AI Agent 框架探秘:拆解 OpenHands(3)--- 启动
AI Agent 框架探秘:拆解 OpenHands(3)--- 启动
0x00 概要
当分析一个系统时,启动部分和用户典型使用场景是比较理想的切入点,因为这两个部分可以覆盖系统大部分功能模块,可以借此深入架构。
因为本系列借鉴的文章过多,可能在参考文献中有遗漏的文章,如果有,还请大家指出。
0x01 背景
1.1 总体架构
以下是 OpenHands 的架构图,这是一个复杂的系统。
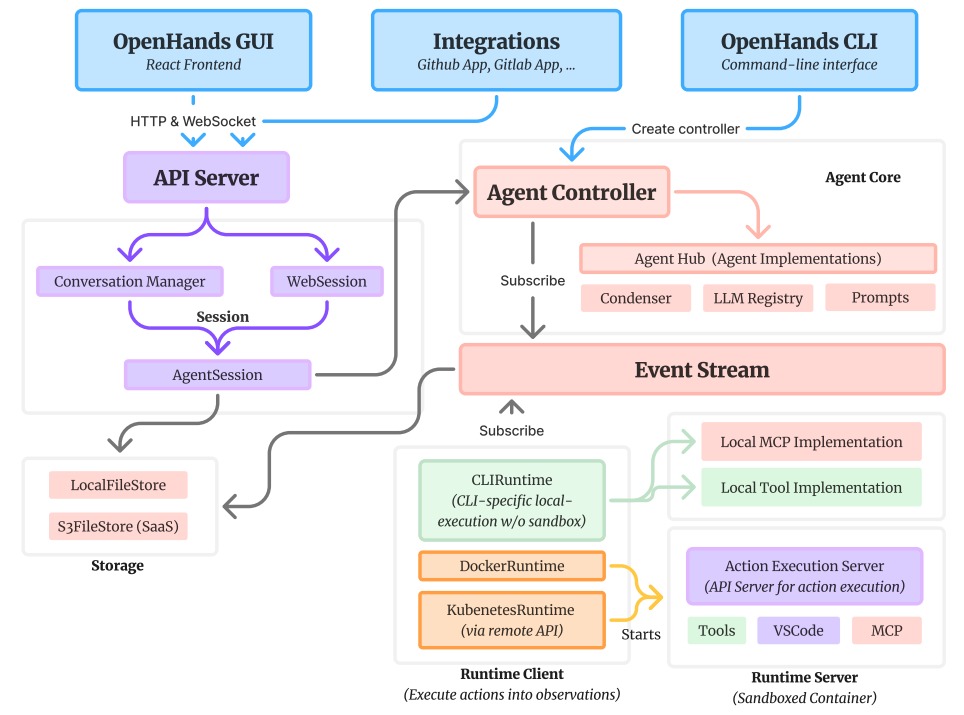
抛开复杂的技术细节,OpenHands Agent 的交互逻辑可提炼为 “初始化 - 事件注入 - 协同处理 - 等待” 的极简流程,核心围绕 EventStream 实现模块联动:
- 初始化就绪:用户创建会话时,系统自动完成 Agent、AgentController、Runtime、Memory 有核心模块的初始化,且每个模块都会自动订阅 EventStream,确保能捕获相关事件;
- 任务发起:用户发送消息本质是向 EventStream 中注入一条事件,这条事件会触发所有订阅相关回调函数的模块,启动协同处理;
- 多模块协同响应:
- Session 模块持续上报事件流中的各类状态事件,保障全局可观测;
- 若用户开启 Security Analyzer,该模块会通过安全分析,自动确认低风险任务,减少用户手动干预;
- AgentController 向事件流注入 RecallAction,Memory 模块判断是否为首次接收的用户信息,据此补充相关记忆并返回 RecallObservation 事件;
- 状态同步:AgentController 更新任务当前状态,并将相关信息传递给 Agent。即AgentController 调用
Agent.step方法处理当前事件,生成 Action 并注入事件流。 - 行动决策:Agent 基于接收的状态信息,向 LLM 发起请求,生成下一步具体行动方案;
- 行动输出:Agent 明确输出行动指令,可能是运行系统命令、读取文件、调用工具等具体操作;
- 行动分发:该行动指令通过 EventStream 传递至 Runtime 组件,等待执行;
- 执行与反馈:Runtime 执行行动指令,生成包含执行结果、错误信息等内容的观察结果;
- 结果回传:观察结果通过 EventStream 回传给 AgentController,完成一次执行闭环;
- 循环或终止:AgentController 根据观察结果判断任务是否完成,若未完成则重复上述流程;若需协同,则委派给其他 Agent,直至任务结束。
1.2 切入点
以下是一个例子。我们由此进入,看看OpenHands如何启动,也可以从此处看看OpenHands的基本逻辑。
config = load_openhands_config()
action = MessageAction(content="Write a hello world program")
state = await run_controller(config=config, initial_user_action=action)
上述代码是直接命令行调用 run_controller,因此我们从run_controller入手。
0x02 初始化 @ run_controller
run_controller 作为 OpenHands 后端单个会话的核心入口协程,核心职责是依据预设配置启动运行时环境、智能体及对应控制器,搭建起从接收用户指令到多步骤执行任务,再到最终将会话状态持久化存储的完整处理链路。其核心设计亮点体现在三方面:
- 实现会话全生命周期的一体化管理,集中完成会话标识(SID)生成、运行时连接建立、代码仓库克隆、MCP 工具嵌入及任务执行轨迹重放等关键操作;
- 构建双重安全管控机制,通过设置最大迭代次数(max_iterations)与单任务最高预算(max_budget_per_task)的硬性限制,有效规避无限循环执行与资源费用超额的风险;
- 强化全流程可观测性,借助 EventStream 实现事件实时分发,支持命令行界面(CLI)、前端界面、日志系统等多端同步订阅,同时生成可回放、可审计的 JSON 格式执行轨迹,便于后续追溯与核查。
2.1 总体流程
openhands\core\main.py 的 run_controller 的总体流程如下。
- 初始化系统组件
- 创建Agent。
