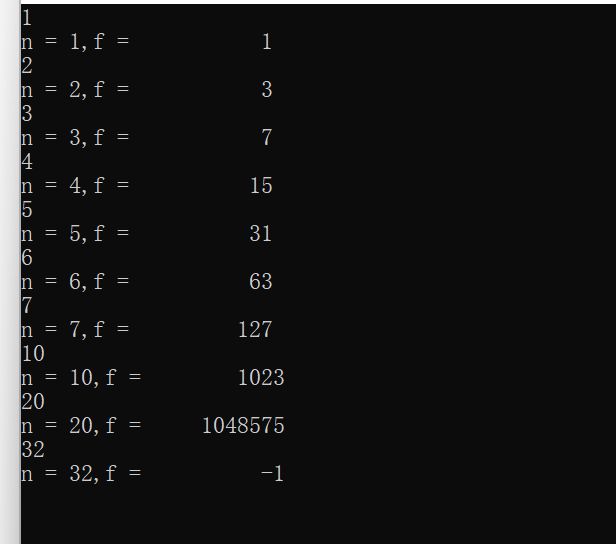
task4:
#include<stdio.h> void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to); void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to); int i=0; int main() { unsigned int n; while(scanf("%u",&n) != EOF) { hanoi(n,'A','B','C'); printf("总共移动了%d次盘子",i); } return 0; } void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to) { if(n==1) { moveplate(n,from,to); } else { hanoi(n-1,from,to,temp); moveplate(n,from,to); hanoi(n-1,temp,from,to); } i++; } void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to) { printf("%u:%c-->%c\n",n,from,to); }
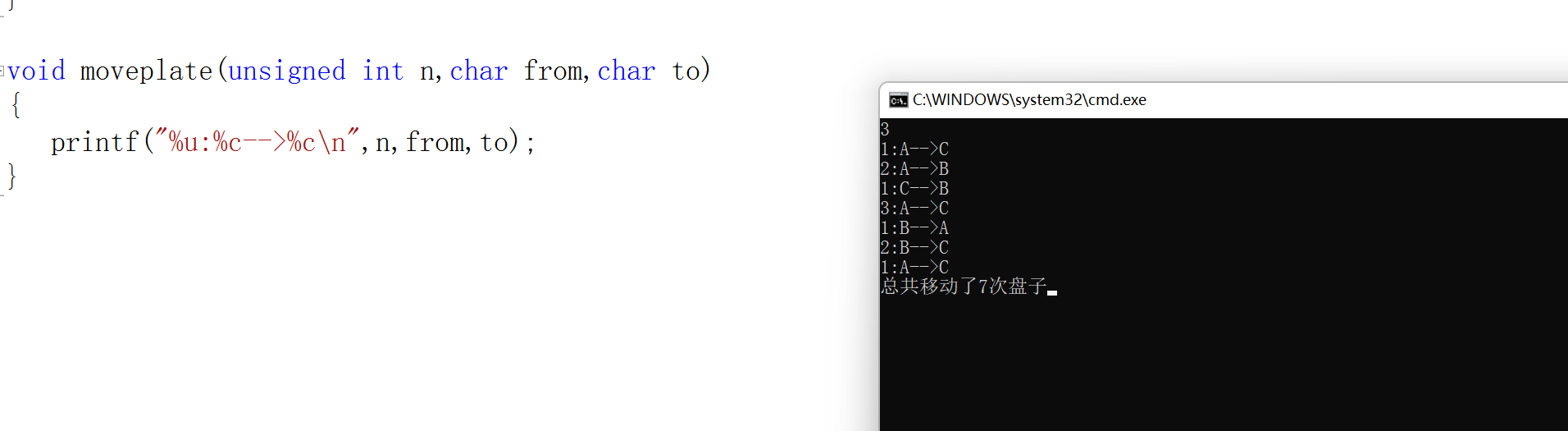
task5:
int main() { int n,a; for(n=4;n<=20;n+=2) { for(a=2;a<=n/2;a++) { if(is_prime(a) == 1 && is_prime(n-a) == 1) { printf("%d=%d+%d\n",n,a,n-a); break; } } } return 0; } int is_prime(int a) { if(a==2) return 1; else { int i=0; for(i=2;i<=(sqrt(a*1.0)+1);i++) { if(a%i==0) return 0; } } return 1; }

task 6:
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> long fun(long s); int main() { long s,t; printf("Enter a number: "); while(scanf("%ld",&s) != EOF) { t = fun(s); printf("new number is: %ld\n\n",t); printf("Enter a number: "); } return 0; } long fun(long s) { long m=0,n=0,k=0,d=0; int i=0; for(;s>=1;s=(s-n)/10) { n=s%10; if(n%2 == 1) { m=m*10+n; i++; } } while (m!=0) { k=m%10; d=d*10+k; m=m/10; } return d; }
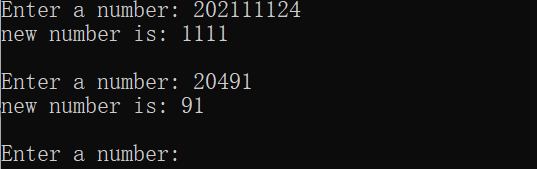


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号