- 创建runtime和内存系统
- 创建controller。
- 运行Agent,具体会:
- 管理任务执行流程。
- 接收初始用户操作
- 处理事件流中的各种事件。
- 监听agent状态变化,特别是等待用户输入的状态。
- 处理用户交互。
- 当agent需要用户输入时,依据配置进行自动响应或者等待真实用户输入。
- 支持mock用户响应函数fake_user_response_fn,这样可以自动化测试。
- 状态管理和持久化。
- 保存会话状态到文件。
- 记录执行轨迹,这样可以分析调试。
- 支持轨迹重放。
- 资源管理。
- 管理MCP集成。
- 控制执行预算(迭代次数和费用限制)
- 正确关闭资源。
- 管理任务执行流程。
具体流程图如下。

我们接下来看看具体流程细节。
2.2 创建注册中心
下面语句会创建 LLM 注册中心 & 对话统计实例。
sid = sid or generate_sid(config)
llm_registry, conversation_stats, config = create_registry_and_conversation_stats(
config,
sid,
None,
)
具体代码如下,其功能是:
- 根据用户设置调整基础配置
- 初始化LLM注册表(管理所有LLM实例)
- 初始化文件存储和对话统计器(跟踪对话数据)
- 建立注册表与统计器的订阅关系
def create_registry_and_conversation_stats(
config: OpenHandsConfig,
sid: str,
user_id: Optional[str],
user_settings: Optional[Settings] = None,
) -> tuple[LLMRegistry, ConversationStats, OpenHandsConfig]:
"""
创建LLM注册表、对话统计实例和用户配置的组合函数。
参数:
config: 基础配置对象
sid: 会话ID(用于标识当前对话)
user_id: 用户ID(可选,用于用户级数据跟踪)
user_settings: 用户自定义设置(可选,用于覆盖默认配置)
返回:
三元组 (LLM注册表, 对话统计实例, 最终用户配置)
"""
# 初始化用户配置(优先使用用户设置覆盖默认配置)
user_config = config
if user_settings:
user_config = setup_llm_config(config, user_settings)
# 确定代理类型(从用户设置或默认配置中获取)
agent_cls = user_settings.agent if user_settings else None
# 创建LLM注册表,关联配置和代理类型
llm_registry = LLMRegistry(user_config, agent_cls)
# 初始化文件存储(用于持久化对话数据)
file_store = get_file_store(
file_store_type=config.file_store,
file_store_path=config.file_store_path,
file_store_web_hook_url=config.file_store_web_hook_url,
file_store_web_hook_headers=config.file_store_web_hook_headers,
file_store_web_hook_batch=config.file_store_web_hook_batch,
)
# 创建对话统计实例(绑定文件存储、会话ID和用户ID)
conversation_stats = ConversationStats(file_store, sid, user_id)
# 订阅注册表事件:当新LLM注册时,自动记录到对话统计中
llm_registry.subscribe(conversation_stats.register_llm)
return llm_registry, conversation_stats, user_config
2.3 创建Agent
此处会根据config信息来创建agent。
agent = create_agent(config, llm_registry)
create_agent代码如下,从缺省配置可以看到,默认生成CodeActAgent。
#default_agent = "CodeActAgent"
def create_agent(config: OpenHandsConfig, llm_registry: LLMRegistry) -> Agent:
agent_cls: type[Agent] = Agent.get_cls(config.default_agent)
agent_config = config.get_agent_config(config.default_agent)
# Pass the runtime information from the main config to the agent config
agent_config.runtime = config.runtime
config.get_llm_config_from_agent(config.default_agent)
agent = agent_cls(config=agent_config, llm_registry=llm_registry)
return agent
CodeActAgent 定义如下。
class CodeActAgent(Agent):
"""
CodeActAgent:极简主义的智能代理,基于 CodeAct 理念实现。
核心逻辑:将模型的行动统一到“代码执行”这一单一行动空间,通过传递“行动-观察”对列表,
引导模型决策下一步操作,兼顾简洁性与执行性能。
核心理念(源自论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.01030):
打破传统代理多行动类型的复杂设计,用代码执行统一所有行动,既简化架构又提升效率。
每一轮交互中,代理可执行两种操作:
1. **对话(Converse)**:用自然语言与人类沟通,例如请求澄清需求、确认操作等。
2. **代码行动(CodeAct)**:通过执行代码完成任务,支持两种形式:
- 执行任意有效的 Linux bash 命令
- 执行任意有效的 Python 代码(通过交互式 IPython 解释器模拟,
实际通过 bash 命令实现,详见插件系统说明)
"""
VERSION = '2.2' # 代理版本号
# 沙盒环境所需插件依赖(按初始化顺序排列)
sandbox_plugins: list[PluginRequirement] = [
# 注意:AgentSkillsRequirement 需在 JupyterRequirement 之前初始化
# 原因:AgentSkillsRequirement 提供大量 Python 工具函数,
# Jupyter 环境需要依赖这些函数才能正常工作
AgentSkillsRequirement(), # 提供代理核心技能函数的插件
JupyterRequirement(), # 提供交互式 Python 执行环境的插件
]
def __init__(self, config: AgentConfig, llm_registry: LLMRegistry) -> None:
"""
初始化 CodeActAgent 实例。
参数:
config (AgentConfig):当前代理的配置对象(包含模型路由、记忆策略等)
llm_registry (LLMRegistry):LLM 注册表实例,用于获取所需 LLM 或路由 LLM
"""
# 调用父类 Agent 的初始化方法,完成基础配置(如 LLM 注册、提示词管理器初始化)
super().__init__(config, llm_registry)
self.pending_actions: deque['Action'] = deque() # 待执行的行动队列(双端队列,支持高效进出)
self.reset() # 重置代理状态(初始化行动历史、观察记录等)
self.tools = self._get_tools() # 获取代理可使用的工具集(从插件或配置中提取)
# 初始化对话记忆实例:存储“行动-观察”对,支持记忆压缩、上下文管理
self.conversation_memory = ConversationMemory(self.config, self.prompt_manager)
# 初始化上下文压缩器:根据配置创建 Condenser 实例,用于压缩长对话历史
self.condenser = Condenser.from_config(self.config.condenser, llm_registry)
# 覆盖父类的 LLM 实例:如需模型路由,优先使用路由 LLM(根据代理配置动态选择模型)
self.llm = self.llm_registry.get_router(self.config)
具体参见下图。
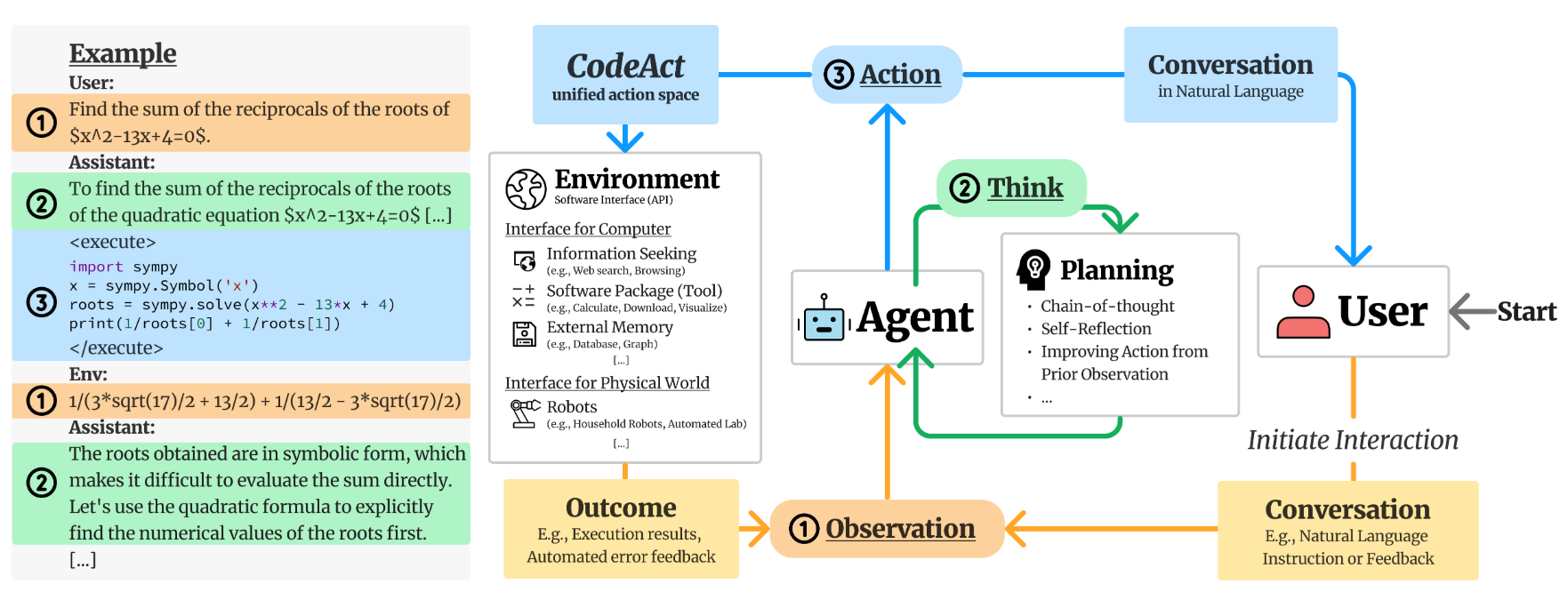
CodeActAgent的初始化流程图如下。

2.4 构建Runtime
create_runtime()构建了AI 代理的 “专属工作间”Runtime。在OpenHands系统中,Runtime扮演着至关重要的角色,它为人工智能代理提供了一个稳定且可控的操作平台。
# 运行时创建后会自动连接并克隆选定的代码仓库
repo_directory = None
if runtime is None:
# 初始化代码仓库(如需)
repo_tokens = get_provider_tokens()
# 创建运行时实例
runtime = create_runtime(
config,
llm_registry,
sid=sid,
headless_mode=headless_mode,
agent=agent,
git_provider_tokens=repo_tokens,
)
# 同步调用异步的运行时连接方法
call_async_from_sync(runtime.connect)
# 初始化代码仓库(如需)
if config.sandbox.selected_repo:
repo_directory = initialize_repository_for_runtime(
runtime,
immutable_provider_tokens=repo_tokens,
selected_repository=config.sandbox.selected_repo,
)
# event_stream 是 event_stream = EventStream(session_id, file_store)
event_stream = runtime.event_stream
Runtime 的__init__会注册EventStreamSubscriber.RUNTIME。
self.event_stream = event_stream
if event_stream:
event_stream.subscribe(
EventStreamSubscriber.RUNTIME, self.on_event, self.sid
)
Runtime只处理可运行的Action事件,执行动作拿到输出Observation发送回事件流中
isinstance(event, MCPAction)执行MCP获取结果
- 其他runtime支持的action则执行获取结果
2.5 构建Memory & Microagent
接下来初始化memory,
# when memory is created, it will load the microagents from the selected repository
if memory is None:
memory = create_memory(
runtime=runtime,
event_stream=event_stream,
sid=sid,
selected_repository=config.sandbox.selected_repo,
repo_directory=repo_directory,
conversation_instructions=conversation_instructions,
working_dir=str(runtime.workspace_root),
)
2.5.1 创建 Memory
create_memory 函数会创建memory。
def create_memory(
runtime: Runtime,
event_stream: EventStream,
sid: str,
selected_repository: str | None = None,
repo_directory: str | None = None,
status_callback: Callable | None = None,
conversation_instructions: str | None = None,
working_dir: str = DEFAULT_WORKSPACE_MOUNT_PATH_IN_SANDBOX,
) -> Memory:
"""Create a memory for the agent to use.
Args:
runtime: The runtime to use.
event_stream: The event stream it will subscribe to.
sid: The session id.
selected_repository: The repository to clone and start with, if any.
repo_directory: The repository directory, if any.
status_callback: Optional callback function to handle status updates.
conversation_instructions: Optional instructions that are passed to the agent
"""
memory = Memory(
event_stream=event_stream,
sid=sid,
status_callback=status_callback,
)
memory.set_conversation_instructions(conversation_instructions)
if runtime:
# sets available hosts
memory.set_runtime_info(runtime, {}, working_dir)
# loads microagents from repo/.openhands/microagents
microagents: list[BaseMicroagent] = runtime.get_microagents_from_selected_repo(
selected_repository
)
memory.load_user_workspace_microagents(microagents)
if selected_repository and repo_directory:
memory.set_repository_info(selected_repository, repo_directory)
return memory
memory初始化的时候有一个event_stream的订阅,会注册 EventStreamSubscriber.MEMORY,当有event的时候Memory 的on_event方法会被调用。
self.event_stream.subscribe(
EventStreamSubscriber.MEMORY,
self.on_event,
self.sid,
)
Memory只处理RecallAction,对于用户首次输入信息则将一些额外的工作空间上下文信息添加到RecallObservation发送回事件流中,对于其他非用户首次的输入信息则加入microagent knowledge(领域强化提示词)到RecallObservation发送回事件流中。
2.5.2 创建Microagent
create_memory函数中会加载Microagent。
# loads microagents from repo/.openhands/microagents
microagents: list[BaseMicroagent] = runtime.get_microagents_from_selected_repo(
selected_repository
)
memory.load_user_workspace_microagents(microagents)
Microagent是主代理的“专业合作伙伴”。
为了高效完成复杂任务,通常需要专业的分工协作,Microagent正是为了这一目的而设计的“专业执行者”。当主代理在执行任务时遇到特定领域的细分工作,它不必亲自处理,而是可以将这部分任务“委托”给相应的Microagent,从而利用其专业能力提高效率和准确性。
从本质上讲,Microagent同样基于大型语言模型构建,比如,其独特之处可以是其内置的专业提示词(Prompt)。这些提示词中融入了特定领域的知识准则与操作规范,例如,与Git相关的Microagent,其提示词会包含Git操作的核心技巧与最佳实践,能够引导模型更精确地处理与Git相关的任务,成为主代理应对细分场景的“得力助手”。
BaseMicroagent 定义如下:
class BaseMicroagent(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all microagents."""
name: str
content: str
metadata: MicroagentMetadata
source: str # path to the file
type: MicroagentType
PATH_TO_THIRD_PARTY_MICROAGENT_NAME: ClassVar[dict[str, str]] = {
'.cursorrules': 'cursorrules',
'agents.md': 'agents',
'agent.md': 'agents',
}
2.6 创建MCP
接下来会创建MCP相关部分。
# Add MCP tools to the agent
if agent.config.enable_mcp:
# Add OpenHands' MCP server by default
_, openhands_mcp_stdio_servers = (
OpenHandsMCPConfigImpl.create_default_mcp_server_config(
config.mcp_host, config, None
)
)
runtime.config.mcp.stdio_servers.extend(openhands_mcp_stdio_servers)
await add_mcp_tools_to_agent(agent, runtime, memory)
2.7 创建Controller
接下来会创建AgentController。
AgentController 是 OpenHands 系统中的核心控制器组件,负责管理代理(Agent)的整个生命周期和行为。是代理与系统其他组件之间的桥梁,确保代理可以安全有效地执行任务,同时管理系统资源。
AgentController作为主要状态管理模块,
- 根据
Observation事件进行状态变换 - 根据
Action进行状态变换和以下处理:- 对于
MessageAction发送RecallAction到事件流中 - 对于
AgentDelegateAction做Agent路由(后续机制解读中再详细介绍)
- 对于
- 根据当前的
event判断进行调用agent.step
controller, initial_state = create_controller(
agent, runtime, config, conversation_stats, replay_events=replay_events
)
create_controller代码如下。
def create_controller(
agent: Agent,
runtime: Runtime,
config: OpenHandsConfig,
conversation_stats: ConversationStats,
headless_mode: bool = True,
replay_events: list[Event] | None = None,
) -> tuple[AgentController, State | None]:
event_stream = runtime.event_stream
initial_state = None
initial_state = State.restore_from_session(
event_stream.sid, event_stream.file_store)
controller = AgentController(
agent=agent,
conversation_stats=conversation_stats,
iteration_delta=config.max_iterations,
budget_per_task_delta=config.max_budget_per_task,
agent_to_llm_config=config.get_agent_to_llm_config_map(),
event_stream=event_stream,
initial_state=initial_state,
headless_mode=headless_mode,
confirmation_mode=config.security.confirmation_mode,
replay_events=replay_events,
security_analyzer=runtime.security_analyzer,
)
return (controller, initial_state)
在 AgentController 的__init__中,会注册EventStreamSubscriber.AGENT_CONTROLLER。
# subscribe to the event stream if this is not a delegate
if not self.is_delegate:
self.event_stream.subscribe(
EventStreamSubscriber.AGENT_CONTROLLER, self.on_event, self.id
)
2.8 发送启动事件
发送一个启动事件MessageAction。
# start event is a MessageAction with the task, either resumed or new
if initial_state is not None and initial_state.last_error:
# we're resuming the previous session
event_stream.add_event(
MessageAction(
content=(
"Let's get back on track. If you experienced errors before, do "
'NOT resume your task. Ask me about it.'
),
),
EventSource.USER,
)
else:
# init with the provided actions
event_stream.add_event(initial_user_action, EventSource.USER)
2.9 订阅事件流:注册用户输入回调函数
把自己注册为 EventStreamSubscriber.MAIN。
def on_event(event: Event) -> None:
if isinstance(event, AgentStateChangedObservation):
if event.agent_state == AgentState.AWAITING_USER_INPUT:
if exit_on_message:
message = '/exit'
elif fake_user_response_fn is None:
message = read_input(config.cli_multiline_input)
else:
message = fake_user_response_fn(controller.get_state())
action = MessageAction(content=message)
event_stream.add_event(action, EventSource.USER)
event_stream.subscribe(EventStreamSubscriber.MAIN, on_event, sid)
end_states = [
AgentState.FINISHED,
AgentState.REJECTED,
AgentState.ERROR,
AgentState.PAUSED,
AgentState.STOPPED,
]
几个模块的初始化范式基本一致,在__init__函数中完成模块的初始化准备工作,并且向事件流中订阅消息并注册各自模块的消息处理函数。事件回调函数会根据当前的事件进行状态机的状态转移。
- Runtime 在事件流中订阅 EventStreamSubscriber.RUNTIME,事件回调函数会处理需要runtine处理的action,比如mcp/tool等等。
- Memory 在事件流中订阅 EventStreamSubscriber.MEMORY。事件回调函数根据当前的
event生成一个带microagent_knowledge的Observation并以ENVIRONMENT作为源添加回事件流中,这里的microagent_knowledge是一种特定提示词增强的方法。 - AgentController 在事件流中订阅 EventStreamSubscriber.AGENT_CONTROLLER。
- run_controller 在事件流中订阅 EventStreamSubscriber.MAIN。
2.10 运行代理
运行代理直到进入结束状态。
try:
await run_agent_until_done(controller, runtime, memory, end_states)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f'Exception in main loop: {e}')
# save session when we're about to close
if config.file_store is not None and config.file_store != 'memory':
end_state = controller.get_state()
# NOTE: the saved state does not include delegates events
end_state.save_to_session(
event_stream.sid, event_stream.file_store, event_stream.user_id
)
await controller.close(set_stop_state=False)
2.11 run_controller全部代码
run_controller全部代码如下:
async def run_controller(
config: OpenHandsConfig,
initial_user_action: Action,
sid: str | None = None,
runtime: Runtime | None = None,
exit_on_message: bool = False,
fake_user_response_fn: FakeUserResponseFunc | None = None,
headless_mode: bool = True,
memory: Memory | None = None,
conversation_instructions: str | None = None,
) -> State | None:
"""主协程,用于运行代理控制器,支持灵活的任务输入。
仅在通过命令行直接启动 OpenHands 后端时使用。
参数:
config: 应用配置实例
initial_user_action: 包含初始用户输入的 Action 对象
sid: (可选) 会话 ID。重要提示:非必要请勿手动设置,
错误设置可能导致 RemoteRuntime 出现异常行为
runtime: (可选) 代理运行的运行时环境实例
exit_on_message: 当代理请求用户消息时退出(可选)
fake_user_response_fn: (可选) 接收当前状态并返回模拟用户响应的函数
headless_mode: 代理是否以无头模式运行
返回:
代理的最终状态;若发生错误则返回 None
异常:
AssertionError: 若 initial_user_action 不是 Action 实例
Exception: 执行过程中可能抛出各类异常,均会被记录日志
注意:
- 状态持久化:若配置了 config.file_store,代理状态将在会话间保存
- 执行轨迹:若配置了 config.trajectories_path,执行历史将以 JSON 格式保存用于分析
- 预算控制:执行受 config.max_iterations 和 config.max_budget_per_task 限制
示例:
>>> config = load_openhands_config()
>>> action = MessageAction(content="Write a hello world program")
>>> state = await run_controller(config=config, initial_user_action=action)
"""
# 若未提供会话ID,则生成一个
sid = sid or generate_sid(config)
# 创建 LLM 注册中心、对话统计实例,并处理配置
llm_registry, conversation_stats, config = create_registry_and_conversation_stats(
config,
sid,
None,
)
# 基于配置和 LLM 注册中心创建代理实例
agent = create_agent(config, llm_registry)
# 运行时创建后会自动连接并克隆选定的代码仓库
repo_directory = None
if runtime is None:
# 初始化代码仓库(如需)
repo_tokens = get_provider_tokens()
# 创建运行时实例
runtime = create_runtime(
config,
llm_registry,
sid=sid,
headless_mode=headless_mode,
agent=agent,
git_provider_tokens=repo_tokens,
)
# 同步调用异步的运行时连接方法
call_async_from_sync(runtime.connect)
# 初始化代码仓库(如需)
if config.sandbox.selected_repo:
repo_directory = initialize_repository_for_runtime(
runtime,
immutable_provider_tokens=repo_tokens,
selected_repository=config.sandbox.selected_repo,
)
# 从运行时获取事件流实例(组件间通信核心)
event_stream = runtime.event_stream
# 记忆系统创建后会从选定仓库加载微代理
if memory is None:
# 创建记忆系统实例
memory = create_memory(
runtime=runtime,
event_stream=event_stream,
sid=sid,
selected_repository=config.sandbox.selected_repo,
repo_directory=repo_directory,
conversation_instructions=conversation_instructions,
working_dir=str(runtime.workspace_root),
)
# 为代理添加 MCP 工具(若启用)
if agent.config.enable_mcp:
# 默认添加 OpenHands 的 MCP 服务器配置
_, openhands_mcp_stdio_servers = (
OpenHandsMCPConfigImpl.create_default_mcp_server_config(
config.mcp_host, config, None
)
)
runtime.config.mcp.stdio_servers.extend(openhands_mcp_stdio_servers)
# 异步将 MCP 工具添加到代理
await add_mcp_tools_to_agent(agent, runtime, memory)
# 加载回放事件(若启用轨迹回放)
replay_events: list[Event] | None = None
if config.replay_trajectory_path:
logger.info('Trajectory replay is enabled')
# 断言初始用户动作必须是空动作(回放场景)
assert isinstance(initial_user_action, NullAction)
# 从指定路径加载回放日志和初始用户动作
replay_events, initial_user_action = load_replay_log(
config.replay_trajectory_path
)
# 创建控制器和初始状态
controller, initial_state = create_controller(
agent, runtime, config, conversation_stats, replay_events=replay_events
)
# 断言初始用户动作必须是 Action 实例,否则抛出异常
assert isinstance(initial_user_action, Action), (
f'initial user actions must be an Action, got {type(initial_user_action)}'
)
# 记录调试日志:控制器初始化信息
logger.debug(
f'Agent Controller Initialized: Running agent {agent.name}, model '
f'{agent.llm.config.model}, with actions: {initial_user_action}'
)
# 发送启动事件(恢复会话或新会话)
if initial_state is not None and initial_state.last_error:
# 恢复之前的会话(存在历史错误)
event_stream.add_event(
MessageAction(
content=(
"Let's get back on track. If you experienced errors before, do "
'NOT resume your task. Ask me about it.'
),
),
EventSource.USER,
)
else:
# 新会话:添加初始用户动作到事件流
event_stream.add_event(initial_user_action, EventSource.USER)
# 定义事件回调函数:处理代理等待用户输入的场景
def on_event(event: Event) -> None:
# 监听代理状态变更事件
if isinstance(event, AgentStateChangedObservation):
# 当代理进入等待用户输入状态时
if event.agent_state == AgentState.AWAITING_USER_INPUT:
if exit_on_message:
# 需退出时发送 /exit 指令
message = '/exit'
elif fake_user_response_fn is None:
# 读取真实用户输入
message = read_input(config.cli_multiline_input)
else:
# 调用模拟用户响应函数
message = fake_user_response_fn(controller.get_state())
# 创建消息动作并添加到事件流
action = MessageAction(content=message)
event_stream.add_event(action, EventSource.USER)
# 订阅事件流:注册 MAIN 订阅者和回调函数
event_stream.subscribe(EventStreamSubscriber.MAIN, on_event, sid)
# 定义代理结束状态列表
end_states = [
AgentState.FINISHED,
AgentState.REJECTED,
AgentState.ERROR,
AgentState.PAUSED,
AgentState.STOPPED,
]
try:
# 运行代理直到进入结束状态
await run_agent_until_done(controller, runtime, memory, end_states)
except Exception as e:
# 记录主循环异常日志
logger.error(f'Exception in main loop: {e}')
# 关闭前保存会话(若配置文件存储)
if config.file_store is not None and config.file_store != 'memory':
end_state = controller.get_state()
# 注意:保存的状态不包含委托事件
end_state.save_to_session(
event_stream.sid, event_stream.file_store, event_stream.user_id
)
# 关闭控制器(不设置停止状态)
await controller.close(set_stop_state=False)
# 获取控制器最终状态
state = controller.get_state()
# 保存执行轨迹(若配置)
if config.save_trajectory_path is not None:
# 若路径是文件夹,则以会话ID为文件名
if os.path.isdir(config.save_trajectory_path):
file_path = os.path.join(config.save_trajectory_path, sid + '.json')
else:
file_path = config.save_trajectory_path
# 创建目录(如需)
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(file_path), exist_ok=True)
# 获取执行轨迹历史
histories = controller.get_trajectory(config.save_screenshots_in_trajectory)
# 写入 JSON 文件
with open(file_path, 'w') as f: # noqa: ASYNC101
json.dump(histories, f, indent=4)
# 返回最终状态
return state
0xFF 参考
https://docs.all-hands.dev/openhands/usage/architecture/backend
当AI Agent从“玩具”走向“工具”,我们该关注什么?Openhands架构解析【第二篇:Agent 相关核心概念】 克里
当AI Agent从“玩具”走向“工具”,我们该关注什么?Openhands架构解析【第一篇:系列导读】 克里


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号